Biology I Unit 2: Cells
1/58
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
What are the three tenets of the Cell Theory?
All living things are made of cells, cells are the basic unit of life, all cells come from pre-existing cells
What are the organelles found in prokaryotic cells?
Cytoplasm, ribosomes, cell membranes, cell wall.
What are the four things prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have in common?
DNA
Cytoplasm
Ribosomes
Cell membrane
Golgi bodies
Eukaryotic;
In animals and plant cells
Modify, sort, and ship proteins
Mitochondria
Eukaryotic
In animal and plant cells
Powerhouse of the cell and creates ATP
Vacuole
Eukaryotic
In animal and plant cells
Handles waste products; takes in products and stores food, water, waster; digest bacteria
Lysosome
Eukaryotic
In animal cells
Breaks down cell parts, destroy viruses, digests bacteria
Centrosome/ Centrioles
Eukaryotic
In animal and plant cells
Creates spindle fibers to aid in cell division (mitosis)
Cell Wall
Eukaryotic
In plant cells
Provides structure, supports, protection for plant cells
Chloroplast
Eukaryotic
In plant cells
Produce energy through photosynthesis and oxygen (site of photosynthesis)
Central vacuole
Eukaryotic
In plant cells
store water, regulate turgor pressure
Cell membrane
In both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
In animal and plant cells
Maintains homeostasis by controlling what goes in an out of the cell
Cytoplasm
In both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
In animal and plant cells
Transport, maintain cell shape and structure
Ribosome
In both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
In animal and plant cells
Synthesis and create proteins
Cytoskeleton
In both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
In animal and plant cells
Network of protein filaments and tubules in cytoplasm; gives shape
Nucleus
In eukaryotic cells
In animal and plant cells
Stores genetic info/DNA
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
In eukaryotic cells
In animal and plant cells
Folds proteins, does transportation of proteins and sorting
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
In eukaryotic cells
In animal cells and plant cells
Responsible for the synthesis of essential lipids such as phospholipids and membranes
Detoxifies liver
Stores calcium
what organelles are found in only plant cells
Cell wall, chloroplast, central vacuole
What organelles are found only in animal cells
Centrosome/centrioles
Lysosome
Be able to label organelles in a cell
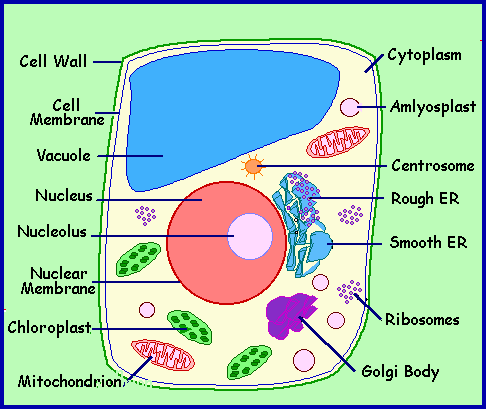
How is the cell membrane related to homeostasis?
a cell membrane maintains homeostasis by controlling the movement of substances across the cell membrane
What are the parts of the cell membrane
Phospholipids
Proteins
Carbohydrates
Cholesterol
What are the two main types of transportation
passive and active
What types of molecules can easily pass through the membrane
Small and non polar
Oxygen
Carbon dioxide
What are the types of passive transport
Diffusion
Facilitated diffusion
Osmosis
Does passive transport move up or down the concentration gradient
DOWN
What are the types of active transport
Bulk transport (endocytosis and exocytosis)
Protein pumps
What type of transport requires the use of energy?
Active
What type of solution is an isotonic solution? How does it affect the cell?
It means that the amount of solution outside the cell is the same as inside the cell. The cell stays the same (animals)
What is osmosis?
The movement of high to low concentration of water
what type of solution is a hypertonic solution? How does it affect the cell?
Solution outside the cell is more than inside.
It shrinks
What type of solution is a hypotonic solution?? How does it affect the cell?
Solution outside the cell is less than inside the cell.
