Lecture 8 -- Adnexa of the Eye
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Describe the structure of the eye.
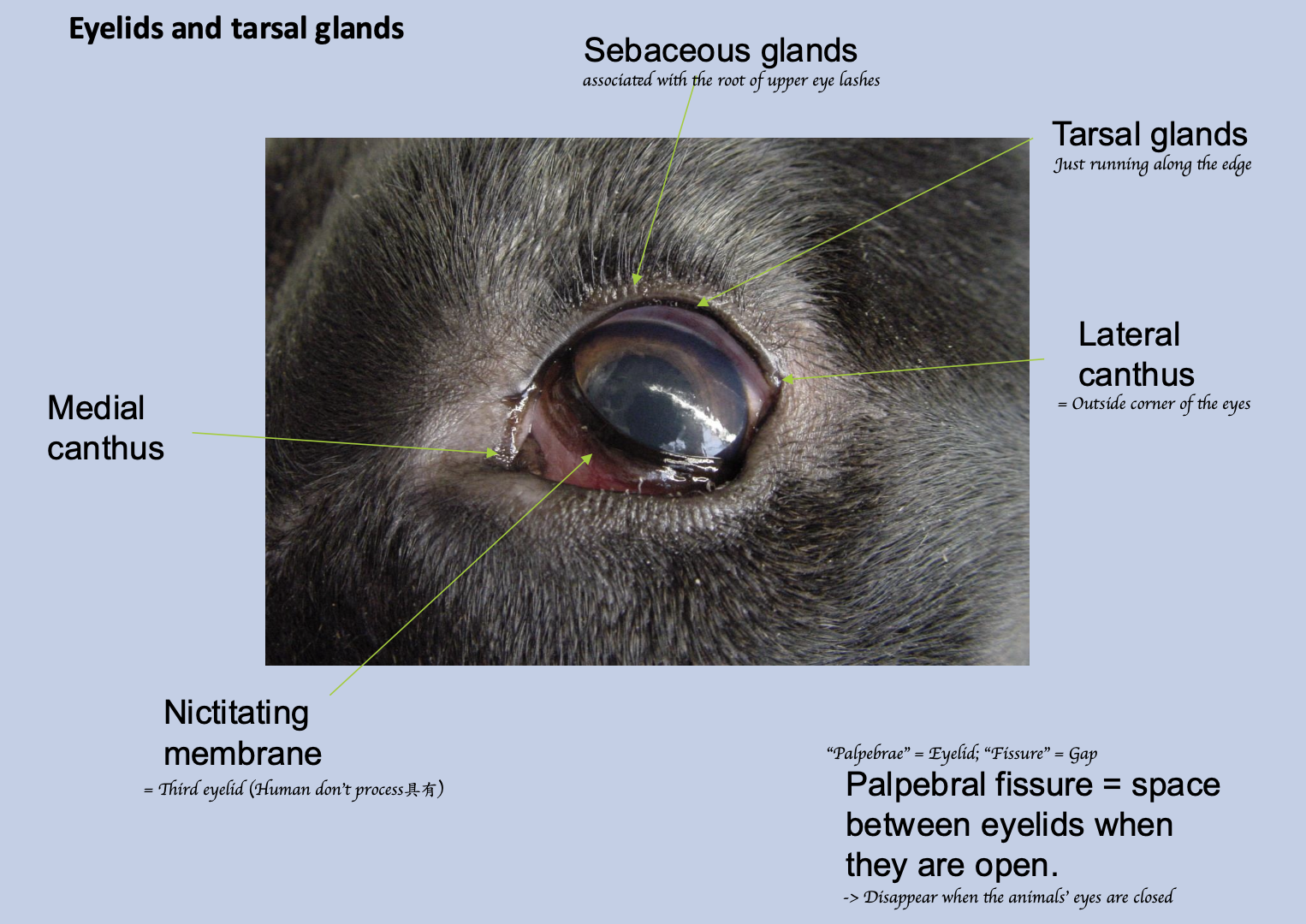
What is the nictitating membrane?
Third eyelid, associated with the root of upper eyelashes.
What is the palpebral fissure?
Space between eyelids when they are open.
What are the three layers of the eyelids?
Skin, Musculofibrous, Palpebral conjunctiva
What is the Fornix?
Where the palpebral conjunctiva turns into the bulbar conjunctiva.
What is the function of the tarsal gland?
Secreting waxy substance → Prevents tears from spilling out of the eye
Where do the tarsal gland present?
