(2) Sludge Treatment (Anaerobic Stabilization to the end)
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
(Anaerobic Stabilization to the end pg. 13-20)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
anaerobic digester
Most important factors effecting the performance of ___
SRT
HRT
Temp
pH
toxic materials
Standard (Low) Rate Process
what type of anaerobic digestion process
does not employ sludge mixing/ heating
SRT - 30-60 days
high rate process
what type of anaerobic digestion process
w/ mixing and heating
SRT - 15-20 days
2 digesters operating in series separate the functions of fermentation and solid-liq separation and residual gas extraction
Primary Digester
Kind of Anaerobic Digester
to increase the reaction rate, reactor is;
covered
heated
mixed
35C sludge
Secondary Digester
Kind of Anaerobic Digester
not mixed/ heated
used
storage of gas
concentrating of sludge by settling
gas is high enough in CH4 to be used as a fuel and is usually used to heat the primary digester
Anaerobic Digester Gas Production
810 to 1120L of digester gas/ kg volatile solids
65-69% methane
31-35% CO2
if more than 35% CO2 there is something w the digestion
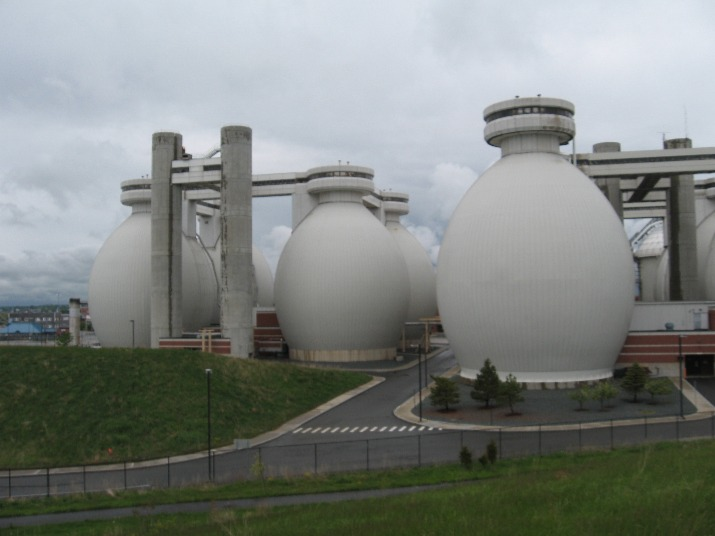

Egg-shaped digester
Digester
first installed in Germany 1950s
American Digester
shallow cylindrical vessel w moderate floor and roof slopes
Conventional German Digester
deep cylindrical tank w steeply sloped top and bottom cones
