Science 9-Unit E Astronomy
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/76
Last updated 2:32 AM on 4/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
1
New cards
Ancient views of Cosmos
The first nations people of pacific northwest believed the north sky was a pattern on a great blanket overhead, which was held up by a spinning 'world pole' resting on the chest of a woman named Stone Ribs
2
New cards
Solstice
Represents the longest and shortest periods of daylight
Summer solstice:June 21
Winter solstice:December 21
Summer solstice:June 21
Winter solstice:December 21
3
New cards
Equinox
represents periods of equal day
Vernal Equinox:March 21st
Autumnal Equinox:September 22st
Vernal Equinox:March 21st
Autumnal Equinox:September 22st
4
New cards
Planetary Motion
Geocentric model:Aristoles Model(Pythagoras and Euclid)Earth was at Centre
\
Heliocentric model:Copernicus model,(Galileo and Kepler) sun at centre, Brahe added ellipses, which basically is the way planets orbit.
\
Ellipses:Planet orbits the sun in an elliptical, oval, motion around the sun.
\
Heliocentric model:Copernicus model,(Galileo and Kepler) sun at centre, Brahe added ellipses, which basically is the way planets orbit.
\
Ellipses:Planet orbits the sun in an elliptical, oval, motion around the sun.
5
New cards
Sun Dial
tells the passage of time(tells time)
6
New cards
Merkhet
Charts astronomical positions, and predicts star movements
7
New cards
Quadrant
Measures starts above horizon
8
New cards
Astrolabe
Accurate chart of stars movements
9
New cards
Cross staff
measures angle between moon and stars
10
New cards
Telescope
Allows us to see details in our neighbouring planets, and discover new ones. Also to see whats beyond our earth
11
New cards
Astronomical Unit(AU)
Measures local distance in our solar system, uses the distance between centre of sun to centre of earth or 149,599,000km
12
New cards
Lightyear
Measures distances between galaxies, uses the distance light travels in one year, or 9.5 trillion km
13
New cards
Parsec
Measures distance between stars and galaxies, about 3.26 lightyears.
14
New cards
Light from different astronomical bodies
Sun-8 minutes
light from pluto-5.5 hours
light from stars in the centre of universe-25,000 years
\
Rule
The more further away, the longer it takes to reach earth.
light from pluto-5.5 hours
light from stars in the centre of universe-25,000 years
\
Rule
The more further away, the longer it takes to reach earth.
15
New cards
stars
hot, glowing ball of gas, made up of mostly hydrogen, and some helium, hot stars of bluish/purplish, and colder stars are redish,yellowish.
\
They spend of their lives converting hydrogen into helium.
\
Very stable because of the outward pressure of radiation is counteracted by gravity
\
They spend of their lives converting hydrogen into helium.
\
Very stable because of the outward pressure of radiation is counteracted by gravity
16
New cards
hertzspring russell model
\
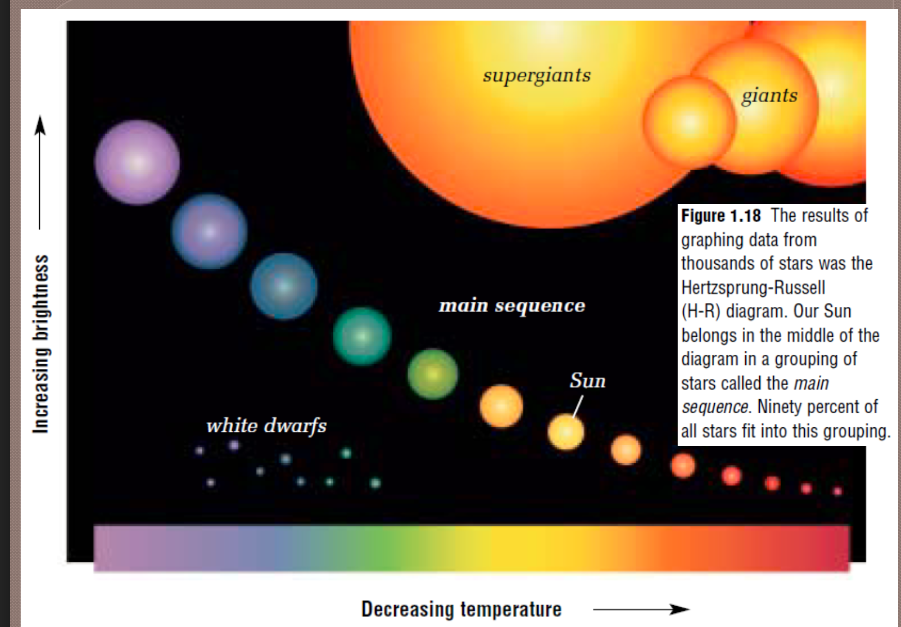
17
New cards
Star lifecycle
Starts off made up of gas and dust called interstellar matter and the stage is called nebulae.
