BIOL 1510 Midterm Exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/126
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
1
New cards
Macroevolution
the broad pattern of evolution above the species level
2
New cards
Protocell
an abiotic precursor of a living. ell that had a membrane-like structure and that maintained an internal chemistry different from that of its surroundings
3
New cards
Hydrothermal Vents
an area on the deep sea floor where heated water and minerals from Earth’s interior gush into the seawater
4
New cards
Alkaline Vents
a deep sea hydrothermal vent that releases water that is warm rather than hot and that has a high pH
5
New cards
Ribozymes
an RNA molecule that functions as an enzyme, such as an intron that catalyzes its own removal during RNA splicing
6
New cards
Radiometric Dating
a method for determining the absolute age of rocks and fossils, based on the half-life of radioactive isotopes
7
New cards
Half-Life
amount of time it takes for half of a sample of a radioactive isotope to decay
8
New cards
Geologic Record
a standard time scale dividing Earth’s history into time periods, grouped into four eons - Hadean, Archaean, Proterozoic, and Phanerozoicand further subdivided into eras, periods, and epochs
9
New cards
Stromatolites
layered rock that results from the activities of prokaryotes that bind thin films of sediment together
10
New cards
Endosymbiont Theory
the theory that mitochondria and plastids, including chloroplasts, originated as prokaryotic cells engulfed by a host cell. the engulfed cell and its host cell evolved into a single organism
11
New cards
Serial Endosymbiosis
a hypothesis for the origin of eukaryotes consisting of a sequence of endosymbiotic events in which mitochondria, chloroplasts, and perhaps other cellular structures were derived from a small prokaryotes that had been engulfed by larger cells
12
New cards
Cambrian Explosion
a relatively brief time in geologic history when many present-day phyla of animals first appeared in the fossil record. 535-525 million years ago, the emergence of the first large, hard-bodied animals
13
New cards
Plate Tectonics
the theory that the continents are part of great plates of earth’s crust that float on the hot, underlying portion of the mantle. movements in the mantle cause the continents to move slowly over time
14
New cards
Pangaea
the supercontinent that formed near the end of the Paleozoic era, when plate movements brought all the landmasses of Earth together
15
New cards
Mass Extinction
the elimination of a large number of species throughout Earth, the result of global environment changes
16
New cards
Adaptive Radiations
period of evolutionary change in which groups of organisms form many new species whose adaptions allow them to fill different ecological roles in their communities
17
New cards
Heterochrony
evolutionary change in the time or rate of an organism’s development
18
New cards
Paedomorphosis
the retention in an adult organism of the juvenile features of its evolutionary ancestors
19
New cards
Homeotic Genes
any of the master regulatory genes that control placement and spatial organization of body parts in animals, plants, and fungi by controlling the development fate of groups of cells
20
New cards
Phylogeny
the evolution of history of a species or group of related species
21
New cards
Systematics
a scientific discipline focused on classifying organisms and determining their evolutionary relationships
22
New cards
Taxonomy
a scientific discipline concerned with naming and classifying the diverse forms of life
23
New cards
Binomial
the two-part latinized format for naming a species, consisting of the genus and specific epithet
24
New cards
Linean Classification
Domain → Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species
25
New cards
Taxon
a named taxonomic unit at any given level of classification
26
New cards
Phylogenetic tree
a branching diagram that represents a hypothesis about the evolutionary history of a group of organisms
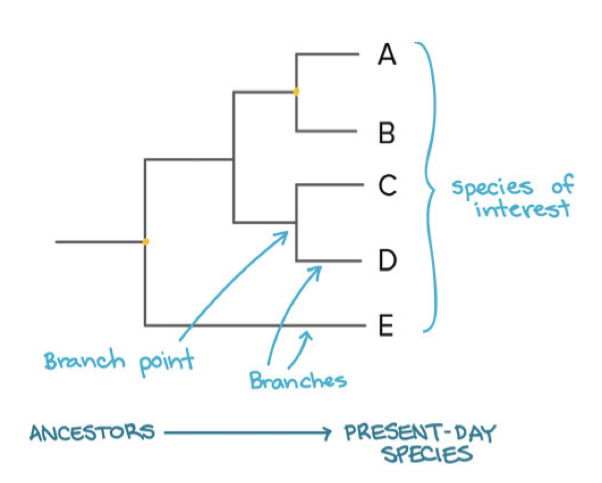
27
New cards
Phylocode
proposed system of classification of organisms based on evolutionary relationships: only groups that include a common ancestor and all of its descendants are named
28
New cards
Branch Points
