Unit 9: Concepts of Electric Circuits and Current
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Electric Current
Charge per unit time passing through a surface.
Conventional Current
Hypothetical flow of positive charges in circuits.
Direct Current (DC)
Current flowing in one direction only.
Alternating Current (AC)
Current that reverses direction periodically.
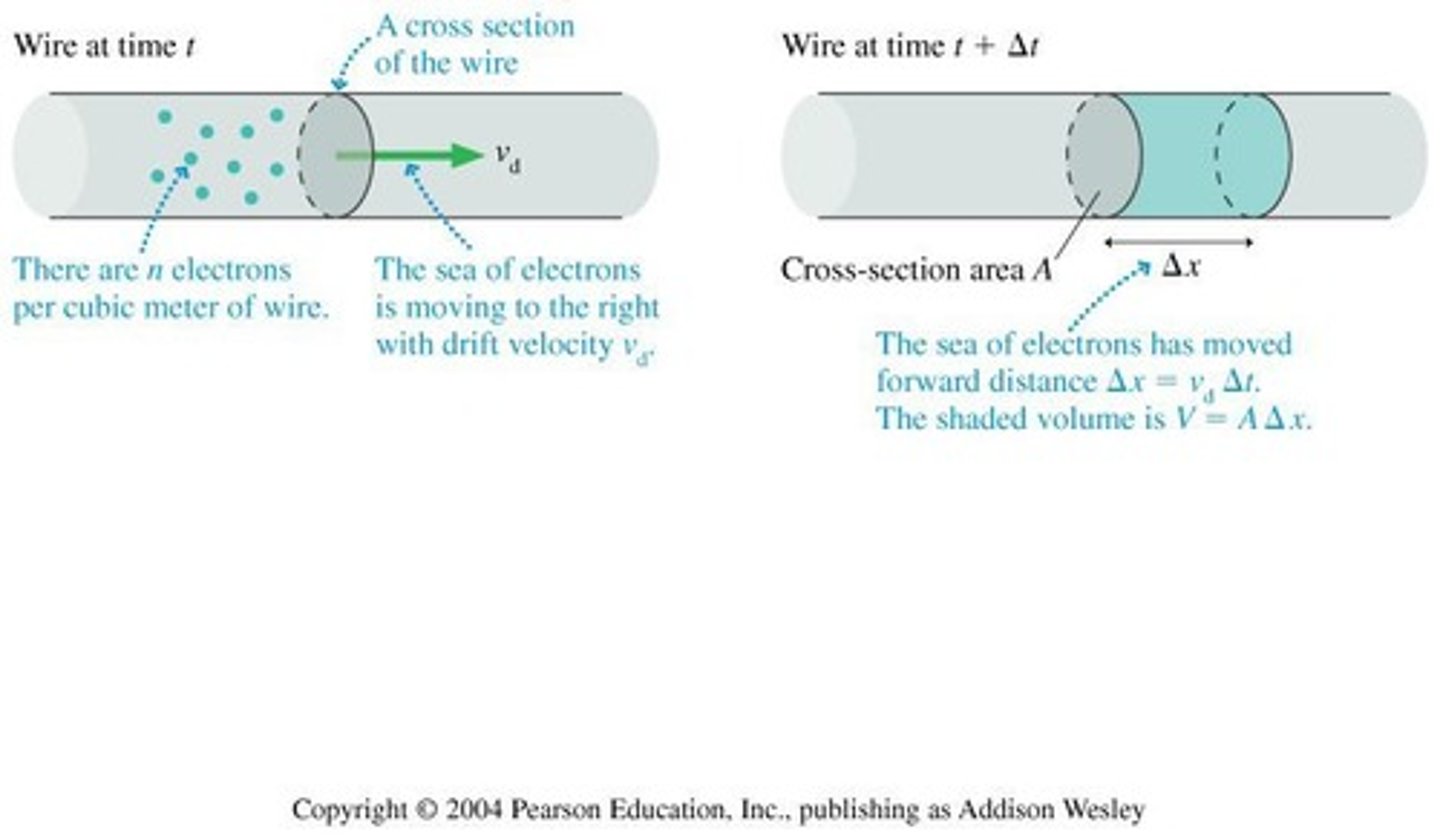
Drift Velocity (vd)
Average velocity of charge carriers in a conductor.
Current Density (J)
Current per unit area in a conductor.
Electromotive Force (emf)
Maximum potential difference across battery terminals.