\
Protostar happens when gravity acts on nebulae collapse and rotate, starbuilding is called fusion.
\
Stars get grouped into 2 different groups by their mass, massive stars, and sun like stars.
\
Protostar happens when gravity acts on nebulae collapse and rotate, starbuilding is called fusion.
\
Stars get grouped into 2 different groups by their mass, massive stars, and sun like stars.
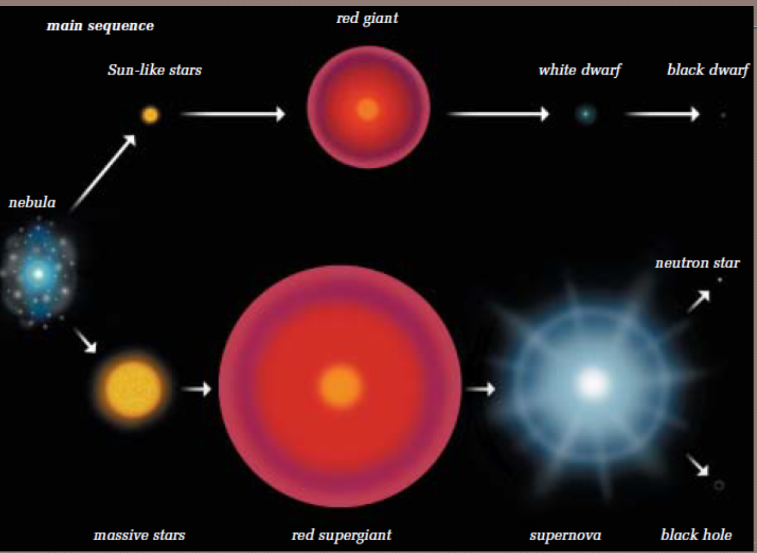
18
New cards
Main squence
Also known as sun like stars, main sequence go like this
Nebulae→Sun like stars→red giant→white dwarf→black dwarf
Nebulae→Sun like stars→red giant→white dwarf→black dwarf
19
New cards
Massive stars
Massive stars go like this
Nebulae→Massive stars→Red supergiant→Supernova→Black hole or neutron star
Nebulae→Massive stars→Red supergiant→Supernova→Black hole or neutron star
20
New cards
Constellations
Grouping of stars we see as patterns in night sky
ex:ursa major
88 constellations
ex:ursa major
88 constellations
21
New cards
Asterisms
Grouping of stars, but not an official recognized as a constellation
ex:big dipper is apart of ursa major
ex:big dipper is apart of ursa major
22
New cards
Galaxies
Grouping of dust, stars, and gas held together by gravity, 3 types
\-Spiral(our galaxy milky way, is a spiral galaxy)
\-elliptical
\-irregular
\-Spiral(our galaxy milky way, is a spiral galaxy)
\-elliptical
\-irregular

23
New cards
Blackholes
They are invisible to telescopes, but is only known through indirect method. We know they exist because when celestial bodies that get near black holes get very bright and very hot.

24
New cards
protoplanet hypothesis
How solar systems become solar systems
1\.cloud dust and gas starts swirling
2\.90% or more of the dust and gas turns into sun
3\.the rest circles the sun
1\.cloud dust and gas starts swirling
2\.90% or more of the dust and gas turns into sun
3\.the rest circles the sun
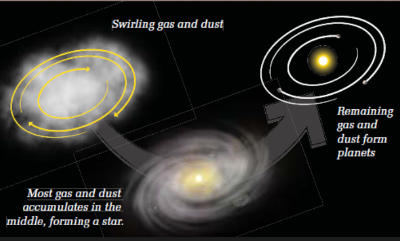
25
New cards
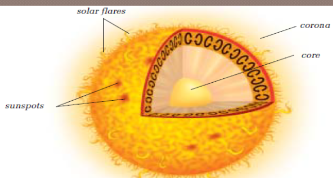
Sun
Centre of solar system, surface is 5000 degrees, and centre is 15,000,000 degrees. A million earths could fit into sun
26
New cards
Solar wind
charged particles traveling pass 400km/s, earth is protected because of magnetic field
27
New cards
Asteroids
Orbits in narrow belt between jupiter and mars, scientists dont know where they come from
28
New cards
comets
known as dirty snowballs, made up of dust and ice, and when ice melts it creates trail
29
New cards
meteoroids, meteors, meteorites
Meteoroids, traveling in space, outside of earth’s atmosphere, meteors aka known as shooting stars entered earth's atmosphere but hasn’t hit ground, meteorites hit ground.
