BAN QUIZ 4
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
164 Terms
G2 and M checkpoints, growth/replication controlled by signalling, tumor suppressors, programmed cell death
how does the body prevent cancer
rituximab
monoclonal antibody targeting CD20 protein on B cells, leading to their destruction.
elevated WBCs on CBC with differential
what lab test would make you suspicious of leukemia
lymph node biopsy
how is definitive diagnosis of lymphoma determined
pembrolizumab
a immune checkpoint inhibitor that inhibits the PD-1 pathway, enhancing T-cell responses against cancer
Non-hodgkin lymphoma
hematologic condition associated with invasion of Waldeyer’s ring
oral hygiene, chlorohexidine, chemotherapy (kills blast cells)
treatment of leukemic gingivitis
acute leukemias
rapid onset and progress, REQUIRE treatment within hours and days
aphthous major, diffuse ecchymosis
initial presentation of AML
stage III lymphoma
spread of cancer to lymph nodes below diaphragm
swollen, painless, fixed or rubbery mobile nodes
characteristics of lymphadenopathy
dysphagia, paresthesia (numbness), pain
symptoms of oropharyngeal lymphoma
MALT lymphoma
sjogrens disease increase risk of what
non-hodgkin lymphoma
second most common ORAL cancer
larger than 1 cm
size of lymph nodes persisting for more than 4 weeks that should be biopsy
myeloid sarcoma
a solid tumor of myeloid cells, often associated with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Can cause EXPANSION OF MANDIBLE
rapid progression, bilateral viral infection, decreased inflammation (neutropenia)
in what ways can infection present abnormally in leukemia
tumor encroaching on nerve
what is numb chin syndrome an indication of
blast crisis
a life-threatening phase of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) where immature blood cells proliferate uncontrollably, resembling acute leukemia.
oral ulcerations (stomatitis), dry mouth, opportunistic infections
adverse effects of immunotherapies
budesonide
corticosteroid can be CONTINOUSLY used to treat Immunotherapy-induced stomatitis/mucositis
stomatitis/mucositis
most prevalent adverse effect of mTOR inhibitors (immunotherapy)
Bevacizumab
immunotherapy that can cause mucocutaneous bleeding
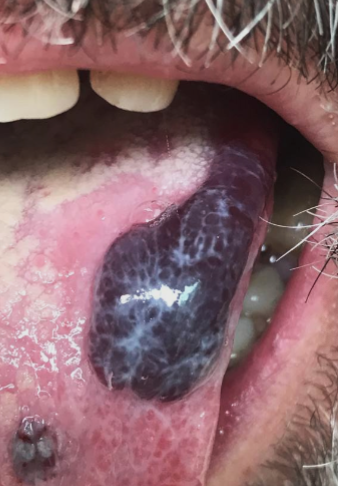
swelling, progressive infection, pain, trauma, suspicious lesion
examples of when treatments would be medically necessary
late onset dryness
what raises suspicion for salivary GVHD
mucoceles
non dangerous clear fluid filled bumps that can develop at sites of minor salivary glands, may realte to GVHD or decreased salivary function
pilocarpine (salagen)
sialogogue used to manage dry mouth as a result of radiation-induced hyposalivation
elective treatment
Any treatment that does not need to be completed for a medical reason
acute iritis, narrow angle glaucoma, uncontrolled asthma
Siagologues should not be used when pts have which conditions
head and neck radiation with chemotherapy
what causes most severe MUCOSITIS with longest duration
removal of potential irritants
general management for Mucositis caused by cytotoxic chemotherapy and/or head & neck radiation
viscous lidocaine, benzocaine, magic mouthwash
topical anesthetic that may be used for pain associated with mucositis
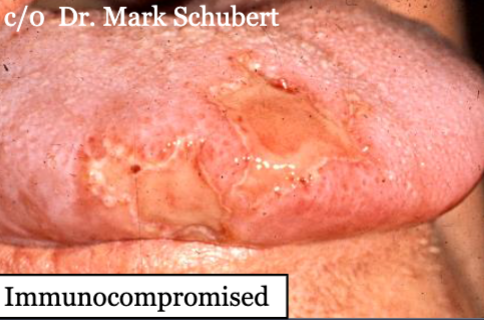
recurrent HSV
In immunocompromised hosts, lesions may be widespread (not isolated to bone-bound tissue) and are EXTREMELY painful
microdontia (small teeth/roots) or hypodontia/oligodontia (missing teeth)
potential effect of chemotherapy and radiation in pediatric pts
severe aplastic anemia, severe combined immunodeficiency, sickle cell disease
non-malignancies that require HCT
at least 28 days before transplant
when should pre HCT dental health stabilization occur
prevent acute infection
goal of dental treatment prior to HCT
pre treatment antibacterial rinse (chlorohexidine), limit aerosols during procedure
dental treatment protocol when treating pt with neutropenia
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
Leukemic gingivitis is most likely to be seen in which type of leukemia?
without immunosuppression pts develop GVHD
why is immunosupression important after transplant
mild-moderate
GVHD level associated with highest survival rates
Multiple Myeloma (MM)
“Punched out” radiolucencies are a characteristic feature of which hematologic malignancy?
