BIOL 1407 - Green Plants
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
archaeplastida
red algae, chlorophytes and charophytes (green algae), land plants
streptophytes
group that includes green algae and land plants (green plants)
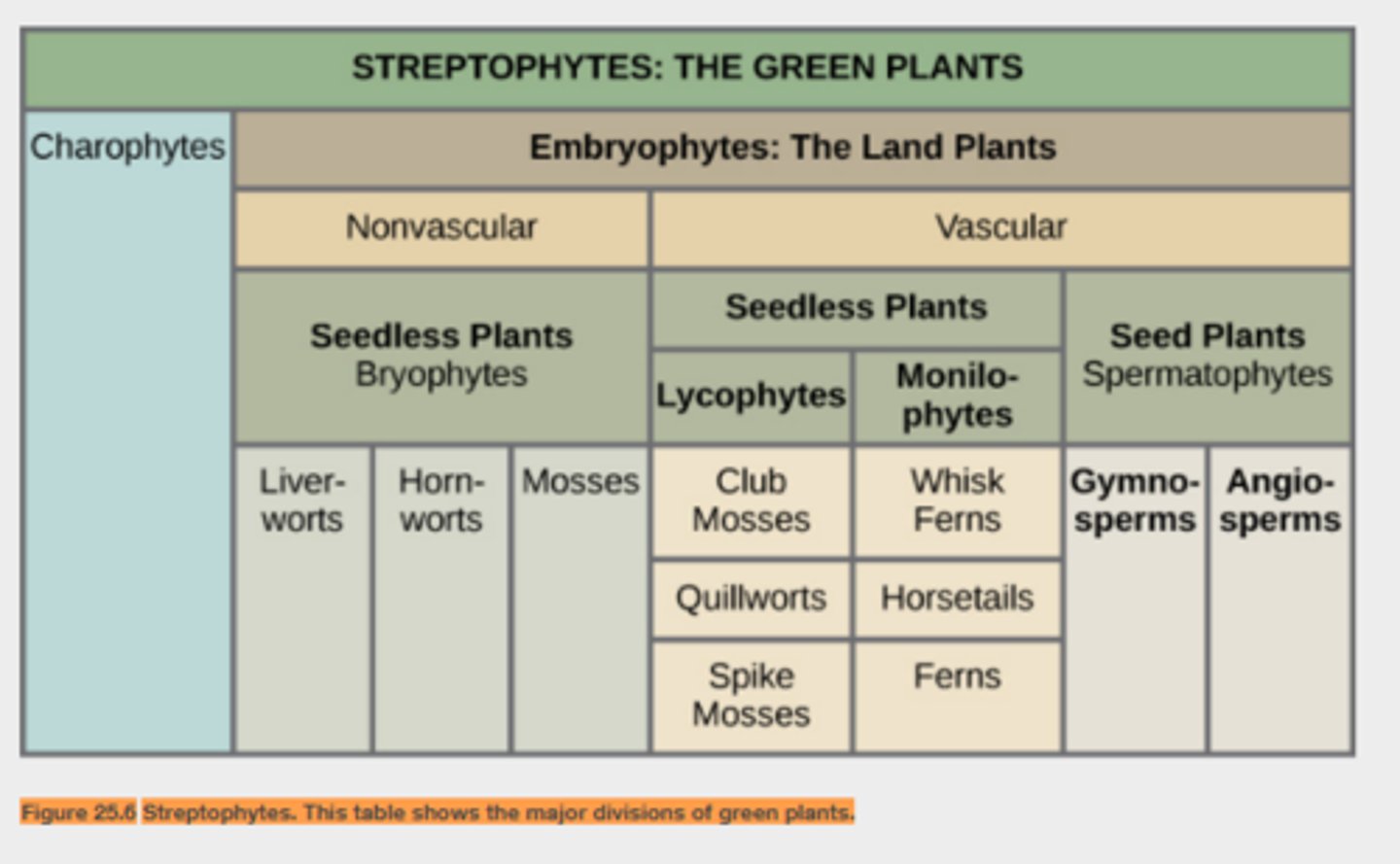
embryophytes
Another name for land plants, recognizing that land plants share the common derived trait of multicellular, dependent embryos.
Bryophytes
A moss, liverwort, or hornwort; a nonvascular plant that inhabits the land but lacks many of the terrestrial adaptations of vascular plants.
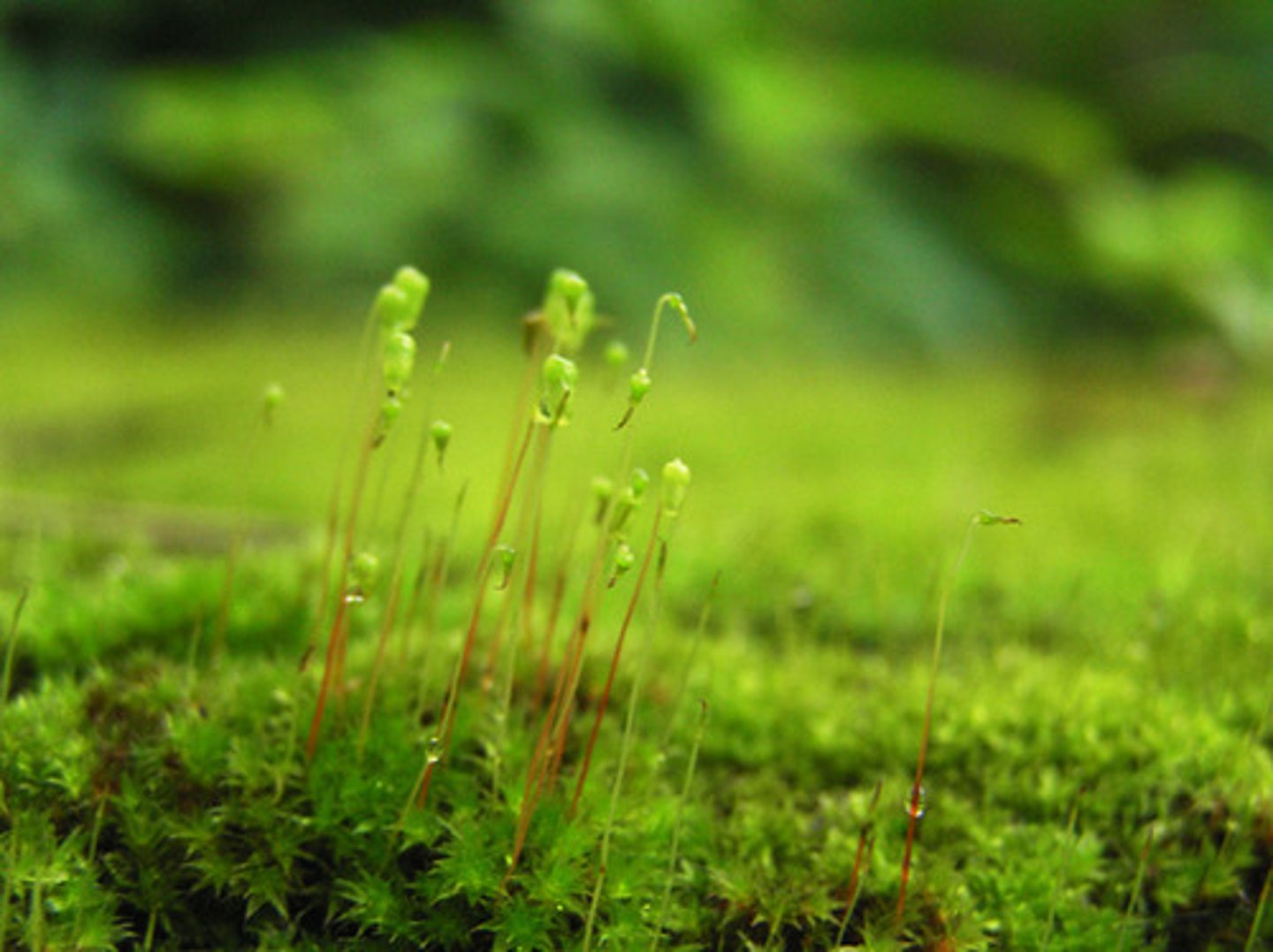

lycophytes
includes club mosses, spike mosses, and quillworts. These lack seeds.