aerobic digestion
used to sltabilize;
primary sludge
secondary sludge
combination
process converts organic sludge to CO2, NH3, H2O
bacteria
lack of organic matter leads to the death of __
CO2
organic matter is consumed by bacteria and converts it into __
Conventional
Type of Aerobic Digestion
concentration VSS influent - 3% max for RT of 15-20 days
by batch (mostly), semi batch, continuous basis
Activated sludge - SRT 15-20 days
Primary & Activated Sludge - SRT 20-25 days
Conventional batch basis
The way of Conventional Aerobic Digester introduces the sludge
digester is filler w raw sludge and aerated for 2-3 weeks then stopped
Conventional semi batch basis
The way of Conventional Aerobic Digester introduces the sludge
raw sludge is added every couple of days
supernatant is decanted periodically
settled solids are held long time before removing
Conventional Aeration period
200 to 300C-days
multiplying digester’s temp in C by the sludge age
AutoThermal Thermophilic Aerobic Digestion (ATAD)
Type of Aerobic Digestion
variation of both conventional and high purity oxygen aerobic digestion
reqs
insulated reactors 120-140F
aerators
foam controllers
sludge
70% removal rate of the biodegradable organics at 3-4 days
Biofilter
ATAD Challenge - odor control
High Purity Oxygen Aerobic Digestion
Type of Aerobic Digestion
used in lieu of air
applicable in cold weather
costing disadvantage
cryophilic aerobic digestion
Type of Aerobic Digestion
