Ch 10 The Organization of Global Business
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Stateless Corporation
Corporation transcending nationality for efficiency.
Global Company Stage 1
Produces goods in one country, exports to others.
Global Company Stage 2
Establishes foreign subsidiaries for exports.
Global Company Stage 3
Sets up operations in foreign countries.
Global Company Stage 4
Locates functions globally for competitive advantage.
Organizational Structure
Formal system controlling task and authority relationships.
Division
Subunit responsible for specific products or services.
Purpose of Organizational Structure
Facilitates coordination through labor division and specialization.
Export Department
Initial step for domestic firms entering global markets.
International Division
Concentrates international efforts in one location.
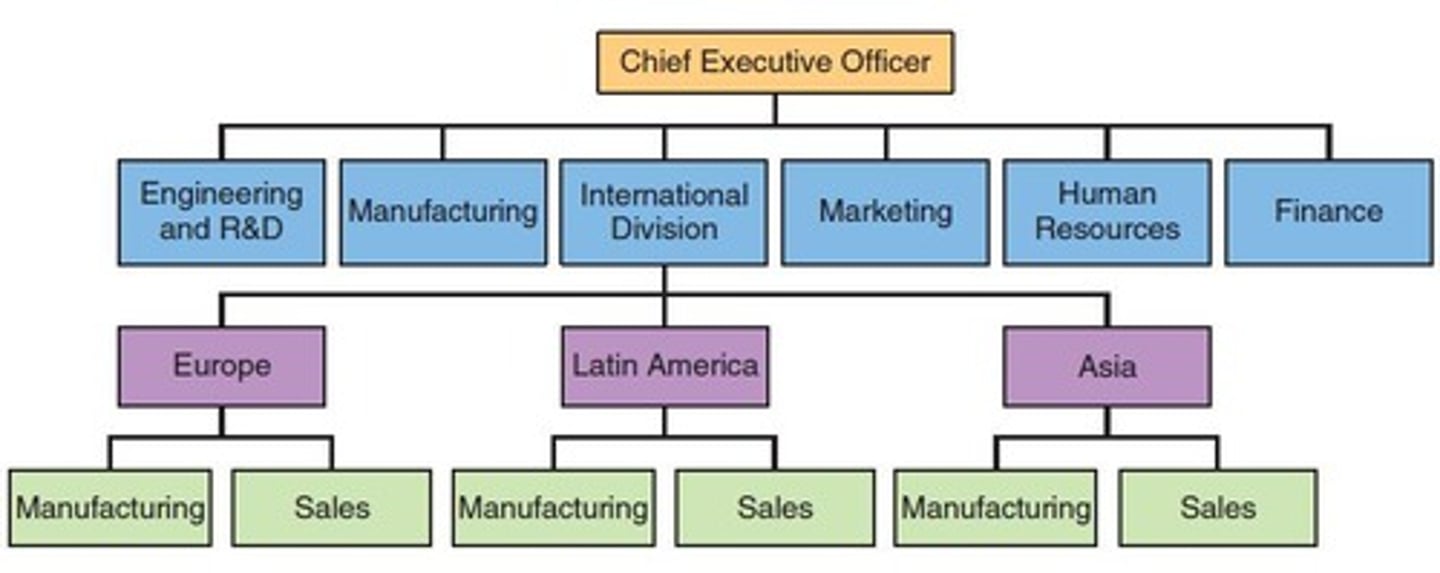
Advantages of International Division
Signals importance to international customers and fosters global mindset.
Joint Ventures
Partnerships to share risks and investments in foreign markets.
Local Partner Role
Helps navigate domestic economic and political environments.
Export Growth
Increased demand leads to larger export departments.
Hierarchical Supervision
Management structure ensuring coordination and integration.
Formal Rules and Procedures
Guidelines regulating organizational activities and interactions.
Training and Socialization
Processes for integrating new employees into the organization.
Departmentalization
Grouping activities based on function or product.
Standardization
Establishing uniform procedures across the organization.
Specialization
Focusing tasks on specific functions or roles.
Organizational Boundaries
Defines limits of organizational activities and interactions.
Competitive Advantage
Edge gained through strategic resource location.
Export Products
Goods sold internationally from domestic production.
Functional Structure
Groups employees by similar tasks or skills.
Divisional Structure
Organizes functions by products, markets, or regions.
Hybrid Structure
Combines multiple organizational structures for flexibility.