Upper and lower lids
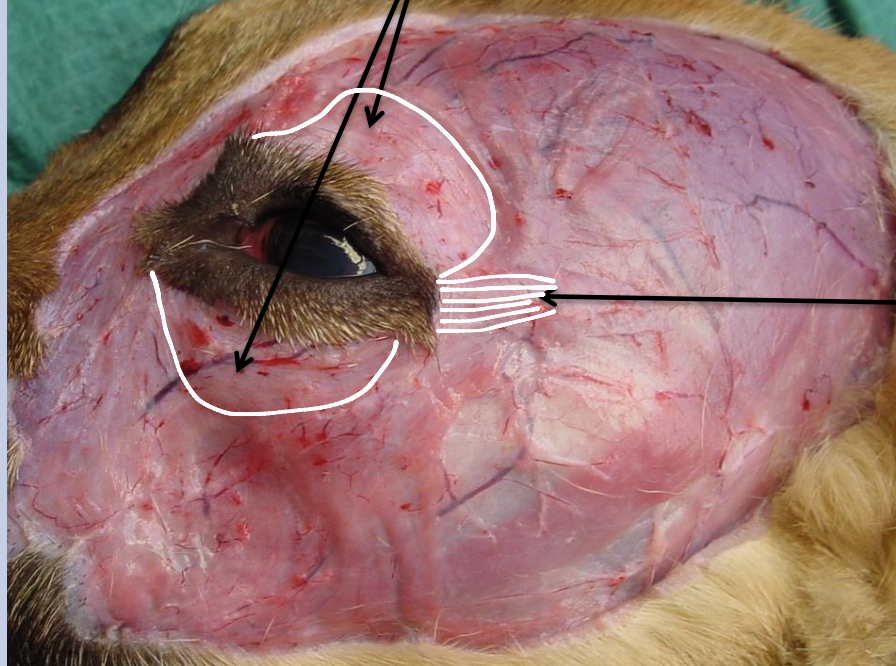
What muscles are these? What are their functions? Which nerve innervate these muscles?
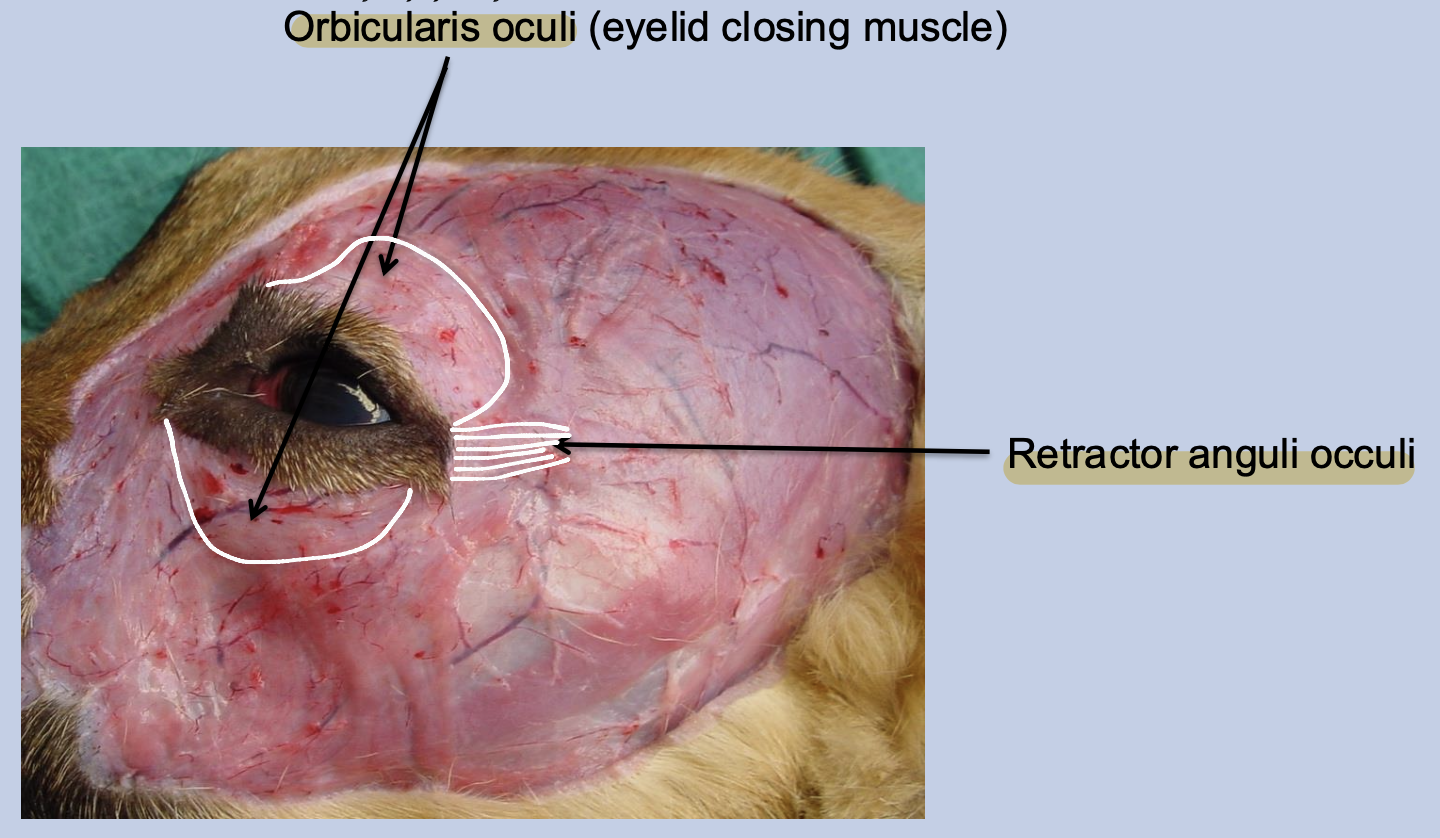
Orbicularis oculi - Close the eyelid → Sweep tears across the front of the eye → Keeping it clean + moist
Retractor anguli occuli - Draws the lateral palpebral angle posteriorly
Innervated by the auriculopalpebral branch of facial nerve (SVE)
What happens if the orbicularis oculi is not able to work? How this disease can be treated?