ow temp - less than 20C
sludge age increase = operating temp increase
Composting
biological degradable to a stable end product
microorganisms involved are
bacteria - meso and thermophilic
actinomycetes
fungi
20-30% of volatile solids converted to CO2
Water at temp in the pasteurization of 50-70C
optimum moisture content is 50-60%
40C at least 5 days
Composting PSRP Req
min temp & days
55C at least 3 days
Composting PFRP Req
min temp & days
Agitated Composting
Principal Method of Composting examples are;
window composting
in vessel composting
Static Composting
Principal Method of Composting examples are;
static aerated pile composting
Sludge conditioning
to improve its dewatering characteristics
2 methods
adding chemicals
heat treatment
Sludge Dewatering
physical unit operation used to reduce moisture content of sludge and biosolids by subjecting it to vacuum, pressure, drying
Cake
the dewatered solids coming out from a dewatering device
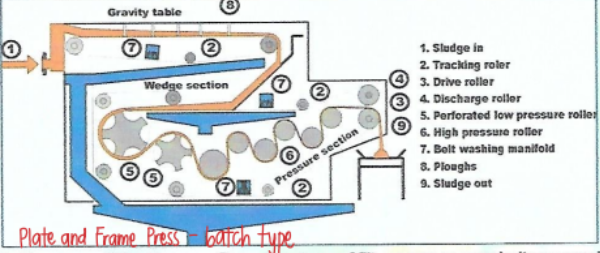
Belt Filter Press
Device used in sludge dewatering
continuously feed sludge dewatering device
involve
chemical conditioning
gravity drainage
mechanically applied pressure
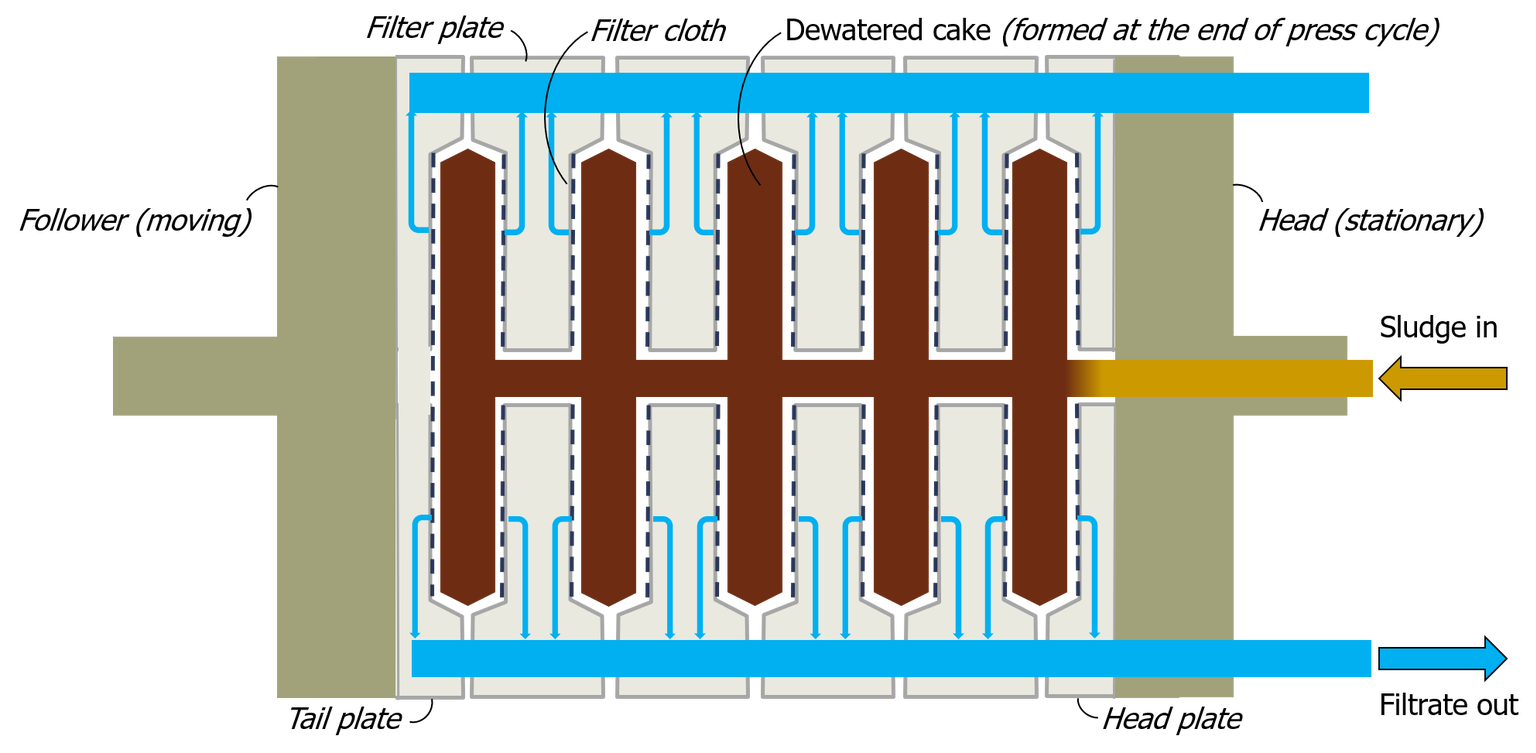
Pressure Filter Press
Device used in sludge dewatering
req lower polymer input due to higher pressure and finer cloths
sludge is pumped into the press at pressured up to 225 psi for less than 2hrs
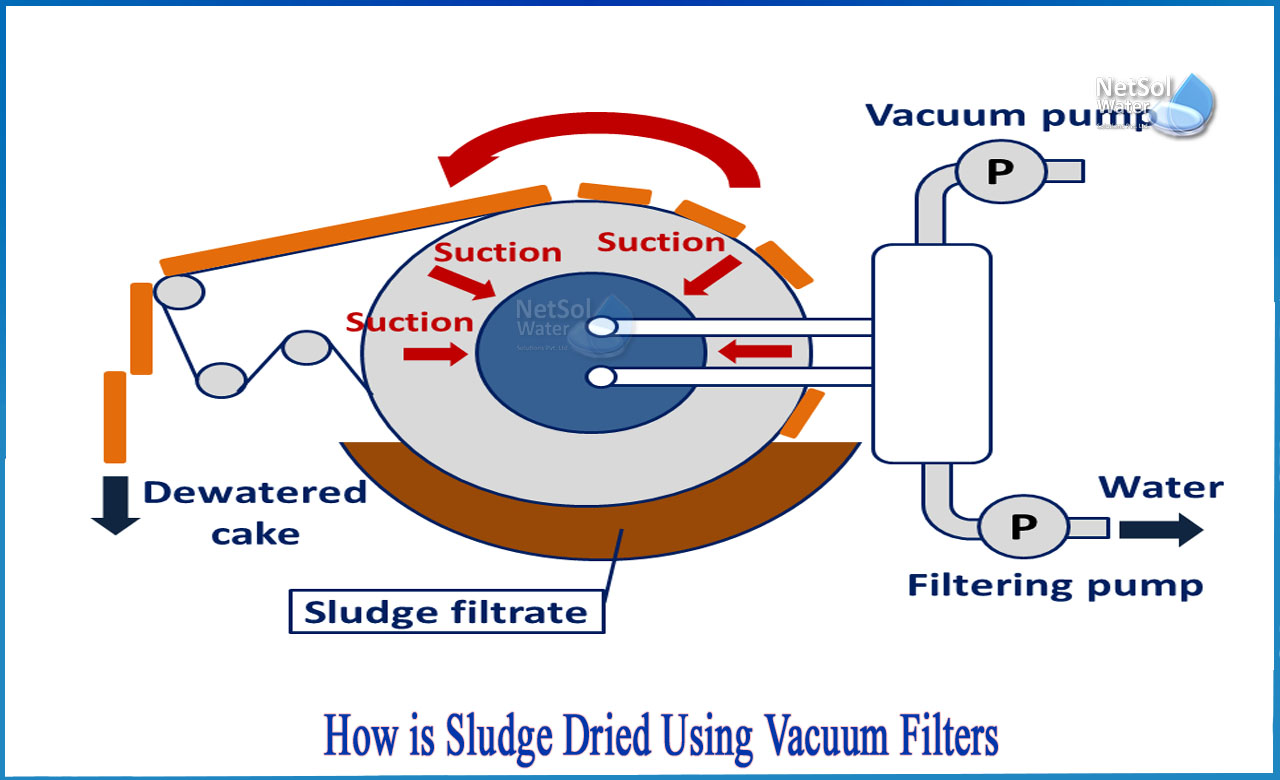
