Module 3- Cell Division
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Cell Division
multiplication of cells for growth and development; plays a key role in repairing injured body parts of animals
Interphase
cell undergoes growth and prepares for cell division; comprises 90% of the cycle; microtubule proteins are synthesized at this stage ; actual replication of DNA occurs
Mitosis phase
comprises 10% of the cell cycle
Interphase
intact nuclear membrane.
Chromatin Fibers
genetic materials inside the nucleus appearing as thin, thread like structures
Nucleoli
dark dense stained bodies inside the nucles that serves as chromosomal materials
Centrosome
near the nucleus, contains the centrioles
M-Phase
consist of Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis
Prophase
nuclear membrane starting to disintergrate. Chromatin fibers are coiled, thickened, condensed. Centrioles are seen in opposite poles. Nucleoli disappears.
Asters
ray-like microtubule bodies radiating around each centriole
Mitotic spindles
forming between centrioles
Metaphase
cells are aligned at the equatorial region. replicated chromosomes are shorter and condensed (sister chromatids). joined together at the central region called centromere.
Kinetochores
protein complexes to which the spindle fibers are attached to
Anapahase
sister chromatids are separated and pulled apart toward opposite poles
Telophase
cleavage furrow exist. the nuclear membrane and nucleolus start to reappear. chromosomes uncoil and assume threadlike appearance. asters and mitotic spindles disappear.
Cytokinesis
division of cytoplasm. completely separated daughter cells are formed
Anaphase, Chromatid
what is the phase of the cell? What does the pointer point to?
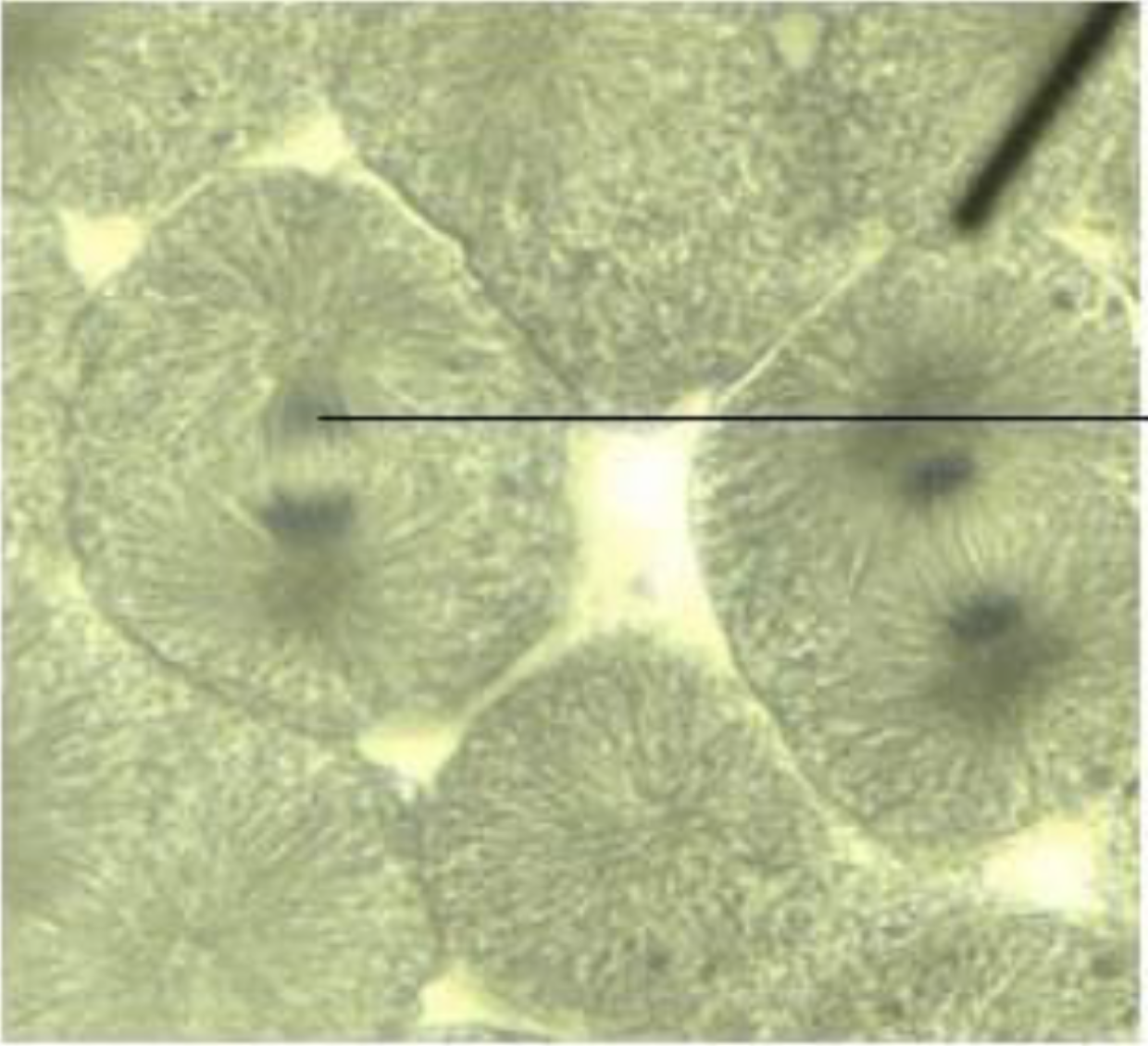
Metaphase, Asters, Chromosomes at Equitorial Plane
What is the phase of the cell? What do the pointers point to?
