Nurs 213 Quiz 1 -> bowel elimination, Ng tubes, specimen collection, and blood glucose
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
colostomy
a surgical operation that creates an opening from the colon to the surface of the body to function as an anus
constipation vs diarrhea
-Hard, slow stools that are difficult to eliminate; often a result of too little fiber in the diet
-frequent liquid bowel movements
fecal impaction
a mass of dry, hard stool that remains packed in the rectum and cannot be expelled
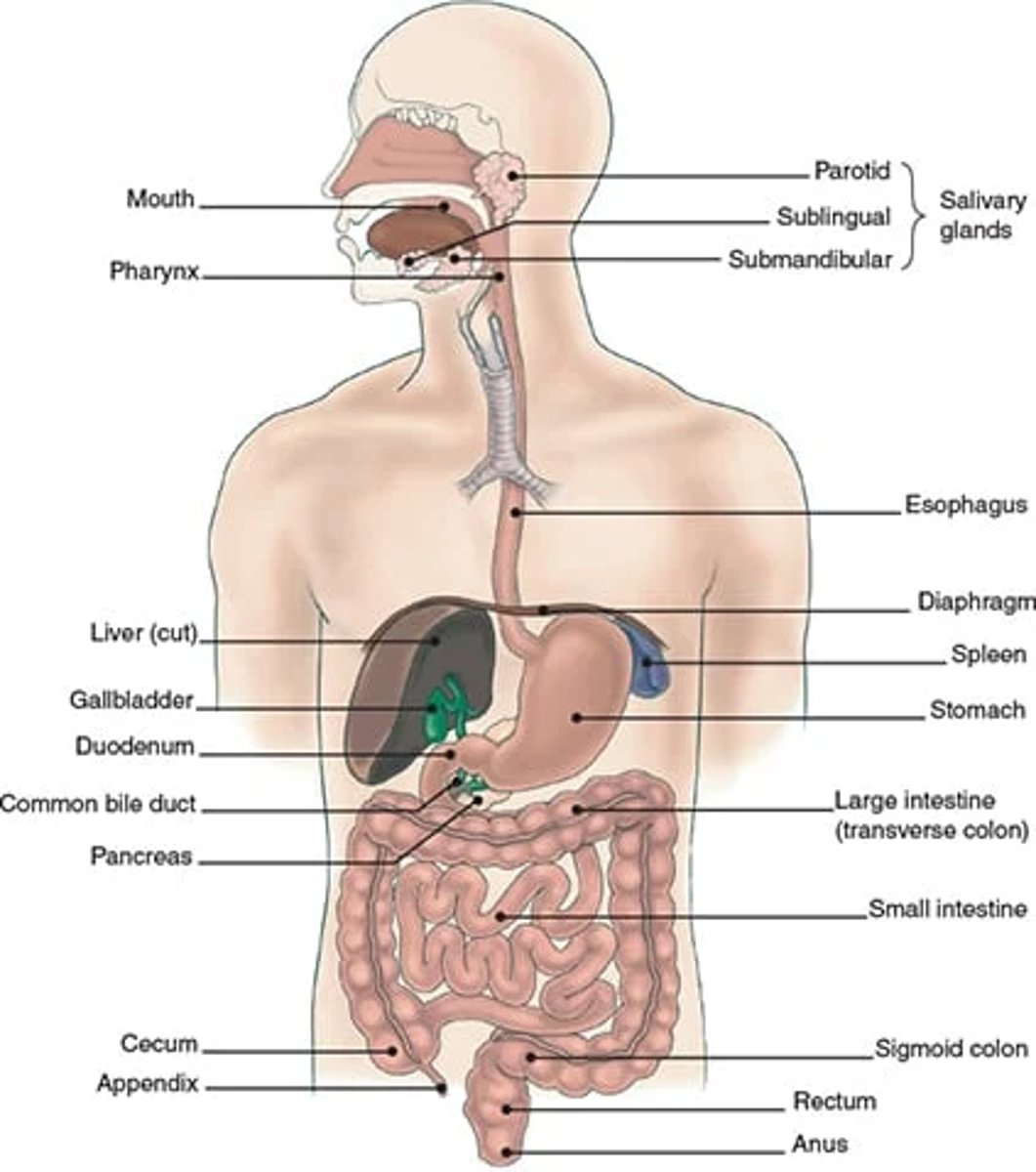
anatomy of GI tract
mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus
factors that affect bowel elimination
1. developmental -> infant (depends on breast/formula); toddler (voluntary control); older adult (increased risk of constipation)
2. daily patterns-> changes cause constipation
3. food and fluid-> 25-38g of fiber; 2000 ml of fluid
4. activity-> improved GI motility
5. psychological effects->anxiety facilitates
6. pathologic conditions
7. medications
8. surgery and anesthesia->inhibits peristalsis
9.lifestyle-> occupation, activity etc
10. diagnostic studies-> fasting, barium etc
paralytic ileus
paralysis of intestinal peristalsis for 3-5 days after surgery
treatment for constipation
1. prevention (diet, fluid, exercise)
2. laxatives
3. enemas
- in this order
cleansing enemas
tap water, normal saline, hypertonic solutions, soapsuds
to remove feces, relieve constipation, before surgery to promote visualization
Retention Enemas: Oil-retention
lubricate the stool and intestinal mucosa, easing defecation
-retained for 30 mins
Hypertonic, isotonic, hypotonic cleansing enema
hyper (small volume)-> draws fluid from the body into the colon; cells shrivel
hypo (large)-> water absorbed by body; cells swell; pts who are dehydrated; tap water
iso (large)-> saline solution; cells are stable
important things to remember when administering a large volume enema
- have a bedpan, commode of bathroom nearby
-provide privacy
-solution should be at body temp or warmer (105-110)
-pt should be in sims position
-solution should be about 18 inches above pt
-lubricate 2-3 inches of rectal tube
-angle tube 4-5 inches towards umbillcus not bladder
-document solution type and amount, pts reaction and stool return
-try to hold solution as long as possible