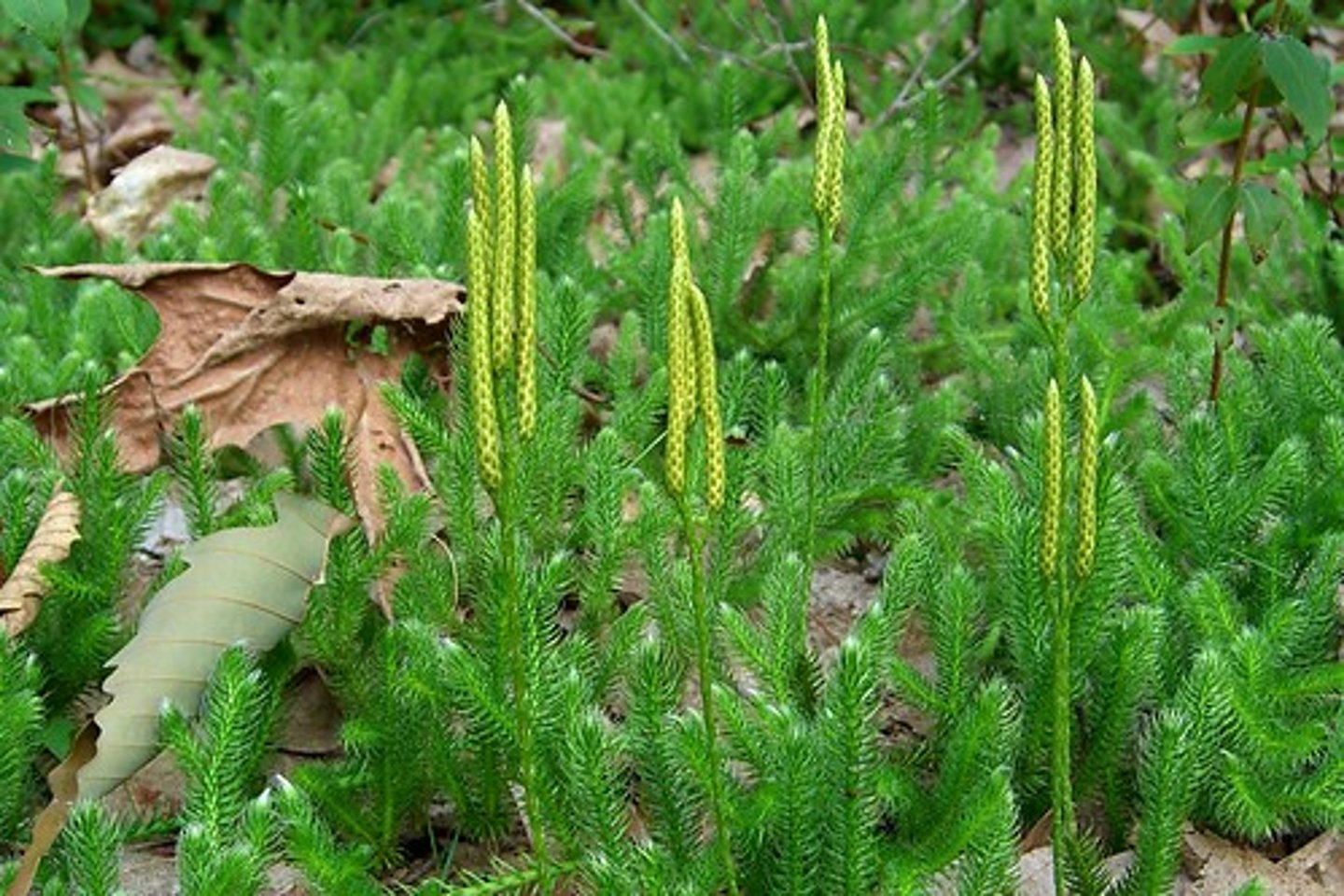

pterophytes
Group of seedless plants that includes ferns, horsetails and whisk ferns
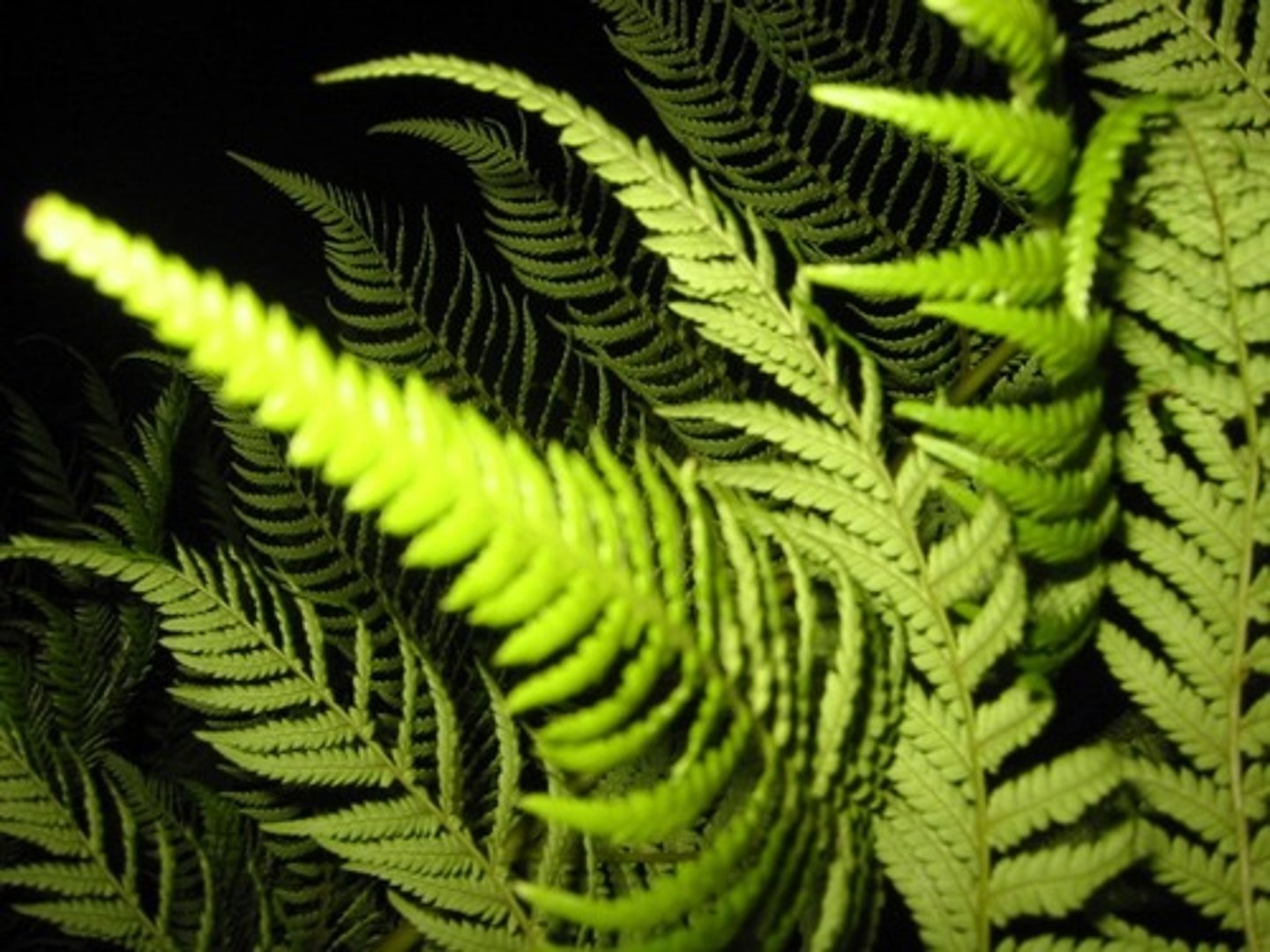

Spermatophytes
Seed plants (gymnosperms and angiosperms)
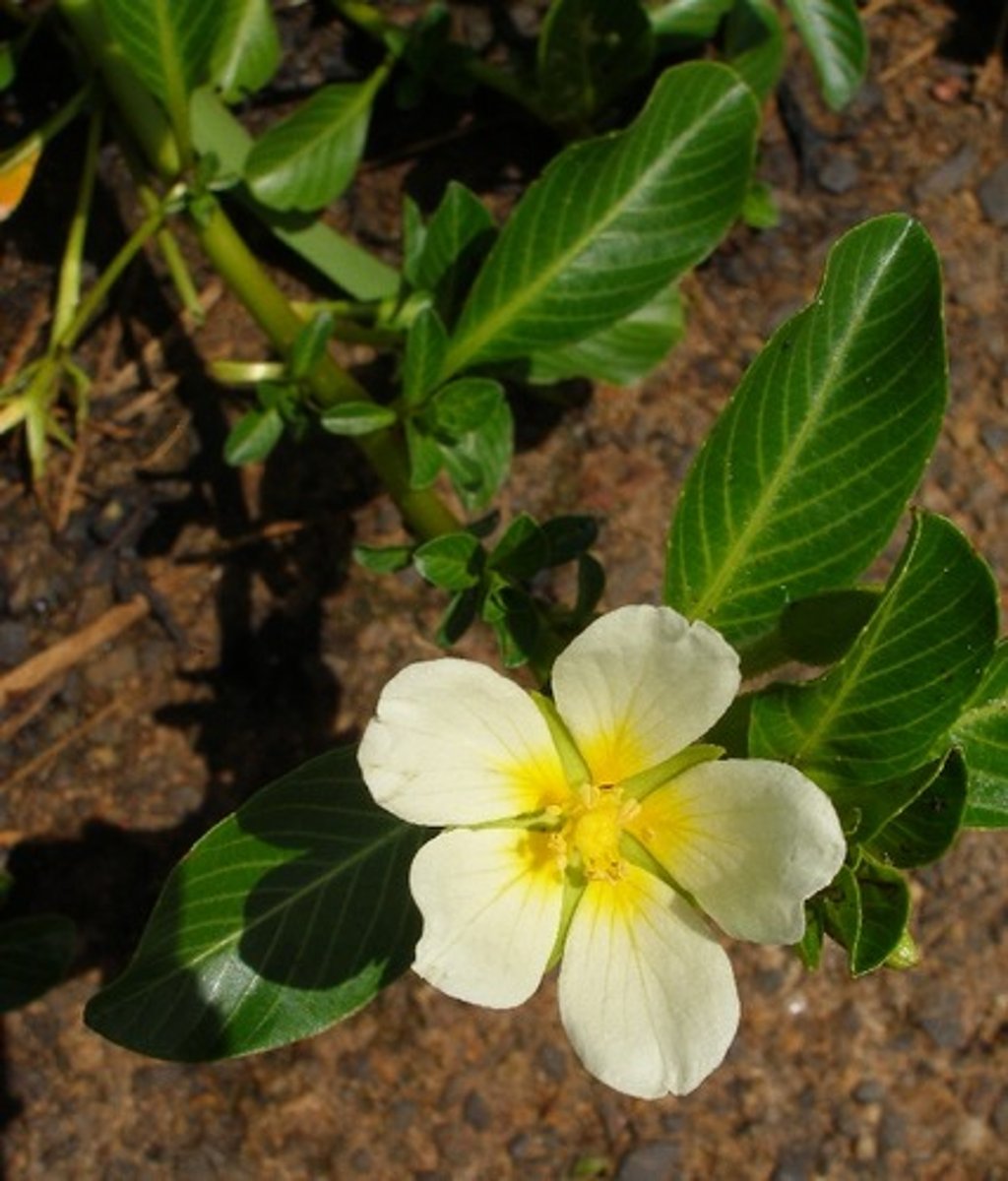

gymnosperms
A plant that produces seeds that are exposed rather than seeds enclosed in fruits
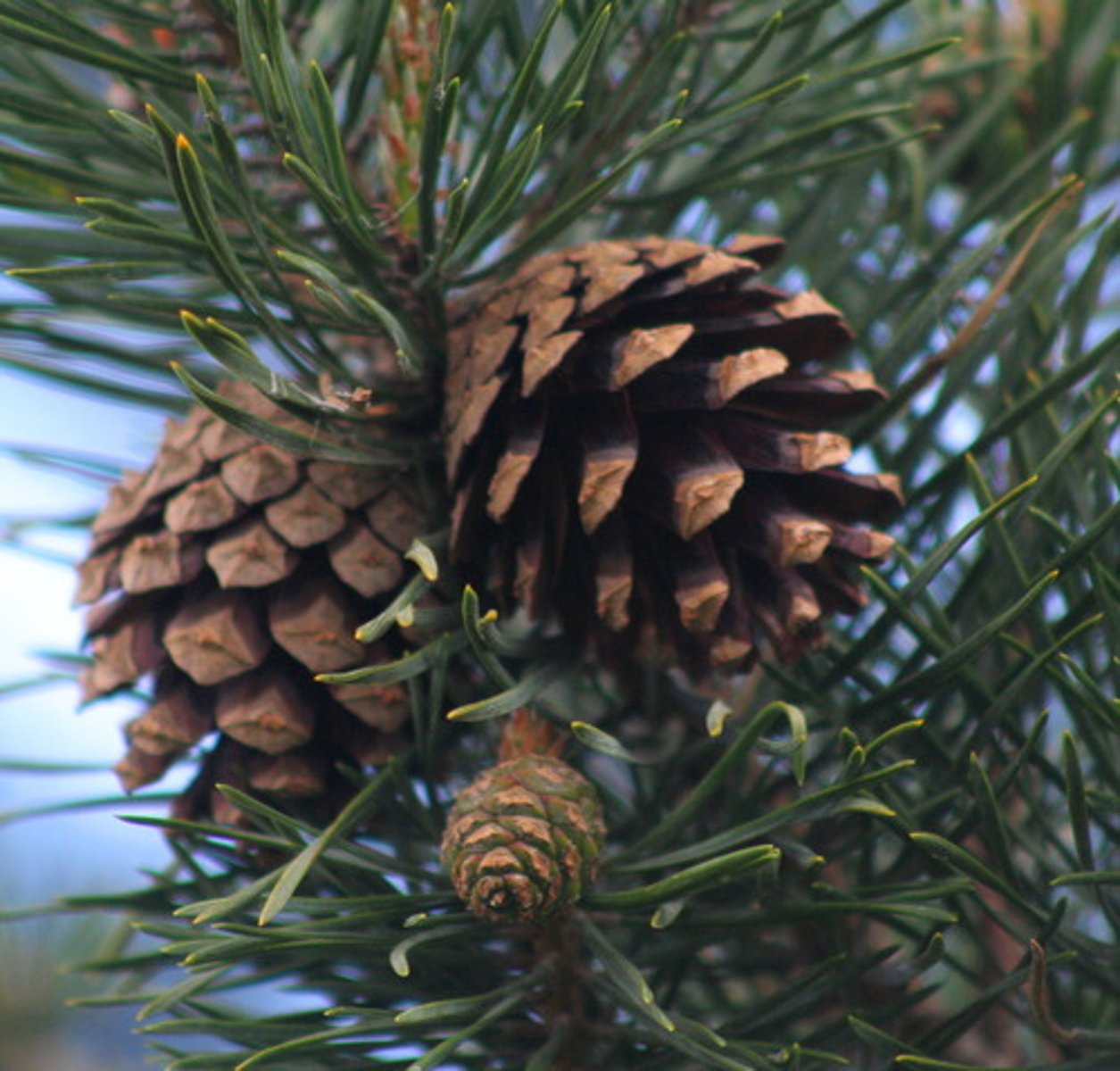

angiosperms
A flowering plant which forms seeds inside a protective chamber called an ovary.