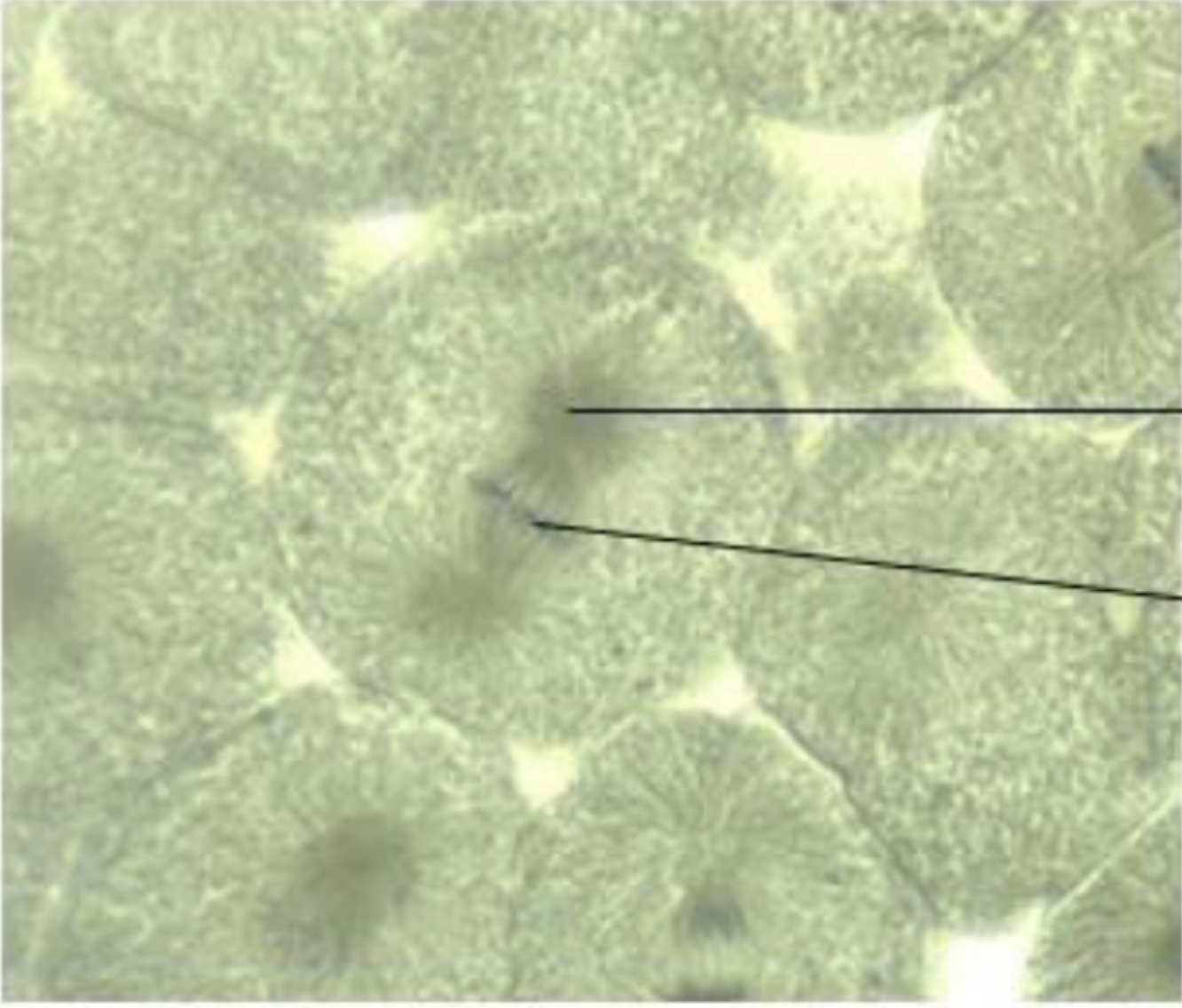
Telophase, Sprout Sister ChromatidÍ, Cleavage Furrow
What is the phase of the cell? What do the pointers point to?
