MLT 118 Exam 1
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
the limit of chemical subdivision for matter (ex. NaCI)
Atoms
After heating, a pure substance, A, is found to produce both B and C. What can be said about the substance A?
It is a compound
It is an ion
It is an element
It is a atom
It is a compound
a chemical bond formed when the outermost electrons of one atom are permanently transferred to another atom
Ionic bond
two nonmetal atoms share electrons (ex. CO2)
Covalent bond
attracts an electronegative atom electrostatically (ex. H2O)
hydrogen bond
positive metal attract conducting electrons (ex. iron, copper — pure metals)
Metallic bond
________________are forces that hold the atoms together in a molecule.
Chemical bond
the limit of physical subdivision of a pure substance
molecule
pure substance made up of homoatomic molecules or individual atoms of the same kind (ex. oxygen, copper)
Element
pure substances made of of heteratomic molecules or individual atoms of two or more different elements (ex. water, h2O)
compound
composition is the same throughout (ex. soda)
Homogeneous (mixture)
Heterogeneous (mixture)
homogeneous (mixture)
composition is not the uniform (ex. oil in water, blood)
Heterogeneous (mixture)
loses and electron; is a positive charge
anions or cations?
Cations
gains a electron; has a negative charge
Anions or cations?
anions
Urea (CH4N2O) is an end-product of protein metabolism. Measurement of urea is one of the Renal Function Test (RFT) performed in clinical chemistry department. Calculate the molecular weight of urea. (Atomic mass of C= 12; N=14; O=16)
60 grams/mol
the study of structure, properties, composition, reactions and preparation of carbon-containing compounds
Organic chemistry
the study of properties of inorganic compounds (metals, minerals and organic-metallic compounds))
inorganic chemistry
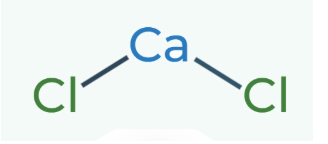
This image shows the structural formula of an inorganic compound. True or False?
True
the study of chemical processes related to living organisms (lab based science/biology n chemistry)
biochemistry
What is “clinical chemistry”?
science focused on chemical analysis of body fluids such as blood urine, spinal fluids etc
Table salt dissolving in water is what kind of change?
physical change
Baking soda reacts to vinegar is what kind of change?
chemical change
What is required for a heterogeneous mixture (medicine) to be effective?
to be shaken; because the composition isn’t uniform (ex. oil n water for baking brownies)
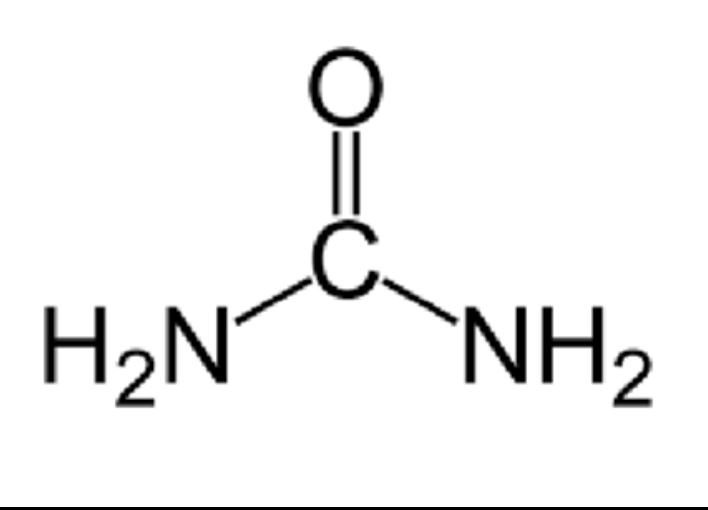
A element that is a key indicator of organic substances. (It is present in the human body.)
