BIOL 208 Unit 2 - Natural History: Climate and Soils
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Albedo
The fraction of solar energy reflected by an object.
Eutrophication ________ albedo.
Decreases
The sun’s position during the equinoxes is:
Over the equator
The sun’s position during the June solstic is:
Over the Tropic of Cancer (23.5° North)
The sun’s position during the December solstic is:
Over the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5° South)
Saturation Point
The maximum amount of water vapour that a mass of air can hold at a particular temperature.
Adiabatic Cooling and Heating
As air rises, it expands and cools. As air sinks, it compresses and warms due to molecule collision.
Intertropical Convergence Zone
The area of Earth over the equator where the Hadley Cells converge and cause large amounts of precipitation.
Hadley Cells
The two air circulation cells between the equator and 30° North and 30° South.
Rain shadows occur on the _____ side of mountains.
leeward
Leeward
Situated on or toward the side sheltered from the wind; downwind.
Windward
Facing the wind or situated on the side facing the wind.
Soil
The layer of chemically and biologically altered material that overlies bedrock or other unaltered material on Earth’s surface.
Soil Horizon
A distinct layer of soil.
Soil Profile
A distinct cross-section of soil
Parent Material
The layer of bedrock that underlies soil and determines the composition of the soil above.
Leaching
The process in which groundwater dissolves soil substances and moves them to lower soil layers.
Alluviation
The process of depositing sediments by means of moving water.
Weathering
The physiscal, chemical, and biological processes that break down rocks and minerals.
Permafrost
A phenomenon in cold climates where water stored in soil is frozen year-round.
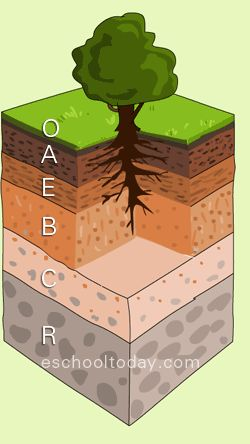
O Horizon
The topmost soil layer constising of dead organic litter.
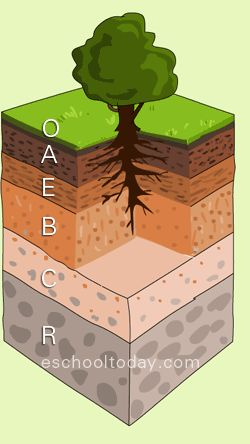
A Horizon
The soil layer containing humus, partially decomposed organics and mineral sediment.
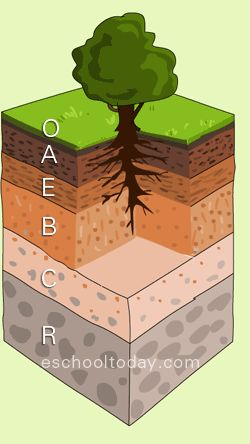
E Horizon
The soil layer that has been leeched of its minerals.
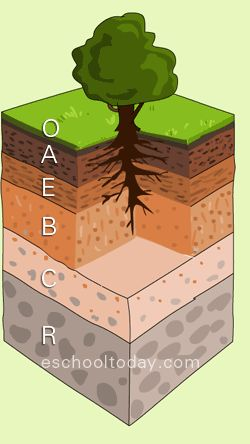
B Horizon
The soil layer that has a similar compostion to the parent material with leeched minerals from the soil layer above.
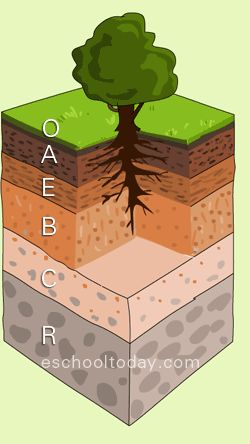
C Horizon
The soil layer containing large rocks and broken down parent material.
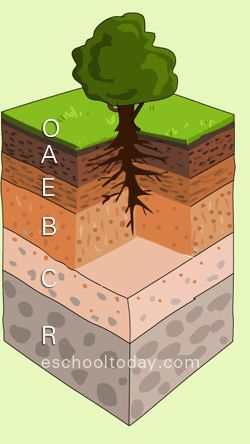
R Horizon
The soil layer comprised of the parent material, which is usually bedrock.