30
New cards
Solar eclispes
Moon passes between sun and earth casting shadow
31
New cards
lunar eclipse
earth travels between sun and moon casting shadow over moon.
32
New cards
Azimuth
compass direction, north is 0 degrees, east is 90 degrees, south is 180 degrees, and west is 270 degrees
33
New cards
altitude
how how in the sky 0-90 degrees
34
New cards
zenith
highest point overhead
35
New cards
motion of objects in space
planet comes from greek word for wanderer
\
ecliptic, path in the sky sun appears to move
\
celestial sphere, name given to imaginary sphere surrounding earth, aka the atmosphere
\
ecliptic, path in the sky sun appears to move
\
celestial sphere, name given to imaginary sphere surrounding earth, aka the atmosphere
36
New cards
what are the 3 biggest challenges to get to space?
1. Speed: to travel fast enough to break free of
Earth’s gravity & travel to other planets
\
2. Extreme environments: to keep equipment
operating in space
\
3. Transport of people: safe travel back and
forth
37
New cards
gravitational escape velocity
For an object to go to space, they must overcome the force of gravity which is 28,000km/h
38
New cards
Physics law\*\*\*
for every action, there is an equal opposite reaction
39
New cards
Structural and mechanical part of rocket aka machinery
rocket, engine, storage tank, and fins, makes up 3 percent
40
New cards
fuel
liquid oxygen, gasoline, and liquid hydrogen is ignited in a combustion chamber which causes gas to expand leave as exhaust, makes up 91% of rocket
41
New cards
payload
materials that are needed for the flight, people, food, water, air, etc. Makes up the last 3%
42
New cards
What are ion drives?
Engines that are electrically charged and uses xenox gas. Accelerated and leaves as exhaust, which pushes rocket direction opposite of emission. Thrust lasts a long time, and only needs 1/10 of fuel
43
New cards
What are solar sails?
Like boats, they have sails that catches the suns lights, more specifically the photons(electromagnetic energy). The photons hit the sails and causes the spacecraft to move, these are 5 times more effective than rockets.
44
New cards
what are space probes?
robots used for exploration of space
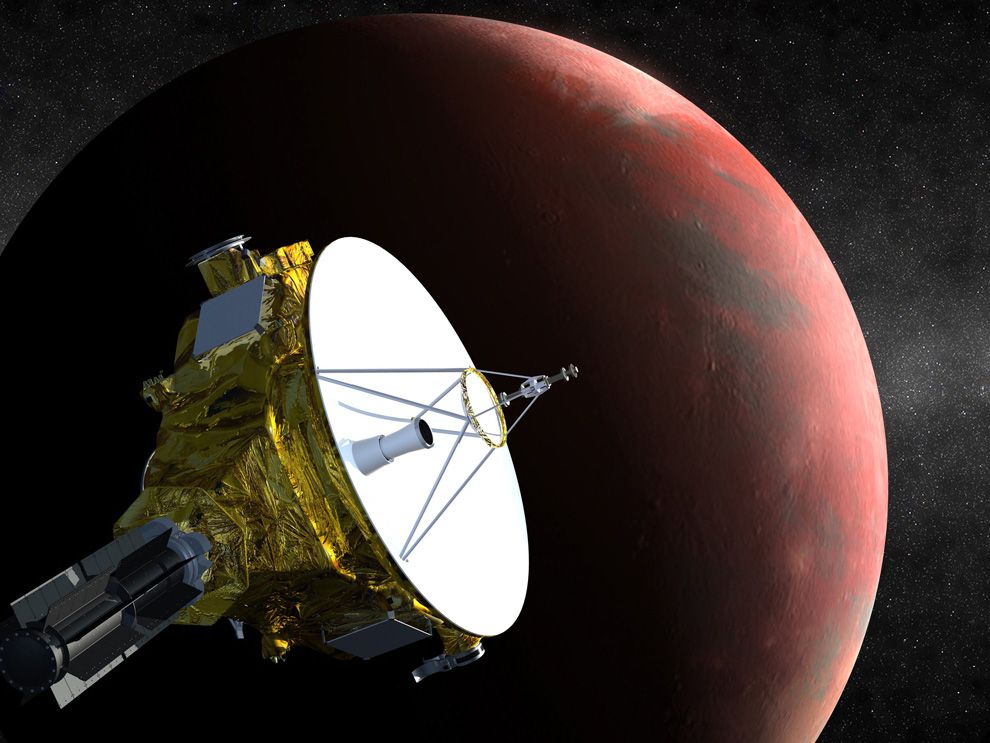
45
New cards
what are shuttles used for?