Corneal ulcer
Treatment: Conjunctival flap
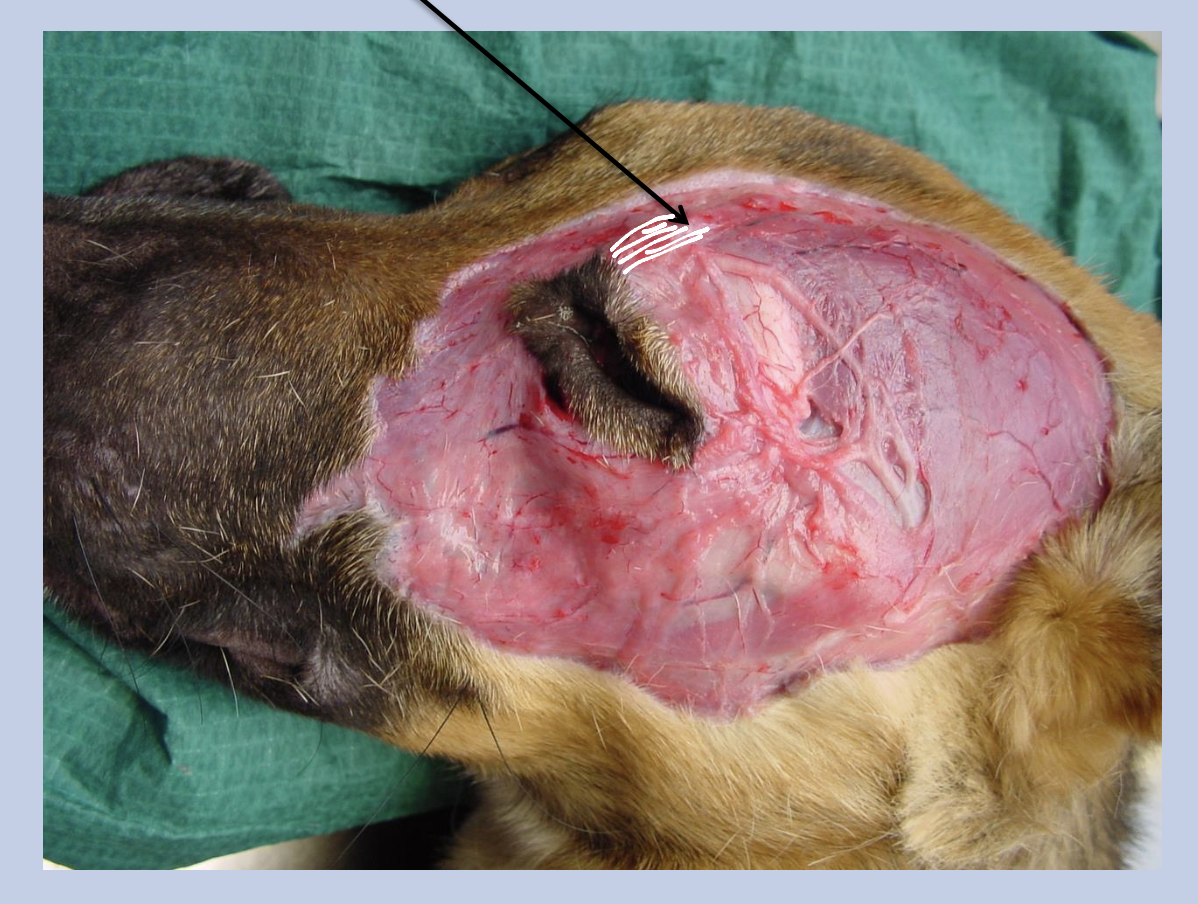
What muscle is this? What is its function?