similarities of green algae and land plants
-same chloroplast structure
-similar thylakoids arrangements
-similar cell walls, sperm, and peroxisomes
-their chloroplasts synthesize starch as a storage product
Evolution of land plants
alternation of generations, growth from apical meristems
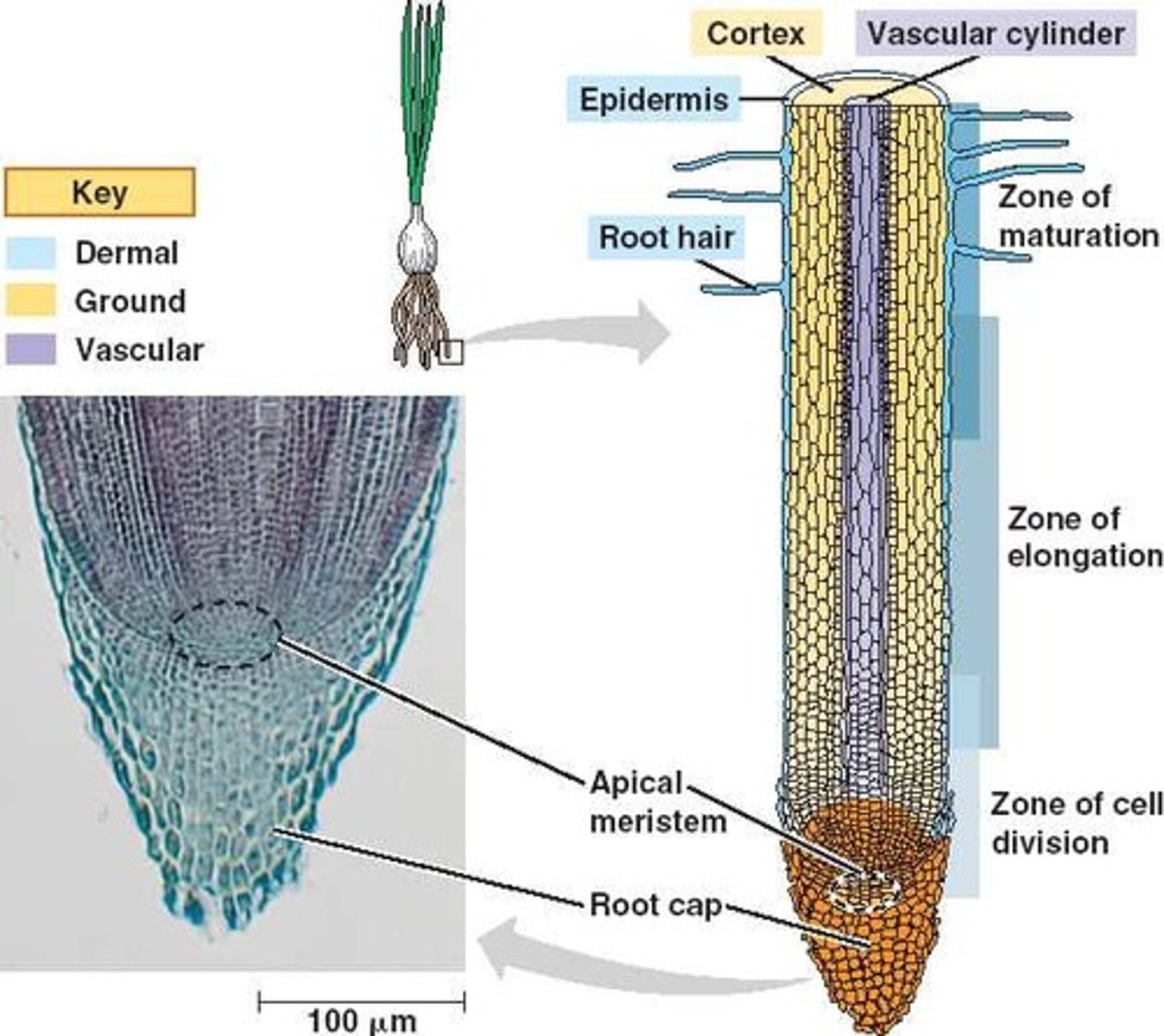
apical meristems (land plants)
Embryonic plant tissue in the tips of roots and in the buds of shoots that supplies cells for the plant to grow in length.