If pt experiences dizziness, lightheadedness, nausea, diaphoresis, and clammy skin during enema administration you should...
stop the procedure, monitor the pt, and contact care provider
When is a large volume enema contraindicated?
pt has low platelet or WBC count, bowel inflammation or infection
vagal response
Stimulation of vagus nerve causing heart rate and blood pressure to drop.
stool characteristics
volume-> varies
color-> infant= yellow/brown; others= brown
odor-> pungent or not
consistency->soft, semisolid, formed
shape-> 1 in diameter; tubular
constituents-> bile, bacteria, seeds, meat etc.
warning signs of colon cancer
Rectal bleeding
Change in the bowel elimination pattern
Blood in the stool
Cramping pain in the lower abdomen
feeling bowel doesnt empty after BM
weakness/fatigue
losing weight w/o trying
digital stool removal guidelines
1. place in left side-lying
2. drape and place protective pad underneath
3. assess for swelling, bleeding, prolapse, excoriation or hemroids
- dont continue if present
4. lubricate index finger
5. insert into anal canal
6. slowly/gently move finger circularly to break up mass
7.have pt bear down
8. avoid hooked finger
Stoma appearance
beefy red= normal
black=nacrotic (dying; needs intervention)
pale= anemia
blue/purple=ischemia
-note size (new may protrude)
Ostomy care
-keep skin around stoma clean (soap and water) and dry
--leaking causes skin erosion or infection
--if leaking use paste to create a seal
-measure size of stoma and cut 1/8 inch larger
-ensure wafer is flush to skin
-push stomach away instead of ripping when removing
Stool Collection
- Void first, the results may be inaccurate if the stool contains urine
- Defecate into the container, such as bedpan or bedside commode
- Do not place toilet tissue in the specimen
- Put on gloves and use tongue blades
-Usually 1 inch of formed stool or 15 to 30 mL of liquid stool
- If portions of the stool contain blood, mucus, or pus include these in the specimen
-package, label and transport specimen quickly, usually in a biohazard bag
-document amount, color consistency, time and type of test
External factors that may cause a false reading of a hemocult test...
false += nose/throat bleed, hematuria, iron, steroids, anticoagulants, diet (red meats, salmon, tuna, soy beans etc.)