transport people, and equipment to orbiting spacecrafts
46
New cards
Spacestations
an orbiting spacecraft that people live in, work, and life supports systems needed to live in space for a long time
47
New cards
international space station(ISS)
Serves as a permanent laboratory in space, and a command post for building and launching interplanetary rockets
Joint project of the US, Canada, Japan, Russia, Brazil and 11 other nations
Joint project of the US, Canada, Japan, Russia, Brazil and 11 other nations
48
New cards
What are the environment hazards of living in space?
Space is a vacuum with no water and/or air, cosmic rays, solar radiation, and getting hit by meteoroids can have damaging effects, no atmosphere so temperatures can be really hot or really cold, also means no pressure that regulates heartbeats.
49
New cards
Psychological Challenges to Confined Living
Enclosed, small spaces shared by more than one person
50
New cards
Microgravity
Condition where forces acted on mass is greatly reduced, bones have less pressure causing them to expand, heart doesn’t need to pump as hard to regulate blood, muscles get weaken, and visual depth is effected.
51
New cards
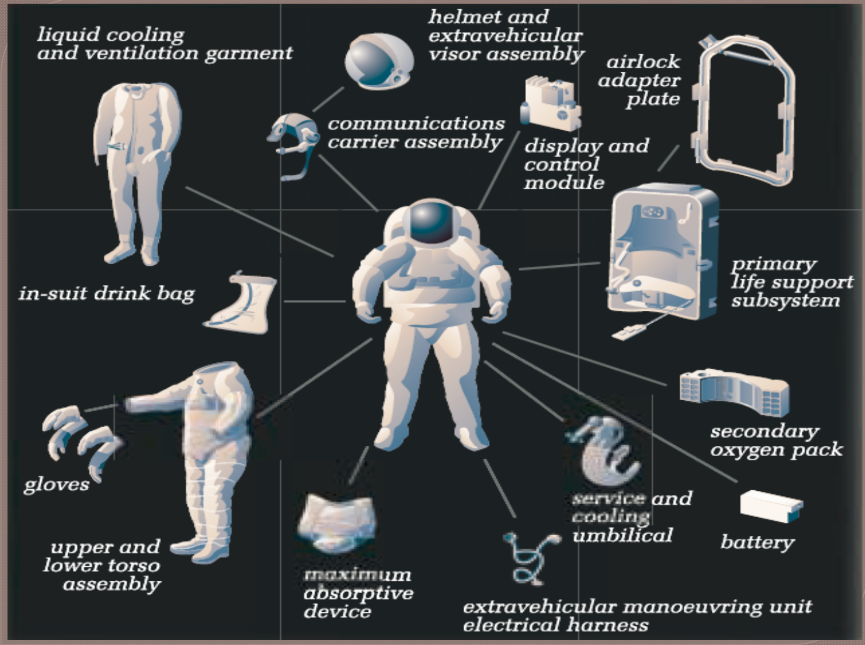
Space suit
Space suits are used when astronauts(people in space) leaves spacecraft. everything they need, needs to be brought with them, such as air, water, heating/cooling system, and portable toliet. Suits must be flexible enough to hold a wrench and to twist a bolt incase something of the spacecraft breaks, and has to be custom fit.
52
New cards
Home in space aka spacecrafts
station must provide own power for energy for its own life systems.