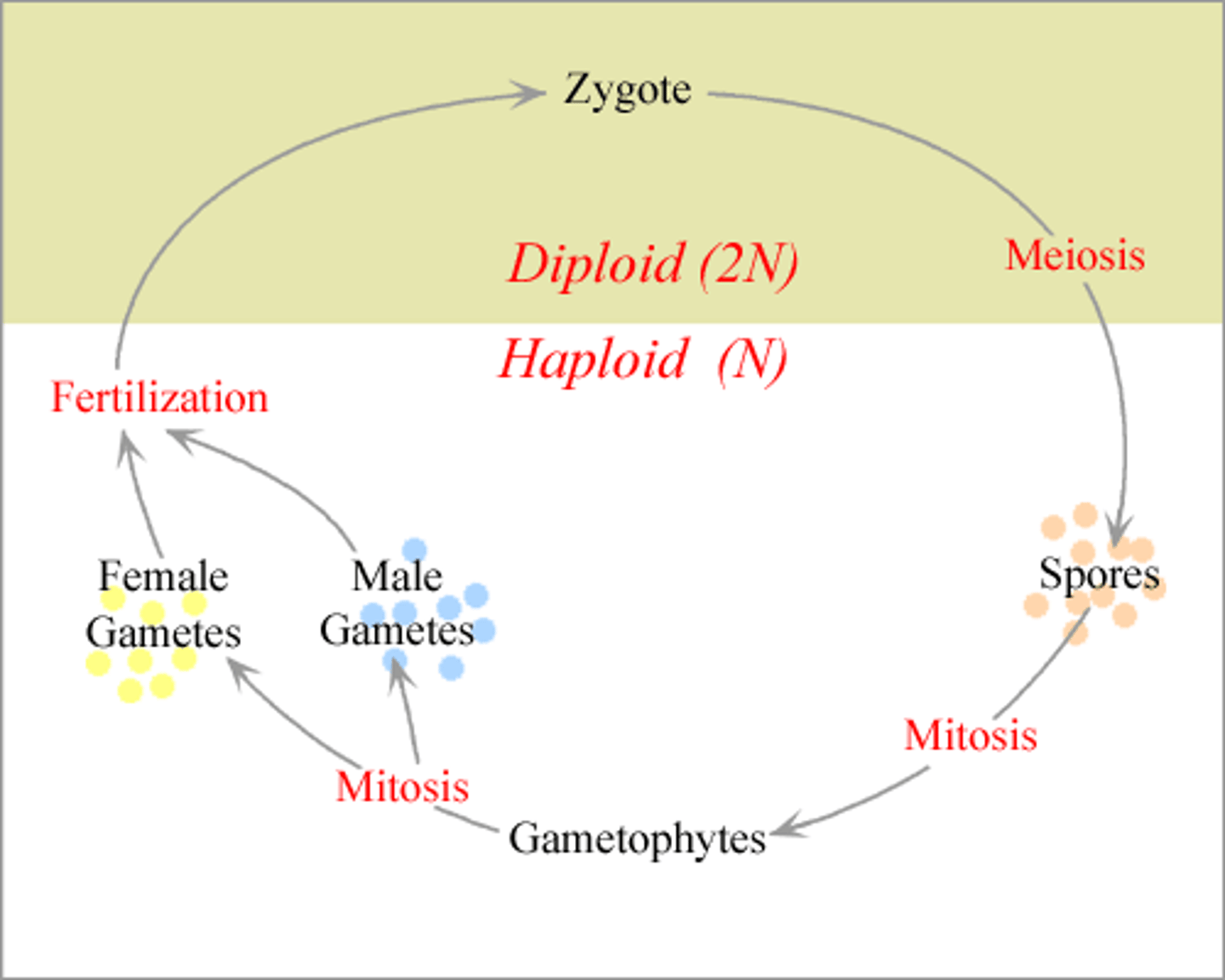
haplontic
having a life cycle in which the main form is haploid, with a diploid zygote being formed only briefly
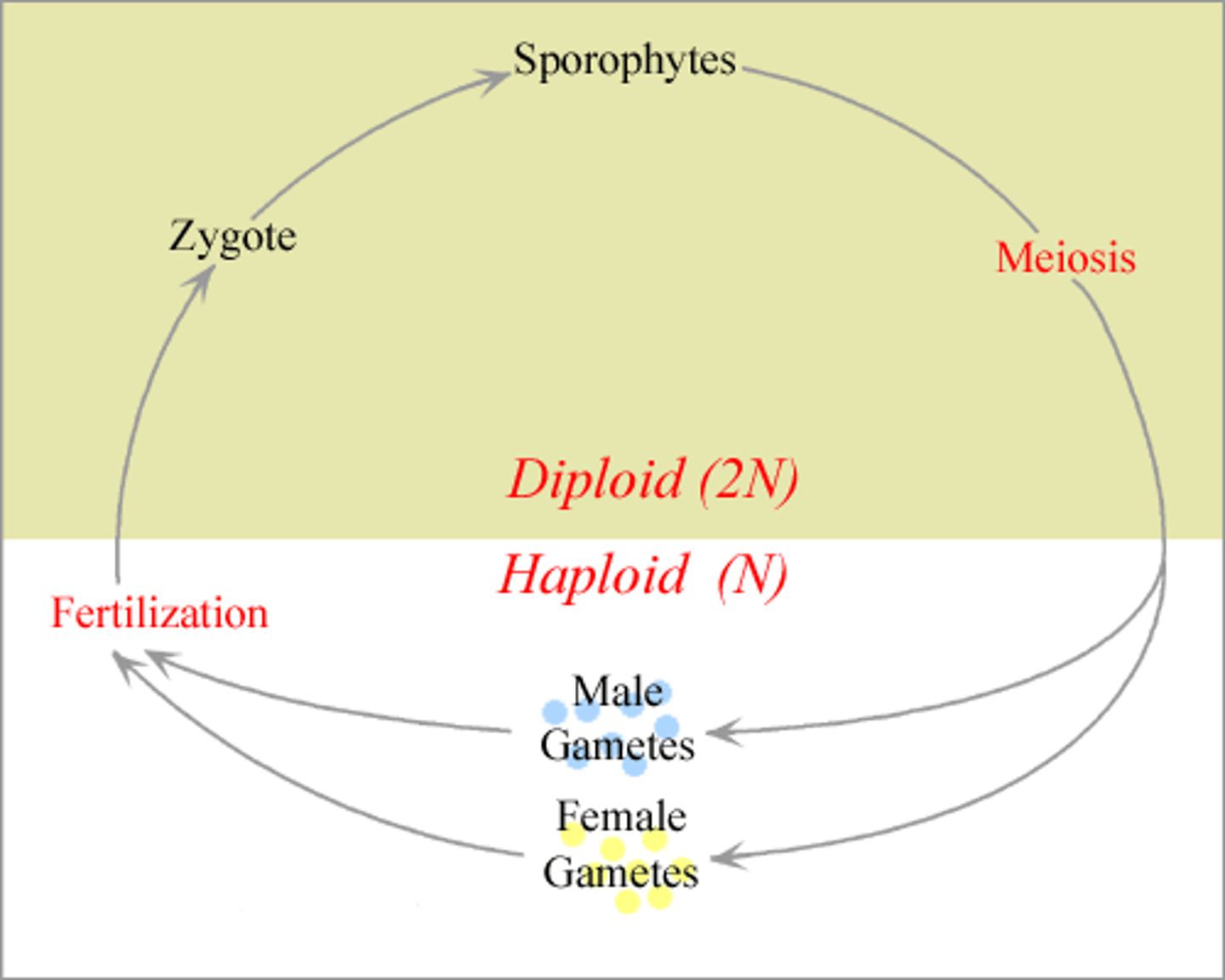
diplontic
A type of life cycle in which gametes are the only haploid cells and mitosis occurs only in diploid cells
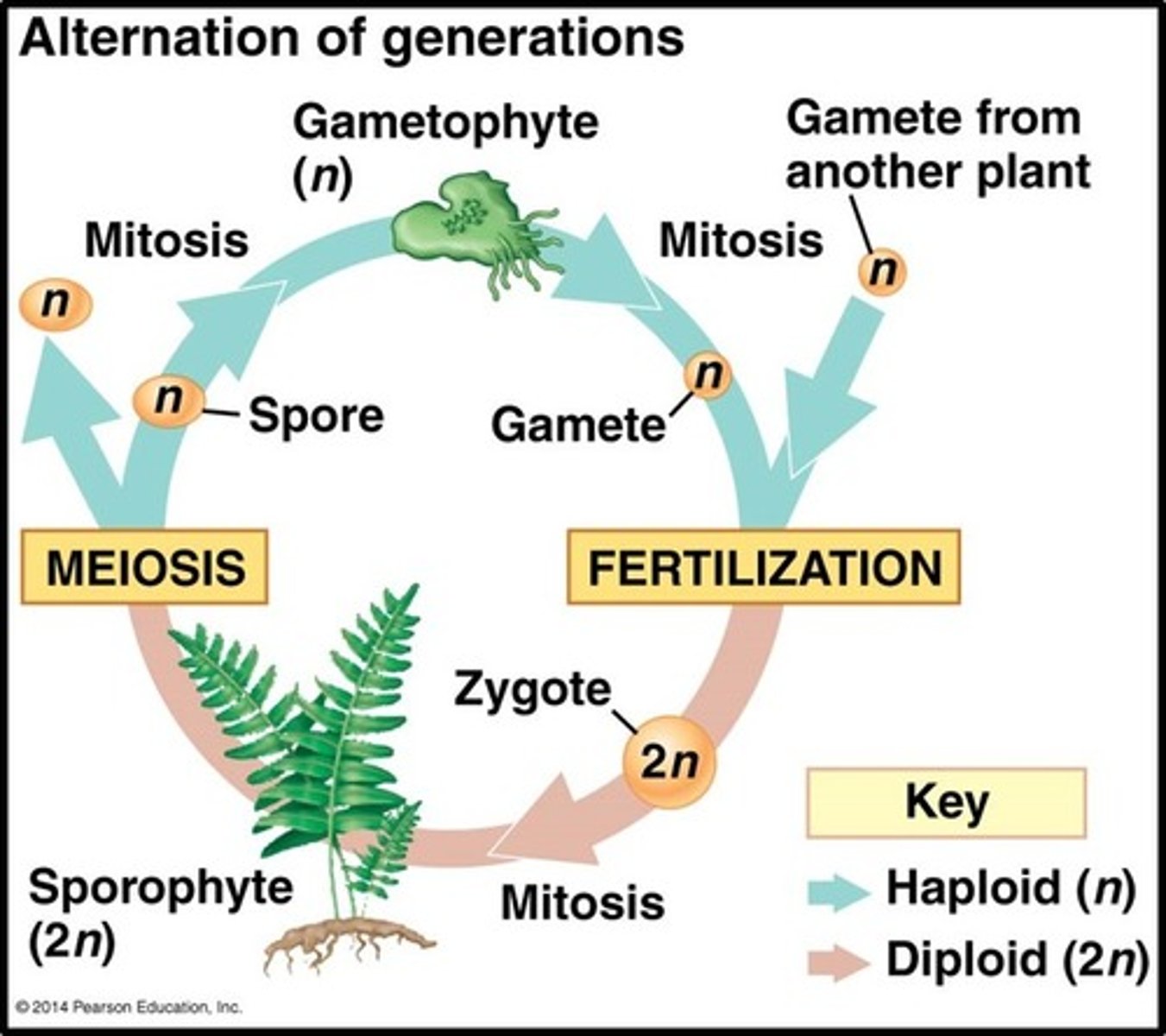
haplo-diplontic
referring to a life cycle in which the organism spends significant time in both the haploid and diploid stages
sporophyte
Diploid, or spore-producing, phase of an organism, sporophyte dominant is evolutionary trend in land plants
gametophyte
Haploid, or gamete-producing, phase of an organism, dominant in lower plants
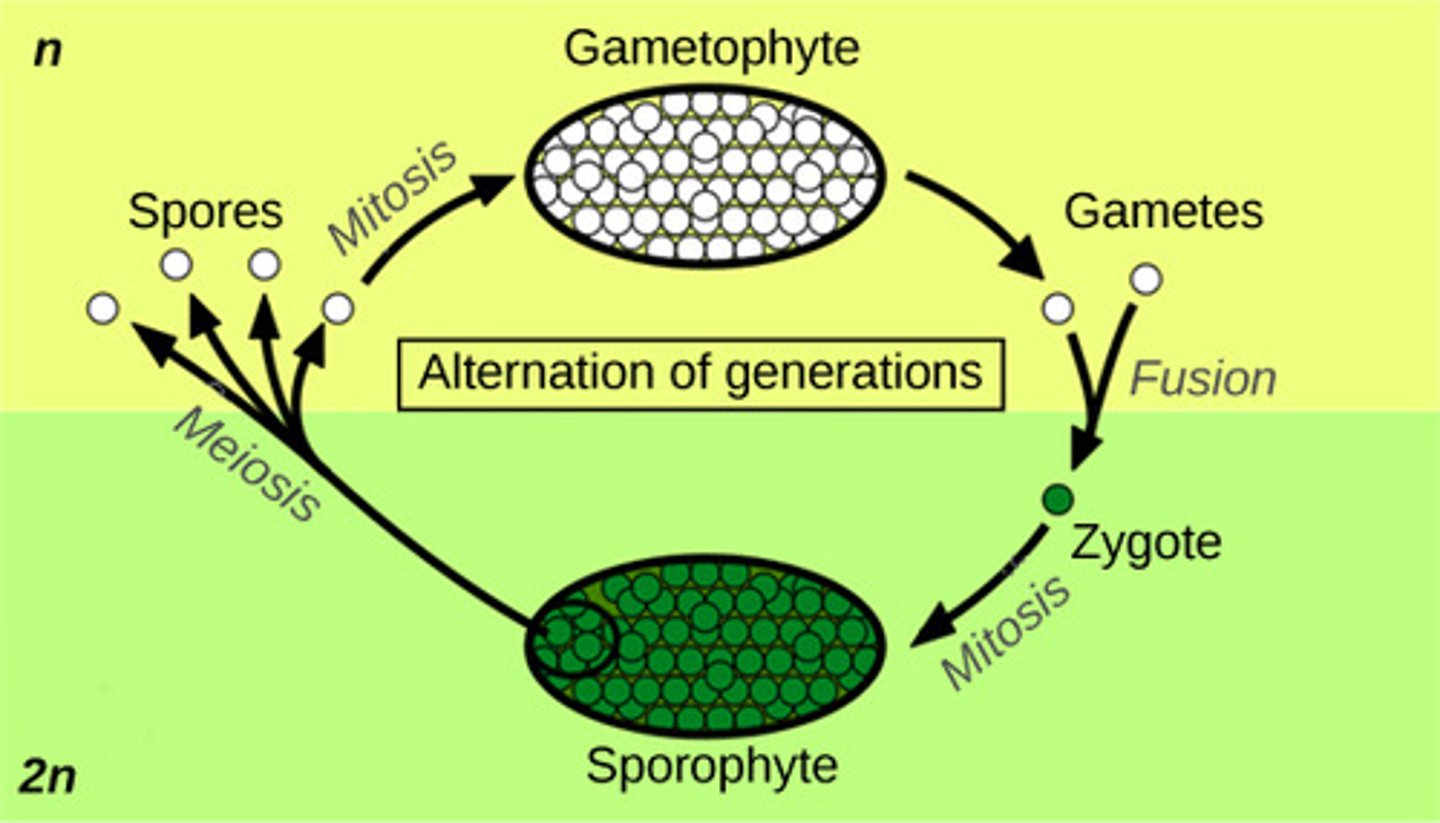
alternation of generations
the alternation between the haploid gametophyte and the diploid sporophyte in a plant's life cycle, both haploid and diploid cells multicellular
adaptations of evolving land plants
water loss, uv light (pigments), upright growth (vascular tissue)
nonvascular plants
