Nursing 101 - exam 3 part 1 (1st semester)
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
What part of the stethoscope do we use to listen for vital signs?
diaphragm - used for high frequency sounds
What type of data do you collect first?
subjective data
what the the blood flow of the heart?
-oxygen poor blood from inferior and superior vena cava enters Right Atrium
- blood goes thru Tricuspid Valve into Right Ventricle
-Right Ventricle is full and squeezes which closes tricuspid valve and opens Pulmonary Valve.
- Blood goes thru Pulmonary Artery to lungs to get oxygenated.
- Oxygen rich blood travels from lungs to Left Atrium thru L/R Pulmonary Veins
-Left Atrium to Left Ventricle thru Mitral Valve
- Left Ventricle is full, squeezes which closes Mitral valve
- Aortic semilunar valve opens
- blood goes into Aortic Semilunar Valve to Aorta to go through the body and start over again.
When do you use the Bell on your stethascope?
when looking for a LOW frequency sound
Bruit
abnormal blowing or swishing sound heard during auscultation of an artery or organ
what should you hear when listening to a carotid artery?
nothing
What is a bruit?
blood flow turbulence, generated by a wave
what causes the wave in Bruit usually?
carotid artery narrowing
what causes carotid artery narrowing?
plaque buildup
teaching pt when taking carotid artery assessment?
have pt hold their breathe because you may hear the larynx or pharynx otherwise because of their breathing
- have pt exhale first and then hold breath
assessment areas of carotid artery
upper carotid
middle carotid
lower carotid
if patients heart is beating 80 bpm how many waves are being produced per minute?
- bruits per minute?
- pulses per minute?
80
first thing we do with assessment of the chest?
inspection
inspection of the chest consists of?
- is it symmetry
- are there any lumps
- any pulsations or pulsating outside of chest
- look for Heave/Lift
- Thrills
Heave on chest means what?
a visible pulsation which is seen with hypertrophy of ventricle (enlargement of ventricle)
Palpate for thrills n chest
Using the ball or back of hand of the hand, palpate for thrills, (vibration) of turbulent flow transmitted to the chest wall surface by a damaged heart valve.
Palpate PMI (point of maximum impulse)
apical area
Whoosing sound heard on carotid auscultation?
Bruit
Right ventricular hypertrophy is seen how?
will observe heave or lift closer to the sternal board
left ventricular hypertrophy seen how?
observe heave or lift closer to the mid clavicular line
Auscultation of heart sounds 1st with?
diaphragm
Auscultation of heart sounds 2nd time with?
the bell
normal heart sounds are what?
high frequency sounds
S1 & S2 heart sounds are?
lubb dubb
low frequency heart sounds are heard with what?
bell of stethoscope
abnormal heart sounds are heard
by low frequency
Whoosing sound heard on heart auscultation?
murmur
whooshing/swishing sound in any of our peripheral vessels?
Bruit (sounds like brew-E)
whooshing/swishing sound in our heart is called
a murmur
"Lubb SHH Dubb" sound?
means a bruit or murmur is present
where do you place stethoscope when ausuctating heart sounds?
