DNA Repair Mechanisms
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
One Step Repair
Direct reversal of DNA damage
EX: Chemotherapy
Methylated resides due to alkylating agents
EX: Repair Enzyme
alkyl transferase
MGMT
methyl guanine methyl transferase
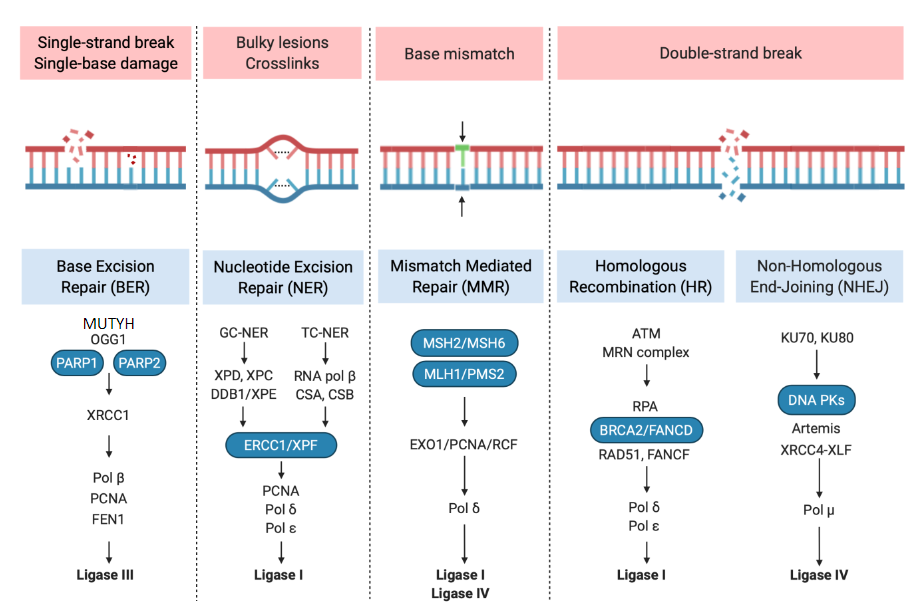
Base Excision Repair
single strand break or single base damage
Caused by
radiation, chemo, oxygen radicals
Target
chemically altered bases (single base damage)
Site
apurinic/apyrimidinic site also known as abasic site
scan base pairs for lesions and cleave the base
Glycosylases OGG1 and MUTYH
Endonuclease cleaves the DNA and polymerase
and polymerase replaces the nucleotide and ligase fills gap
what does the PARP interaction with BER proteins do?
Relaxes chromatin for increase DNA accessibility.
Mutations in MUTYH are cause of
MAP syndrome —> germline colon cancer
Nucleotide Excision Repair (NER)
Specific for helix-distorting lesions or Pyrimidine dimers (UVB) and bulky adducts (PAHs).
Lesion is removed by
endonucleases
DNA Polymerase
adds nucleotides
Ligase
seals DNA
Two Sub Pathway
GC-NER
Global genome coupled
Recognizes helix distortion
TC-NER
Transcription coupled
Recognized transcription problems
Xeroderma pigmentosum (XP)
Inherited disorder
Mutation in XP proteins
Hypersensitive to sun – 1000x risk for skin cancer.
Can occur in all races
Mismatch Repair (MMR)
Corrects errors that have escaped editing by polymerases/exonuclease
Can also repair
base insertion/deletion that would otherwise cause slippage of strand
Which proteins recognize this error
MSH2/MSH6, MLH1 and PMS2
MMR is removed by
exonuclease, repaired by polymerase, and ligase seals back
Mutations in MMR MSH proteins linked to
Lynch Syndrome
Double Stranded Break Repair
Homologous Recombination (HR)
uses an undamaged DNA template to repair the break, leading to the reconstitution of the original sequence
Uses __ for templates
sister chromatids
How accurate
more accurate
Restricted to which phases
S and G2
Proteins
ATM, BRCA, RAD
Non-Homologous End-Joining (NHEJ)
modifies the broken DNA ends, and ligates them together with no regard for homology, generating deletions or insertions
Does it use the sister template?
no
How accurate
less
When is it active in the cell cycle
throughout the entire cycle
Proteins
DNA-PK, Ku, Artemis proteins
Ataxia telangiectasia
Inherited syndrome
• Mutation in ATM kinase.
• Patients sensitive to X-rays increased
risk of lymphoma
BRCA1/2
Mutations linked to Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Syndrome.
• FANCD proteins include BRCA1/2 and PALB2
Overall Schematic