Plants that lack a well-developed system of tubes for transporting water and other materials

seedless vascular plants
Plants that have vascular tissue but reproduce by spores (ferns, club mosses, and horsetails)

seed plants
have vascular tissue and make seeds, angiosperms

cuticle
A waxy covering on the surface of stems and leaves that acts as an adaptation to prevent desiccation in terrestrial plants.
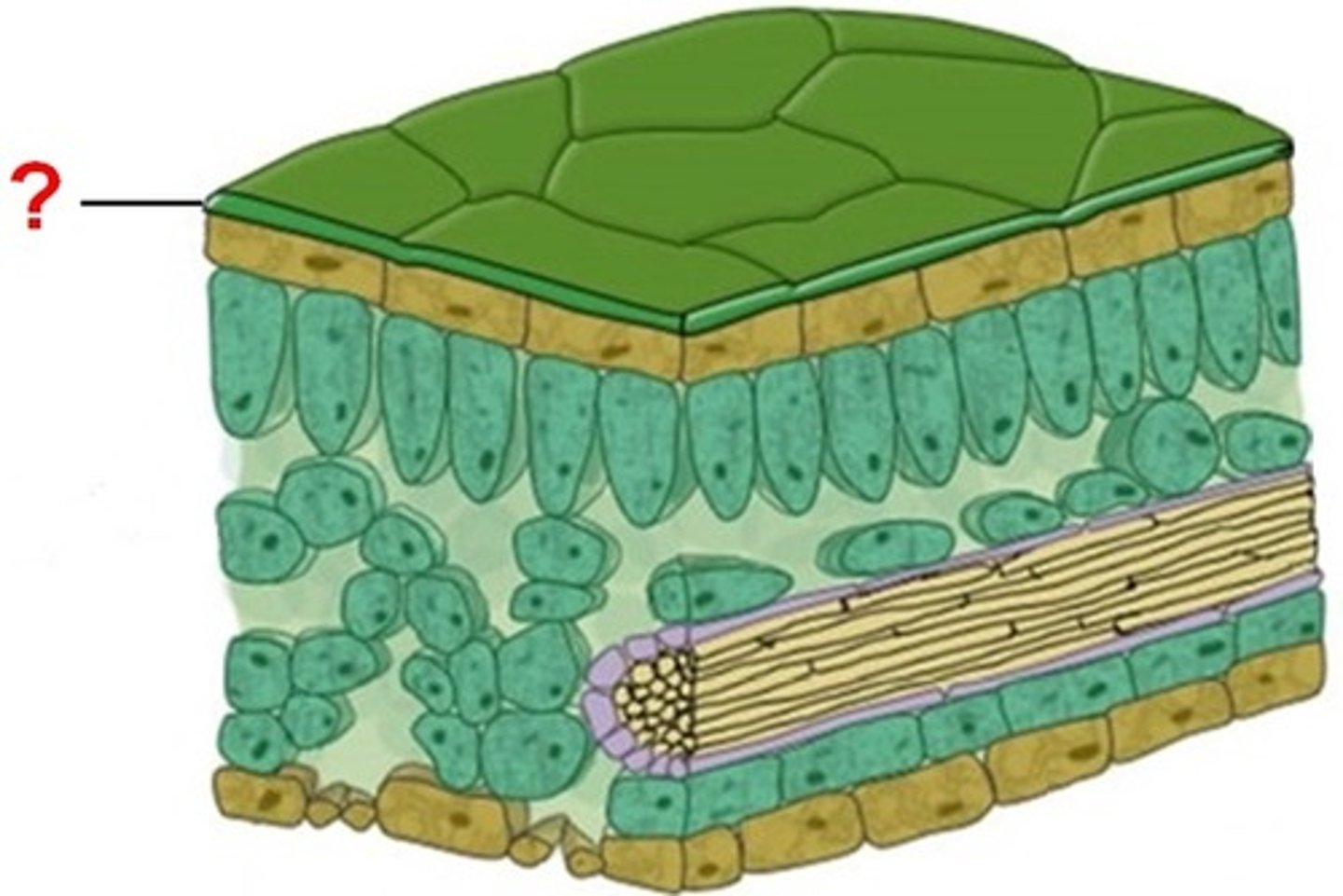
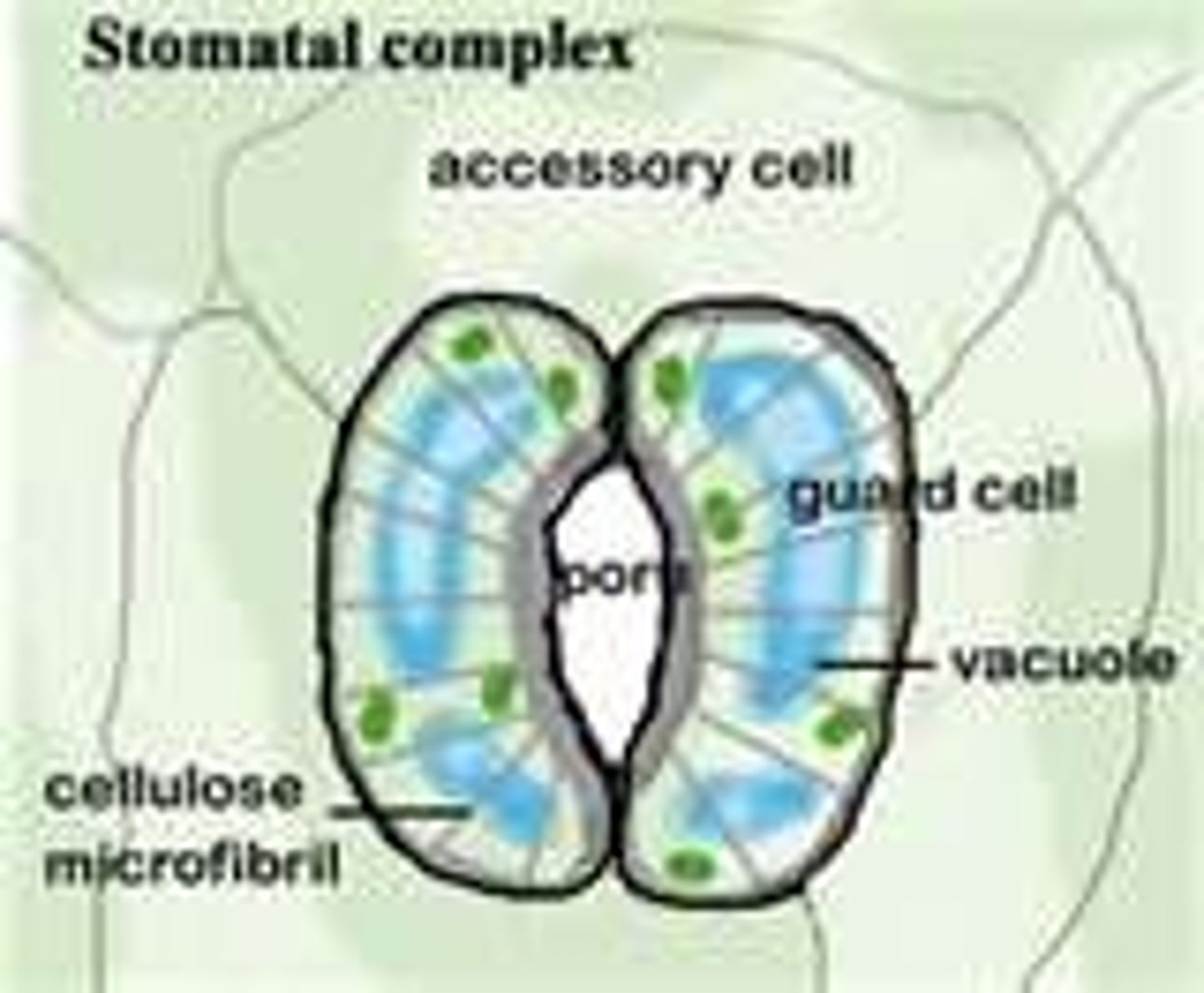
stomates
Openings in leaves to exchange photosynthetic gases: water vapor, carbon dioxide, and oxygen
vascular tissues
xylem and phloem
homosporous
Referring to a plant species that has a single kind of spore, which typically develops into a bisexual gametophyte, nonvascular plants
heterosporous
A term referring to a plant species that has two kinds of spores: microspores that develop into male gametophytes and megaspores that develop into female gametophytes, seed plants
sporophyte dependent
Sporophyte relies on gametophyte for nutrition.
