A brief intro to your brain
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Common misconceptions
Parts of the hemispheres
Left hemisphere used more = more mathematical
Right hemisphere more artistic; more out there
However, we use both at all times
Misconceptions come from some kind of truth
Correct idea: the behaviour is associated more with some area of the regions than others
Misconception: Only use one percent of your brain
No kernel of truth
Correct idea: use all of your brain
However, where did this come from is the question
65% believe about this misconception
Misconception: believed that if there is a lump or something; then there is a certain area that is used more to be a particular type of person with a particular kind of skill
David Eagleman analogy
where is love, memory, or etc produced in the brain
The brain is a city
Where is the economy located? and: there is no certain particular spot
Many different places that interact
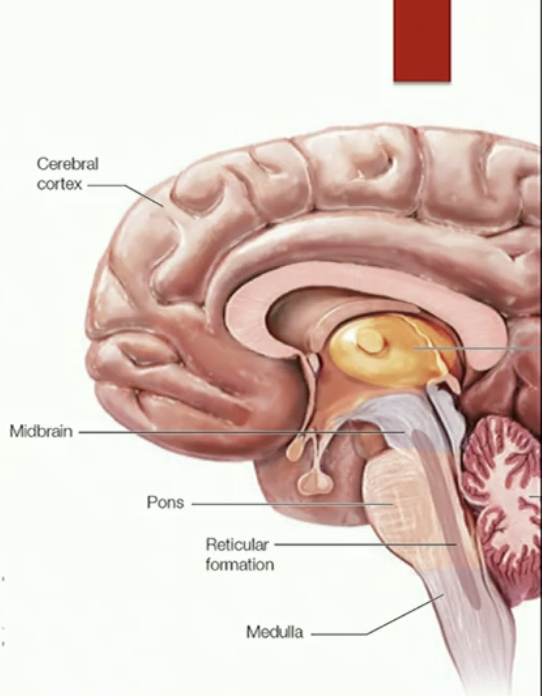
The brainstem
what is its function
Reticulur formation: cells are firing fast vs cells are firing slow
controls life sustaining functions of the autonomic nervous system
e.g. breathing, digestion, heartbeat, balance, movement
Reticular formation: managment of arousal
Alertness, sleep
General arousal, sleep-wake state
Firing fast: awake
Firing slow: deep sleep or unconscious
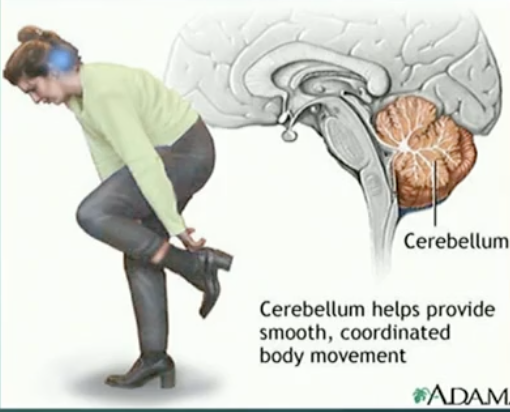
Cerebellum
where is it located
What is the latin translation
What is its main role
What affects this part of the brain
base of the brain stem
latin for little brain
