APD Hepatobiliary Physiology & Liver Metabolic Functions (Lecture 10)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/109
Last updated 4:03 AM on 2/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
1
New cards
basolateral membrane
Hepatocytes uptake substances from capillary via what membrane?
2
New cards
apical membrane
Hepatocytes modify compounds/material before excretion across what membrane?
3
New cards
1. Chenodeoxycholic acid
2. Cholic acid
3. Protonated form
What are 3 examples of bile acids?
4
New cards
1. Glucoronate
2. Glycine
3. Sulfate
4. Taurine
What are 4 examples of bile salts?
5
New cards
heme
Free iron in the blood; travels with transferrin in the blood
6
New cards
biliverdin
Reduced to bilirubin
7
New cards
bilirubin
Transported with albumin--not soluble in blood
8
New cards
jaundice
Build up of bilirubin causes ____________.
9
New cards
urobilinogen
Bilirubin in the small intestine is metabilized to _____________ by microbes in the natural flora.
10
New cards
stercobilin; urobilin
Urobilinogen is metabolized to ________ to be excreted through the feces and is oxidized to ____________ to be excreted as urine.
11
New cards
1. Heme
2. Biliverdin
3. Bilirubin (w/ albumin)
4. Conjugated bilirubin (in liver)
5. Urobilinogen (GI bacteria)
6. Urobillin (urine)
Using numbers 1 through 6, list the metabolism of heme when converted to bilirubin to be excreted in the urine.
12
New cards
1. Heme
2. Biliverdin
3. Bilirubin (w/ albumin)
4. Conjugated bilirubin (in liver)
5. Urobillinogen (GI bacteria)
6. Stercolbin (feces)
Using numbers 1-6, list the metabolism of heme when converted to bilirubin to be excreted in feces.
13
New cards
1. Heme
2. Biliverdin
3. Bilirubin (w/ albumin)
4. Conjugated bilirubin (in liver)
5. urobilinogen (GI bacteria)
6. Reabsorption in small intestine (made to bile)
Using numbers 1-6, list the metabolism of heme when converted to bilirubin to be reabsorbed in GI tract.
14
New cards
Make molecules more water soluble
During biotransformation in the liver, what is the overall purpose of this process?
15
New cards
3
How many phases make up biotransformation in the liver?
16
New cards
P-450 cytochromes
What catalyzes phase 1 of biotransformation in the liver?
17
New cards
Adds oxygen
What is the mechanism of action for P-450 cytochromes?
18
New cards
Conjugation; makes product more water soluble
What major process occurs in phase 2 of biotransformation? What does this do to the phase 1 product?
19
New cards
excretion of phase 2 product into blood or bile
What major process is occurring in phase 3 of biotransformation in the liver?
20
New cards
Reduced glutathione (GSH)
What is the starting material of mercapturic acids (phase 2 conjugation)?
21
New cards
1/2
Out of all the bile produced from hepatocutes, how much bile (relatively) is diverted to the gallbladder between meals (instead of the small intestine through the duodenal papilla)?
22
New cards
cholesterol
What do hepatocytes make bile acids from?
23
New cards
1. Bilirubin
2. Cholesterol
What are the 2 major organic solutes that make up bile?
24
New cards
Normal lipid absorption and digestion
What is the primary function of bile?
25
New cards
mixed micelles
Bile salts form soluble ___________________ with fat to aid in passage from lumen.
26
New cards
Cholestyramine (Questran)
What increases excretion of bile in the feces?
27
New cards
1. Heavy metals
2. Lipophilic compounds
What are 2 main bile excretory products?
28
New cards
bacteria
Secondary bile acids are formed by dehydroxylation by __________.
29
New cards
cholesterol
What levels decrease within the blood due to bile acid production?
30
New cards
secretin
What major player is responsible for secretion of bicarbonate rich fluid?
31
New cards
somatostatin
What major player is responsible for inhibiting the cAMP pathway in bile duct secretion?
32
New cards
Secretin; Somatostatin
___________ increases bile duct secretion. ______________ inhibits bile duct secretion.
33
New cards
cystic fibrosis
What condition decreases bicarbonate in bile secretions?
34
New cards
Glucagon (pancreatic alpha cells)
What is indicated by number 1 in the image?