megaspore
A spore from a heterosporous plant species that develops into a female gametophyte.
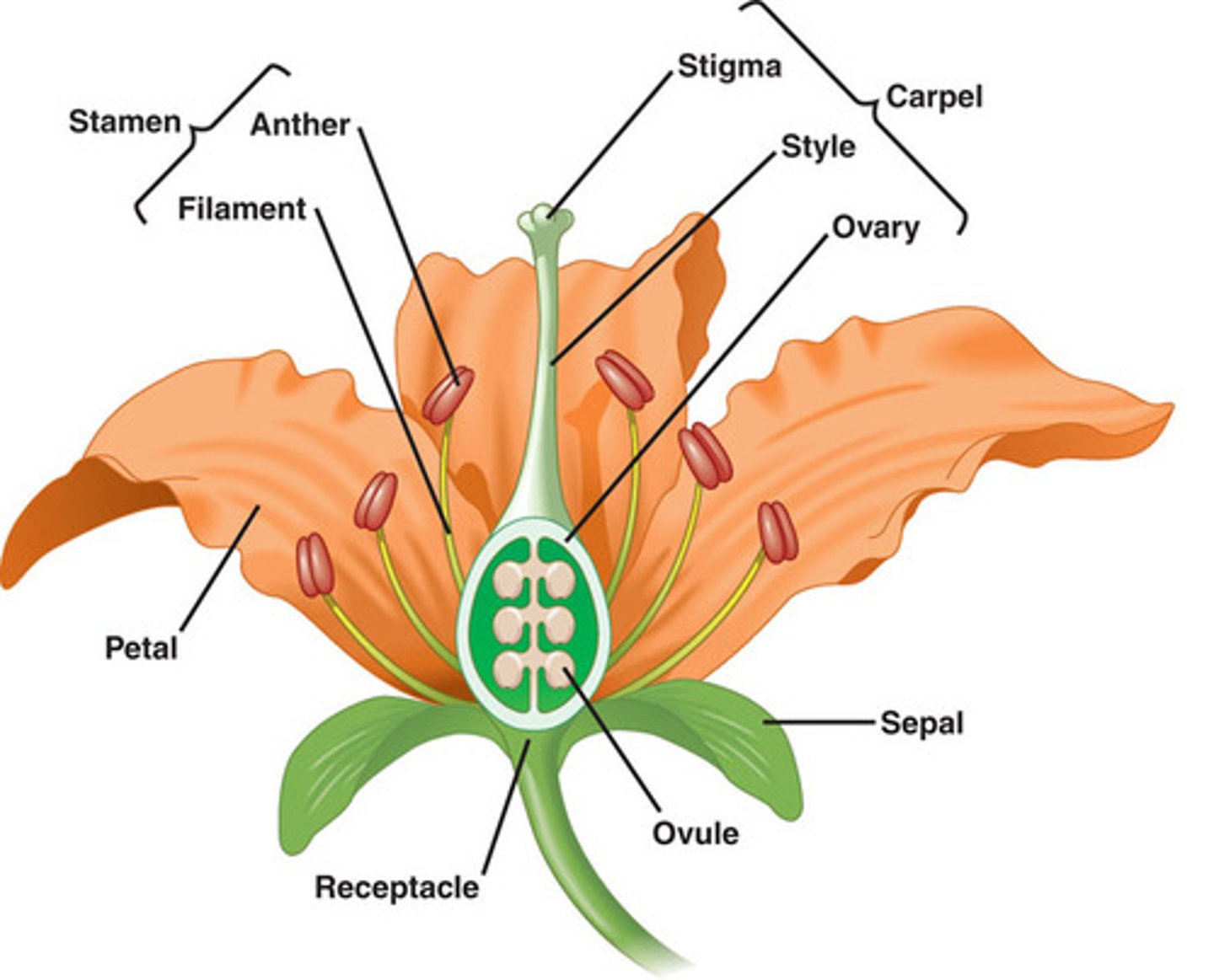
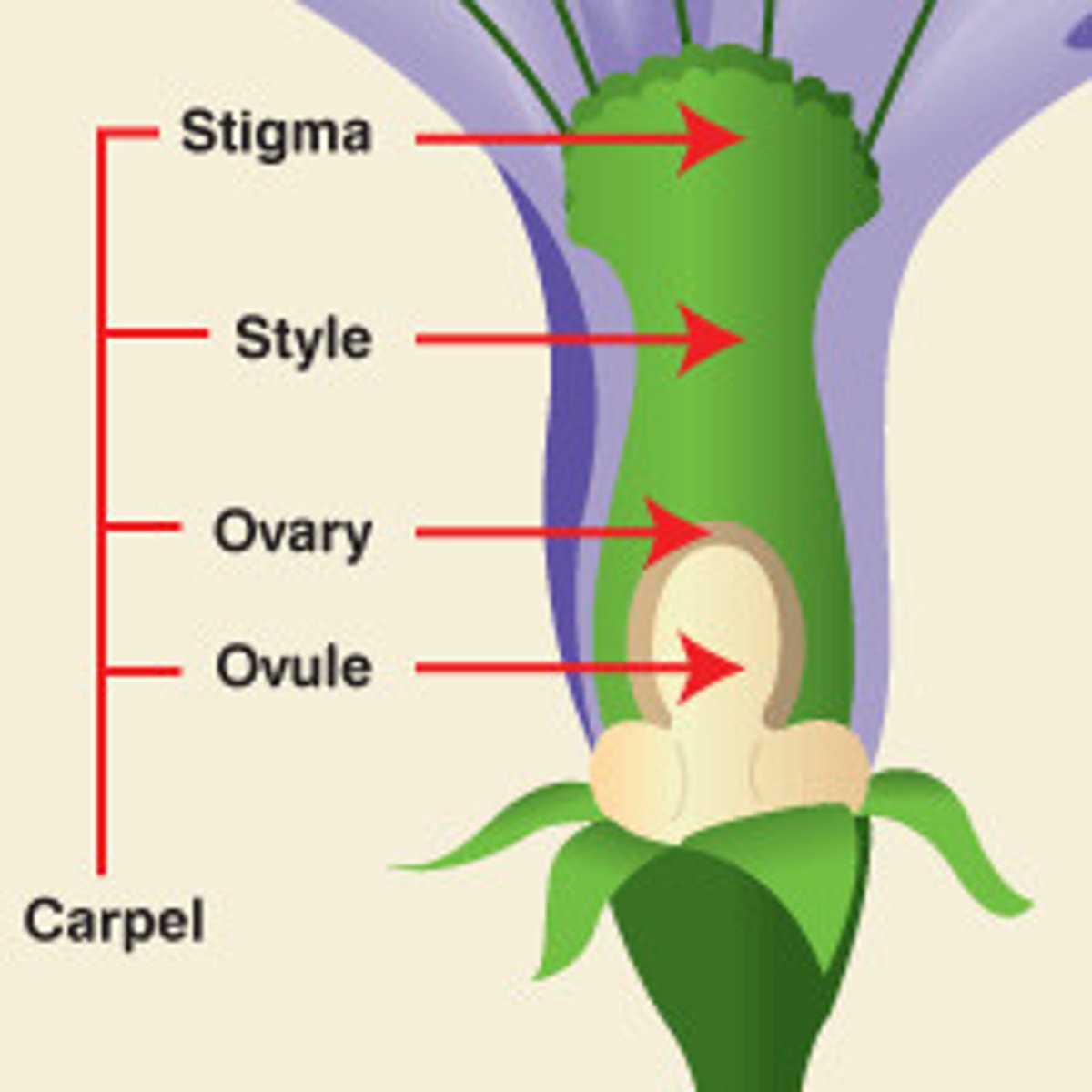
Gynoecium (carpels)
the female part of a flower, consisting of one or more carpels.