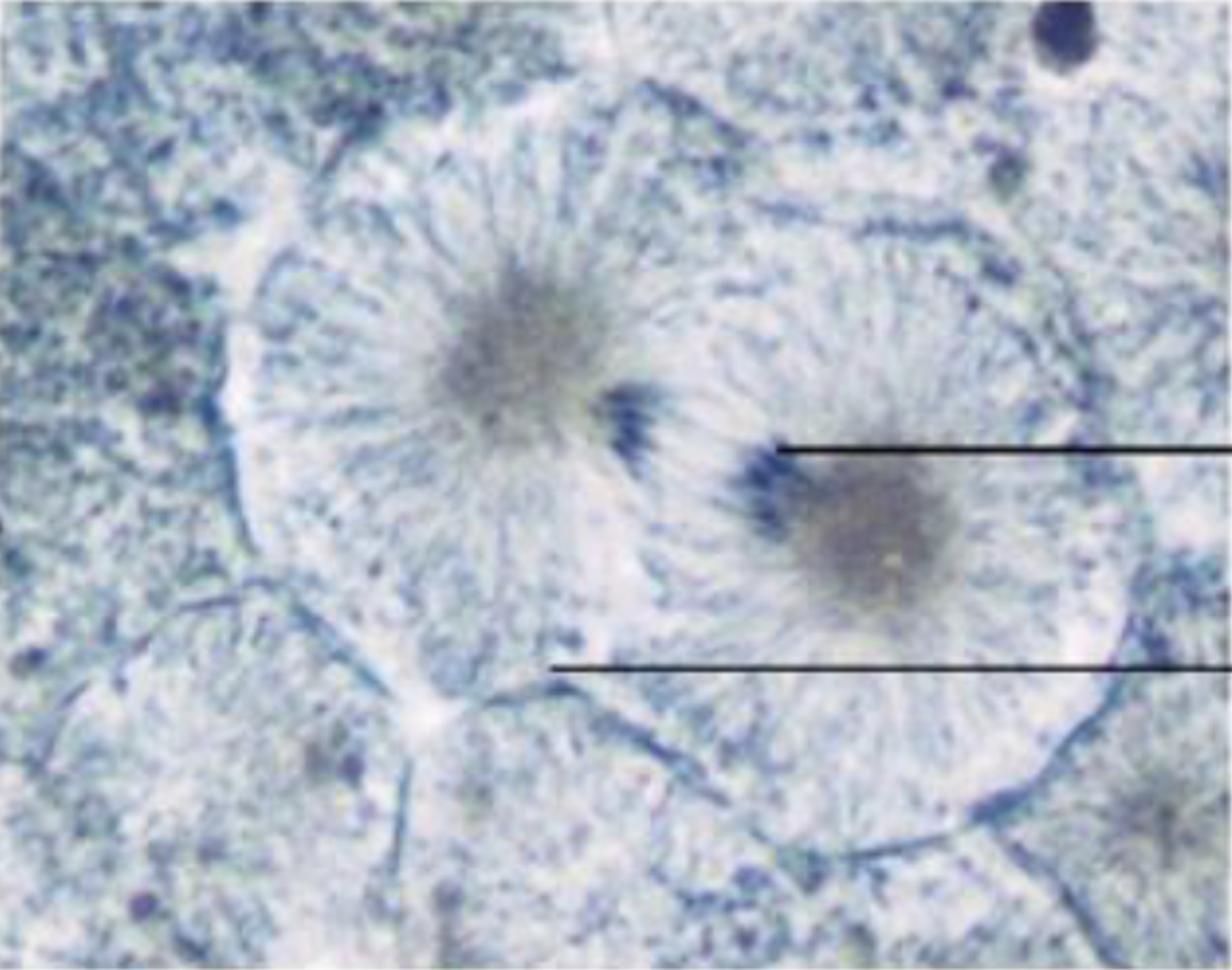
Interphase, Nucleus
What is the phase of the cell? What do the pointers point to?