chronic GVHD
presents with similar symptoms to many autoimmune diseases (dry eyes, sclerosis, xerostomia)
recognize neoantigens on tumor cells
how do T cells prevent cancer
create antibodies against damaged cells
how do B cells prevent cancer
when they touch similar cells
when do cells normally stop growing
stimulate growth, resist inhibition, avoid apoptosis, angiogenesis, metastasis, mutation
properties of cancer cells
cytotoxic chemotherapy
kills ALL rapidly dividing cells
targeted chemotherapy
interferes with specific proteins involved in cancer growth and spread
hormone chemotherapy
slows or stops the growth of sex-hormone related cancers
adjuvant therapy
chemotherapy given AFTER surgery or radiation to kill remaining cancer cells
neoadjuvant therapy
chemotherapy given to shrink a tumor BEFORE surgery
blood, GI,hair, skin, epithelial
CELLS other than cancer cells that are AFFECTED by CYTOTOXIC CHEMOTHERAPY
gives patient time to recover (from adverse effects)
why would cytotoxic chemotherapy is administered in cycle
toxicities and time needed for body to recover
important considerations for length of treatment
imatinib (Gleevec)
A targeted therapy used primarily used to treat Philadelphia chromosome associated chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
fewer side effects
benefit of targeted chemotherapy
small molecule drugs (nibs)
targeted chemotherapy drugs that ENTER CELL and target specific substance within cell
large molecule drugs/monoclonal antibodies (mabs)
targeted chemotherapy that target proteins or enzymes from CELL SURFACE
immunotherapy
a type of Targeted treatment that uses the body's own immune system to fight cancer,
angiogenesis inhibitors
targeted chemotherapy that inactivates vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
mucositis (mucous membrane inflammation)
ADR of angiogenesis inhibitors
signal transduction inhibitors
targeted chemotherapy that interferes with intracellular signaling pathways to inhibit cancer cell growth
proteasome inhibitors/monoclonal immunoglobulins (mibs)
targeted chemotherapy that activate cell signaling to cause apoptosis
synthetic cytokines
immunotherapy that is a synthetic version of IL-2 that increases growth and activity of T and B cells
checkpoint inhibitors
immunotherapy that blocks checkpoint proteins to enhance T and B cell responses against tumors
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy
immunotherapy that modifies T cells to find specific tumor cell
monoclonal antibodies
can be both targeted chemotherapy and immunotherapy
ceritinib, crizotinib
drugs that target ALK in non-small cell lung cancer
tobacco use
Which modifiable risk factor has the greatest impact on overall cancer incidence in the United States?
tumor supressor, mutation leads to loss of regulation
How does p53 mutation influence cancer risk?
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Which type of lymphoma is more common?
bone marrow biopsy
most definitive study for the diagnosis of acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
myelodysplastic syndrome
A group of disorders caused by poorly formed or dysfunctional blood cells, often leading to ineffective hematopoiesis and an increased risk of AML
infection (neutropenia) and bleeding (thrrombocytopenia)
risks of myelodysplasia (pancytopenia related)
blood smear and bone marrow biopsy
tests for differential diagnosis of blood disorders/ cancers
hypercellular marrow
hallmark of MDS characterized by many abnormally shaped,
immature forms of blood cells and a high number of myeloid progenitors.
flow cytometry
test used to look for specific marker of disease
gentetic
test to look for specific muations realted to disease
0.8
threshold ANC under which a pt would require antibiotics
50
threshold PLT under which a pt would require platelet transfusion
24
threshold HCT under which pt would require RBC transfusion
oral hygiene, antibiotics, chlorhexidine, EXT when safe
how would you treat a periodontal abscess oin a pt with pancytopenia
platelet transfusion, prophylactic antibiotics, no NSAIDs, anti-fibrinolytic agent
what is the treatment plan for a pt with pancytopenia who requires emergent extraction
discuss with oncology, temporary stabilization if possible
approach for extraction in pts with cancer
allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplant
a procedure that infuses healthy stem cells from a DONOR into a patient to replace damaged or diseased bone marrow, usually for LEUKEMIA
autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant
a procedure that infuses a patient's OWN healthy stem cells back into their body after high-dose chemotherapy or radiation therapy, typically used for LYMPHOMA and MYELOMA
conditioning/myeloablation
the process of preparing a patient for a stem cell transplant by destroying diseased bone marrow and suppressing the immune system, often using chemotherapy or radiation.
infection,bleeding mucositis, xerostomia, taste dysfunction, acute GVHD
acute oral complications that may occur after ALLOGENIC HCT
Chronic GVHD, 2nd malignancies (oral squamous cell carcinoma), infections ect.
chronic complications that may occur after ALLOGENIC hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT)
xerostomia, decay, relapse, 2nd malignancies
chronic complications that may occur with AUTOLOGOUS HCT
HLA matching
How are donors chosen for Allogeneic HCT?
decreased survival and increased graft rejection and risk of GVHD
risks with single antigen mismatch in A,B,C, or DR in HLA region
infection risk, bleeding risk, long term dental prognosis, timing of procedures
main considerations for treating oncology pts
open and broach, SDF, perio therapy (scaling)
examples of temporary stabilization in dentistry
dental stabilization, conditioning, transplant, recovery
order of events of HCT treatment
oral mucositis
complication of cancer therapies, especially HCT and head and neck radiation that causes painful inflammation and ulceration of the mucous membranes in the mouth
non-keratinized tissues
most suscptible tissue to mucositis
within 3 weeks
when does mucositis typically develop after HCT
palifermin
used to decrease severity of mucositis by thickening epithelial tissue before chemo