APETM
(APE-To-Man) aka Z pattern
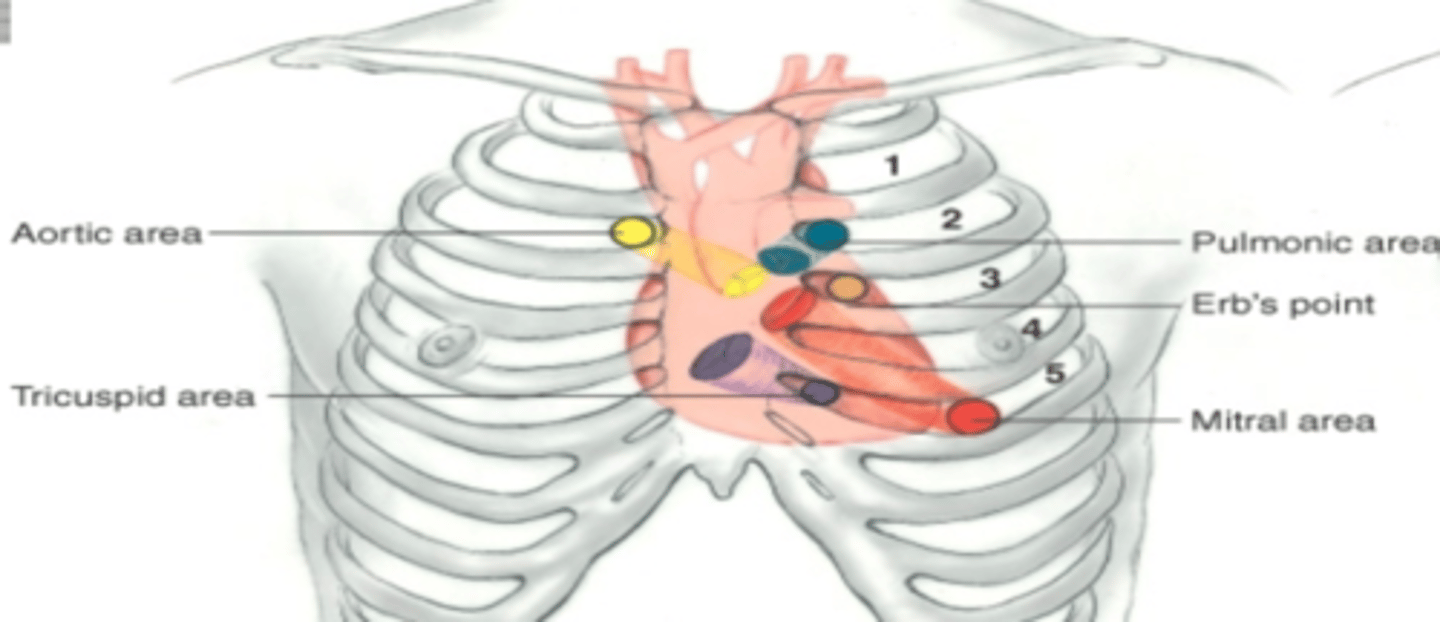
exact body landmarks for placing stethoscope when ausuctating heart sounds?
1. A - second intercostal space RIGHT sternal border (AORTIC AREA)
2. P - second intercostal space LEFT sternal border (PULMONIC)
3. E - third intercostal space LEFT sternal border (ERBS POINT)
4. T - fifth intercostal space LEFT sternal border (TRICUSPID)
5. M - slide across to midclavicular line of that 5th intercostal space (MITRAL)
S2 is louder where?
base of the heart (higher point)
S1 is louder where?
apex of the heart (lower part)
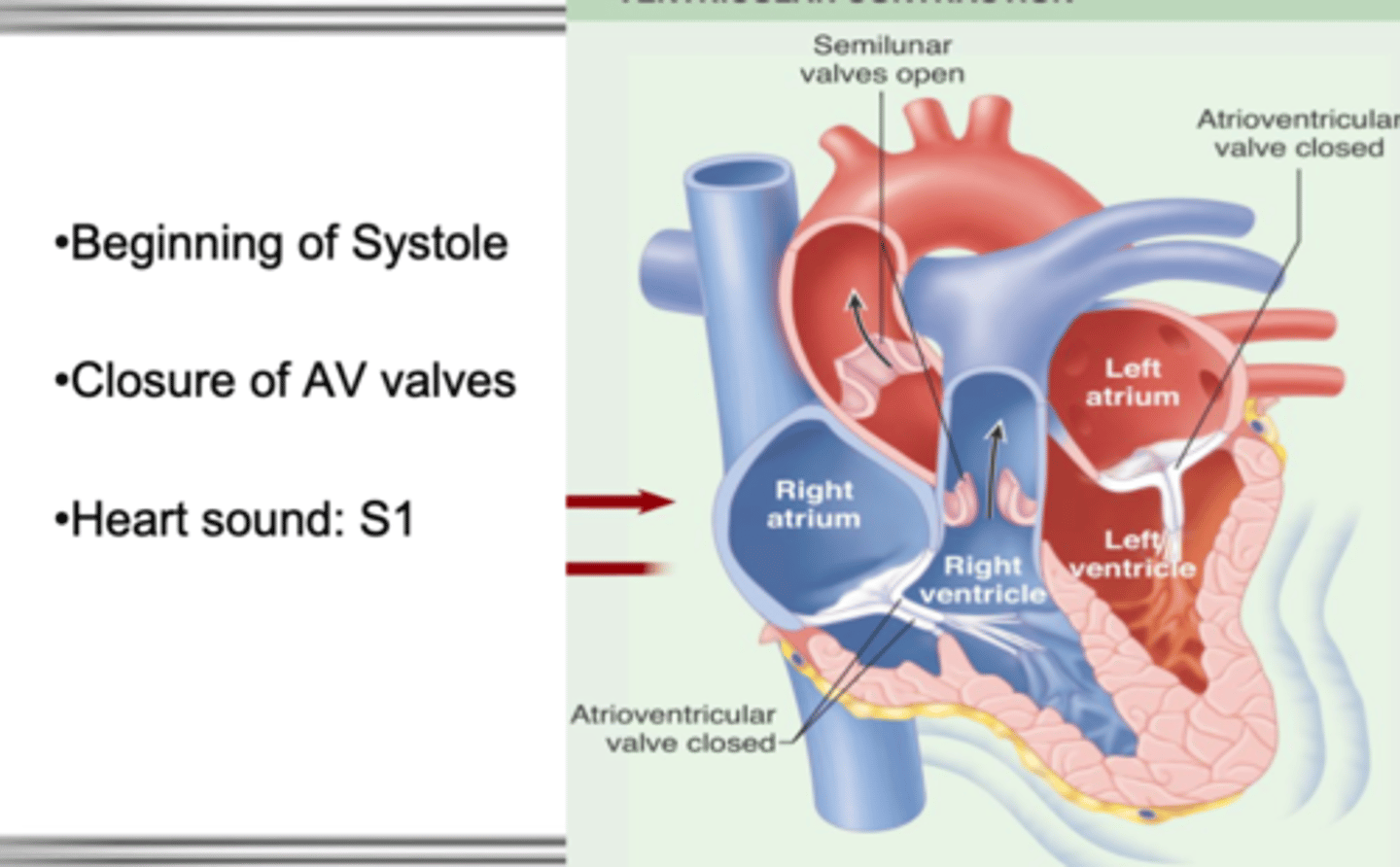
S1
closure of AV valves, loudest at the apex
S1
beginning of systole
closure of AV valves
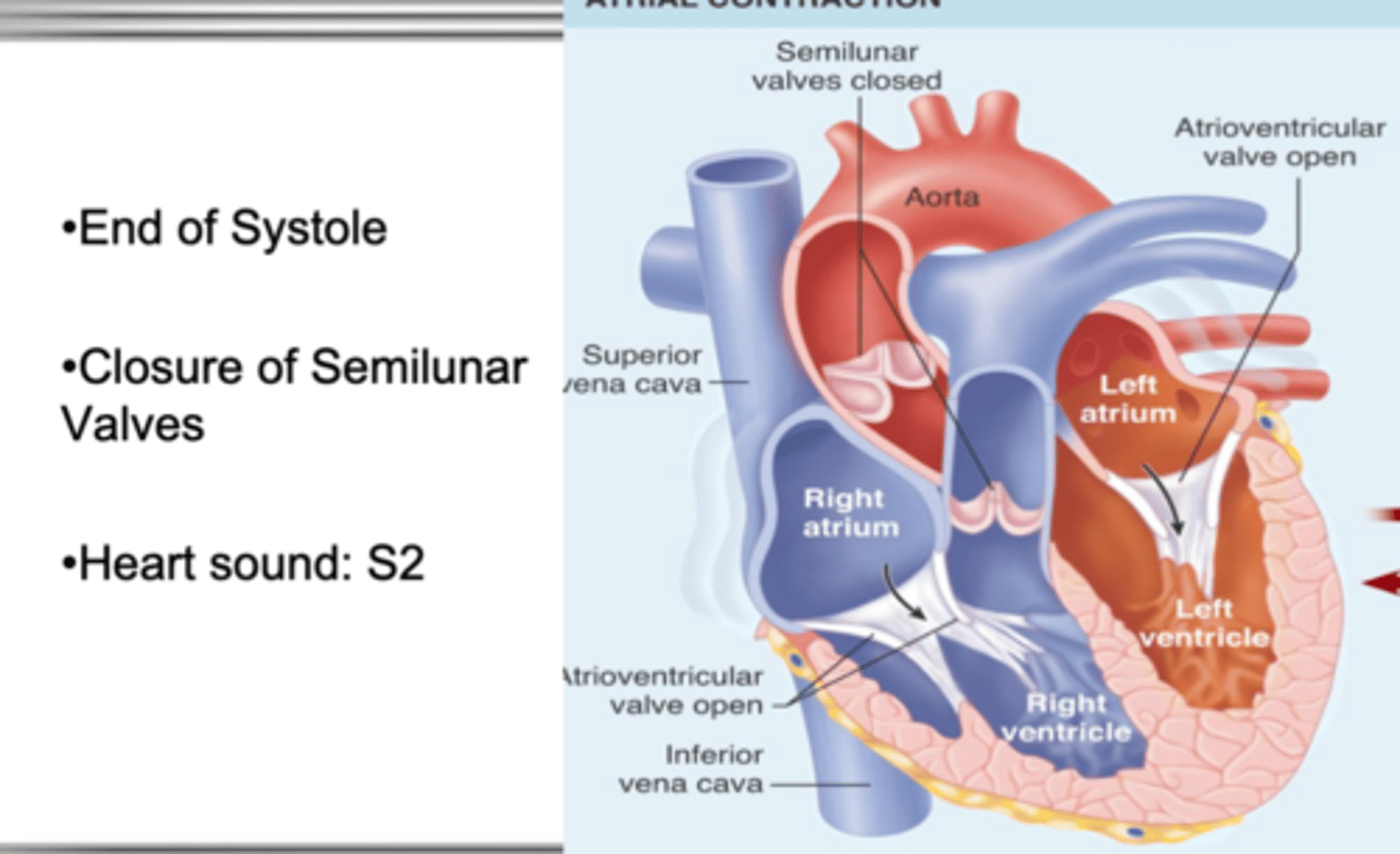
S2
- end of systole
-closure of semilunar valves
murmurs are caused by