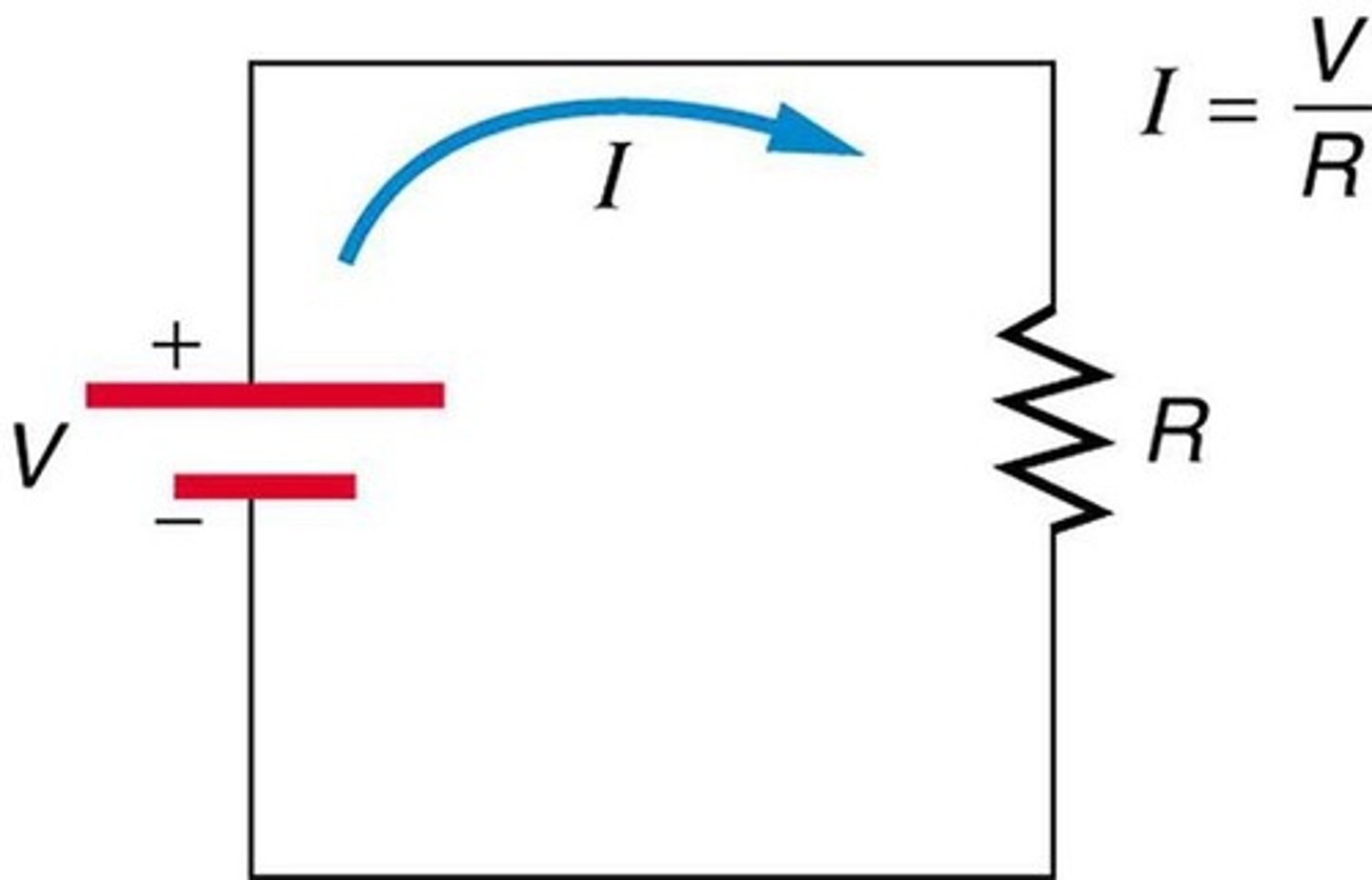
Ohm's Law
Voltage equals current times resistance (V=IR).
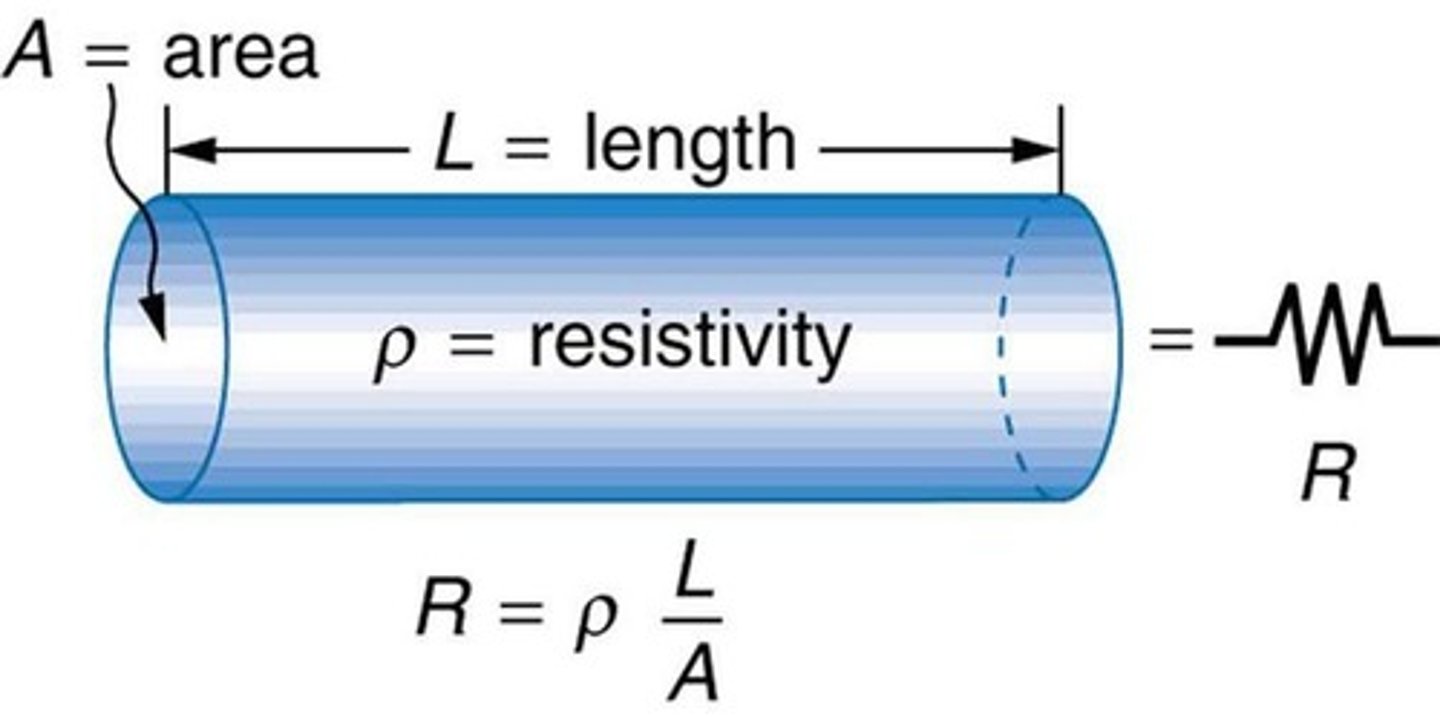
Resistance (R)
Ratio of voltage across material to current through it.
Resistivity (ρ)
Material property affecting its resistance.
Conductivity (σ)
Inversely related to resistivity; measure of material's ability to conduct.
Power (P)
Rate of energy dissipation in a circuit.
SI Unit of Current
Ampere (A), equivalent to C/s.
SI Unit of Voltage
Volt (V), energy per unit charge.
SI Unit of Resistance
Ohm (Ω), volt per ampere.
SI Unit of Power
Watt (W), joules per second.
Charge (q)
Amount of electricity carried by a particle.
Energy (E)
Capacity to do work, measured in joules.