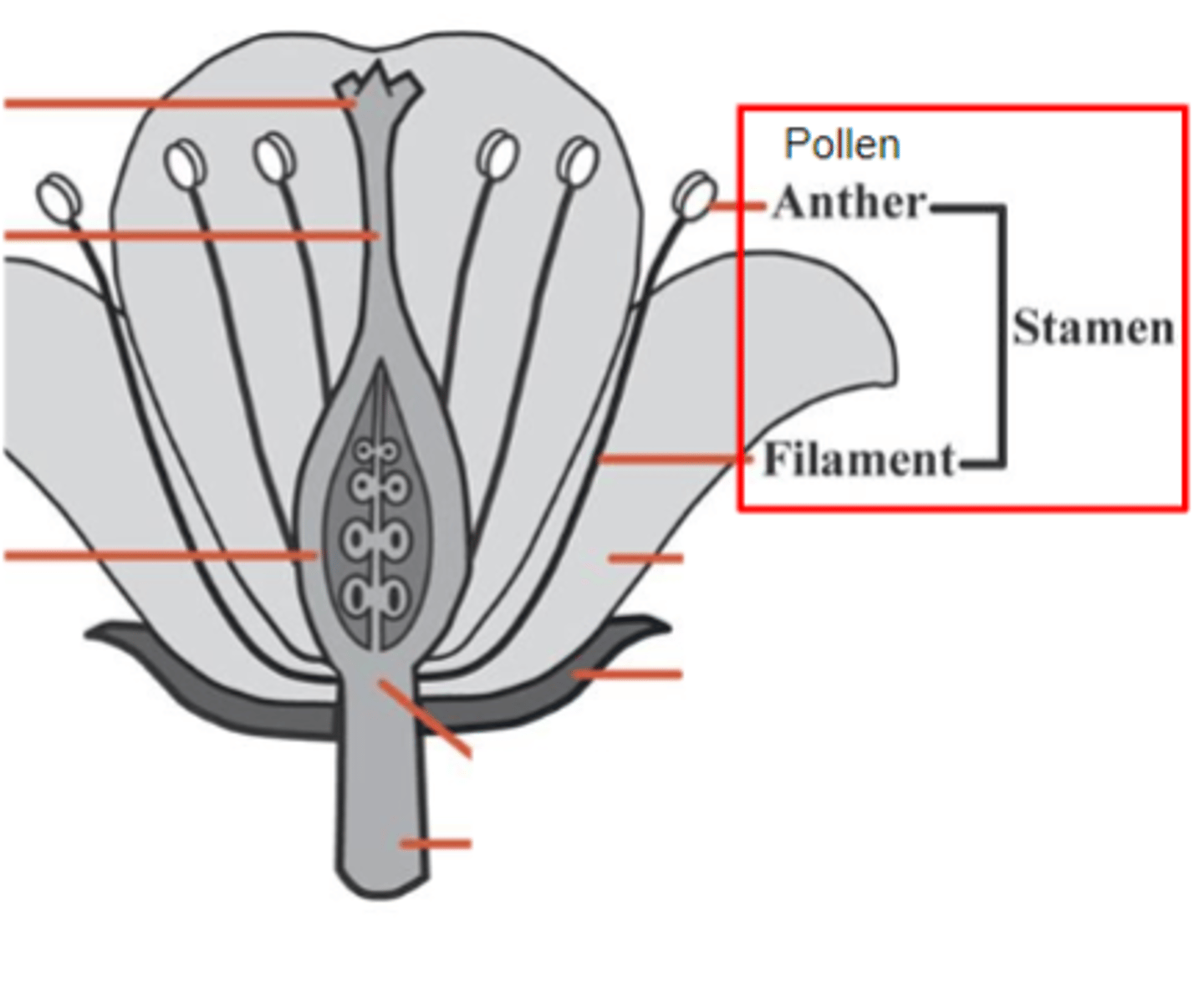
androecium (stamen)
The male reproductive part of a flower
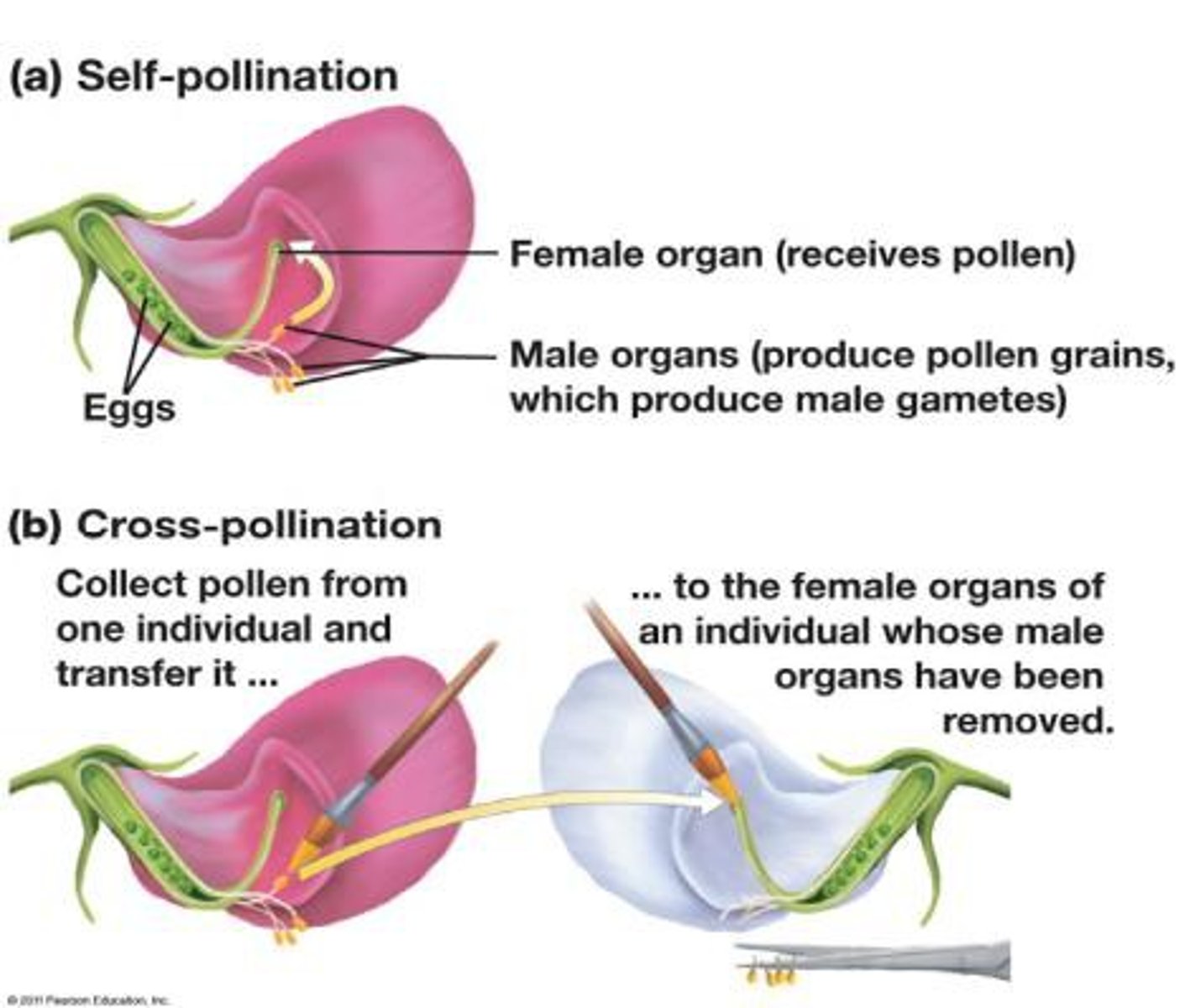
pollination
The transfer of pollen from male reproductive structures to female reproductive structures in plants, helped by other organisms such as bees, or natural forces such as wind or water movement in aquatic plants
tracheids
A water-conducting and supportive element of xylem composed of long, thin cells with tapered ends and walls hardened with lignin.
