Lecture 9 (Viral Diseases of Dogs II)
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
c) Paramyxovirus
Canine Distemper is a:
a) Poxvirus
b) Parvovirus
c) Paramyxovirus
d) Papovavirus
b) Morbillivirus (Like Measles & Rinderpest)
Canine Distemper is from the virus genus:
a) Pneumovirus (like BRSV)
b) Morbillivirus (like Measles & Rinderpest)
c) Rubulavirus (like Mumps)
d) Respirovirus (like Bovine Parainfluenza virus 3)
b) Canine distemper
-highly contagious // largely incurable // often fatal
-causes multi organ disease (attacks the respiratory, GI tracts, and CNS)
-the most common cause of seizures in dogs less than 6 months of age
a) Canine encephalitis
b) Canine distemper
c) Canine parvovirus
d) Canine pseudorabies
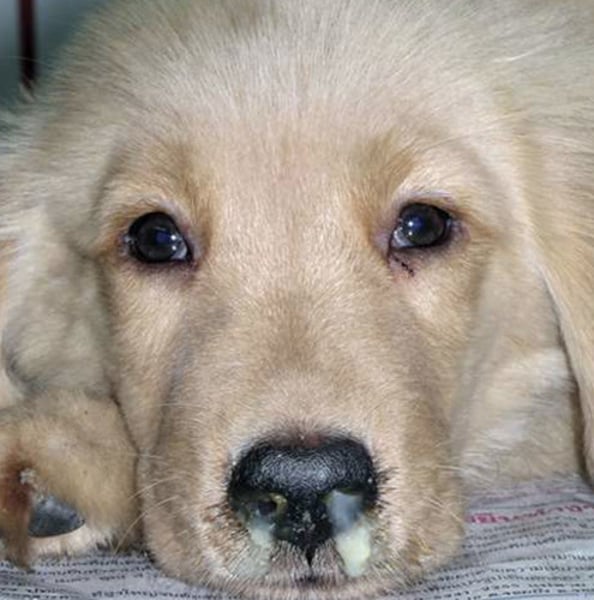

c) immunosuppression
what is the predominant effect of infection with CDV?
a) diarrhea
b) respiratory signs
c) immunosuppression
d) abortion
a) Canine distemper
fever, conjunctivitis, nasal discharge, bronchitis, and gastroenteritis are all signs of:
a) Canine distemper
b) Canine influenza
c) Canine parvovirus
d) Rabies
a) Canine distemper
neurologic signs of this virus include:
-incoordination // clumsiness
-head pressing // poor balance
-chorea (muscle tremors)
-myoclonus (jerky movements)
-paresis (weakness of all four limbs)
-hyperalgesia (heightened sensitivity to pain)
-seizures (chewing gum seizures)
-nystagmus (uncontrollable eye movement)
a) Canine distemper
b) Canine influenza
c) Canine parvovirus
d) Rabies
d) clinical signs appear within 24-72hrs of exposure
*signs are absent for first week while the virus is carried in WBC during a primary viremia to the bone marrow, lymph tissues, and macrophages of the lamina propria of the stomach and SI
which of the following is FALSE regarding the transmission of CDV?
a) virus is shed in all bodily secretions, and particularly respiratory exudates
b) transmission occurs via inhalation of aerosols or droplets
c) the virus initially infects respiratory epithelium and alveolar macrophages, then spreads to mononuclear cells in the lymph nodes and tonsils
d) clinical signs appear within 24-72hrs of exposure
b) fever
one of the first signs of CDV infections that can often go unnoticed:
a) encephalitis
b) fever
c) dysorexia
d) ataxia
true
t/f: there are PCR tests available for animals in the acute stage of CDV disease; this has replaced the need for immunofluorescence
a) Canine distemper
if the supportive care you are giving for a virus is:
-keeping eyes/nose discharge free
-giving broad spectrum antibiotics
-discontinue food & water if patient is V/D
-giving fluids as needed
-giving bronchodilators and mucolytics
-managing CNS signs with anticonvulsant drugs and glucocorticoids
you are probably treating for:
a) Canine distemper
b) Canine influenza
c) Canine parvovirus
d) Rabies
a) Canine distemper
the long term problems associated with _________________ infection include the development of lifelong seizures needing medical management, chronic tear deficiency, "hard pads", crusts on the nose, damage to the retina that stops short of blindness, and abnormal enamel deposition
a) Canine distemper
b) Canine influenza
c) Canine parvovirus
d) Rabies
a) Canine distemper
this virus used to be called "Hard Pad Disease" due to the characteristic changes in the footpads which result in a hard crust on the edges of the pads occurring in some patients in the long term
a) Canine distemper
b) Canine influenza
c) Canine parvovirus
d) Rabies
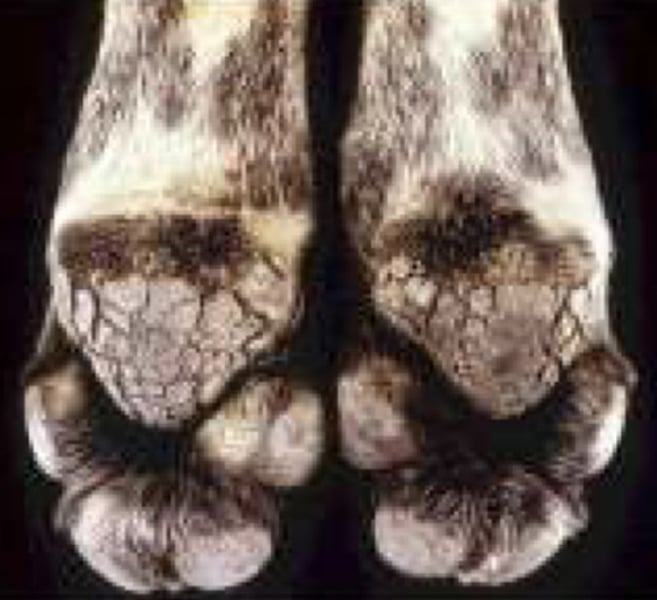
c) Modified Live