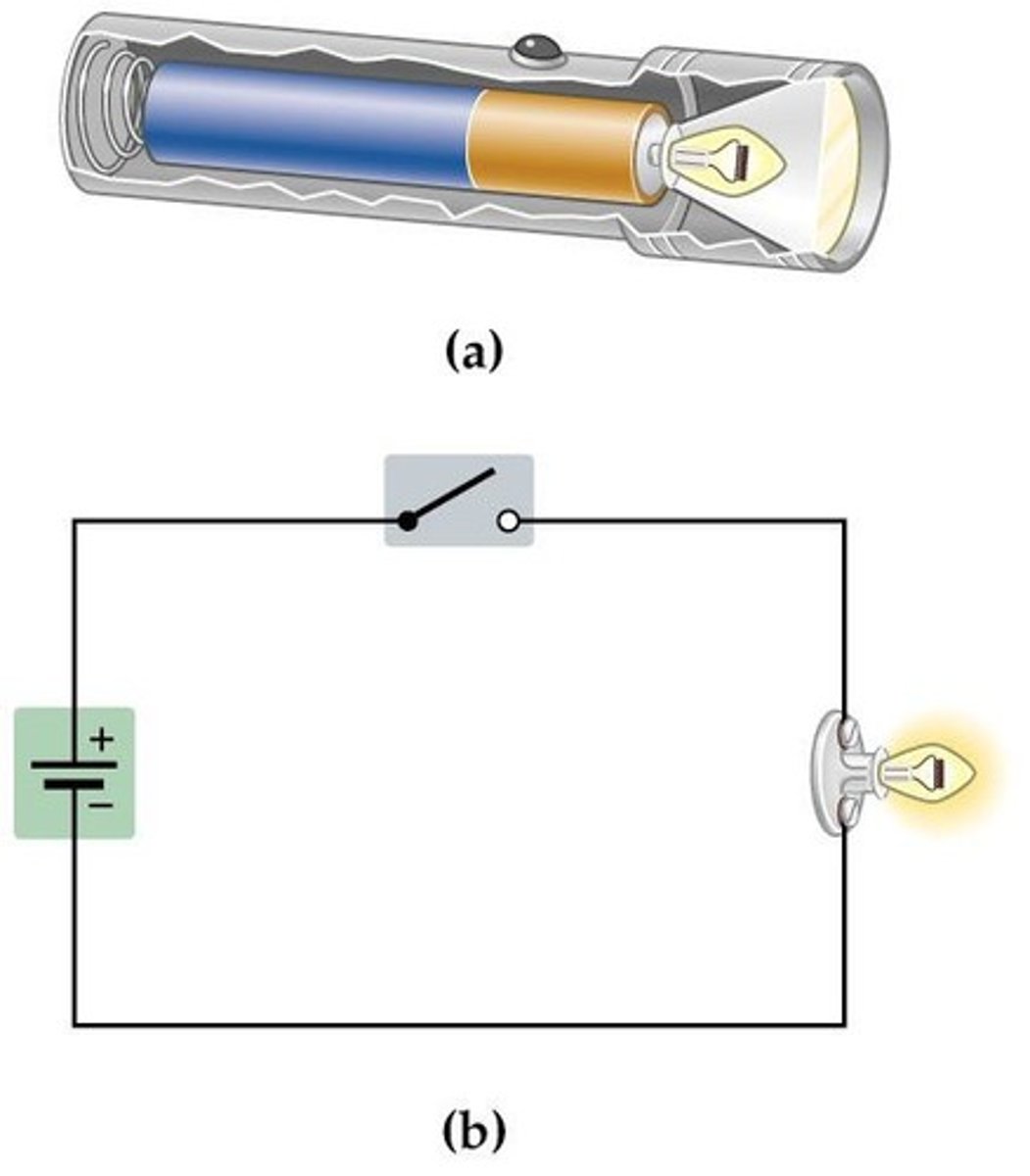
Electric Circuit Components
Includes batteries, wires, resistors, and switches.
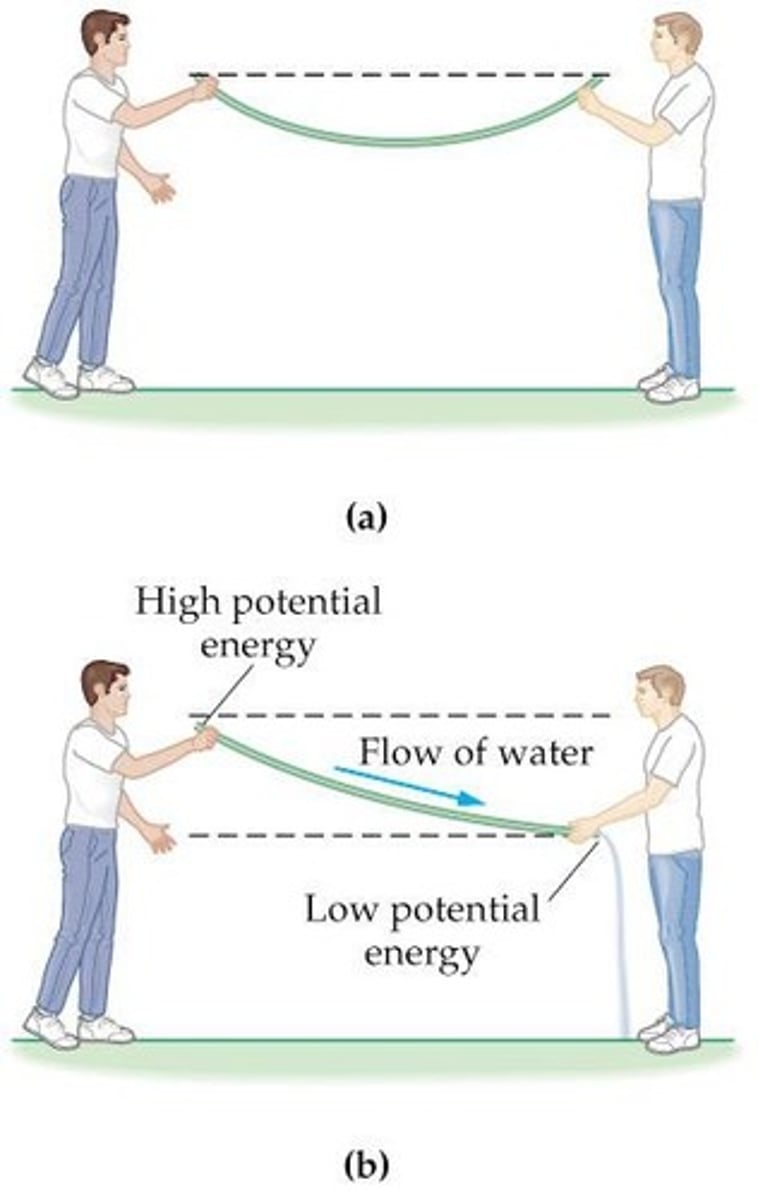
Water Circuit Analogy
Compares electric current to water flow.