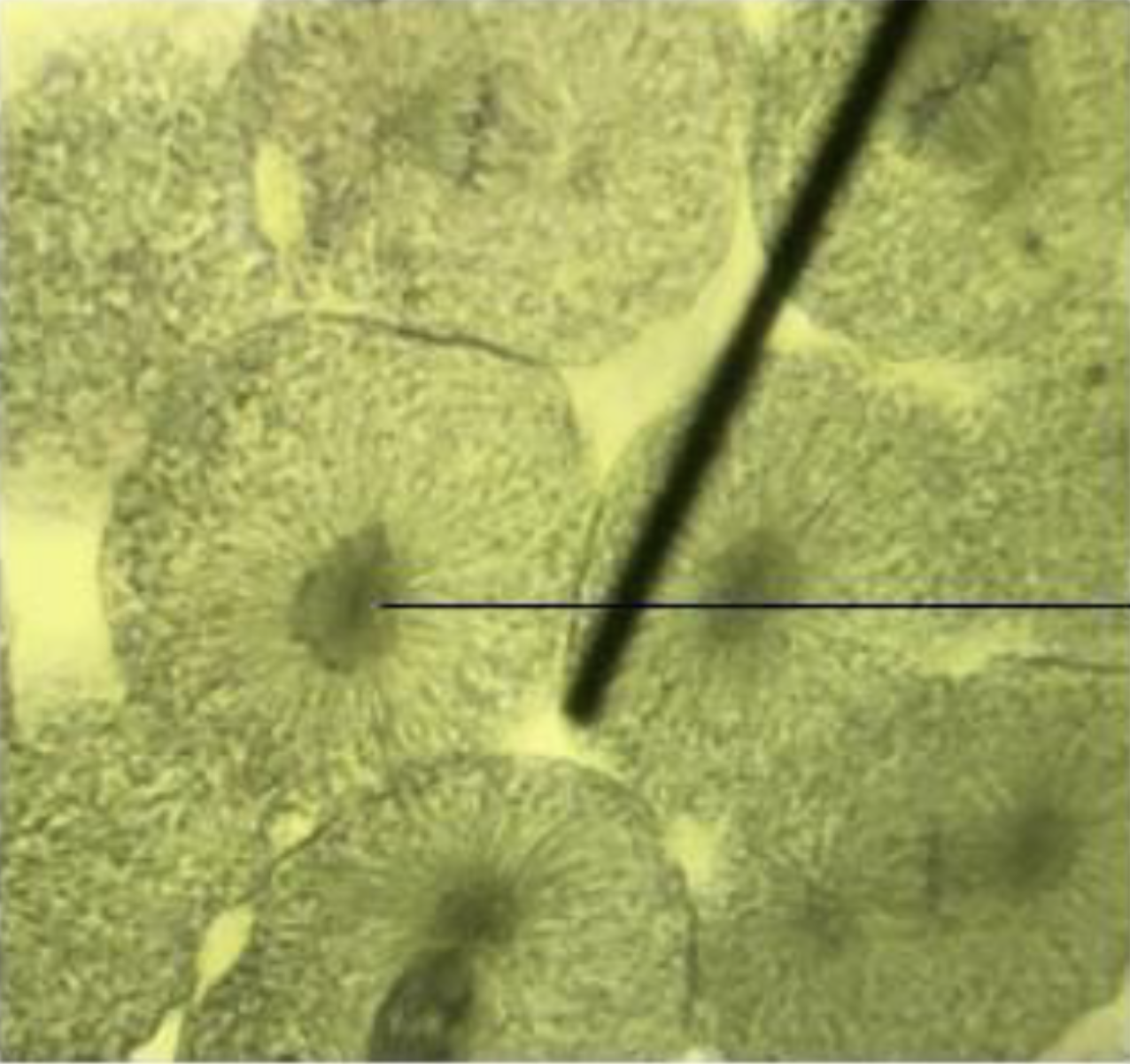
Prophase, Chromosome
What is the phase of the cell? What do the pointers point to?