Superciliaris/ Retractor anguli oculi medialis - Lift the upper eyelid and eyebrow
Innervated by the auriculopalpebral branch of facial nerve (SVE)
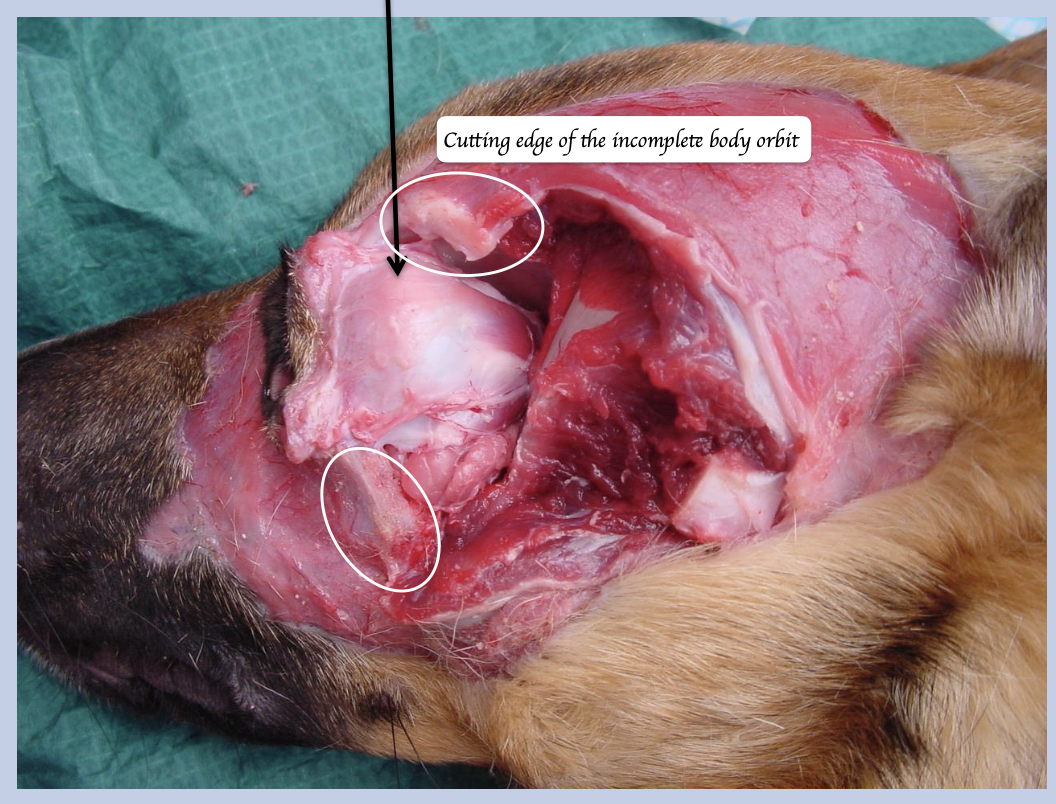
What muscle is this? What is its function?
Levator palpebrae superioris (Deeper muscle)
→ Elevates the upper eyelid
Innervated by oculomotor nerve (SE)
Which nerve supplies the motor function of smooth muscles of the upper and lower eyelids?
Sympathetics (AE) from the cranial cervical ganglion
What supply the sensory nerve around the upper eyelid (both frontal and zygomaticotemporal region) of the horses?
Ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve
What supply the sensory nerve around the lower eyelid (zygomatic region) of the horses?
Maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve
What supply the sensory nerve around the lower eyelid (zygomaticotemporal region) of the dogs?
Different from horses, it is supplied by the maxillary branch of trigeminal nerve
What is Entropion?
Inward rolling of the eyelid margin
What is Ectropian?
Eversion of the eyelid margin
What is the purpose of a conjunctival flap?
To treat deep corneal ulcers by swinging a conjunctival flap to the cornea.
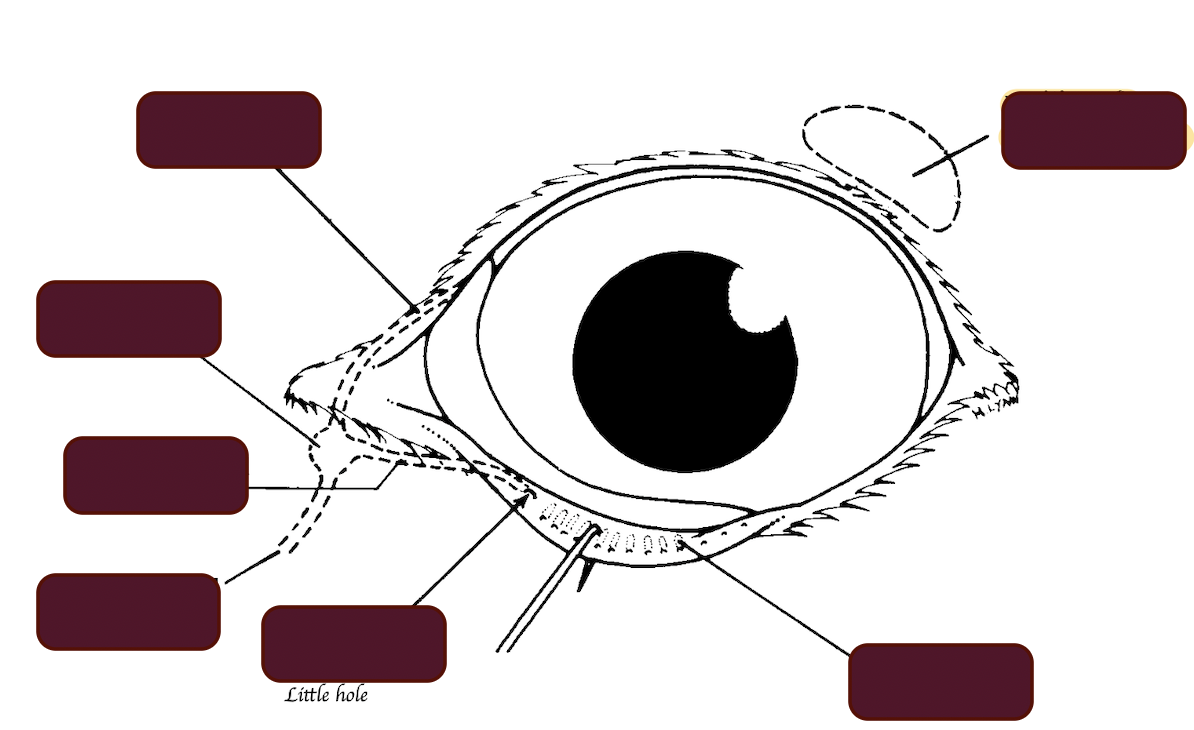
Name the structure of the lacrimal apparatus.