Water floods into the cell causing the cell to burst (plants)
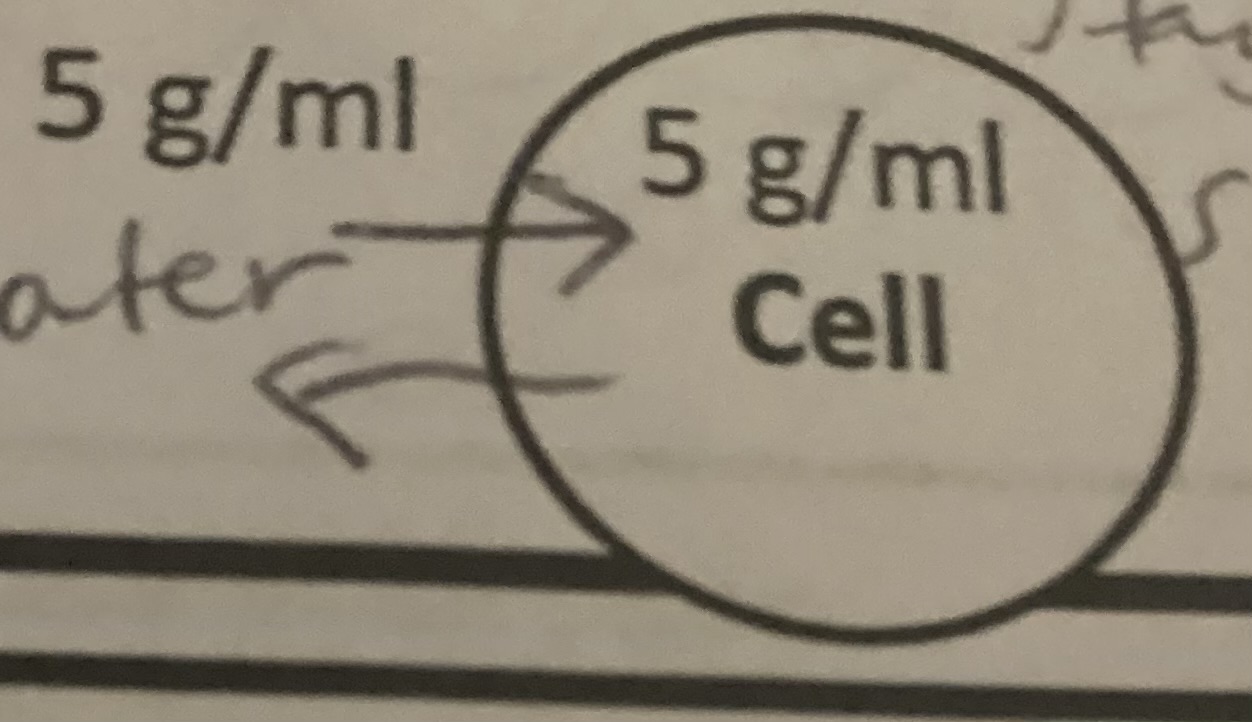
Is the image isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic?