Temperature Coefficient of Resistivity
Change in resistivity with temperature variation.
Superconductors
Materials with zero resistance at low temperatures.
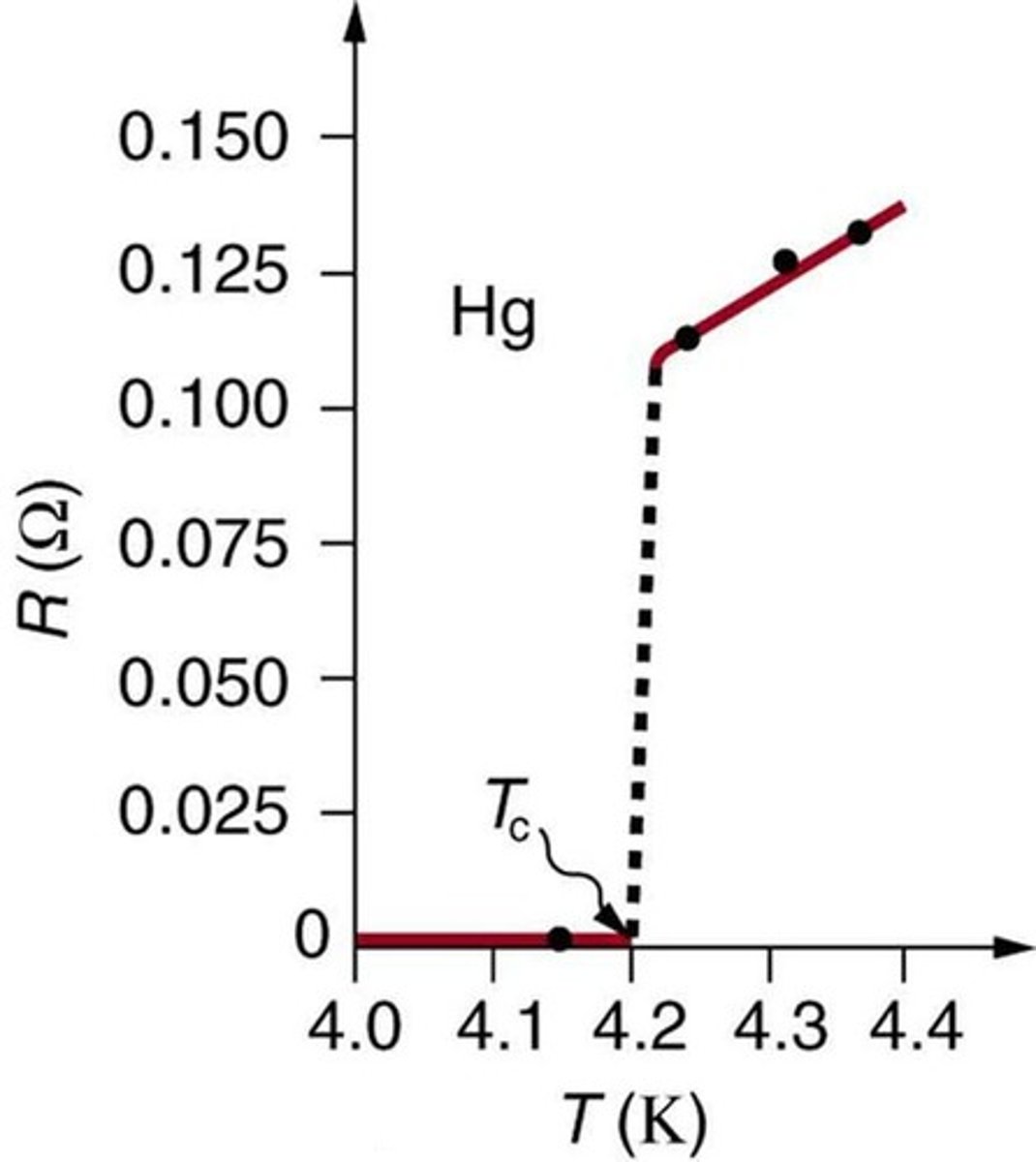
Semiconductors
Materials that conduct under specific conditions.

Current in a Circuit
Flow of electric charge through components.
Voltage (V)
Electric potential difference between two points.
Total Current (I)
Sum of currents through all paths in a circuit.
Energy Stored in Batteries
Expressed in amp-hours (Ah).
Electric Power Formula
P = IV, where I is current and V is voltage.
Current Density Formula
J = I/A, where A is cross-sectional area.
Resistivity Formula
ρ = E/J, where E is electric field and J is current density.
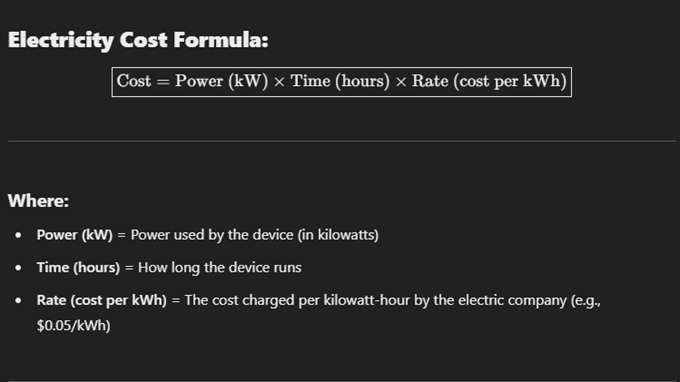
Energy Consumption Measurement
Measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
Example of Energy Cost
1 kWh costs about $0.1.