false-= Vitamin C
-instruct to change diet 4 days before and meds 7 days before
when to empty an ostomy bag
1/3 to 1/2 full or has gas
Factors for consideration when determining selection of feeding tubes
1. Aspiration risk
2. anticipated duration of feeding tube
3. function of the GI tract
4. pts overall condition and prognosis
5. pts wishes
short term nutritional support
Using the nasogastric or nasointestinal route
Nasogastric tubes
-Inserted to decompress or drain the stomach of fluid or unwanted stomach contents
-disadvantages= aspiration
-Levin= single lumen, decompression, feedings, intermitent suction
-dobhoff=gastric feedings, flexible, weighted
-salem sump=continous or intermitent suctioning, double lumen, decompression, blue vent for air pressure
nasointestinal tube
tube inserted through the nose and into the upper portion of the small intestine
-indictated for patients at risk of aspiration, decreased gag reflec or slowed gastric motility
-weighted, feedings
Ng tubes are contraindicated if...
1. dysfunctional gag reflex
2. high risk of aspiration
3. gastric stasis
4. Gerd
5. nasal injuries
6. unable to raise head of bed at least 30 degrees
confirmation of ng tube placement
-most reliable confirmation of placement is Xray
-aspirate to confirm pH to see that it is stomach contents and that it looks like bile
insertion of NG tube
1. high fowlers
2. measure nostril to earlobe to xiphoid process; mark tube
3. lubricate tube
4. advance tube up until pharynx is reached
5. have pt check chin to chest; drink water through a straw
6. if coughing or gagging check placement w light
7. secure tube to face
8. check placement w two methods
stop insertion of the NG tube if...
signs of distress
- gasping, coughing, cyanosis, or inability to speak or hum
if tube is a double lumen...
secure vent attached to blue port above stomach level
removing an NG tube
1. raise bed to 30 to 45 degrees
2. put on gloves
3. discontinue suction
4. check placement and flush
4. remove tube while client holds breath
5. wrap the tube around hand to avoid spillage
Long-term nutritional support
gastrostomy (stomach) tubes -> PEG tubes, surgically placed tubes
Administering Enteral Feedings
-can be continuous, intermittent or cyclic
-check placement
-check residual before each feeding or every 4-6 hrs if continuous
--> 200-250 mL increases risk pf aspiration
--> hold feedings if this is the case for two assessments
-assess abdomen and bowel sounds to ensure peristalsis
-keep head of bed 30 degree or higher
--pt should remain upright for 1 hr after feeding
-disinfect cans with alcohol swab
-maintain oral hygiene
change open feeding systems...
every 24 hrs or by facility policy
change closed feeding systems...
every 48 hrs or by facility policy
Administering meds through enteral feeding tubes
1. stop feeding
2. use liquid med forms
3. flush before, between and after med administration
flush tube with 20 to 50 ml of water...
1. every 4 to 8 hrs during continous feedings
2. before and after med administration
3. before and after bolus feedings
4. to irrigate
Testing pH of gastric content
1. allow 1 hr after pt recieves meds or feedings.
2. attach syringe to tube insert 30 mL of air
3. aspirate 5-10 ml of gastric secretions
4. If unable to attain sample, reposition and flush again with 30 mL of air
5. place drop onto pH test strip and compare
Normal pH ranges
stomach= <5.5; grassy, green, tan, off white, bloody or borwn
intestines= 7 or >; golden yellow; greenish brown is stained with bile
resp. tract= 6 or >; off white and mucous
Obtaining a capillary blood sample for glucose testing
1. check monitoring schedule
2. check expiration date on test strips
3. turn on monitor and enter pt code
4. remove test strip and immediately recap
5. check code # on strip matches glucose monitor
6. place strip into monitor
7. wash pt finger w alcohol swab
8. hold lancet perpendicular
9. wipe first drop with gauze and use second drop for testing
-normal is 80-120
how to encourage bleeding for glucose testing
1. lower the hand
2. stroke finger from the base up
hypoglycemia
low blood glucose
symptoms of hypoglycemia
shaky, fast heartbeat, sweating, dizzy, anxious, hungry, blurry vision, weakness or fatigue, headache, irritable
How to treat hypoglycemia
treat by eating glucose tablets, candies, fruit juice, regular soda
-recheck blood glucose
hyperglycemia
high blood sugar
symptoms of hyperglycemia
extreme thirst, frequent urination, dry skin, hunger, blurred vision, drowsiness, slow healing wounds
how to treat hyperglycemia
administer insulin if necessary; monitor blood sugar
Still learning (24)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!