Canine Distemper vaccination is a ____________ vaccine and is important because distemper is still present in most areas and is hard to treat successfully
a) mRNA
b) Canarypox Vector
c) Modified Live
d) "Killed" / Inactive
a) Canine distemper
the vaccine for _____________________ is considered one of the best vaccines in vet med for its sterilizing immunity
a) Canine distemper
b) Canine influenza
c) Canine parvovirus
d) Rabies
a) Canine distemper
this vaccine is a key example of the fact that an attenuated virus may not remain attenuated in all species // when it was used in ferrets it resulted in fatal infections
a) Canine distemper
b) Canine influenza
c) Canine parvovirus
d) Rabies
false - unstable
t/f: Influenza Virus is relatively stable in the environment
hemagglutinin
glycoprotein H found on the surface of the influenza viruses stands for __________
neuraminidase
glycoprotein N found on the surface of the influenza viruses stands for __________
H - 16 subtypes
N - 9 subtypes
how many H and N subtypes are there in the influenza virus?
in greyhounds: can be an acute disease associated with hemorrhagic pneumonia and death
in other breeds: generally associated with a fever, nasal discharge, and a cough that persists for several days
explain the symptoms seen in H3N8, the Canine Influenza outbreak in 2004
raw horse meat being fed to racing greyhounds
what was the possible suspected origin of Canine Influenza in 2004?
strain was previously seen in Chinese and South Korean dogs and these dogs were imported into the U.S. to be adopted
how did H3N2, the Canine Influenza outbreak in 2015 begin?
b) Canine influenza
associated with an antigenic shift event relatively recently:
a) Canine distemper
b) Canine influenza
c) Canine parvovirus
d) Rabies in dogs
d) Horses
H3N8 existed in ____________ for decades before an antigenic shift allowed it to infect and become endemic in dogs
a) Cats
b) Racoons
c) Cattle
d) Horses
a) H is Hemagglutinin and there are 16 subtypes
d) N is Neuramindase and there are 9 subtypes
which two of the following statements are true regarding the H#N# naming of flue strains:
a) H is Hemagglutinin and there are 16 subtypes
b) N is Neuramindase and there are 16 subtypes
c) H is Hemagglutinin and there are 9 subtypes
d) N is Neuramindase and there are 9 subtypes
d) H3N8
now endemic Canine Influenza, originally spread in the racetracks in 2004, is:
a) H1N1
b) H5N1
c) H3N2
d) H3N8
c) H3N2
there was a canine influenza outbreak of ___________ in 2015 from a new-to-the-US strain previously seen in China and South Korea
a) H1N1
b) H5N1
c) H3N2
d) H3N8
a) H3N2 - the New-to-the-US strain
which appears to be able to be secreted for longer (10-15 days vs. 5-9) and seems to cause disease in cats too:
a) H3N2 - the New-to-the-US strain
b) H3N8 - the now Endemic strain originally from horses
c) Greyhounds
in __________ Canine Influenza can be an acute disease associated with hemorrhagic pneumonia and death
a) French Bulldogs
b) Siberian Huskies
c) Greyhounds
d) Basset hounds
b) Canine influenza
in most breeds, _________________ is associated with a fever, nasal discharge, and cough that persist for several days
a) Canine distemper
b) Canine influenza
c) Canine parvovirus
d) Rabies in dogs
b) Canine influenza
transmission of _____________ is by contact, short distance aerosols, and fomites // thus this is a concern for shelter dogs and dogs being boarded
a) Canine distemper
b) Canine influenza
c) Canine parvovirus
d) Rabies in dogs
false - but it is indicated for dogs with lifestyles of high exposure (dog parks, boarding, go to groomers etc.)