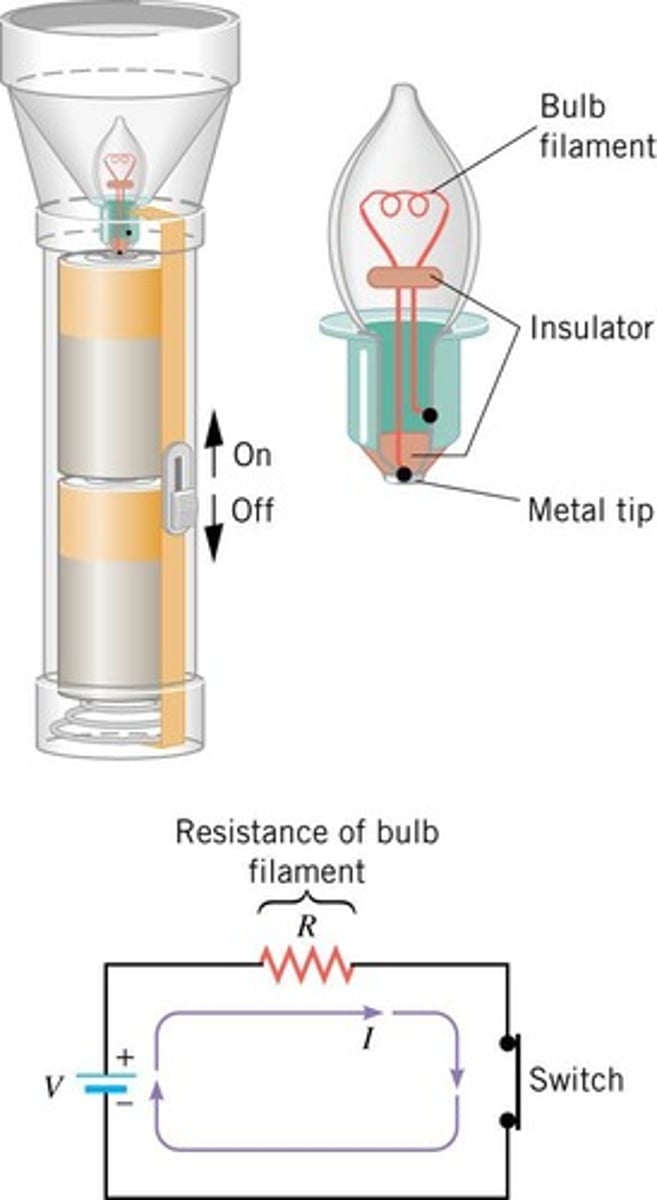
Flashlight Resistance Example
Resistance calculated using voltage and current.
Cylindrical Wire Current Density
J(r) = (2.0×10^5 A/m³) r.
Power Dissipation in Resistors
Power is proportional to current squared.

Electric Company Billing
Charges based on energy consumed in kWh.
Electric Circuit Analogy
Compares electric flow to water flow.
Battery Current Example
0.17 mA from a 3.0 V battery.
Temperature Effect on Resistance
Resistance changes with temperature variations.
Hollow Wire Current Loss
Determines current loss in hollow cylindrical wire.
Extension Cord Resistance
Resistance varies with wire gauge and length.
Energy Delivered by Battery
Calculated from current and operating time.
Power in Flashlight Example
Calculated from current and voltage.
Electric Current Measurement
Measured in amperes (A).
Voltage Measurement
Measured in volts (V).
Resistance Measurement
Measured in ohms (Ω).
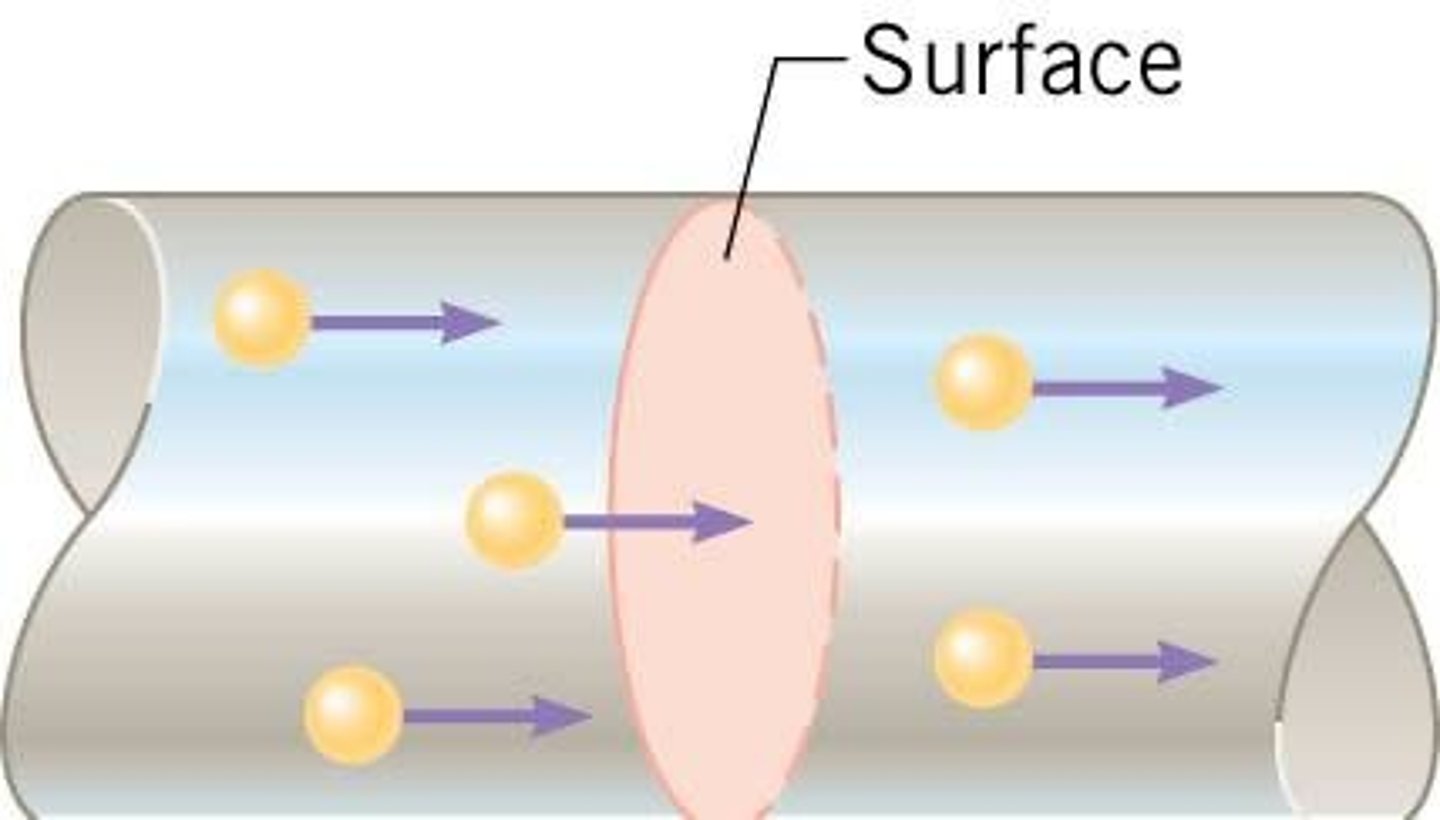
What is necessary for electric current to flow through a surface?