Clean water, breathable air, and comfortable air
temperatures and pressures must be provided
Clean water, breathable air, and comfortable air
temperatures and pressures must be provided
53
New cards
Recycling water
ISS recycles 100% of its water
54
New cards
Environmental Control and Life Support System
functions:
functions:
Environmental Control and Life Support System
functions:
Recycling wastewater (urine) to produce drinking
water
Using recycled water to produce oxygen
Removing carbon dioxide from the air
Filtering micro-organisms & dust from air
Keeping air pressure, temperature & humidity stable
functions:
Recycling wastewater (urine) to produce drinking
water
Using recycled water to produce oxygen
Removing carbon dioxide from the air
Filtering micro-organisms & dust from air
Keeping air pressure, temperature & humidity stable
55
New cards
Producing oxygen
electrolysis uses energy to split water into hydrogen and oxygen, when it happens hydrogen is sent off into space, and oxygen is breathe in.
56
New cards
Satellites and artificial satellites
Satellites are objects that orbits earth, a natural satellite would be the moon. Artificial satellites are satellites we send out to orbit earth.
57
New cards
Role of artificial satellites
Communication: wireless technology
Observation & Research: monitor & forecast weather,
follow ships at sea, monitor soil quality, track forest fires,
report environmental change & search for natural resources
Remote Sensing: observe Earth’s surface, environment,
natural resources, urbanization
Personal Tracking Devices: GPS (global positioning
system) – uses 3/24 satellites to track you
Observation & Research: monitor & forecast weather,
follow ships at sea, monitor soil quality, track forest fires,
report environmental change & search for natural resources
Remote Sensing: observe Earth’s surface, environment,
natural resources, urbanization
Personal Tracking Devices: GPS (global positioning
system) – uses 3/24 satellites to track you
58
New cards
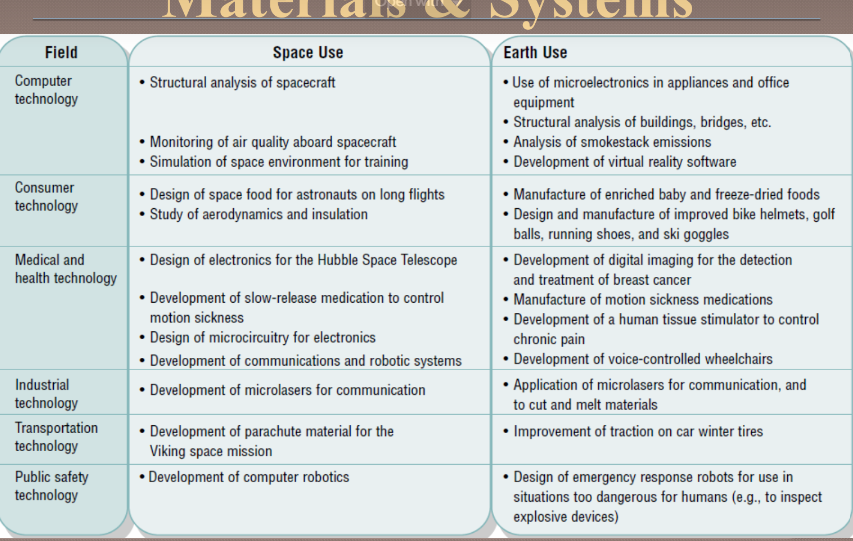
Space age inspired systems plus material
59
New cards
Who is credited with inventing the first telescope to study the sky?
Galileo but in 1608 Hans lippershey made one of the first telescopes
60
New cards
Light collectors
objects that gather and focus from stars;larger the area of lenses or mirrors, the greater the ability to see objects
61
New cards

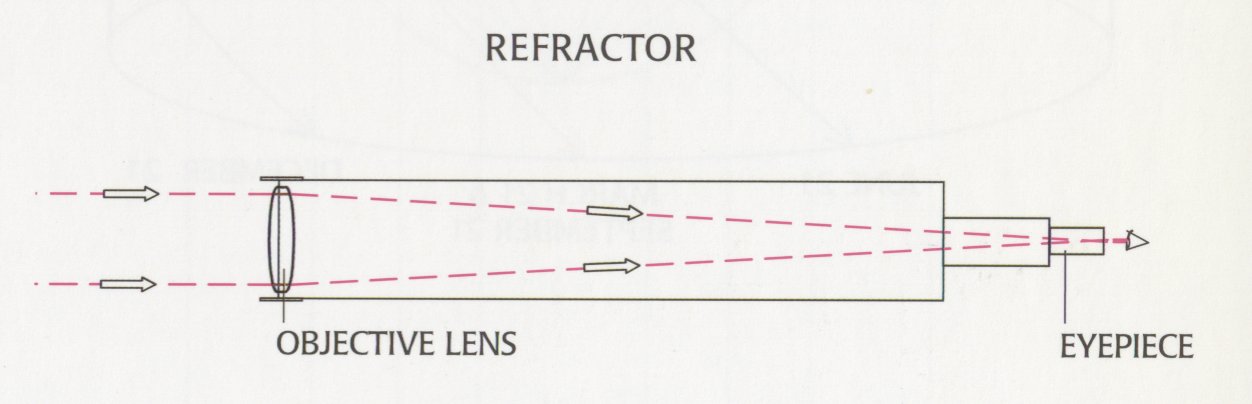
Refracting Telescope
Uses two lenses to gather and focus starlight.