Helps for coordinated movement and balance, and possible higher cognitive processing
e.g. riding a bike
A particular part of the brain that is affected by alcohol
about 10% of overall brain volume
but holds 50% of brain’s neurons
Pointing out it is also responsible for higher order brain activities
The diencephalon
what parts does it consists
Consists of the thalamus, hypothalamus, and cerebellum
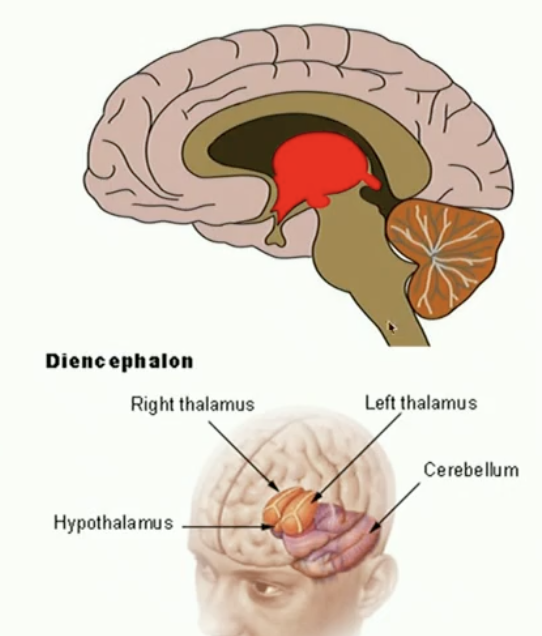
Hypothalamus
very small part of the brain
Very powerful, the brain’s master regulatory structure
Regulates hormone secretion
Connected nervous to the endocrine system
maintain homeostasis
Main temperature: if too cold or too hot; then must take some action to maintain action
The four F’s: basic drives
fighting
fleeing
Feeding
Fornicating

Thalamus
main job
What doesn’t it do
Unique case study: craniopagus twins
Case study: Patient Geore
referred to the relay station
Handles all incoming sensory info except smell
e..g touch, sense, see, all info goes to the thalamus first
Case study
Craniopagus twins
Share the head, main region they share is the thalamus
Therefore: both experience the same thing; if one have a sensory experience, the other can receive that even if they didn’t experience
E.g. one covered eyes, other sees something, the one whose eyes are covered can be able to know what the other girl is seeing
Patient George
How the brain reacts to music compared to normal people
View music very differently
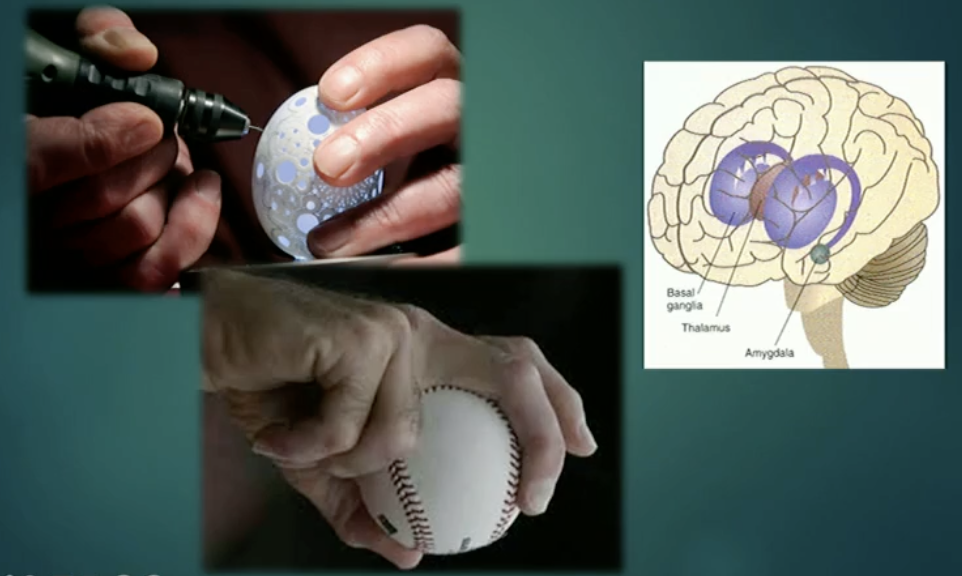
The Basal Ganglia
What is it responsible for
What does the nucleus accumbens do?