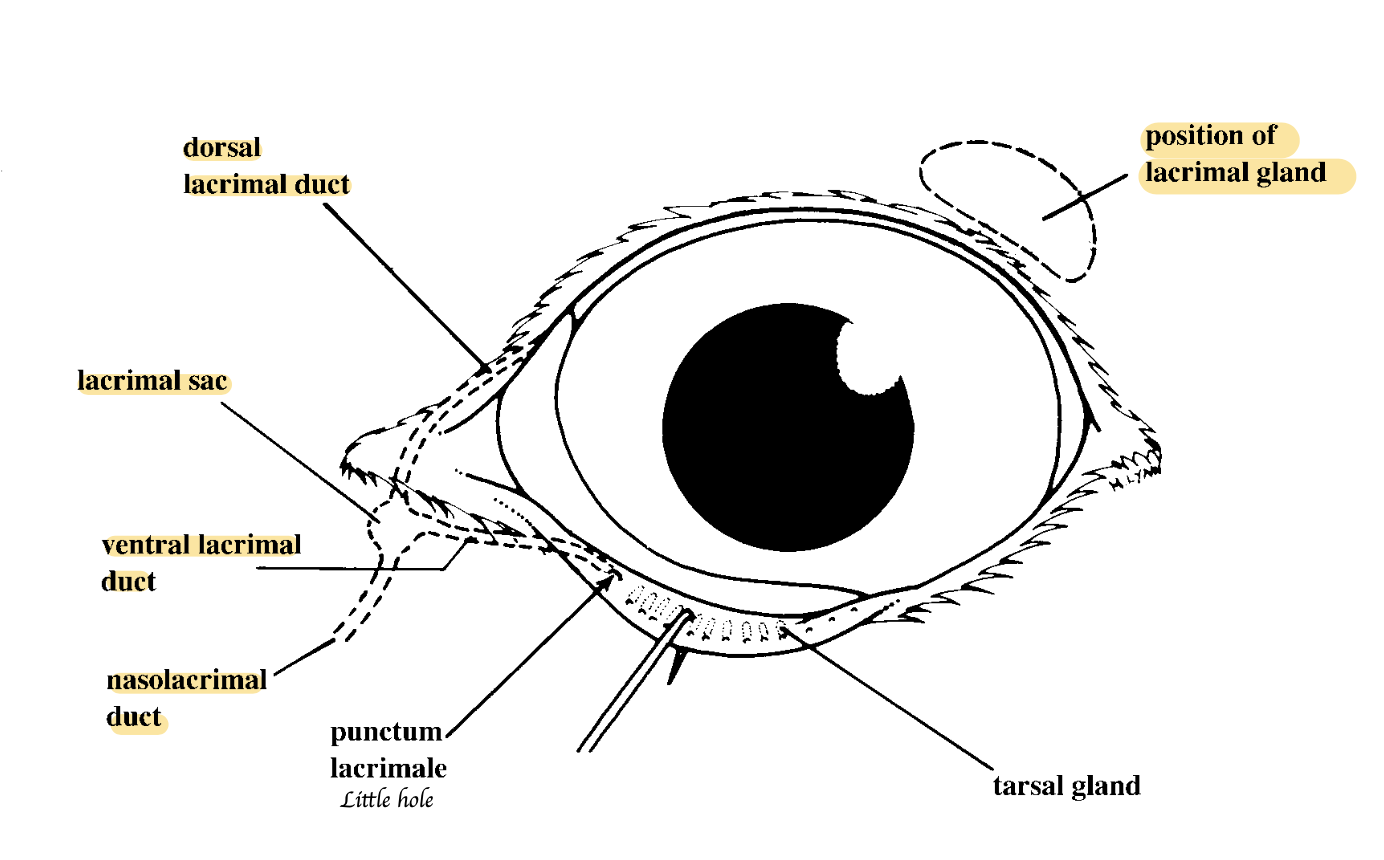
What are the components of the lacrimal apparatus?