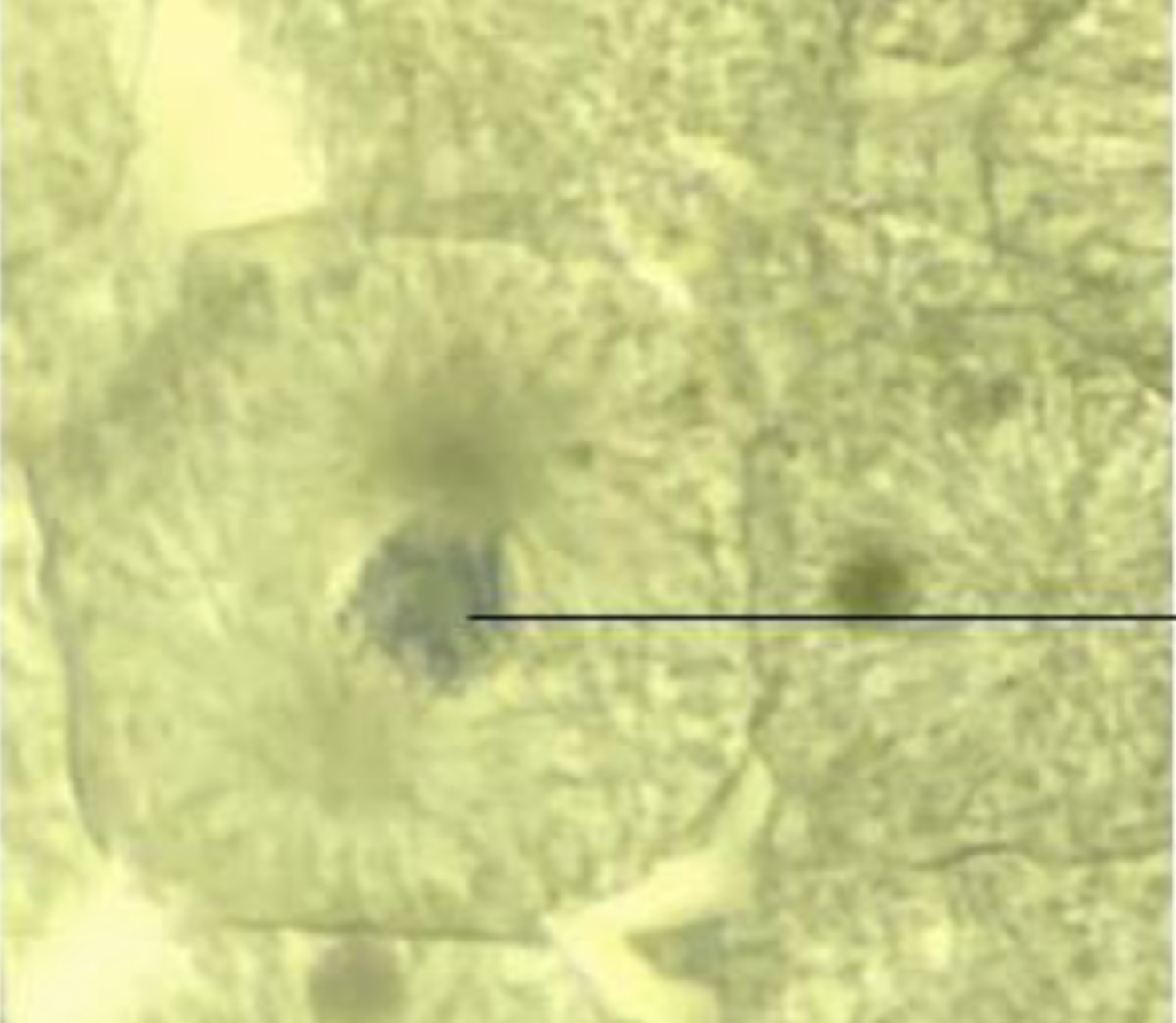
Cytokinesis
What is the phase of the cell?