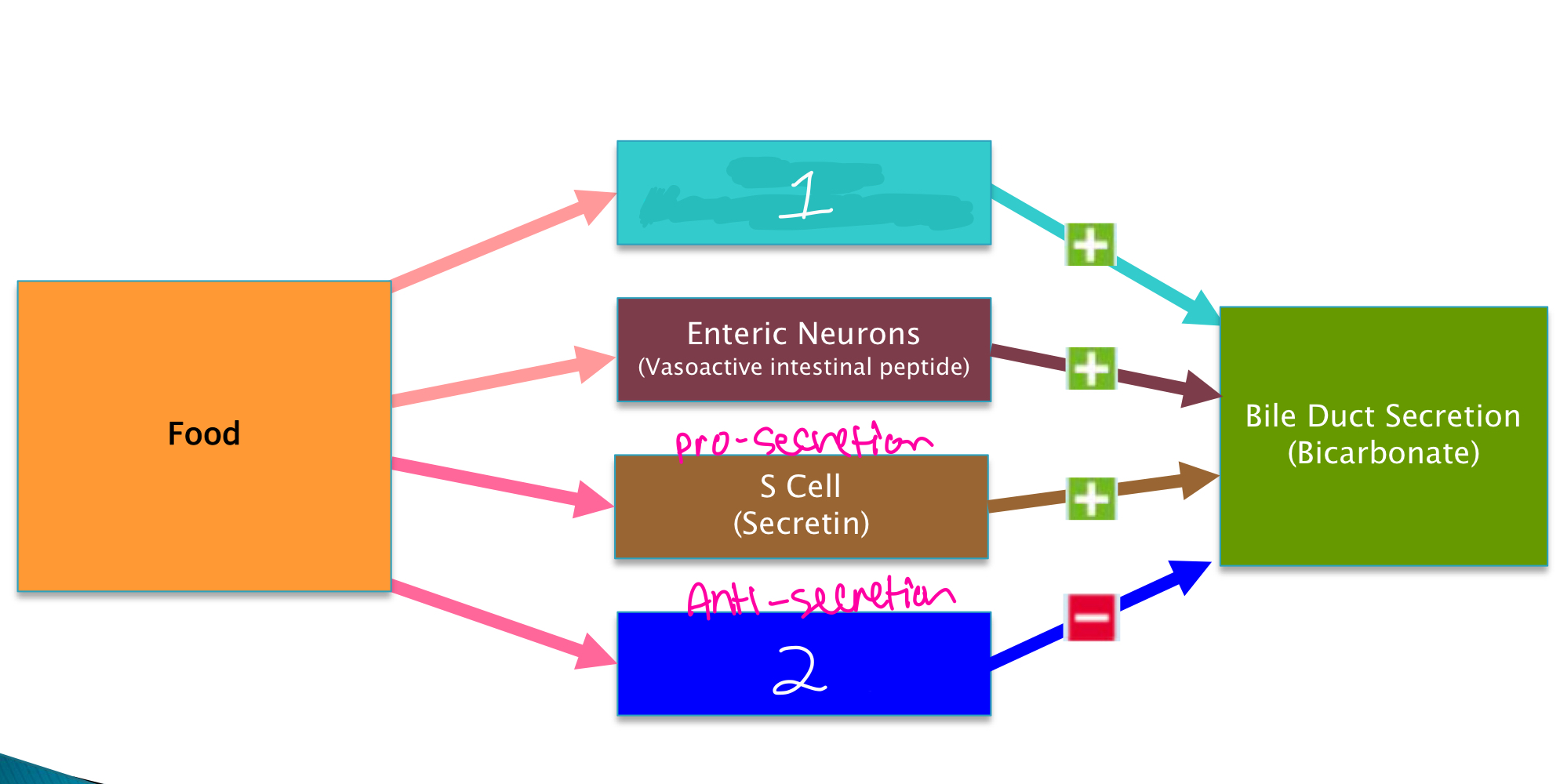
35
New cards
D cell (somatostatin)
What is indicated by number 2 in the image?