Isotonic
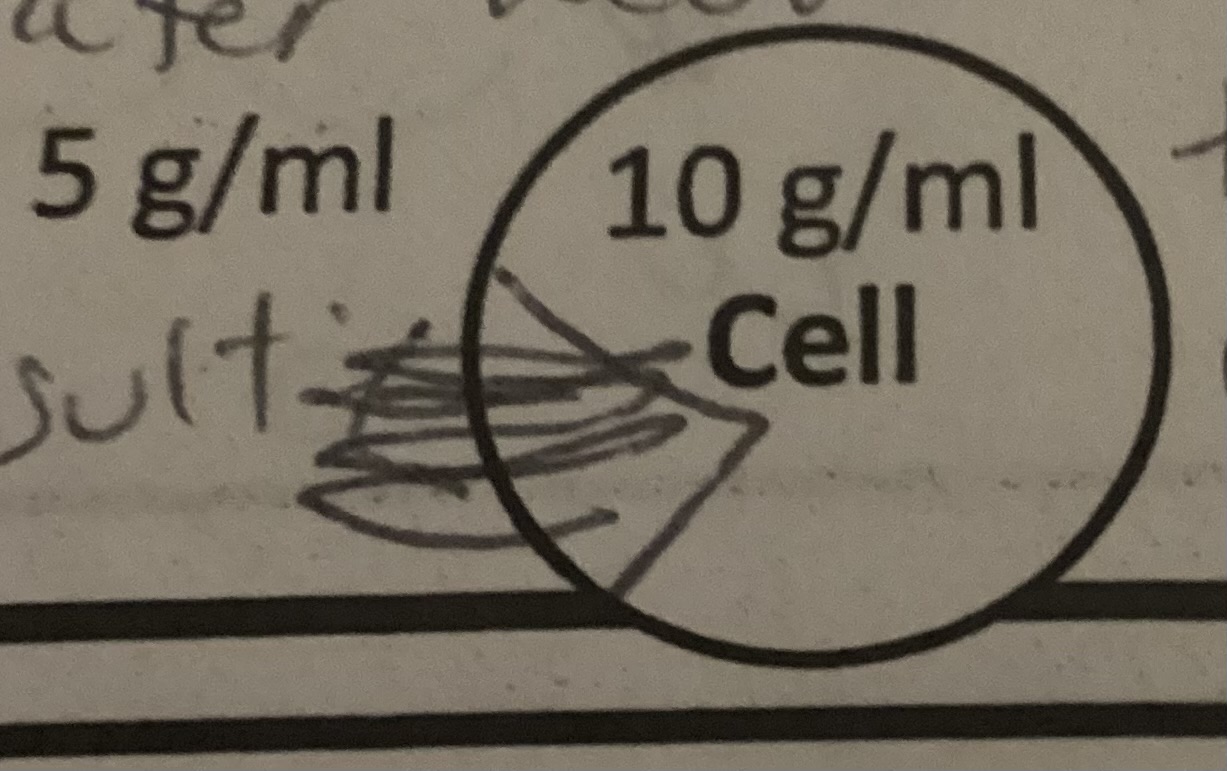
Is the image isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic?
Hypotonic
Is the image isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic?
Hypertonic
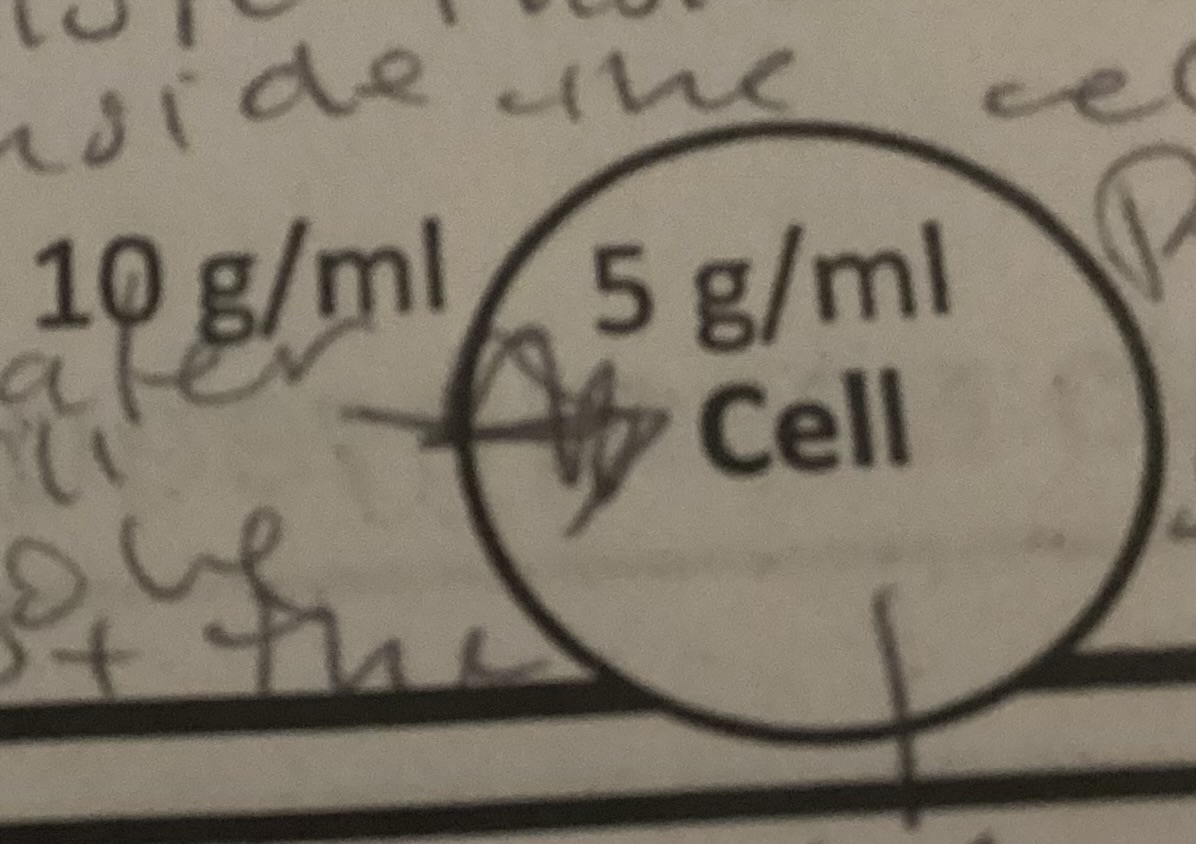
what are the parts of Interphase and what occurs in each step?
G1: Growth and protein synthesis
S: DNA replication
G2: More growth and protein synthesis; prepares for Mitosis
What are the functions of the cell cycle?
To repair and replace damaged cells. Growth (multicellular)
Reproduction (unicellular)
what is the name of asexual reproduction in bacteria?
Binary fission
what is mitosis?
The cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new daughter cells that are identical to the original parent cell?
what are the stages of mitosis in order?
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
What happens in Prophase?
Membranes around nucleus disintegrates
Chromosomes condense and become sister chromatids
Centrioles migrate to the opposite poles of the cell
Spindle fibers emerge from the Centrosome/centrioles
What happens in Metaphase?
Sister chromatids move toward the middle of the cell on. A line called the metaphase plate.
Centrioles send out spindle bribers that attach to the centromere of each sister chromatids
What happens in Anaphase?
Centrioles start pulling on the spindle fibers to pull the sister chromatids apart
They are now called chromosome
What happens at Telophase?
The nuclear membrane forms around each sex of chromosomes
What is the difference between cytokinesis in plants and animals?