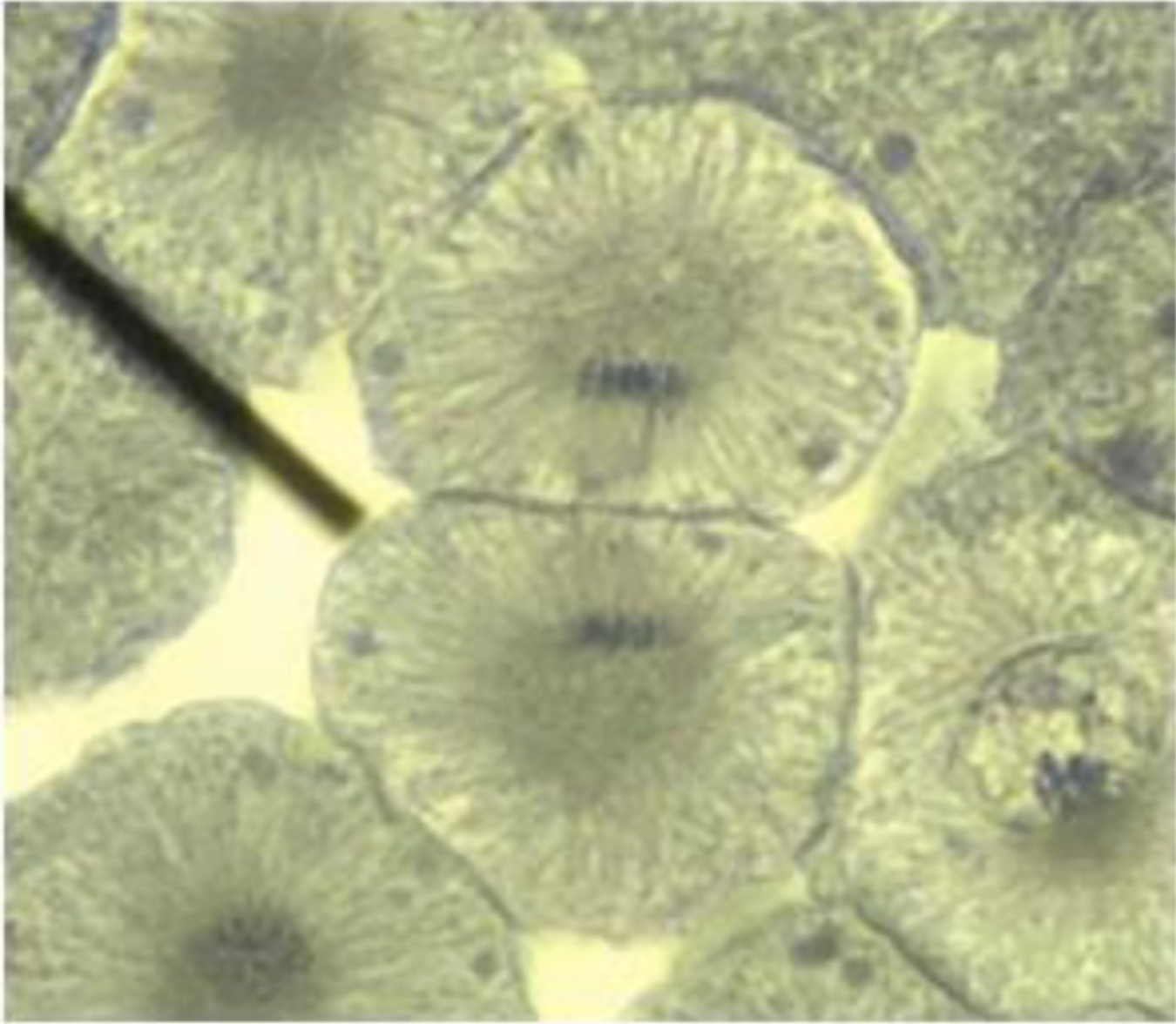
Chromatin
thread-like structures composed of DNA and proteins. These proteins are called histones enveloped by thread-like structures
Chromosomes
where the genetic material is found. interchangeably used as sister chromatids
Chromatids
condensed version of chromatin. considered as one side of chromosome joined by a centromere