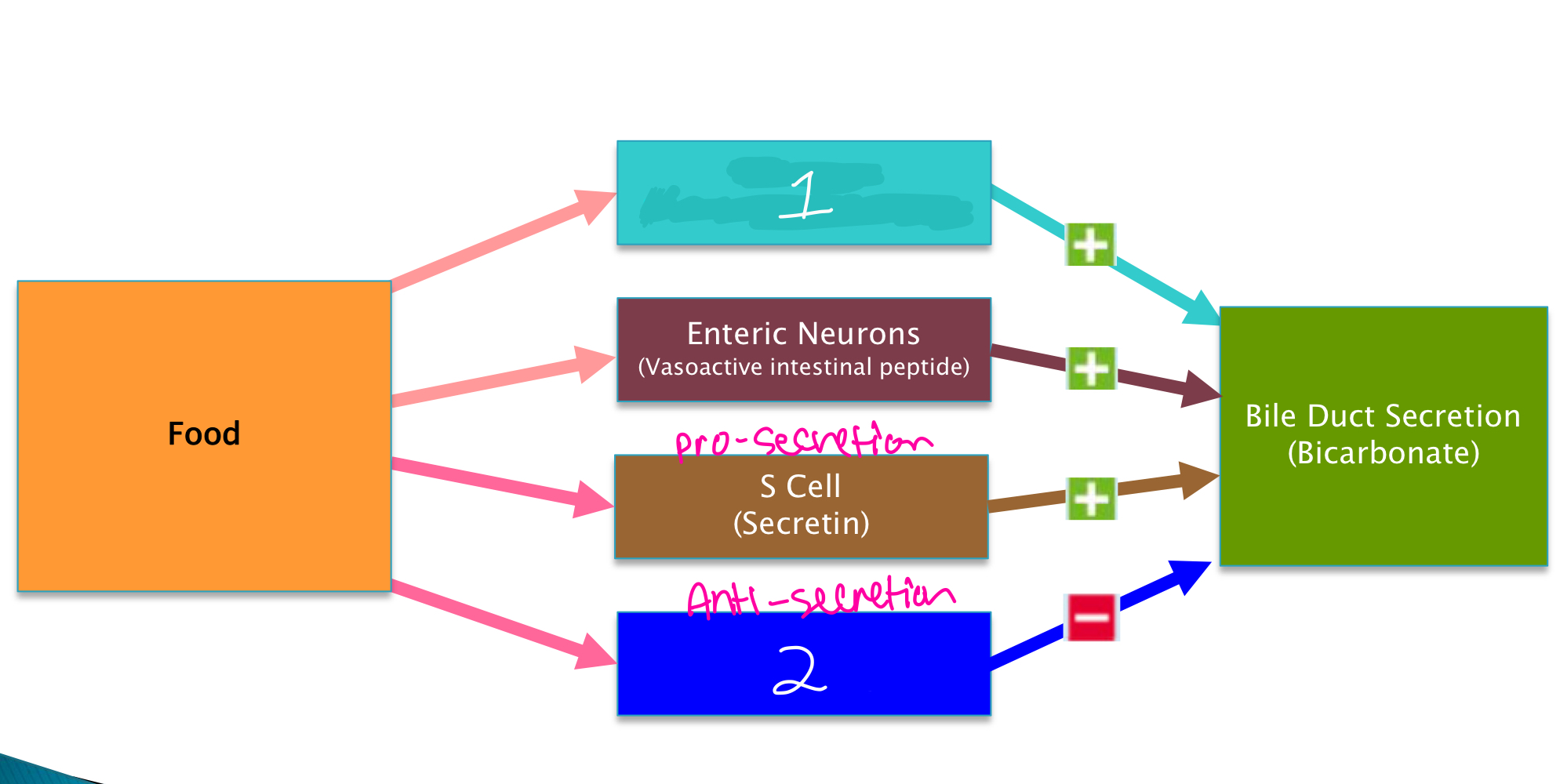
36
New cards
1. Cystic duct to gallbladder
2. Common bile duct to duodenum
What are the 2 parts of the common hepatic duct bifurcation?
37
New cards
CCK
What mediator relaxes the sphincter of Oddi?
38
New cards
False
True/False: CCK decreases bile secretion.
39
New cards
True
True/False: Most bile acids are recycled.
40
New cards
terminal ileum & colon
What parts of the GI system reabsorb bile acids?
41
New cards
fat; blood
Bile is used to absorb ____. Bile helps this be absorbed then drops it off in the __________ and cycles back to help more be absorbed.
42
New cards
gluconeogenesis; glycogenolysis
Between meals in low blood glucose conditions, ____________ occurs to make glucose from amino acids. In addition, _______________ can also occur to breakdown glycogen to glucose.
43
New cards
glycogen synthesis; fat
After meals, during high glucose conditions, ________ can occur to store glucose for later usage (glycogen). After glycogen is made, unused carbohydrates are converted to _____.
44
New cards
False
True/False: Glucose entry into the liver depends on insulin.
45
New cards
glycolysis
Excess glucose can be used in what process?
46
New cards
fat
During lipogenesis, excess glucose is converted to what?
47
New cards
1. Albumin
2. Globulins
3. C-reactive protein (CRP)
4. Glutathione
What are 4 major plasma proteins produced by the liver?
48
New cards
systemic inflammation
C-reactive protein is used to measure what within the body?
49
New cards
Removing free radicals
What is glutathione responsible for?
50
New cards
1. Protein S
2. Protein C
3. anti-thrombin III
What are 3 major coagulation inhibitors in hemostasis/fibrinolysis (anti-clot)?
51
New cards
plasminogen
What is a major player of fibrinolysis?
52
New cards
angiotensinogen
What is a prohormone plasma protein made by the liver?