1\.Objective lense
2\.Eyepiece lens
This limits how large it can be →Diameter has to greater that 1m causes the glass to warp under own weight
1\.Objective lense
2\.Eyepiece lens
This limits how large it can be →Diameter has to greater that 1m causes the glass to warp under own weight
62
New cards

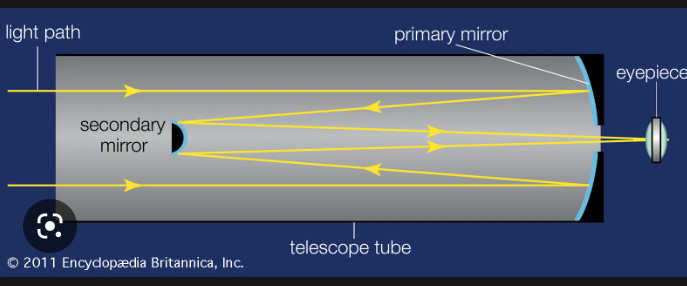
Reflecting telescope
Uses mirrors to gather and focus light
1\.Large concave mirror
2\.Secondary flat mirror
\-Mirrors made from glass-like material that has been coated with thin layer of metal(aluminum)
\-Uses a spin casting technique to form large mirrors
1\.Large concave mirror
2\.Secondary flat mirror
\-Mirrors made from glass-like material that has been coated with thin layer of metal(aluminum)
\-Uses a spin casting technique to form large mirrors
63
New cards

Segmented mirror telescope
\-uses several lightweight segments to build one big mirror
\-increases light gaterhing capability and resolving power(ability to distinguish details in an object)
\-increases light gaterhing capability and resolving power(ability to distinguish details in an object)
64
New cards
Inferferometry
Technique that combines 2 or more observations from telescopes to produce images that have better resolution than what one telescope could produce alone.
65
New cards
Problems of telescope use on land
Light and air pollution, the weather clouds humidity and high winds
66
New cards
Electromagnet Energy
objects in space emit radio waves, infrared(heat) waves, and X-rays. Energy travels at the speed of light(300,000 km/s) but has different wavelengths and frequences from those light.
67
New cards
Wavelength
Measurement of distance from one point on the wave to the same point on the next wave
68
New cards
Frequency
number of waves that pass a single point in one second
69
New cards
electromagnetic spectrum
complete wavelengths over which electromagnetic energy extends
70
New cards
How are radio telescopes useful and how do they work?
Radio waves give astronomers data not available from visible spectrum. Signals are mapped through a sophisticated electronics and computers
71
New cards
What are radio telescopes made up of, its shape, and how does it work?
THey are made up of metal mesh, they have a shape of a satellite dish, curved inwards with reciever in the middle, the curved part intercepts and focuses the radio waves before transmitting it to a reciever. Waves are transformed into electrical signals that is fed into a computer to be interpreted.
72
New cards
Radio interferometry
Combining 2 small radio telescopes to achieve greater resolving power. Two or more radio telescopes is called an array
73
New cards
space probes
Umanned satellites or remote controlled lands that put equipment close to planets
they gather information about planets that optical and radio telescopes can’t
they gather information about planets that optical and radio telescopes can’t
74
New cards
what is triangulation and what is it used for?
It uses the geometry of a triangle, measures the angles between the baseline of the object, and estimates distance to object.
75
New cards
parallax
shift of an object seen in two different places, used to determine objects distance from earth through triangulation.
76
New cards
Refracting light
white light shone through a prism seperated into different colours
77
New cards
Spectroscopy
black line patterns from stars known as spectra compared to spectra to elements to see what makes up the star