Electric current requires a net flow of charge through a surface.
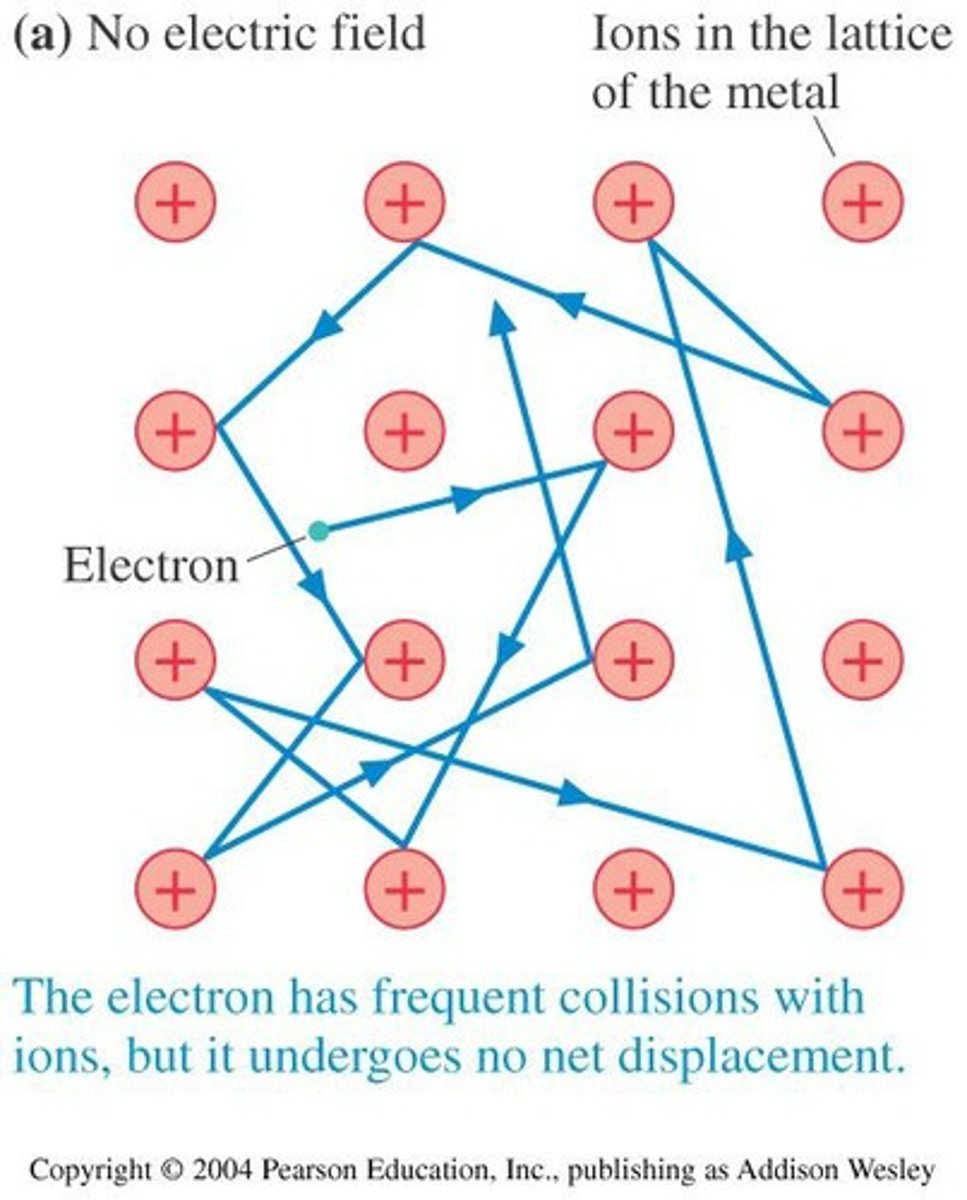
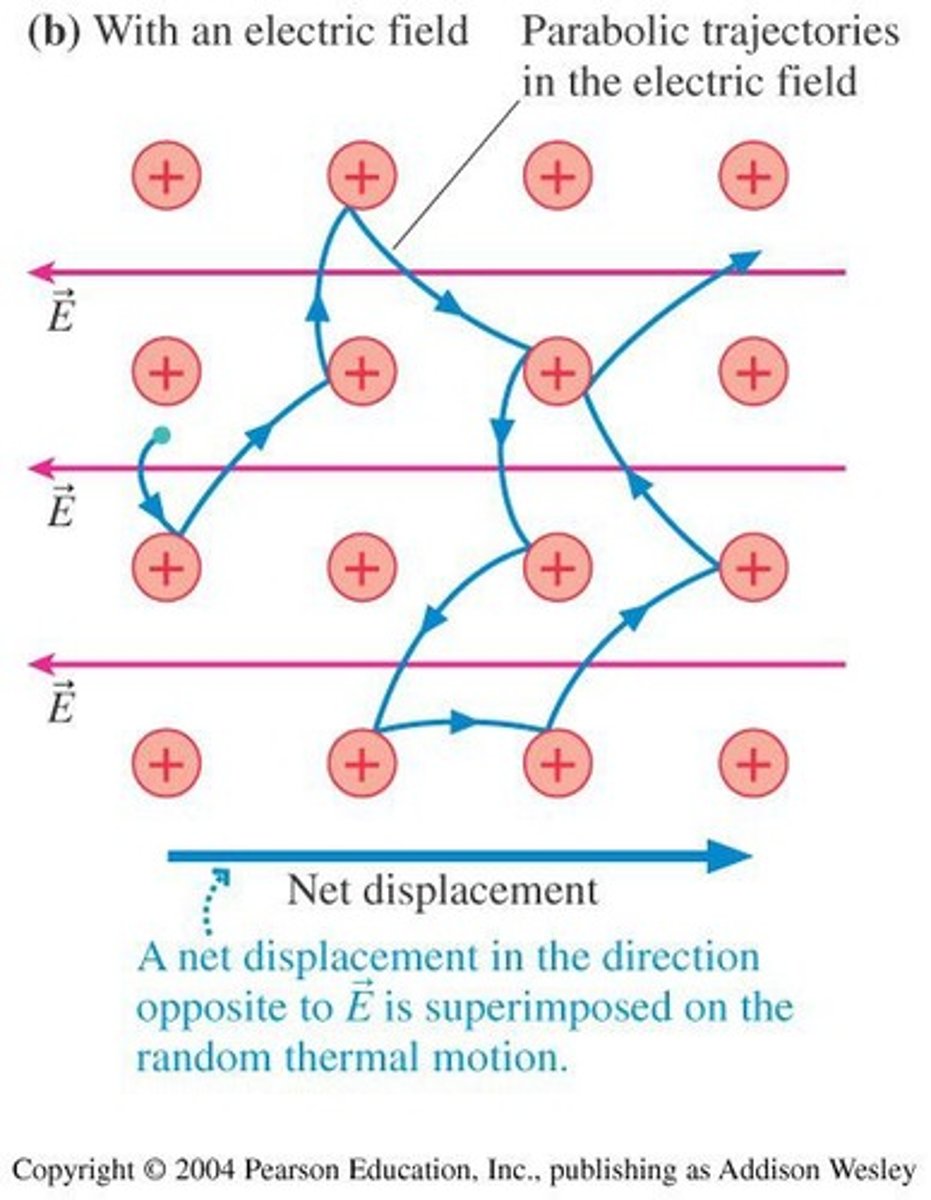
Do random motions of conduction electrons create electric current?
No, random motion of conduction electrons in a wire does not create a current.
How does a battery influence electron movement in a wire?
A battery provides an electric field that biases electron movement, creating a net charge flow (current).