Lacrimal gland, Small associated glands, Gland of the third eyelid, Lacrimal duct
What does the lacrimal gland secrete? What are the function of those secretion?
Serous and mucous fluid → Moisten the eye + supply the cornea with nutrients.
What is the innervation of the lacrimal gland?
Autonomic efferents
Parasympathetic: Facial nerve → Running via the pterygopalatine ganglion → Ophthalmic division of trigeminal nerve
Sympathetic: Cranial cervical ganglion
How do tears drain?
From the lacrimal lake to the lacrimal sac → Lacrimal duct and into the nasal cavity
→ Runs first through the wall of the maxilla → Internal surface covered by mucosa → Dorsolateral wall of nostrils
Where is the third eyelid situated at rest?
Medial canthus.
In which animal does nasolacrimal duct occlusion frequently occur due to dental issues?
Rabbits
How can the third eyelid return to its original position?
When the eye opens, the retractor bulbs muscles stop pulling the eyes backward
What is third eyelid? Where is the third eyelid located? What is its function?
→ T shaped cartilage support a fold of conjunctiva
→ Medial canthus
→ Function: It sweep across the cornea when the eyeball is retracted by retractor bulbi
What innervates the smooth muscle within the third eyelid?
Sympathetic nerves.
What are the three layers of the periorbital fascia?
Periorbita (Superficial), Superficial muscular fascia (Middle), Deep muscular fascia (Deep)
What do the superficial muscular fascia + deep muscular fascia envelopes?
Superficial muscle fascia: Lacrimal gland + Levator palpebrae superioris
Deep muscular fascia: Extraoccular muscle + Optic nerve
Identify all the extraocular muscles.

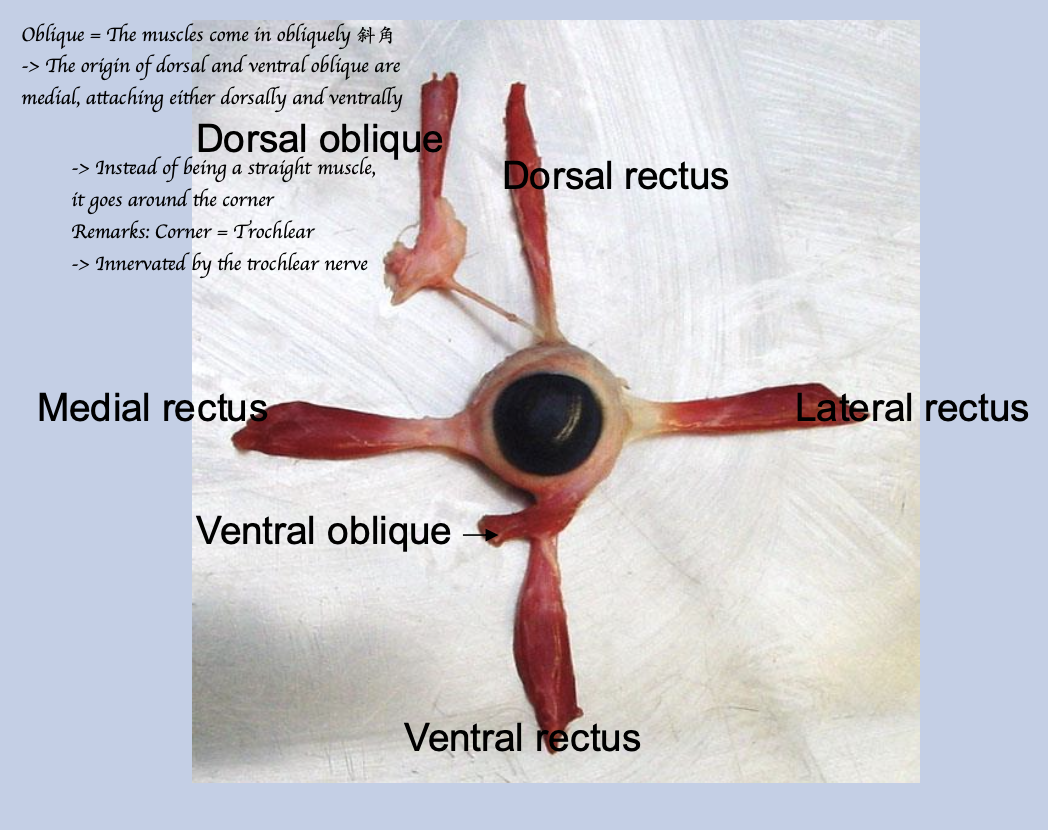
4 rectus; 2 Oblique; 1 Retractor
Where do the rectus muscles insert?
Rostral to the equator.
Where do the oblique muscles insert?
Rostral to equator
Where does the retractor bulbi muscle insert?
Caudal to the equator.