Controls the production of movement and perpetual movement
Responsible for coordinating the movement; what should the next movement and what should not be the next movement
Behaviour reinforced, reward for behaviour, home of dopamine receptors at a particular part of basal ganglia
e.g. throwing a baseball, what is the appropriate pressure when holding an egg for a particular activity
Nucleus accumbens
Reward and pleasure circuitry
Related to inclusion
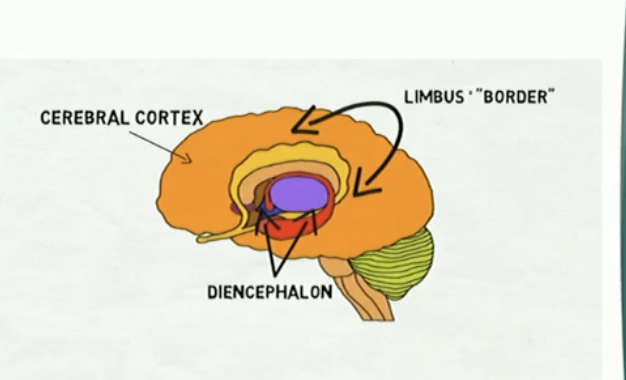
The Limbic System
very new system; researchers still not sure what parts are involved, tooo simple
associated with emotion
The limbic system
Amygdala
Hippocampus - more assictaed with memory than emotion
Parahippocampal gyrus
Septal nuclei
cingulate cortex
Fornic
Mammillary body
Hypothalamus
Hippocampus
role
case study: Patient HM
research study: cab driver in 2000s
role: vital of the formation and storage of long-term memory
Patient HM
Hippocampi removed, resulted in memory-loss, after a certain time stamp he couldn’t form any long term memories
Helped scientists understand a lot of the hippocampus
Black cab driver
must pass test about the knowledge
takes 12 attempts to pass the text; includes 25000 different streets and landmarks (need to know everything memorized)
Researchers see if spatial memorization, would it lead to physical differences of the hippocampus
Say big difference in the posterior hippocampus, role is spatial memory
Therefore higher cognitive = physical changes in the brain -→ contributing to the nature vs nurture
The Cingulate Cortex
what is it/where is it located