carbon (C)
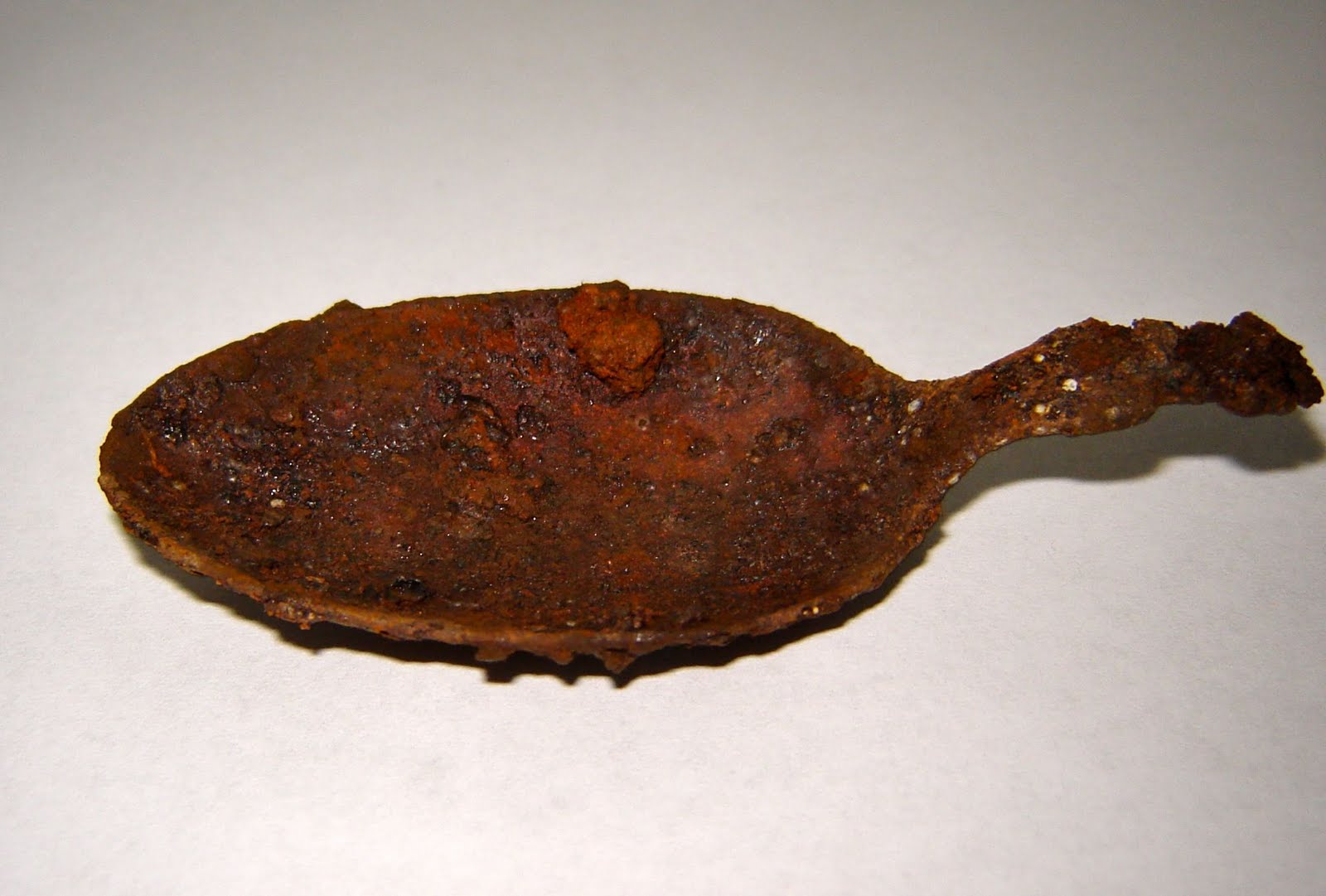

What kind of change is this:
chemical change
Which of the following is a physical property of matter?
a. produces a gas when placed in an acid
b. does not burn
c. a substance freezes at −70°C
d. the surface turns black in air
a substance freezes at −70°C
Table Salt (NACI) dissolves in water is what kind of change?
Physical change
An antacid seltzer tablet dissolved in water, correctly classified as:
Chemical change
In order for matter to change from a liquid to a gas, which of the following is true?
A) Energy must be removed from the liquid
B) The chemical composition of the gas must be altered
C) Energy must be applied to the liquid
D) The chemical composition of the liquid must be altered
C) Energy must be applied to the liquid
Which one of the following is not element in the human body?
A) Carbon
B) Oxygen
C) Plutonium
D) Hydrogen
E) Nitrogen
C) Plutonium
The chemical formula for methane is CH4. How many atoms are in a compound of methane?
A) 4
B) 3
C) 5
D) 6
C) 5
The atomic mass of Carbon is 12, and the atomic mass of oxygen is 16. What is the molecular weight of ONE molecule of carbon dioxide (CO2)?
A) 24
B) 28
C) 32
D) 44
D) 44 Exp.) 12(1)+16(2)
A particular laboratory reagent is a heterogeneous mixture. Since heterogeneous mixtures are consistent throughout, this reagent does not need to be shaken.
A) True B) False
B) False
(heterogeneous mixture Consist of two or more substances, needs to be mixed)
Which of the following is an example of a homogeneous mixture?
A) Table salt
B) Physiological saline
C) Opened soda
D) Oil & water suspension
B) Physiological saline
Air is a mixture of several gases, so it is a
heterogeneous mixture.
A) True
B) False
B) False
Blood is a heterogeneous mixture including red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets and plasma.
A) True
B) False
A) True
Which statement is true of micropipettes?
Some have preset volumes.
all of the above
A one-use disposable plastic tip is used for each sampling.
Some are adjustable in a narrow range.
all of the above
all of the above
The melting of frozen urine to liquid urine is correctly classified as:
a chemical change.
a physical change.
both a chemical and a physical change.
neither a chemical nor physical change.
a physical change.