Chapter 5- Homologous Recombination
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Two ways meiosis contribute to genetic diversity through
1) Independent Assortment
2) Crossing Over
Each pair of homologous chromosomes segregate freely from each other.
-Unlinked genes
Independent Assortment
Two homologous chromosomes exchange portions of DNA
-Linked genes
Crossing Over
The production of new allelic combinations through genetic exchange between homologous chromosomes is called
Recombination
Chromosomes that carry a mix of alleles derived from different homologous are called
Recombinants
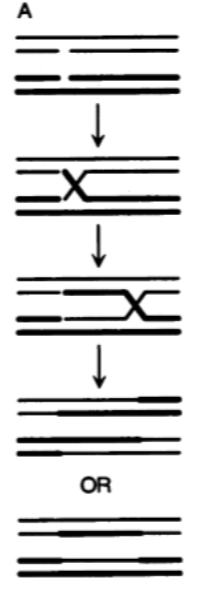
Type of recombination that happens on 2 homologous non-sister chromatids
Holiday Model
What protein initiates recombination
Spo11
How does Spo11 initate recombination
By breaking phosphodiester bonds of both strands on one chromatid
5’ ends of each broken strand are degraded by what enzyme to create a 3’ single strand
Exonuclease
What protein helps the 3’ single strand trail invades non-sister chromatid to form heteroduplex
DMC1 (strand invasion)
Once the second holiday junction forms what 3 things happen
1) Second heteroduplex forms
2) DNA synthesis takes over
3) DNA ligase reseals the DNA backbone
How is the heteroduplex lengthen
Branch migration
The holiday junction is resolved by what type of cuts
Horizontal & Vertical Cuts
What enzyme make these horizontal & vertical cuts
Resolvase
Enzyme that disentangles the invading strand from the non sister chromatid preventing Holiday Junction from forming
Anti crossover helicase
Holiday junctions are nearly random
True
Site specific recombination promotes breakage and rejoining of DNA molecules shorter than
200 bp
Enzyme that catalyzes all breakage and joining steps in site-specific recombination
Recombinase
CRISPR-CAS-9
Uses RNA for case site-specific recombination at genetic locations.
Naturally occurring
FLP/FRI & Cre recombinase / lox p
Scientist manipulated recombination
Artificially occurring
Breakage and rejoining of DNA strands to produce separate chromatids at the end of recombination is called
Resolution
During recombination, the DNA strand displaced by an invading strand forms a
D-loop
As a result of strand invasion, a DNA segment is formed from one strand from each non-sister chromatid. This type of DNA segment is called a
Heteroduplex
During resolution of a double Holiday Junction intermediate __ breaks DNA strands at each junction and __ joins them
Resolvase, DNA Ligase
Movement of a Holiday junctions away from each other is called
Branch Migration
Which of the following can lead to gene conversion during recombination
Mismatch repair of a heteroduplex