turbulent blood flow (blood backflowing)
- incomplete closure of valves
- could be holes in-between the chambers of the heart
What is a nurses job when they hear a murmur? (as a 1st semester student)
to report/document that a murmur is heard, not diagnose.
if murmur sound comes after S1 or inbetween S1 and S2 what is it?
a systolic murmur
(Lubb SHH Dubb) - sound heard
if murmur sound comes after S2?
a diastolic murmur
(Lubb Dubb SHH) - sound heard
if murmur is present how is cardiac output being effected?
it is being decreased
Grade I murmur
barely audible, with difficulty
Grade II murmur
audible, but faint
Grade III murmur
moderately loud, easy to hear
Grade IV murmur
loud, thrill palpable on the chest wall
Grade V murmur
very loud, can hear with part of stethoscope off the chest
Grade VI murmur
loudest, can hear with stethoscope off the chest
What are modifiable risk factors for CAD and stroke?
diabetes
hypertension (both can be controlled dont have to be completely eliminated)
- obesity
- high cholesterol
what is the heart in one word?
Pump
heart failure =
pump failure
cardiac output
stroke volume x heart rate
4/6 liters
fluid from the body will go into what side of the heart?
Right / goes into right atrium
from right ventricle blood goes to ?
the lungs
heart failure presents with?
-lowered cardiac output
- low BP
- pulmonary congestion
-dyspnea
- extremity edema
- JVD
Left sided heart failure
respiratory symptoms
Right sided heart failure
backup into general circulation, edema, venous distention
if blood is backed up into the systemic system what side of the heart is failing?
Right side of the heart
if blood is backing up into the lungs what side of the heart is failing?
