2.1.2 Structure of prokaryotic cells and of viruses
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
What are the distinguishing features of prokaryotic cells?
cytoplasm lacking membrane-bound organelles so genetic material not enclosed in a nucleus.
Describe the general structure of prokaryotic cells. (always present)
Cell wall containing murein , a glycoprotein
Cell-surface membrane
cytoplasm
small ribosomes
circular DNA - free in cytoplasm, not associated with proteins
Describe the general structure of prokaryotic cells. (sometimes present)
Capsule, plasmids, flagella
Are eukaryotic cells larger or smaller than prokaryotic cells overall?
Larger
Does a prokaryotic cell have a nucleus?
No - DNA is free in cytoplasm
Features of DNA in eukaryotic cells
DNA is long and linear - associated with histone proteins
Features of DNA in prokaryotic cells
DNA is short and circular - not associated with proteins
Why are viruses described as acelluar non-living?
Acellular - not made of cells, no cell membrane/ cytoplasm/ organelles
Non-living - have no metabolism, cant independently move/ respire/ replicate/ excrete
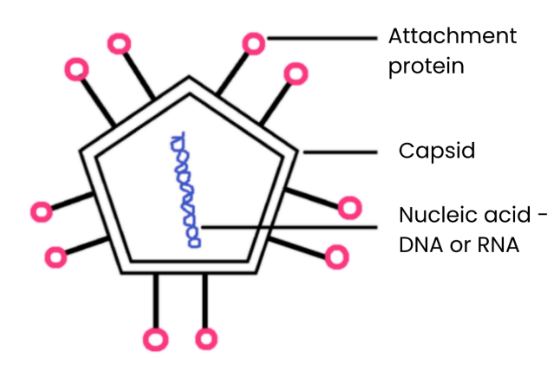
Describe the general structure of a virus particle
Nucleic acids surrounded by a capsid (protein coat)
Attachment proteins allow attachment to specific host cells
Some are surrounded by a lipid envelope e.g. HIV
No cytoplasm/ other organelles