the representation on a phylogenetic tree of the divergence of two or more taxa from a common ancestor
29
New cards
Rooted
describing a phylogenetic tree that contains a branch point representing the most recent common ancestor of all taxa in the tree
30
New cards
Basal taxon
in a specified group of organisms, a taxon whose evolutionary lineage diverged early in the history of the group
31
New cards
Polytomy
in a phylogenetic tree, a branch point from which more than two descendant taxa emerge. a polytomy indicates that the evolutionary relationships between the descendant taxa are not yet clear
32
New cards
Analogy
similarity between two species that is due to convergent evolution rather than to descent from a common ancestor with the same trait
33
New cards
Homoplasies
a similar structure or molecular sequence that has evolved independently in two species
34
New cards
Molecular Systematics
a scientific discipline that uses nucleic acids or other molecules to infer evolutionary relationships between different species
35
New cards
Cladistics
an approach to systematics in which organisms are placed into groups called clades based primarily on common descent
36
New cards
Clades
a group of species that includes an ancestral species and all of its descendants
37
New cards
Monophyletic
pertaining to a group of taxa that consists of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. a monophyletic taxon is equivalent to a clade
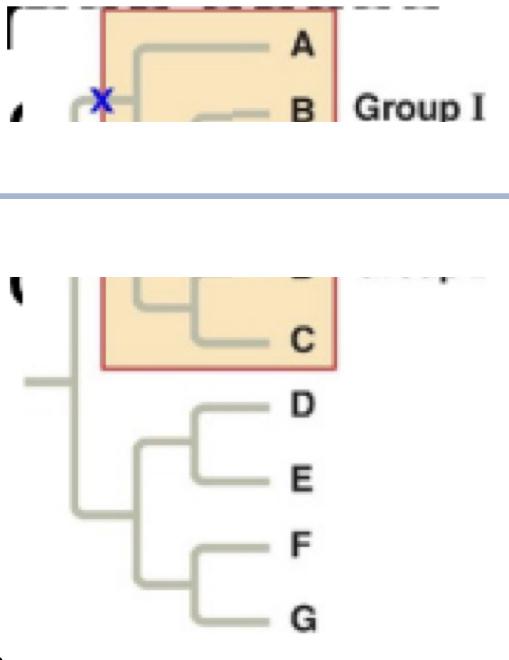
38
New cards
Paraphyletic
pertaining to a group of taza that consists of a common ancestor and some, but not all, of its descendants
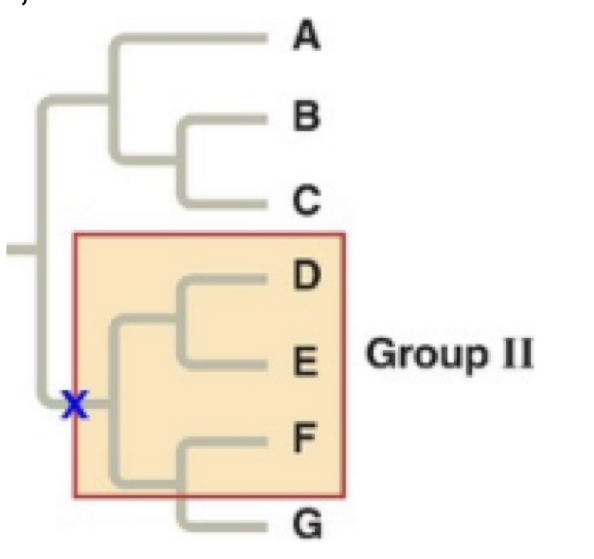
39
New cards
Polyphyletic
pertaining to a group of taxa derived from two or more different ancestors
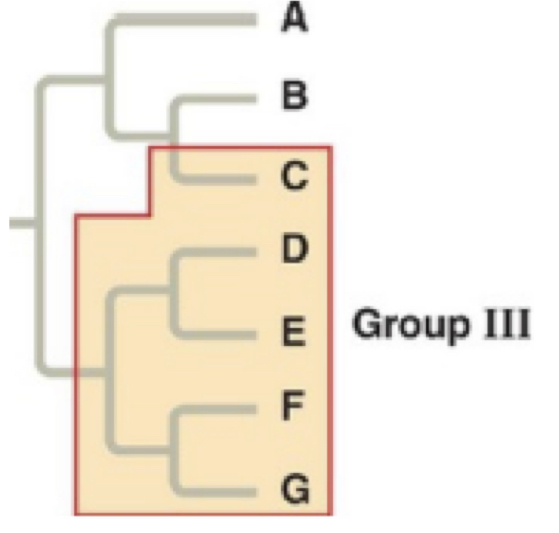
40
New cards
Shared Ancestral Character
a character, shared by members of a particular clade, that originated in an ancestor that is not a member of taht clade
41
New cards
Shared Derived Character
an evolutionary novelty that is unique to a particular clade
42
New cards
Outgroup
a species or group of species from an evolutionary lineage that is know to have diverged before the lineage that contains the group of species being studied. an outgroup is selected so that its members are closely to the group of species being studied, but not as closely related as any study-group members are to each other
43
New cards
Ingroup
a species or group of species whose evolutionary relationships we seek to determine
44
New cards
Maximum Parsimony
a principle that states that when considering multiple explanations for an observation, one should first investigate the simplest explanation that is consistent with the facts
45
New cards
Maximum Likelihood
as applied to molecular systematics, a principle that states that when considering multiple phylogenetic hypotheses, one should take into account the hypothesis that reflects the most likely sequence of evolutionary events, given certain rules about how DNA changes ove time
46
New cards
Orthologous Genes
homologous genes that are found in different species because of speciation
47
New cards
Paralogous Genes
homologous genes that are found in the same genome as a result of gene duplication
48
New cards
Molecular Clock
a method for estimating the time required for a given amount of evolutionary change, based on the observation that some regions of genomes evolve at a constant rate
49
New cards
Neutral Theory
the hypothesis that much evolutionary change in genes and proteins has no effect on fitness and therefore is not influenced by natural selection
50
New cards
Horizontal Gene Transfer
the transfer of genes from one genome to another through mechanisms such as transposable elements, plasmid exchange, viral activity, and perhaps fusion of different organisms
51
New cards
Peptidoglycan
a network of sugar polymers cross-linked by polypeptides
52
New cards
Gram Stain
used to classify bacteria by cell wall composition
53
New cards
Gram-Positive Bacteria
simpler walls with a large amount of peptidoglycan (stains purple)
54
New cards
Gram-Negative Bacteria
have less peptidoglycan and an outer membrane that can be toxic (stains red)
55
New cards
Capsule
the cell wall of many prokaryotes is surrounded by a sticky layer of polysaccharide or proteins