vacuum filters
Device used in sludge dewatering
used for almost 7 decades
drum is partly submerged 20-40% in a vat containing sludge
small plants
35h operation / week
larger plants
16-20hrs operation/ day
optimum solids content for filtration is about 6-8%
chemical conditioners
ferric chloride
lime
polymers
Centrifuge
Device used in sludge dewatering
used in solid bowl decanter
w/o chemical conditioner - 50-80% solids capture
w/ chemical conditioner - 80-95% solids capture
cake - 15-30% dry solids
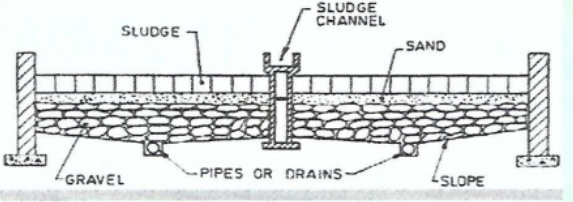
Sludge Drying Bed
Device used in sludge dewatering
remove moisture by natural evaporation, gravity, most widely used in municipal in USA
Lagoon
Device/Location used in sludge dewatering
substitute for drying beds
not suitable for ;
untreated sludge
limed sludge
high strength supernatant
sludge drying - 18 months
clean and rested 6 months
Sand Drying Bed
Type of Sludge Drying Bed
most cost effective
seepage and evaporation mechanism
sand content - 10-23cm
gravel layer - 20-50 cm
15cm deep dewatered sludge
Paved Drying Bed
Type of Sludge Drying Bed
consist of concrete and asphalt
slope 1.5%

artificial media drying bed
Type of Sludge Drying Bed
use of stainless-steel wedge wire
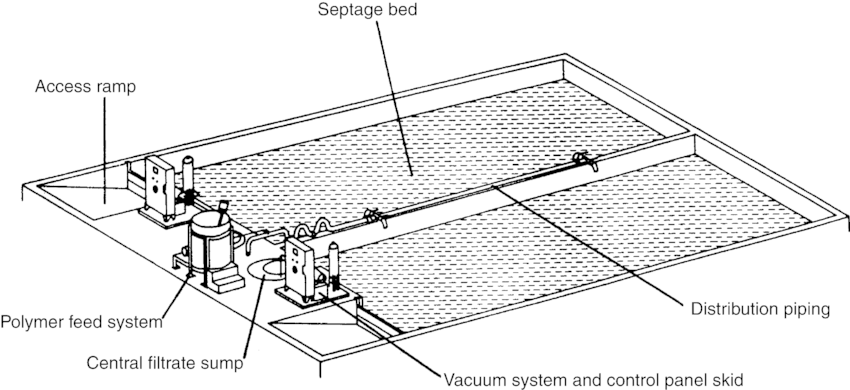
vacuum- assisted drying beds
Type of Sludge Drying Bed
consists of reinforced concrete ground slab, layer of supporting aggregate, rigid porous media plate on top