Wk 7 - Foreign Body Airway Obstruction
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Airway Position
neutral (neutral anatomical spinal alignment - external auditory meatus to mid clavicle)
sniffing (ear in line with sternum)
lateral (on their side)
Back Blows
heel of the hand on the patient’s back at the height of the base of the scapulae and in line with the spinal column
raise a hand and provide a sharp blow rapidly and forcefully
deliver in groups of five
Chest Thrust (Adult & Child)
palm where CPR would happen and make a fist
push hand back into sternum up to 5 times
Chest Thrust (Infants)
use two fingers like in CPR, up to 5 times
Laryngoscope Measurement
Upper incisor > Mandible Angle
Choking CWI
There are 3 stages to deglutition (swallowing) what are they ? Briefly describe them
1. Oral, voluntary phase : chewing (mastication) of food
2. Pharyngeal, tactile receptors in oropharynx stimulated
3. Oesophageal , peristalsis
Endogenous Causes of Choking
airway edema from anaphylaxis
ACE inhibitor-induced angiodema
mucus plug
tongue displacement
infections such as epiglottitis and croup
laryngospasm
Exogenous Causes of Choking
FBAO
trauma, burns, toxic gases
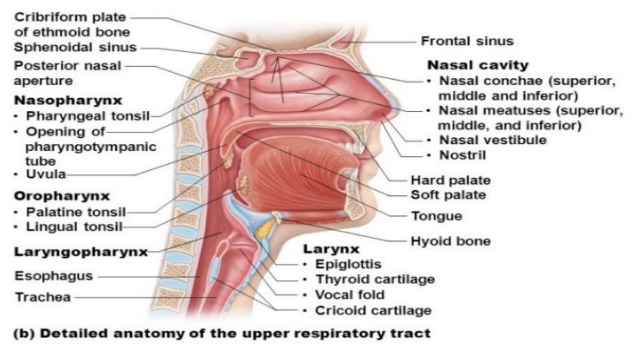
Upper Airway Anatomy
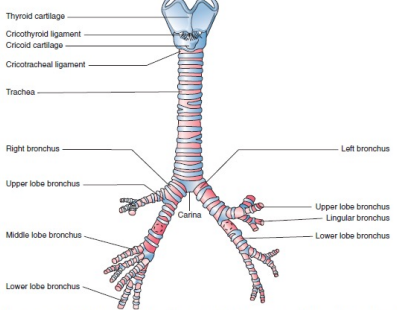
Tracheobronchial Anatomy
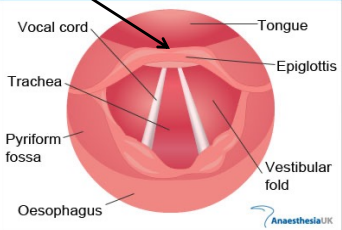
Vocal Chord Anatomy
There are 5 steps involved in the pharyngeal phase of swallowing, name 3
- Tongue blocks oral cavity
- Vocal cords close
- Soft palate blocks nasal cavity
- Larynx moves up
- Epiglottis covers the larynx
What is the point of the epiglottis covering the larynx during swallowing
It prevents food from going into the lungs
There are 3 steps involved in the oesophageal phase of swallowing, name them
- Upper oesophageal sphincter opens
- Involuntary skeletal and smooth muscle moves the food bolus downward
- Once bolus has passed, the epiglottis moves upward and opens up again for respiration
Who is at risk of FBAO
children (anatomy, cognitive differences)
people with dysphagia
acs
neurological problems
What are some differences between an effective cough and an ineffective cough ?
Effective
- Crying or verbal response to questions
- Loud cough
- Able to breath before coughing
- Fully responsive
- Stridor
Ineffective
- Unable to vocalise
- Quiet or silent cough
- Unable to breath
- Cyanosis
- Decreases level of consciousness
There are 4 potential differentials for FBAO, what are they?
Croup, Epiglottitis, Anaphylaxis , Laryngeal spasm
Whilst there are differentials for FBAO, what is the main differences between them and a FBAO
FBAO is sudden onset, other differentials are gradual
For the adult pt, in the upper airway obstruction CPG, it states adult with audible stridor, then it flows into STOP. What are the 2 points under this section of the CPG
MICA must be requested if pt is having an imminent life threatening airway obstruction
This CPG is not for treating stridor associated with anaphylaxis
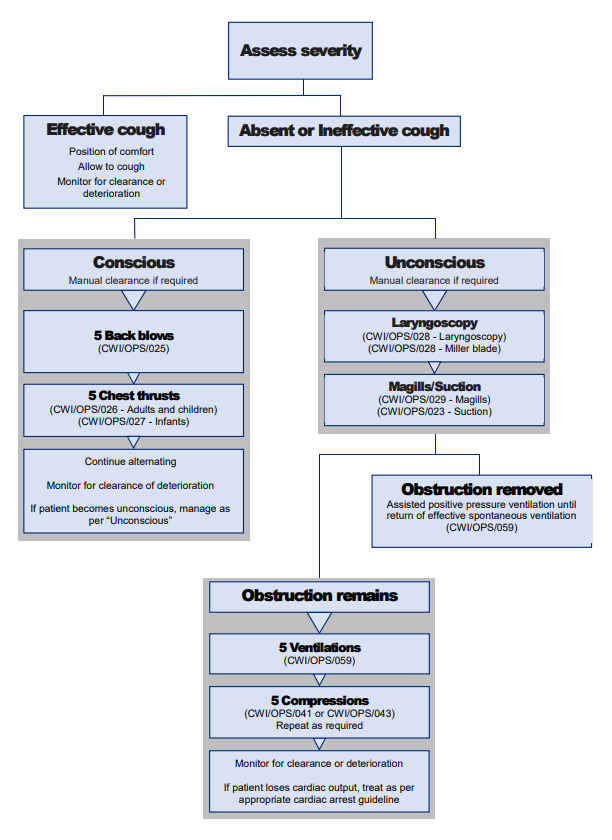
If a pt is having a suspected foreign body obstruction and is conscious what does the flow chart look like in the upper airway obstruction CPG ?
1. Encourage pt to cough it able to
2. 5 back blows
3. 5 chest thrusts
Alternate the above and monitor pt for deterioration
If a pt is having a suspected foreign body obstruction and is unconscious what does the flow chart look like in the upper airway obstruction CPG ?
1. Laryngoscope and Magic's forceps (to remove obstruction)
If unsuccessful then
Commence chest compressions
If pt looses cardiac output treat as per cardiac arrest
As per the CWI 129 Choking pts, if pt is unconscious and use of Laryngoscopy and magills were not successful, what is the procedure for chest compressions?
1. Ventilate pt 5 times
2. Provide 5 chest compressions
3. Inspect airway again
4. If obstruction still remains repeat 5 chest compressions and inspect airway again
5. Once obstruction is removed, ventilate until spontaneous ventilation is adequate
What is the rationale behind back blows and chest thrusts
Increases intrathoracic pressure which increases pressure in airway and specifically in trachea which forces the obstruction to be dislodged
How to pick up Magills Forceps
Pick up Magill's with the right hand (left should be holding laryngoscope) and grip with thumb and third or ring finger. Index finger should be used to steady forceps.