Week 1 Review
1/188
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
189 Terms
cruciate ligament
holds dens in place during rotation of head
longitudinal and transverse bands
PREVENTS POSTERIOR DISLOCATION OF DENS
apical ligament
deep to cruciate
attaches dens to skull
alar ligament
laterally attaches dens to skull
Thoracic vs lumbar vs cervical
cervical- transverse foramen
thoracic- pointed down spinous process, articular facets for ribs, rounded vert body
lumbar-more square spinous process, oval vert body
where do cervical nerves exit
Exit above their respective vert body
except C8
where do non-cervical nerves exit
emerge below vertebral body
at birth, spinal cord ends at
L3
adult spinal cord ends at
bottom of L1/ top of L2
where does adult dura mater end
S2
what does the cauda equina contain
dorsal and ventral roots
what are the 3 layers of spinal membranes
dura mater (subdural matter)
arachnoid mater (subarachnoid/CSF)
pia mater
What do the denticulate ligaments do
separates the ventral and dorsal rootlets from each other
what are denticulate lig composed of
extensions of pia mater
dorsal rami supplies
medial branch - post cutaneous branch
lateral branch- intrinsic muscles of back
ventral ramus supplies
anterior and lateral cutaneous branches
extrinsic muscles of back
where is lumbar puncture done
L3-L4, enters subarachnoid space
spinal cord ends at L2
(where CSF is stored)
Extradural space contains
aka epidural (around dura mater)
epidural fat, internal vert venous plexuses
where does lumbar epidural anesthesia go?
into sacral hiatus
want it below S2 because that is where dura mater ends
main blood supply for spinal cord
anterior and superior spinal arteries
what is significant about lumbar veins
no valves, easy spread of cancer to cranial level
L4-5 disc compression pain/numbness
pain over sacroiliac joint, hip, lateral thigh/leg
numbness on first 3 toes
L4-5 leads to loss of
dorsiflexion of great toe and foot, difficulty walking on heels, foot drop (deep fibular nerve)
internal hamstring reflex diminished
L5-S1 disc compression pain/numbness
pain over sacroiliac joint, hip, posterolateral thigh/leg-heel
numbness on back of calf, lateral heel, foot to 5th toe
L5-S1 disc compression loss of
plantar flexion and great toe may be affected (tibial nerve), difficulty walking on toes
muscle mass of triceps surae
ankle jerk diminished
lumbar laminectomy used to
relieve pressure, due to disc herniation
gray matter vs white matter
gray matter: cell bodies
white matter: myelinated and unmyelinated axons that ascend to brain and descend through spinal cord
purpose of gray and white rami communicantes
distribute sympathetic fibers that will emerge from T1-L2 to respective areas
form symp ganglion that descend or ascend or travel at same level to various organs
ganglia
collection of nerve cell bodies in PNS
Cardiopulmonary plexus
supplies heart, sympathetic outflow
T1-T4
Pain during heart attack
referred pain at left arm, jaw, left chest
due to dermatomal distribution of T1-T4 cardiopulmonary plexus
significance of herpes zoster
varicella zoster virus reactivates from latent state in posterior dorsal root ganglion
shingles rash on skin along dermatome
3 main plexuses
cervical, brachial, lumbosacral
What forms a sacral plexus
ventral rami —> peripheral nerves —> motor
dorsal will receive sensory info
Erbs palsy affect what region of nerve
C5, C6, C7 upper brachial plexus (mostly C5 and 6)
cause of erbs palsy
increase of angle between neck and shoulder —> rupture of fibers from C5, C6, C7 (mostly C6 and C7)
erbs palsy presentation
sensory loss along lateral border of arm, affects entire arm
arm adducted and internally rotated, forearm extended and pronated
klumpkes palsy affects
C8/T1 of brachial plexus (lower brachial plexus)
cause of klumpkes palsy
excessive upward pull of limb
cervical rib can cause compression of lower fibers of brachial plexus
klumpkes presentation
loss of all intrinsic hand muscles- ulnar and medial
sensory loss along medial border and hand and forearm and arm
cartilage in lumbar disc
hyaline
outer annulus fibrosis made of
collagen type I
inner nucleus pulposus made of
type II collagen, PG molecules, water
blood supply to lumbar vertebrae
avascular!