What happens to free electrons in an isolated copper wire without an external influence?
They move randomly at high speeds (~10⁶ m/s), resulting in no net charge transport and thus no current.
How does a battery establish current in a wire?
A battery biases electron flow in one direction, establishing a current.
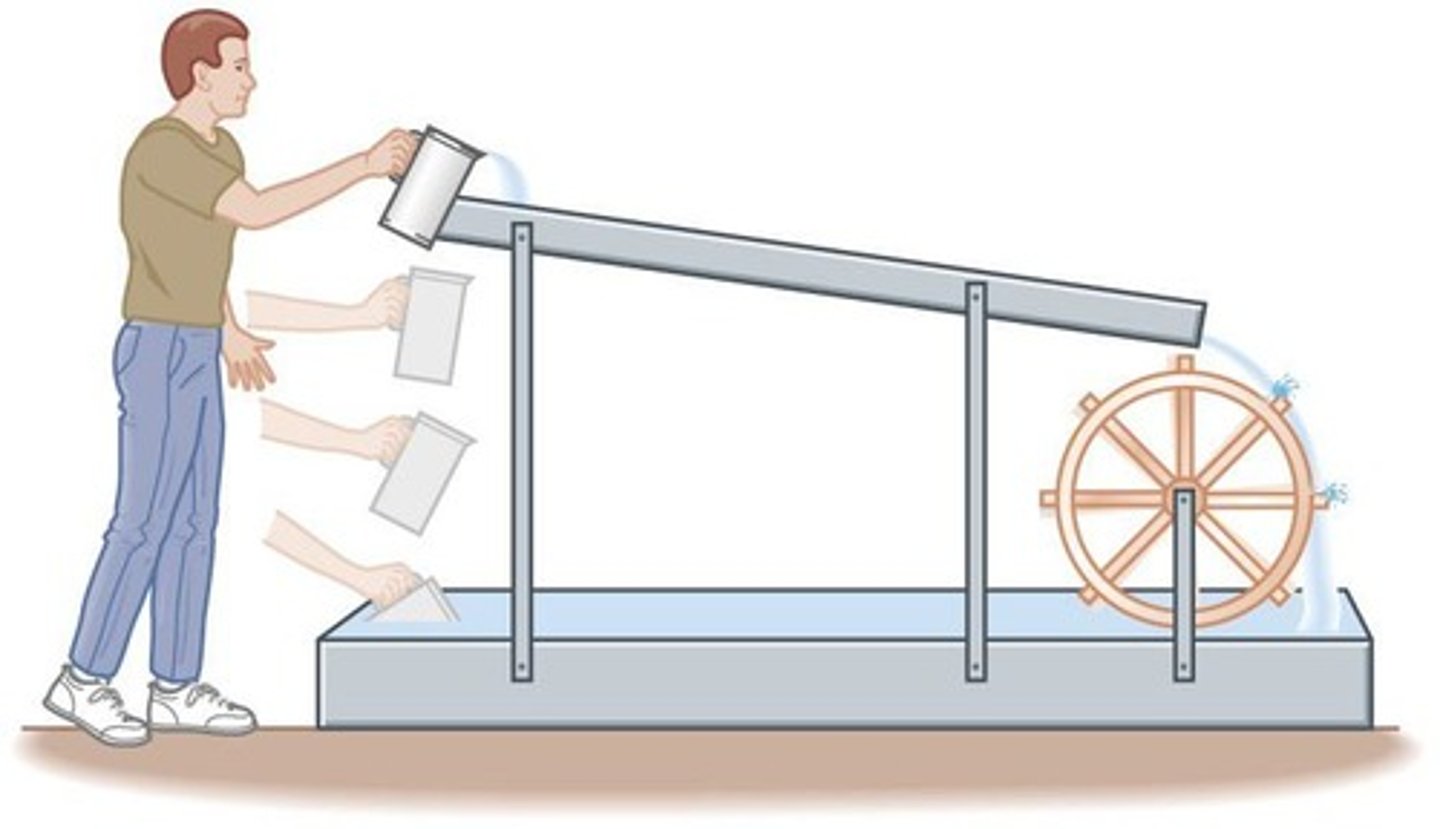
How is electric current similar to water flow?