Matrix Structure
Simultaneously groups by function and division.
Advantages of Functional Structure
Promotes economies of scale and skill development.
Disadvantages of Functional Structure
Limited responsiveness to environmental changes.
Product Structure
Divides products based on similarities or differences.
Market Structure
Divides products based on customer needs.
Geographical Structure
Divides products based on regional needs.
Advantages of Divisional Structure
Focuses activities on specific products or markets.
Disadvantages of Divisional Structure
High operating costs and potential resource competition.
Stateless Corporations
Companies operating without a national identity.
Export Departments
Specialized units managing international sales operations.
International Divisions
Dedicated divisions focusing on global market strategies.
Role of Export Departments
Facilitates international trade and market entry.
Role of International Divisions
Oversees global operations and strategic direction.
Economies of Scale
Cost advantages due to increased production.
In-depth Skill Development
Enhances employee expertise within specific functions.
Collaboration and Efficiency
Encourages teamwork and streamlined processes.
Communication Problems
Issues arising from poor inter-division interactions.
Role Ambiguity
Unclear responsibilities within a matrix structure.
Limited Promotion Opportunities
Lateral movement restricts upward career advancement.
Stateless Corporation
Firms transcending nationality for global operations.
Globalization Stages
Four stages of international business development.
First Stage of Globalization
Producing goods in one country for export.
Second Stage of Globalization
Establishing foreign subsidiaries for exports.
Third Stage of Globalization
Setting up operations in foreign countries.
Fourth Stage of Globalization
Locating core functions across countries for advantage.
Purpose of Organizational Structure
Facilitates coordination and resource utilization to achieve goals.
Division
Business subunit responsible for specific products or services.
International Division
Organizational unit managing international operations.
Departmentalization
Grouping activities based on functions or products.
Standardization
Uniform procedures across organizational functions.
Specialization
Focusing on specific tasks for efficiency.
Integration Mechanisms
Methods coordinating activities within an organization.
Hierarchical Supervision
Management structure overseeing employee activities.
Formal Rules and Procedures
Established guidelines for organizational operations.
Training and Socialization
Processes for integrating new members into the organization.
Competitive Advantage
Edge gained through unique organizational capabilities.
Global Presence
Operating in multiple countries simultaneously.
Resource Coordination
Aligning people and resources to achieve objectives.
Organizational Boundaries
Limits defining an organization's scope and interactions.
Export Department
Specialized unit handling product exports.
International Division
Consolidates global business efforts in one location.
Global Enterprise
Company evolved beyond need for international division.
Functional Structure
Organizational model grouping activities by function.
Divisional Structure
Organizational model grouping functions by product or market.
Market Expertise
Knowledge of foreign markets for successful operations.
Organizational Division
Segment of a company focusing on specific operations.
Global Mindset
Perspective fostering international business awareness.
Coordination
Efforts to align activities across different divisions.
Economies of Scale
Cost advantages from increased production levels.
In-depth Skill Development
Specialized training enhancing employee expertise.
Local Optimization
Focus on local goals over global objectives.
Global Optimization
Alignment of goals across all international operations.
Resource Allocation
Distribution of resources among various divisions.
Long-term Strategy
Company's plan for future growth and direction.
Communication Barriers
Obstacles hindering information flow between divisions.
Conflict Potential
Risk of disagreements between domestic and international operations.
Narrow Product Line
Limited range of products offered by a firm.
High Integration
Close interrelation of products within a company.
Corporate Headquarters
Main office overseeing all company divisions.
Employee Collaboration
Teamwork among staff to achieve common goals.
Environmental Changes
Shifts in market conditions affecting business operations.
Divisional Structure
Organizational structure with autonomous divisions.
Autonomy in Divisions
Degree of decision-making independence for divisions.
Advantages of Divisional Structure
Focus on specific products, markets, or regions.
High-Quality Products
Divisions create products tailored to specific needs.
Common Identity
Shared approach to problem-solving within divisions.
Cohesiveness
Increased unity and performance among division members.
Functional Resources
Complete set of resources within each division.
Accountability
Divisions responsible for their own performance.
Disadvantages of Divisional Structure
High operating costs due to duplicated functions.
Communication Problems
Coordination issues among different division managers.
Resource Competition
Divisions competing for organizational resources.
Product Structure
Divisional structure grouping products by similarities.
Market Structure
Divisional structure based on customer needs.