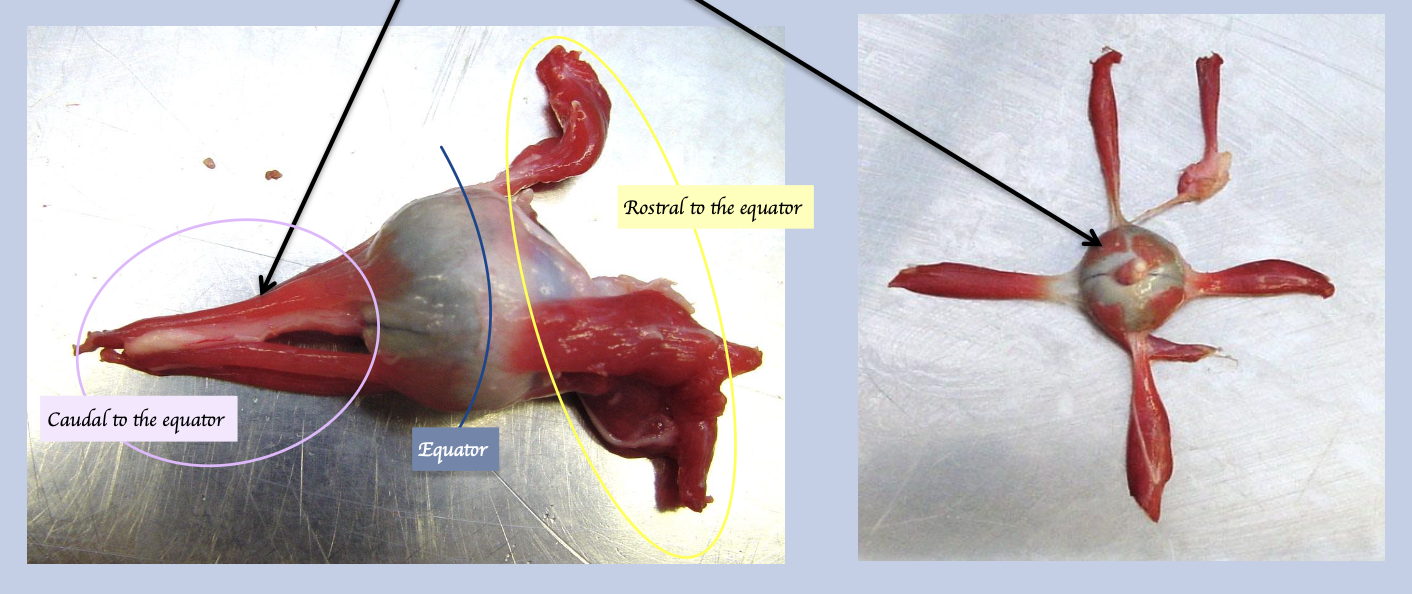
What is this muscle called? What is the insertion of this muscle? What is the function?
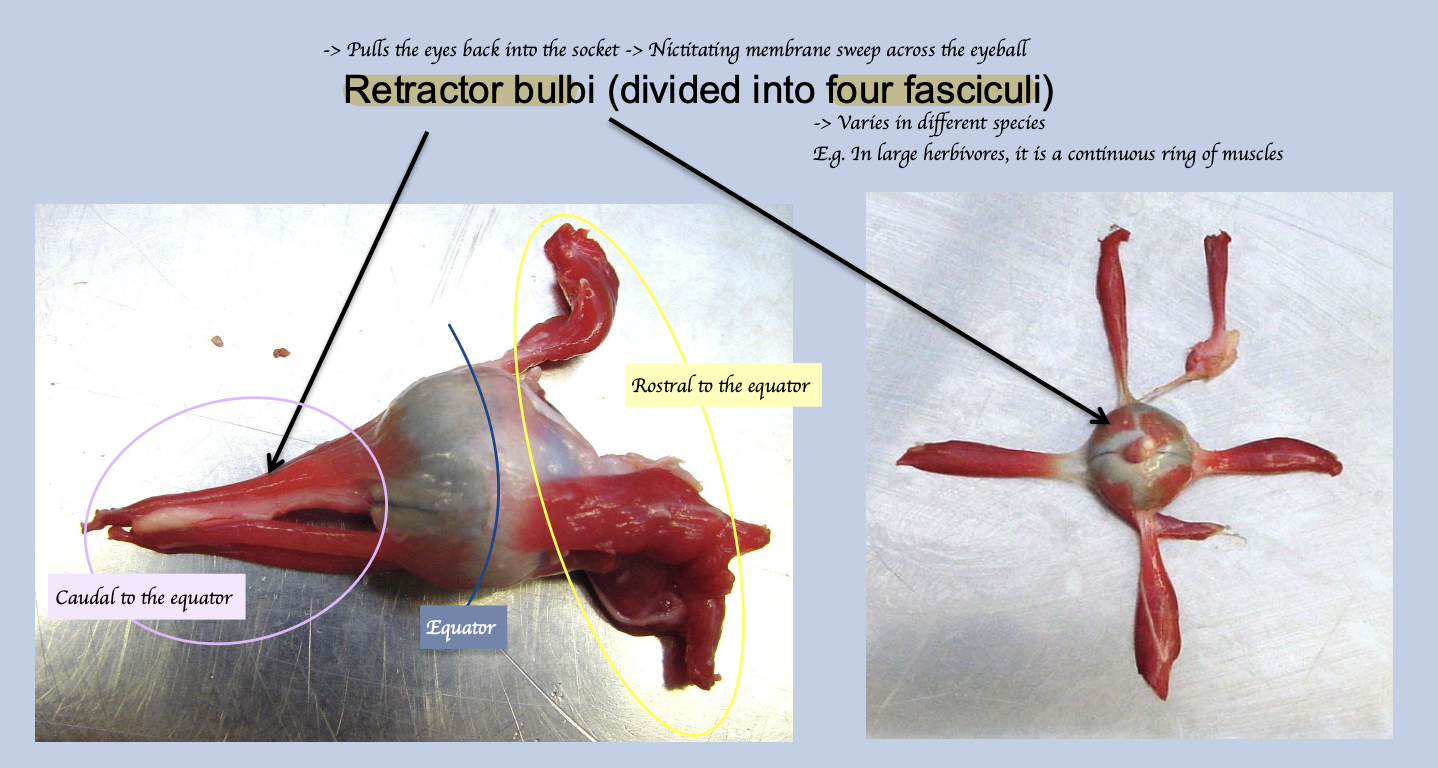
Retractor bulbi
Insert caudal to equator
Pull the eye back into the socket → Nictitating membrane sweep across the eyeball → Protect the eyeball
What is the function of each rectus muscles?
Dorsal - Produces dorsal tilting of pupil
Ventral - Produces ventral tilting of pupil
Lateral - Abduction of the pupil
Medial adduction of the pupil
What is function of oblique muscle?