Left side of the heart
can patients have both Left and Right sided heart failure?
Yes. even though the failure of the heart started on either the left or the right eventually the hearts side that is functioning will have to compensate for the side that is failing and will eventually lead to Left and Right sided heart failure.
CHF (congestive heart failure)
Left sided heart failure
what sounds do you hear with CHF?
crackles, fluid accumulation, ect
if a patient has heart failure why are you told to "weigh the patient daily"?
to check for fluid retention
- with heart failure patient will have decreased cardiac output making the brain think you lost fluid.
- this tells the kidneys to retain fluid, retain sodium (as sodium is retained water follows and is retained as well.
Kidneys action in heart failure?
retain fluid, retain sodium (as sodium is retained water follows and is retained as well.
(fluid overload)
what does the brain do during heart failure/decreased cardiac output?
it thinks the body is bleeding out or going into shock and that you are losing fluid because cardiac output is decreased
treatment for patient who has excessive fluid and the kidneys that are retaining fluid?
will give diuretics
What do diuretics do?
tells kidneys to excrete.
Promote sodium and water excretion, reduce plasma volume, and reduce the vascular response to catecholamines.
what does your nursing note always start out with?
the date and the time
what do your nursing notes always end with?
your name and credentials
Peripheral vascular system
arteries, veins and lymphatic system
arteries
bring fluid to all of our peripheral tissues
veins
take fluid and bring it back to the heart
lymphatic system
the network of vessels through which lymph drains from the tissues into the blood. (general circulation)
- involved in immune system
lymph nodes will enlarge
in a localized area and will show sign of infection
arteries have what kind of system?
high pressure sysem
what makes the arteries have a high pressure system?
the left ventricle
Arteries supply what?
oxygen and essential nutrients to the tissues
arteries for examination
temporal
carotid
brachial
radial
femoral
popliteal
dorsalis pedis
posterior tibial
temporal artery
lies superior to the temporalis muscle; its pulsation is palpable anterior to the ear
carotid artery
artery on each side of the neck that supplies blood to the head
brachial artery
The brachial artery runs along the front part of your bicep. It's a continuation of the axillary artery in your armpit and shoulder. It ends at the cubital fossa (the indentation between your upper and lower arm, at the front of your elbow).
radial artery
runs on the inside of the forearm from the elbow to the thumb. The artery lies just under the surface of the skin. You may be able to see the blue or purple vein inside your wrist where the artery brings blood to the thumb.
femoral artery
is at the top of your thigh in an area called the femoral triangle. The triangle is just below your groin, which is the crease where your abdomen ends and your legs begin. The femoral artery runs to the lower thigh and ends behind the knee
popliteal artery
is located behind your knee and runs behind your knee pit. Below your knee joint, the arteries divide into the anterior tibial artery and the tibioperoneal (or tibiofibular) trunk. This trunk divides into smaller branches that carry blood to your fibula and to the back of your calf.
dorsalis pedis artery
The artery on the anterior surface of the foot between the first and second metatarsals.