53
New cards
ApoA-I & ApoA-II
What type of apolipoproteins are present with HDL?
54
New cards
Apo-B100
What type of apolipoproteins are present with LDL?
55
New cards
Metabolism of amino acids
What is the liver’s role in dealing with amino acids?
56
New cards
urea
The liver converts amino acids to _______ for excretion in the urine.
57
New cards
glycogenolysis
What glucose metabolic pathway occurs during fasting?
58
New cards
1. Amino Acids & urea
2. Angiotensinogen
3. Bile
4. C-Reactive protein
5. Coagulation factors
6. Glucose & Glycogen
7. Cholesterol
8. Glutathione
What are the 8 primary components produced from the liver (think ABCG)?
59
New cards
cholesterol
4 ring lipid molecule
60
New cards
triglyceride
Glycerol with 3 fatty acid chains
61
New cards
cholesterol ester
Cholesterol linked to fatty acid with ester bond
62
New cards
HMG CoA reductase
What is the rate limiting step of cholesterol synthesis?
63
New cards
The -statins
Cholesterol synthesis is inhibited by what drugs?
64
New cards
True
True/False: The liver makes cholesterol endogenously.
65
New cards
dietary fat
Fat that hasn’t yet entered the liver
66
New cards
lipoprotein lipase (LPL)
Chylomicrons are cleaved by what?
67
New cards
1. Triglycerides
2. Fatty acids
3. Cholesterol
When chylomicrons are cleaved, what 3 components are left over?
68
New cards
VLDL
Remnants of chylomicrons that have been cleaves enter the liver and are converted to _______.
69
New cards
False--dietary fat
True/False: Chylomicrons are made of endogenous fat.
70
New cards
thoracic duct
Chylomicrons travel into the blood via the _______________.
71
New cards
fatty acids; glycerol
LPL breaks down triglycerides into ____________ and ____________.
72
New cards
VLDL
The liver packages endogenous fat (& chylomicron remnants) as _______.
73
New cards
lipoprotein lipase
What breaksdown VLDL?
74
New cards
apolipoproteins
What is responsible for transporting lipoproteins?
75
New cards
triacyglycerides
Release of ________________ leads to more and more densely packed cholesterol molecules.
76
New cards
triglycerides
Both chylomicrons & VLDL carry ______________ to tissues.
77
New cards
ketone bodies; kidney
Fatty acids metabolize to ___________ in β oxidation. They are then sent to the brain, muscle, & __________.
78
New cards
HDL
Which is healthier: HDL or LDL?
79
New cards
HDL
What lipoprotein is responsible for removing lipids from blood vessels?
80
New cards
cholesterol
What is present in higher quantities within HDL: cholesterol or triacylglycerides?
81
New cards
ApoA-1 & ApoA-2
What apolipoproteins aid in the transport of HDL?
82
New cards
chylomicrons
Dietary fat is transported as _______________.
83
New cards
1. Cholesterol
2. Triglycerides
3. Phospholipids
What are the 3 main components of chylomicrons?
84
New cards
Lipoprotein lipase; apolipoprotein CII
________________ breaks down triglycerides to release fatty acids to tissues. _______________ inhibits this from occuring.
85
New cards
LDL
_______ is the breakdown product of VLDL.
86
New cards
LDL
What lipoprotein deposits cholesterol in cells & vessels?
87
New cards
Apolipoproteins
________________ bind & transport triacylglycerides & cholesterol.
88
New cards
Chylomicrons, VLDL, IDL, LDL
What lipoproteins contain more triacylglycerides than cholesterol?
89
New cards
HDL
What lipoprotein contains more cholesterol than triacylglycerides?
90
New cards
Apopoliportein CIII
What transports triglycerides from the liver to other organs?
91
New cards
LDL
What lipoprotein transports cholesterol & triglycerides from the liver to peripheral organs using apopoliprotein B100?
92
New cards
HDL
What lipoprotein transports fat from peripheral tissue to the liver using ApoA-I and ApoA-II?
93
New cards
cholesterol
What lipid molecule is needed for cell membranes?
94
New cards
cholesterol
What is needed for the synthesis of steroid hormones?
95
New cards
To produce energy
What is the main purpose of breaking down triglycerides?
96
New cards
HDL > 50
What are the normal levels of HDL in the body?
97
New cards
LDL < 100
What is the normal level of LDL in the body?
98
New cards
Triglycerides < 150 (think 50 x 3)
What is the normal level of triglycerides in the body?
99
New cards
LDL < 70
What is the best with disease level of LDLs?
100
New cards
Patients with a history of cardiovascular disease
In what patients should LDL levels be lower than the norm?