In a water flow example, molecules flow similarly, but balanced positive and negative charges result in no net charge transport, meaning no electric current.
What occurs inside an isolated conducting loop without a battery?
It remains at the same potential, preventing any electric field inside it—hence, no current.
What effect does a battery have on a conducting loop?
A battery introduces an electric field, exerting force on conduction electrons, causing a steady-state current.
formula current charge

The formula for electric current is given by I = Q/t, where I is the current, Q is the charge in coulombs, and t is the time in seconds.
kirchoff current law

The total current entering a junction equals the total current leaving the junction, ensuring charge conservation.
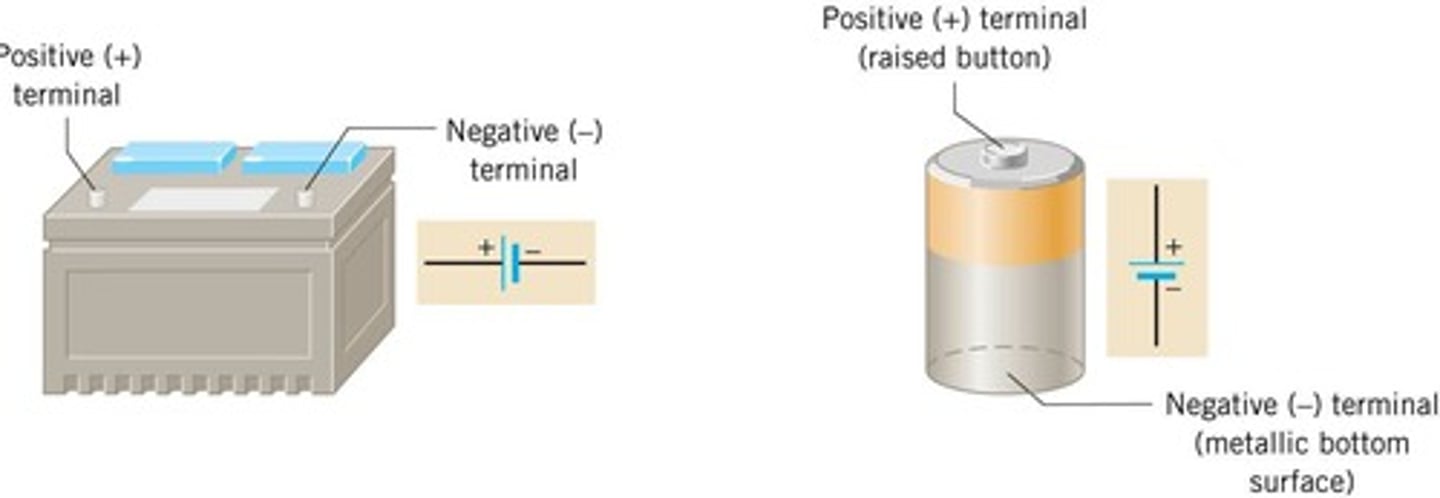
What defines the conventional current direction?
It is defined as the flow of positive charge moving from the positive terminal of a power source to the negative terminal, and it is commonly used in circuit diagrams and electrical engineering applications.
What is meant by electron flow direction?
Electron flow direction refers to the movement of electrons, which carry a negative charge, flowing from the negative terminal to the positive terminal of a power source. This direction is opposite to that of conventional current and represents the actual movement of charge.
How can the direction of current at a junction be evaluated?
To evaluate the current direction at a junction, if the current is positive (i0>0), the assumed direction is correct. Conversely, if the current is negative (i0<0), the actual current flows in the opposite direction.
Current density

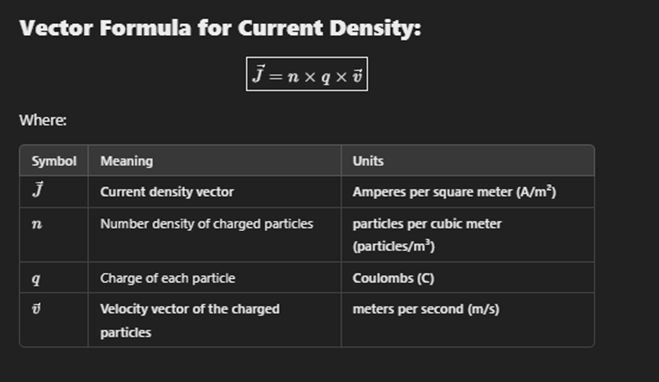
Current density is defined as the amount of electric current flowing per unit area of a cross-section through a conductor. It is typically expressed in amperes per square meter (A/m²) and helps quantify how concentrated the current is at any given point.
Resistivity due to electric field

Resistivity due to electric field is a material property that quantifies how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current when an electric field is applied. It is typically represented by the symbol (\rho) and is measured in ohm-meters (Ω·m).
Conductivity

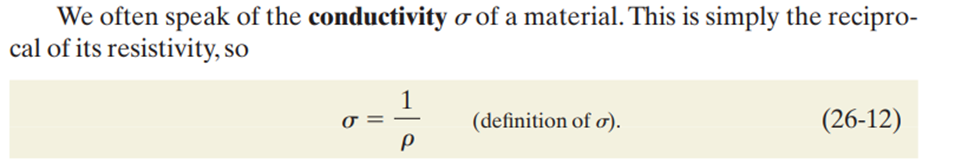
the reciprocal of resistivity, indicating how well a material allows electric current to pass through it. It is measured in siemens per meter (S/m).
Resisitance de to temprateure change

power

the rate at which electrical energy is transferred or converted. It is measured in watts (W).
Heat energy

energy produced by the movement of particles in a substance, often associated with temperature.
power vs joules
Power refers to the rate of doing work or transferring energy, while joules measure the amount of energy used. so like energy transferred to thermal energy will be watts
Electricity cost