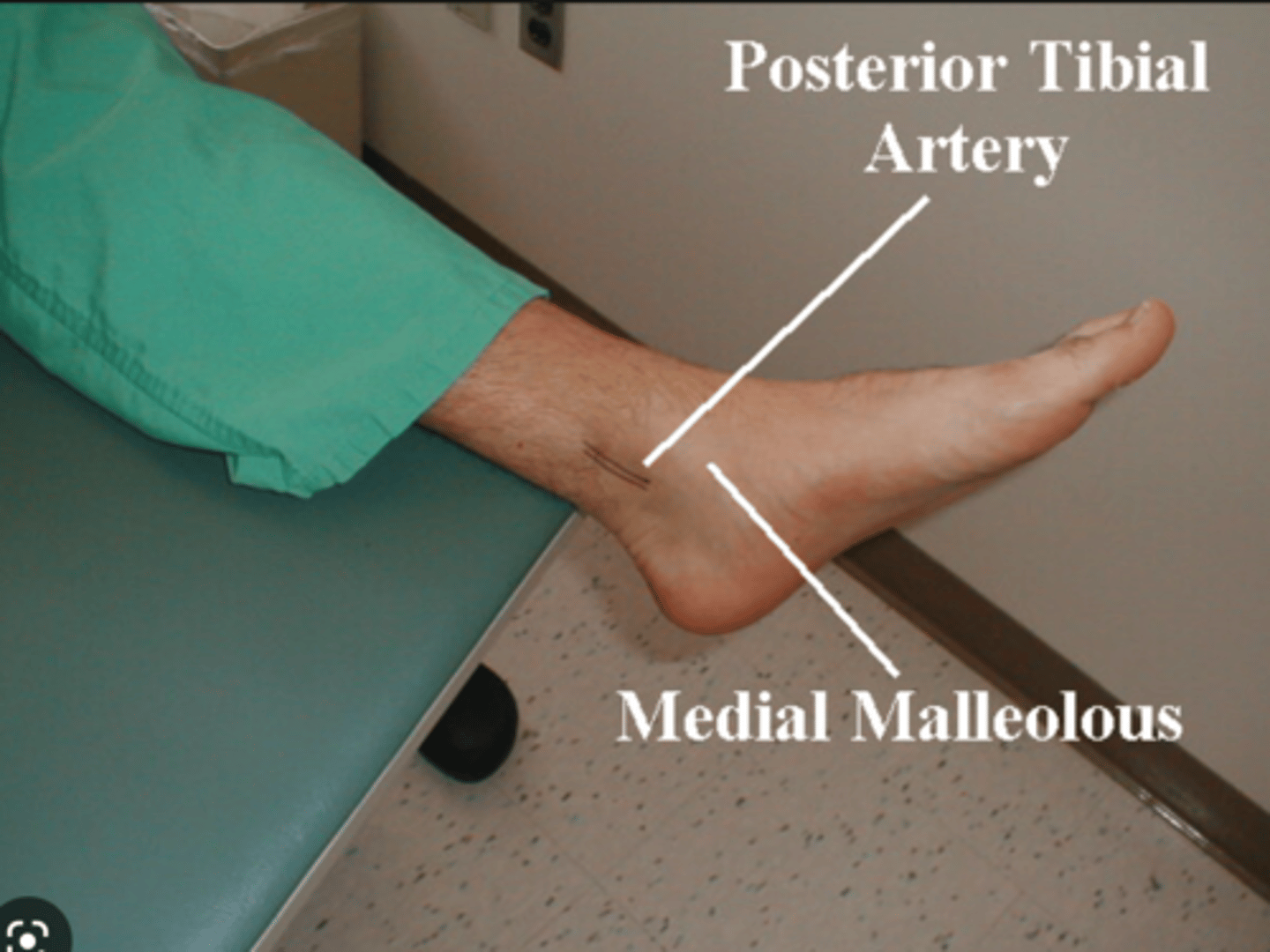
posterior tibial artery
commences at the lower border of the popliteus as one of the two terminal branches of the popliteal arteries, the other being the anterior tibial artery. It supplies the back of the leg, i.e. the two posterior compartments and the sole of the foot.
Veins
Blood vessels that carry blood back to the heart
what is parellel to the arteries?
the veins
low pressure system
veins
what pushes things forward with veins?
muscles // contracting muscles
what prevents backflow of veins?
valves
low pressure system that is contracting skeletal muscles to milk blood proximally back towards the heart
vein system
breathing in and out
milks blood forward - causes a pressure gradient caused by breathing
problem with a patient who is on bedrest?
milking action is nonexistent and blood just sits in the body letting pt to become at risk for blood clots
inspiration
increases abdominal pressure and
decreases thoracic pressure
Intraluminal valves do what?
ensure unidirectional flow
veins for examination
Jugular veins
Subclavian
in the arm - Cephalic, Basilic, Median, Cubital
in the leg - Great Saphenous, Small Saphenous
lymphatic system
drains the fluid
Is the Lymphatic system a separate vessel system?
yes, but it runs parallel to arteries and veins
low pressure system that requires skeletal muscle contraction also?
Lymphatic system