function of nucleus pulposus
resist compressive loads through hydrostatic forces
function of annulus pulposus
resist tensile/torsional loads
if a disc degenerates, load can transfer to
zygapophyseal joints —> spondylolisthesis
lumbar radiculopathy
pain that radiates down leg in specific dermatomal distribution
red flags of radiculopathy —> urgent MRI
bowel or bladder dysfunction
fever chills
known malignancy/metastases
saddle anesthesia
supine straight leg test for
L4-S1 radiculopathy
seated straight leg test
modified supine straight leg
L4-S1
contralateral straight leg test
raising asymptomatic causes pain in symptomatic leg
lasegue test
hip flexed, knee flexion relieves leg symptoms
femoral tension sign
prone, knee passively flexed with hip extended
L2-L4 radiculopathy
timeline of disc herniation healing
improvement in 3 months for 90%
macrophage phagocytosis (3-6 mnths)
12 mnths most symptoms reside w conservative tx
conservative tx of disc herniation
NSAID
PT
corticosteroid
roof of carpal tunnel
transverse carpal ligament aka flexor retinaculum palmar side
muscular effects of carpal tunnel
thenar muscles eventually waste away
muscle weakness —> fine motor tasks difficult
carpal tunnel effect on palm
none, palmar branch upstream and does not enter carpal tunnel so palm unaffected r
risk factors for carpal tunnel
repetitive stress
obesity
pregnancy
underlying conditions like RA
phalens test
flex wrists and hold together for 1 min —> sx of carpal tunnel
tinels sign
tapping transverse carpal ligaments —> sx of tingling, carpal tunnel sx
durkans test
manually compress transverse carpal ligament for 30 seconds —> sx of carpal tunnel
tx of carpal tunnel
behavior mod
PT
splinting
corticosteroids
surgical division of transverse carpal ligament
opioid receptors 3 types
mu, kappa delta
inhibitory neuron in opioid pathway
secrete neurotransmitters signaling other neuron to NOT secrete dopamine
when opioid binds to receptors, this is inhibited —> other neuron secretes dopamine
theories of tolerance to opioids
less sensitive receptors
downregulation (fewer receptors available for binding)
opioids effects
dec HR, BP, wakefulness, respiratory rate
what drugs used to help wean off opioid
methadone (full ag) and buprenorphine (partial ag)- opioid agonists that avoid euphoria sensation
spondylolysis
defect/break in pars interarticularis (aka pars defect)
what typically causes spondylolysis
stress fx/overuse injury in children and adolescents
spondylolisthesis
spondylolysis + anterior slippage of vertebra in relation to vertebra below
break in pars —> disruption of structural integrity of vertebra (grade 1-4)
multipolar neurons have _____
2 or more dendrites, 1 axon
bipolar neurons have _____
1 dendrite, 1 axon
unipolar/pseudounipolar neurons have _____
1 process that splits into 2 “axons”
anaxonic neurons have _____
many dendrites, no axon
CNS supporting cells
astrocytes
oligodendrocytes
microglia
ependymal cells
microglia
macrophages of CNS
engulf infectious/foreign substance
astrocytes
support neurons (CNS)
BBB
structural support
replicates to occupy space of dying neurons
ependymal cells
cover ventricles and central canal (CNS)
CSF pdn and circ
line ventricles of brain and central canal of spinal cord
PNS supporting cells
satellite
schwann
Satellite cells
PNS
electrical insulation of cell bodies
reg nutrient/waste for cell bodies in ganglia
schwann cells
make myelin (PNS)
aka neurolemmocyte
wrap around axon —> faster propagation
oligodendrocytes
make myelin for CNS axons —> faster propagation
unmyelinated axons
smaller diameter —> slower prop
single wrap of schwann cell
oligodendrocyte vs schwann cells
oligo- CNS, sends out multiple process to myelinate more than one axon
schwann- PNS, only one axon
Nerve needs ____ to regenerate
cell body (only in PNS, no regeneration in CNS)
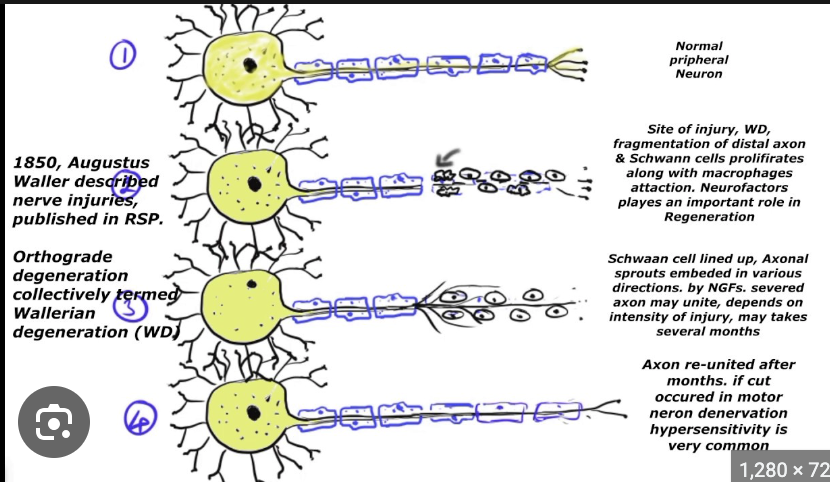
wallerian degeneration
idk what this is
anterograde axonal transport
kinesin - to + end
moves along microtubules
retrograde axonal transport
dynein + to -
moves along microtubules
types of synapses
Electrical (ions)
chemical (neurotransmitters)
Types of synapse depending on where they terminate with regard to another cell
axodendritic
axosomatic
axoaxonic
how to differentiate between neurotransmitter vesicles
small clear (cholinergic, acetylcholine)
small dense (adrenergic, norepi)
large dense (substance P)
vesicle at motor end plate
cholinergic (small clear) e
epi vs peri vs endoneurium
epineurium: around whole nerve
peri: around fascicle
endo: around single process (axon)
when does notochord develop
end of 3rd week
what is the notochord
solid rod like mesodermal structure that extends from head to tail region of embryo
becomes nucleus pulposus
the notochord does not form the
vertebral column!
vertebral column forms AROUND notochord
the notochord induces
the overlying ectoderm to form neural plate, which eventually forms the neural tube —> CNS and spinal cord
abnormal persistence of the notochord gives rise to
malignant tumor (chordoma)
neurulation
formation of neural tube
induced by notochord and paraxial mesoderm —> overlying ectoderm differentiates into thickened plate