t/f: the CIV vaccine is a core vaccine
c) Both H3N2 and H3N8
the modern canine influenza vaccine protects against:
a) H3N2 which has completely replaced H3N8 in relevance
b) H3N8 only. H3N2 only appeared about 5 years ago
c) Both H3N2 and H3N8
a) Genus Lyssavirus
which subset of Rhabdoviruses are associated with neurological signs?
a) Genus Lyssavirus
b) Genus Vesiculovirus
c) Genus Ephemerovirus
b) Genus Vesiculovirus
which subset of Rhabdoviruses are associated with epithelial signs?
a) Genus Lyssavirus
b) Genus Vesiculovirus
c) Genus Ephemerovirus
Genus Lyssavirus (neurological)
what genus of Rhabdoviruses is rabies?
diagnosis by clinical presentation confirmed by Immunofluorescence or PCR
how can Rhabdoviruses be diagnosed?
b) wildlife
in the USA the reservoir of rabies virus is in...
a) cats
b) wildlife
c) feral pigs
b) cats
cats - 241
dogs - 63
cattle - 33
horses/donkeys - 13
in 2018 there were the most cases of rabies in which species:
a) dogs
b) cats
c) cattle
d) horses/donkeys
skunks
*starting to get raccoon rabies
what is the rabies variant in TN?
foxes
what is the rabies variant in TX?
cats
is rabies more commonly seen in dogs or cats?
d) Rabies in dogs
-loss of appetite // anxiety // insomnia
-infection of the limbic system
-restlessness // wandering
-hypersensitivity to stimulus
-blood in vomit // inability to swallow saliva
-hypersexuality
-hydrophobia // muscular spasms of facial, laryngeal, and pharyngeal muscles (triggered by light and odors)
a) Canine distemper
b) Pseudorabies in dogs
c) Canine parvovirus
d) Rabies in dogs
b) Dumb rabies
there are two routes of neurologic clinical signs with rabies; if it primarily targets the neocortex you get
a) Furious rabies
b) Dumb rabies
a) Furious rabies
there are two routes of neurologic clinical signs with rabies; if it primarily targets the limbic system you get
a) Furious rabies
b) Dumb rabies
a) Centripetal spread to neurons in dorsal root ganglia/spinal cord then centrifugal spread to the salivary glands and skin
in the pathogenesis of rabies spreading to the brain the infection of neurons follows what progression?
a) Centripetal spread to neurons in dorsal root ganglia/spinal cord then centrifugal spread to the salivary glands and skin
b) Centrifugal spread to neurons in dorsal root ganglia/spinal cord then centrifugal spread to the salivary glands and skin
c) Centrifugal spread to the salivary glands and skin, then centripetal spread to neurons in dorsal root ganglia/spinal cord
d) Centripetal spread to the salivary glands and skin, then centrifugal spread to neurons in dorsal root ganglia/spinal cord
b) Immunofluorescent antibodies
rabies virus is a strong example of what viral detection technique?
a) Immunohistochemistry
b) Immunofluorescent antibodies
c) PCR
d) Plaque assay
a) 2-3 days before clinical disease develops
prodromal shedding is a concern for rabies virus...this refers to the fact that the virus is possibly shedding
a) 2-3 days before clinical disease develops
b) 2-3 weeks before clinical disease develops
c) 2-3 days after death
d) 2-3 weeks after death
killed
what type of vaccine is the canine rabies vaccine?
negri bodies (inclusions of rabies virus)
in a necropsy, histopathology tests can be performed from sections of brain tissue to confirm diagnosis of rabies...what will we see on histopath?
b) Coronavirus
_____________________ in dogs (like cattle or horses) is a cause of mild enteritis and mild respiratory disease // in cats it is associated with FIP
a) Parvovirus
b) Coronavirus
c) Herpesvirus
c) Canine parvovirus
as a co-infection, enteric coronavirus infections in dogs can exacerbate infection with ________________
a) Canine distemper
b) Canine influenza
c) Canine parvovirus
d) Rabies in dogs
b) Coronaviruses
*Influenzaviruses are relatively unstable
although not as resistant as parvoviruses, ____________ are fairly resistant and remain infectious for several days outdoors even at frozen temperatures // dogs that frequent shows, dog parks, or are boarded frequently should get vaccinated
a) Influenzaviruses
b) Coronaviruses
c) Syncytialviruses
e) Coronaviruses
which is not a core vaccine for dogs?
a) Parvovirus
b) Distemper
c) Hepatitis (Adenovirus)
d) Rabies
e) Coronaviruses
a) Canine distemper
highly contagious, largely incurable, and often fatal disease that attacks the respiratory and GI tracts // most devastatingly attacks the CNS
a) Canine distemper
b) Canine influenza
c) Canine parvovirus
d) Rabies