The area where the cytoplasm punches is known as the cleavage furrow in animals and a cell plate in plants
How is mitosis related to genetic continuity?
Mitosis creases two daughter cell that are identical to the parent cell. Each daughter cell has the exact same genes, thus genetic continuity.
Throughout the cell’s cycle, there are built in _______ that are designed to be a check and balance for the cell. what do these look for?
Checkpoints
Proper cell growth and replication
_______ ________ are proteins that stimulate cell division
Growth factors
Programmed cell death is known as ________.
Apoptosis
What is cancer?
Uncontrolled cell divison
Cancer cells form disorganized clumps called _____
Tumors
what is a carcinogen?
Substances that are known to cause or lead to cancer. It can be environmental or genetic.
Tobacco
Nicotine
Artificial sugars
What is a stem cell?
Cell that lacks specialized function.
what are some real world application of stem cells
You can grow new cell to repair damaged cells
Research how disease occur
Research drugs
what do proteins do in the cell membrane?
transporting molecules into and out of the cell, relaying signals from outside and inside, cell-cell acknowledgment, etc.
what do carbohydrates do in the cell membrane?
identifying cells, and interacting with other cells.
what do the phospholipids to in the cell membrane?
forms a phospholipid bilayer
what do the cholesterol do in the cell membrane?
helps to stabilize the membrane so its not too solid not too fluid. it touches the tails