Anterior vs posterior cortex roles
the tissue on the inner surface of each cerebral hemisphere
Anterior
Controls the autonomic nervous system
Posterior
Controls in memory and visual processing
Amygdala
it’s main role
Other small role that is similar to it
case study of individuals in 9/11
Role is processing fear and agression
help activate flight or fight
Mainly the amygdala will recieve info and produce emotional and motivation output sent to the cerebral cortex
Essential for our ability to associate things with emotional responses
Linking emotion and memory (emotion linked to memory)
Case study: individuals in 9/11
Close people vs very far people
Brought them into MRI scanner on sept 11
Found that been very close, the recalled memory, stronger amygdala memory
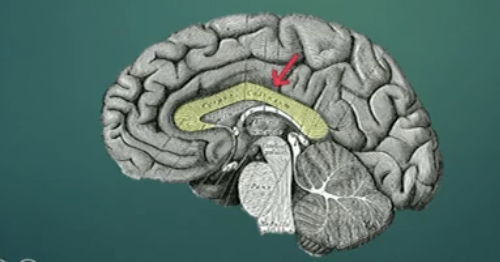
Cerebral Cortex
Where is it located, what parts does it consist of
the corpus callosum
The outer layer of the brain covering the cerebral hemispheres
The hemisphere has four lobes
Corpus callosum
large bridge of axons/nerve fibers that connects the hemispheres and allows information to flow between them
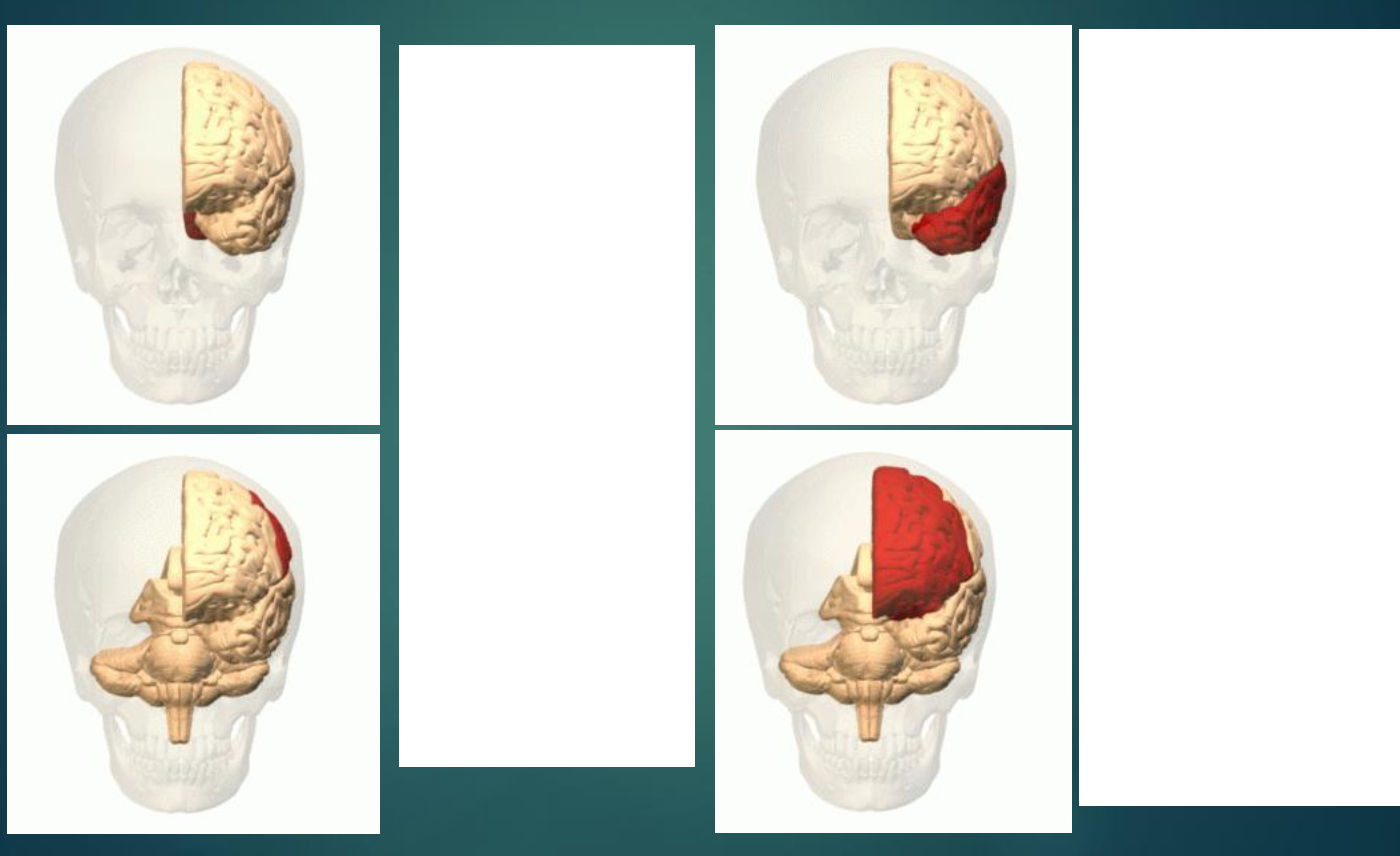
Parts of the cerebral cortex (do not need to describe their roles, but only describe where they are located in the brain)
four lobes
Occipital lobe
located at the very back of the brain
Temporal Lobe
Front to side
Parietal Lobe (located at the top back; right behind the frontol lobe)
Frontal Lobes
Front to top of head
Frontal lobe
roles; primary
Prefrontal cortex and it’s role
Orbitofrontal cortex roles + what happens when it gets damaged?