Dorsal - Pull medially and ventrally
Ventral - Pull medially and dorsally
List out all the nerve supply of each eye muscles.
Dorsal, medial and ventral rectus + Ventral oblique + Part of retractor bulbi:: Oculomotor nerve CN III
Dorsal oblique: Trochlear nerve CN IV
Lateral rectus + Part of retractor bulbi: Abducent nerve CN VI
Where do these extraocular muscle originate?
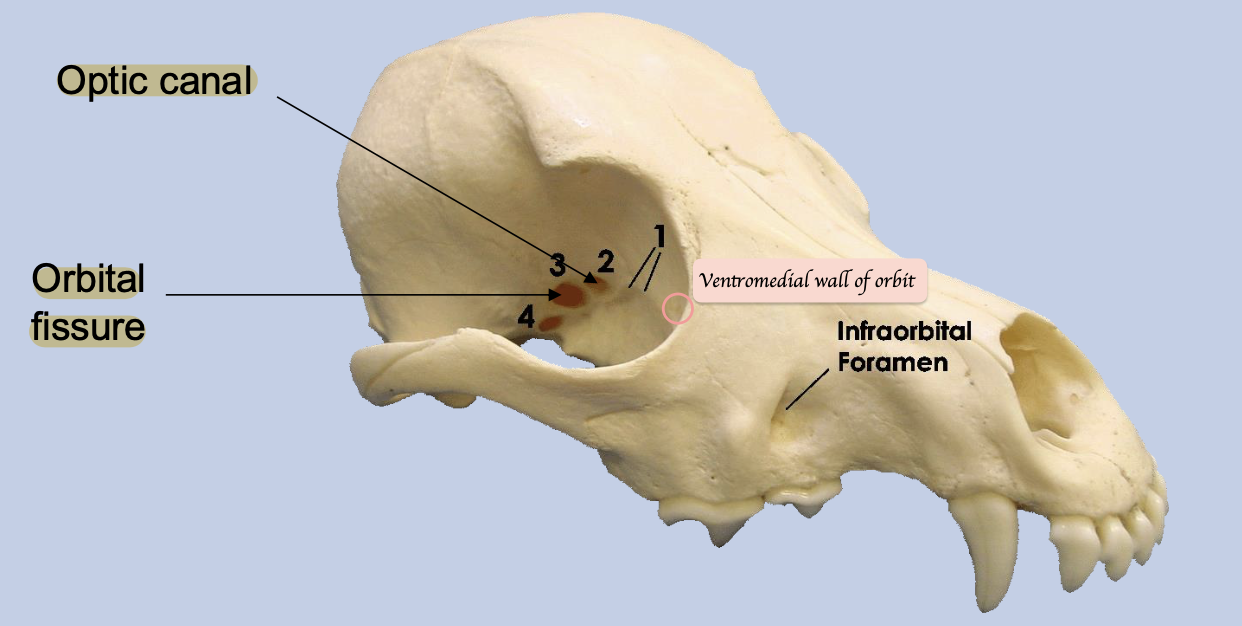
All except the ventral oblique originate from the region of the optic canal + orbital fissure
Ventral oblique arises from ventromedial wall of orbit