56
New cards
Endospores
a way of withstanding harsh conditions, certain bacteria develop resistant cell called this
57
New cards
Fimbriae
hairlike appendages that stick to substrates
58
New cards
Pili (sex-pili)
appendages that pull two cells together prior to DNA transfer from one cell to another
59
New cards
Taxis
the ability to move toward or away from a stimulus
60
New cards
Nucleoid Region
chromosome is located here
61
New cards
Plasmids
some species of bacteria also have smaller rings of independently replicating DNA called this
62
New cards
Three factors that contribute to genetic diversity
Rapid Reproduction, Mutation, Genetic Recombination
63
New cards
Genetic Recombination
the combining of DNA from two sources, contributes to diversity
64
New cards
Transformation
a prokaryotic cell can take up and incorporate foreign DNA from the surrounding environment
65
New cards
Transduction
the movement of genes between bacteria by bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria)
66
New cards
Conjugation
the process where genetic material is transferred between prokaryotic cells
67
New cards
F Factor
piece of DNA that is required for the production of pili
68
New cards
F Plasmid
cells containing this functions as DNA donors during conjugation
69
New cards
R Plasmid
carry genes for antibiotic resistance
70
New cards
Phototrophs
obtain energy from light
71
New cards
Chemotrophs
obtain energy from chemicals
72
New cards
Autotrophs
require CO2 as a carbon source
73
New cards
Heterotrophs
require an organic nutrient to make organic compounds
74
New cards
Obligate Aerobes
require O2 for cellular respiration
75
New cards
Obligate Anaerobes
are poisoned by O2 and use fermentation or anaerobic respiration
76
New cards
Facultative Anaerobes
can survive with or without O2
77
New cards
Nitrogen Fixation
some prokaryotes convert atmospheric nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3)
78
New cards
Heterocysts
nitrogen-fixing cells
79
New cards
Extreme halophiles
live in highly saline environments
80
New cards
Extreme Thermophiles
thrive in very hot environments
81
New cards
methanogens
live in swamps and marshes and produce methane as a waste product
82
New cards
Decomposers
breaking down dead organisms and waste products
83
New cards
Symbiosis
an ecological relationship in which two species live in close contact. a large host and a smaller symbiont
84
New cards
Mutualism
both symbiotic organisms benefit
85
New cards
Commensalism
one organism benefits while neither harming nor helping the other in any significant way
86
New cards
Parasitism
an organism called a parasite harms but does not kill its host
87
New cards
Pathogens
parasites that cause disease
88
New cards
Exotozins
secreted and cause disease even if the prokaryotes that produce them are not present
89
New cards
Endotoxins
released only when bacteria die and their cell walls break down
90
New cards
Algae (alga)
a photosynthetic, plantlike protist
91
New cards
Alternation of Generations
a life cycle in which there is both a multicellular diploid form, the sporophyte, and a multicellular haploid form, the gametophyte; characteristic of plants
92
New cards
Alveolata
a protistan clade that includes dinoflagellates, apicomplexans, and the ciliates. have small membrane-bounded cavities called alveoli under their cell surfaces. function is unknown
93
New cards
Amoeba
a type of protist characterized by great flexibility and the presence of pseudopodia
94
New cards
Apicomplexan
one of a group of parasitic protozoans, some of which cause human diseases
95
New cards
Blades
a leaflike structure of a seaweed that provides most of the surface area for photosynthesis
96
New cards
Brown Algea
one of a group of marine, multicellular, autotrophic protists, the most common type of seaweed. include the kelps
97
New cards
Cellular Slime Mold
a type of protist that has unicellular amoeboid cells and multicellular reproductive bodies in its life cycle
98
New cards
Ciliate
a type of protozoan that moves by means of cilia
99
New cards
Conjugation in bacteria
the direct transfer of DNA between two cells that are temporarily joined
100
New cards
Diatom
a unicellular photosynthetic alga with a unique, glassy cell wall containing silica