Executive function meaning
Primary motor cortex and for complex conginitive thinking
Prefrontal cortex (located on the forehead)
exectutive, higher order cognitive function (planning, long term, so on)
Orbitofrontal cortex: located in the prefrontal cortex right behind the eyes
Involved in emotional lives
Damages = not controlling impulses and the possible negative outcomes of decisions
Executive functions
The range of cognitive function and how you can regulate yourself in terms of behaviour
Occipital Lobe
role
What role does it not do
Where is the occipital lobe connected to in order for that role to be done
responsible for visual processing
However, not for analyzing the image
Connected to the temporal lobe which can then interpretate what you see
The temporal lobe
role
primary auditory cortex: the processing of incoming sounds
Also for higher visual processings
The Parietal Lobe
roles
What happens if this lobe is damaged
primary semantic cortex
Damaged will result in feelings of neglect because of the lack of spatial and visual awareness

Case study Phineas Gage
tamping iron that shot through his brain during railway workings
Lost one his eyes
1848 - where metal rod goes through his frontal cortex
Image on the right is the assumption of where the damages are
Results
Survived before doctors knew to wash his hands - so he is very lucky
Recovered a lot of his functionings that he lost from his injury (including physical aspect and personality and social recovery)
His personality changed a lot, including how to interact with other people
**anything about his wife is not true because he didn’t marry
Results in the social recovery hypothesis
Death: he died due to a seizure
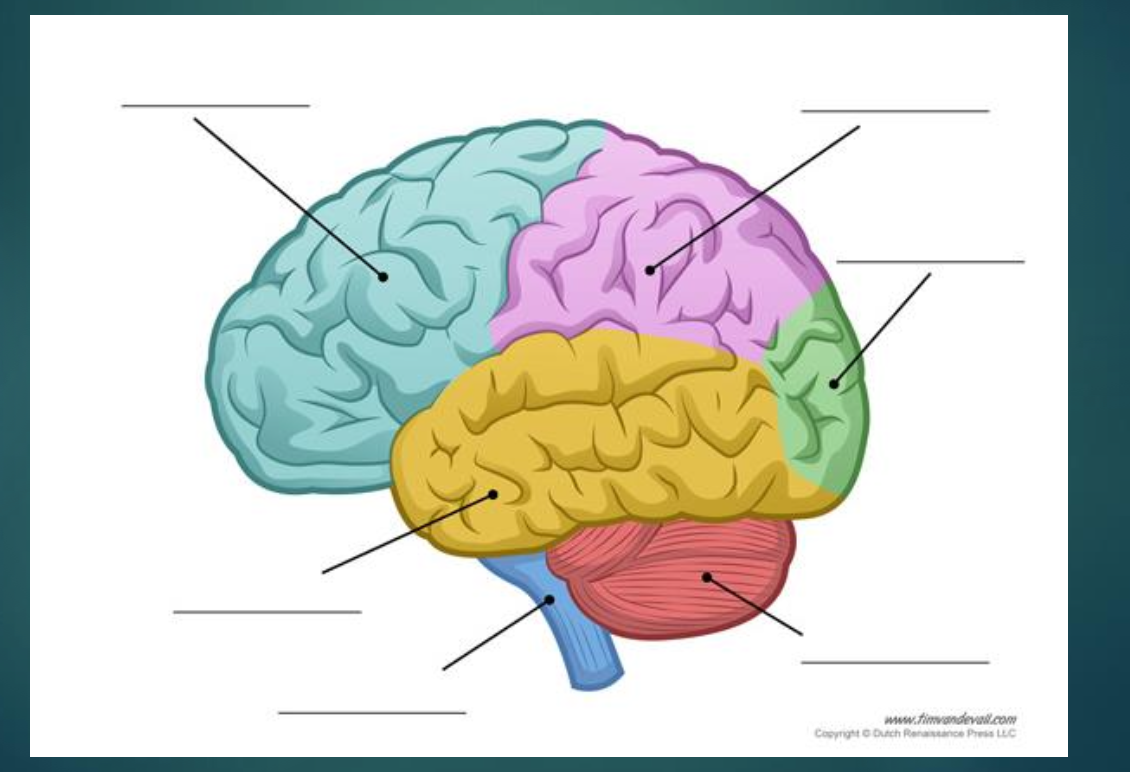
Practice: label and describe functions