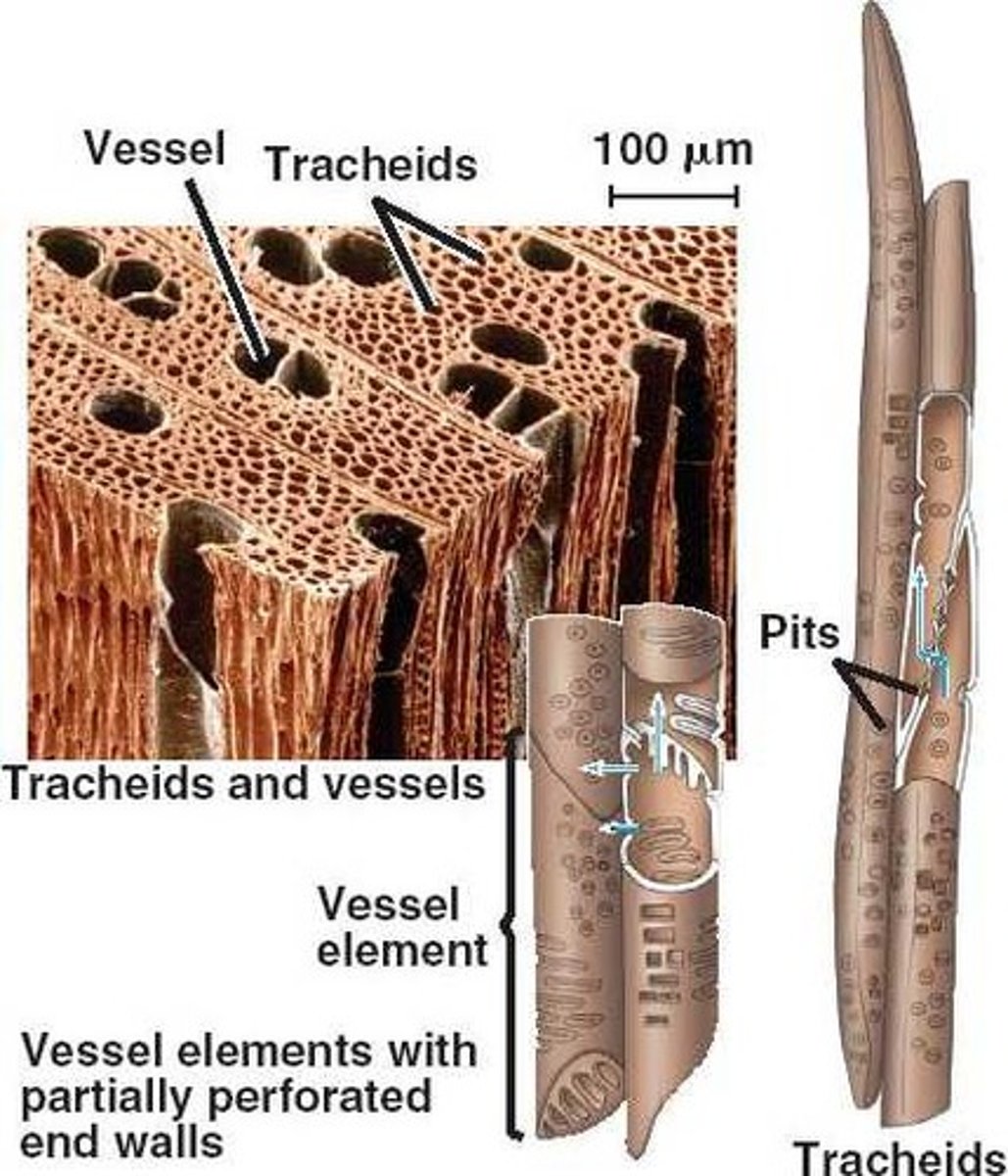
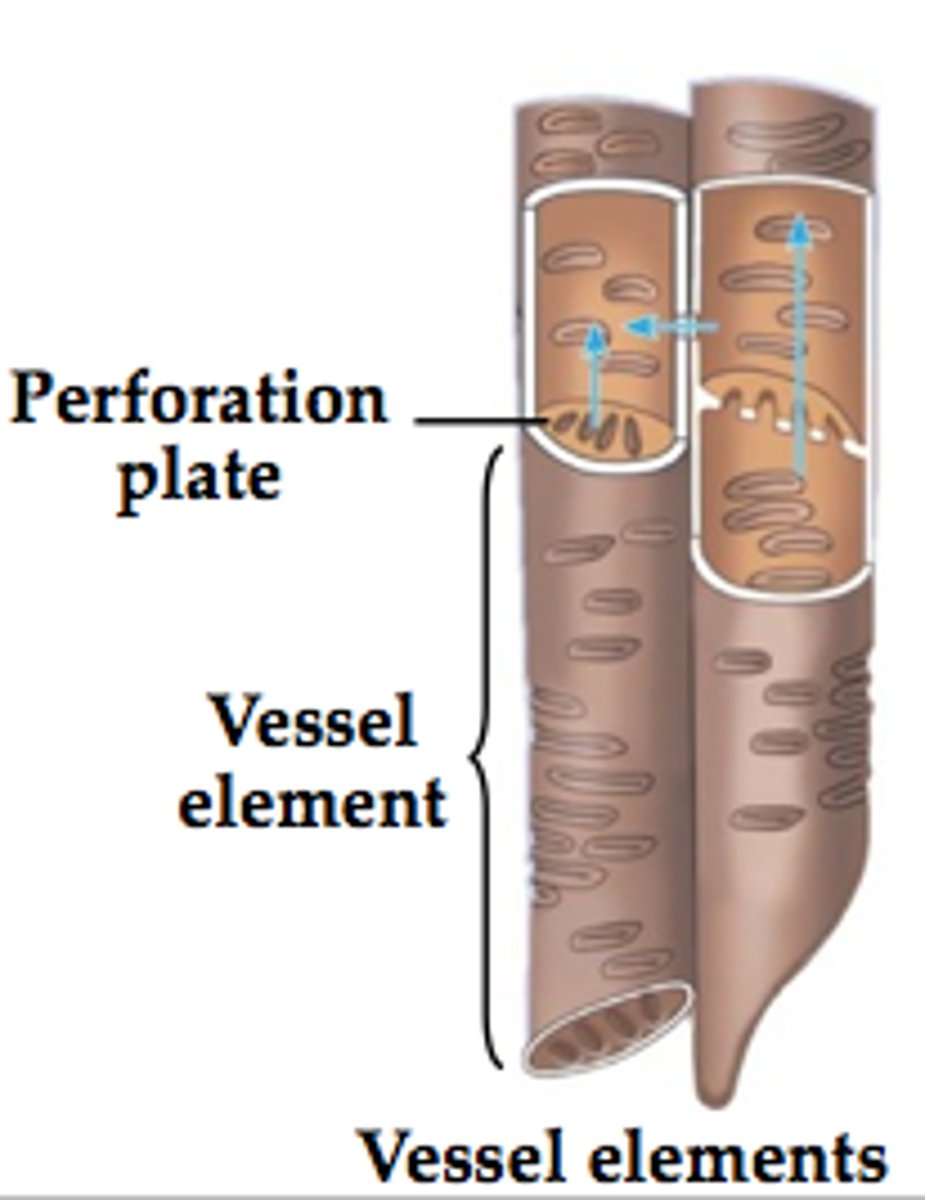
vessel elements
A short, wide, water conducting cell found in the xylem of most angiosperms and a few nonflowering vascular plants. Dead at maturity, vessel elements are aligned end to form micropipes called vessels.
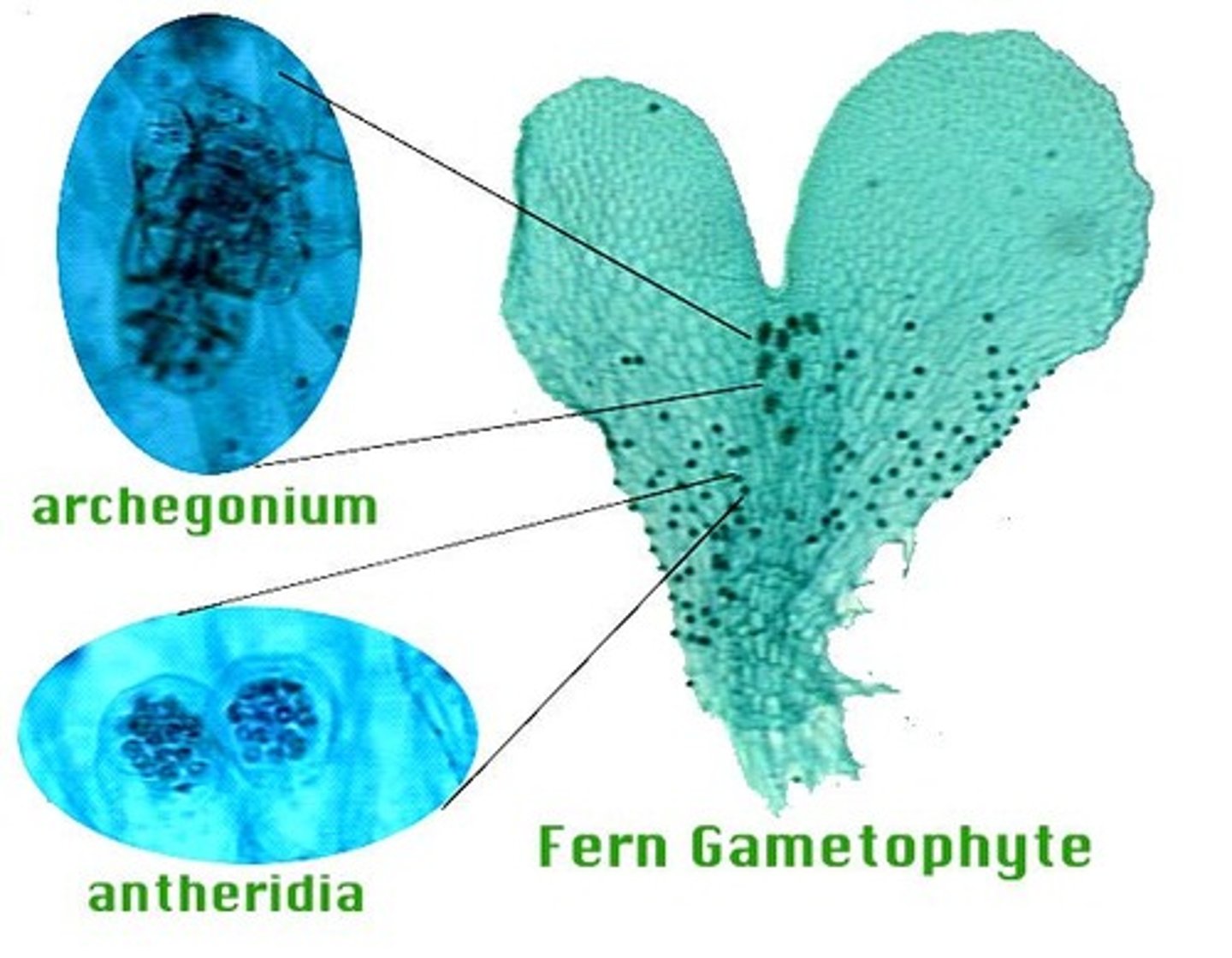
gametangia
A reproductive organ that houses and protects the gametes of a plant
antheridia
Structures in plants that produce male gametes
archegonia
Female reproductive part of a nonvascular plant