Year 9 Biology
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
.
Last updated 2:54 AM on 3/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
1
New cards
what is the nervous system
communication system, controls all parts of your body
2
New cards
structure of CNS
made up of brain and spinal cord
3
New cards
CNS purpose
receives info from all over body, processes it and sends out msgs that tell body how to respond
4
New cards
structure and purpose of PNS
made up of nerves that carry out nerve impulses to & from CNS
5
New cards
brain purpose
control centre of body
tells diff parts of body what to do through NS nerve impulses
tells diff parts of body what to do through NS nerve impulses
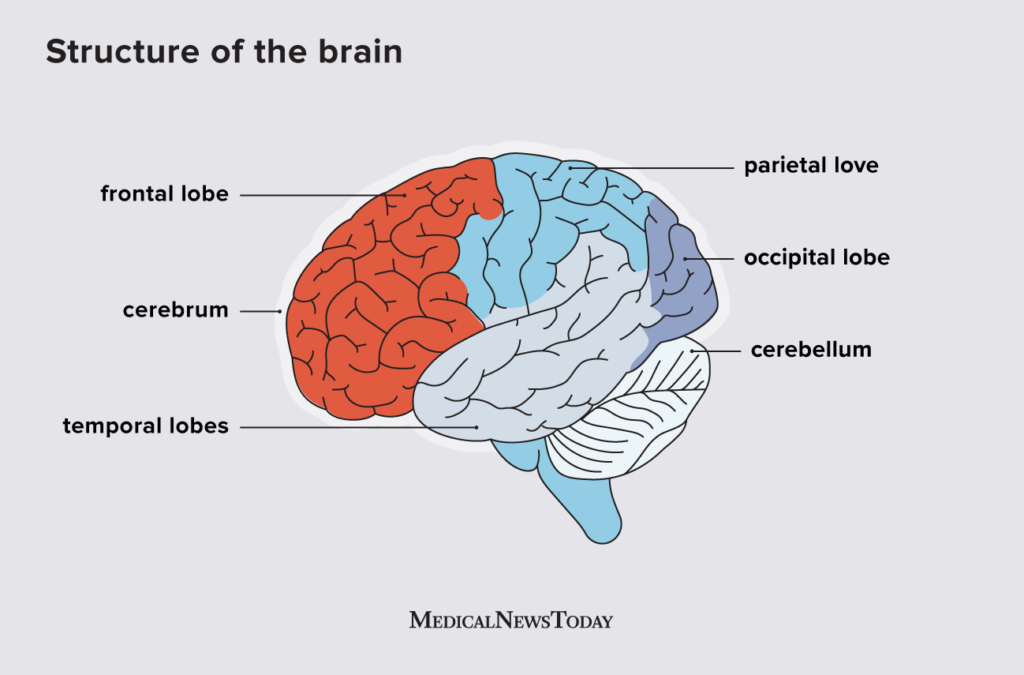
6
New cards
cerebrum
largest part of brain, made of 4 lobes
7
New cards
frontal lobe
higher thought (critical thinking, emotions)
8
New cards
occipital lobe
vision (colour, spatial awareness, movement)
9
New cards
parietal lobe
processes sensory info (4 other senses, body position)
10
New cards
cerebellum location + purpose
near rear, lower part of brain
responsible for balance, coordination + fine & gross motor movement
responsible for balance, coordination + fine & gross motor movement
11
New cards
brainstem location
connects brain to spinal cord, located at base of brain
12
New cards
brainstem purpose
responsible for many involuntary processes (heartbeat, movement of stomach and intestines
13
New cards
midbrain location
top part of brainstem
14
New cards
pons location
below midbrain
15
New cards
medulla location
bottom-most part of brain
16
New cards
hypothalamus location
directly above brainstem, below thalamus + above pituitary gland
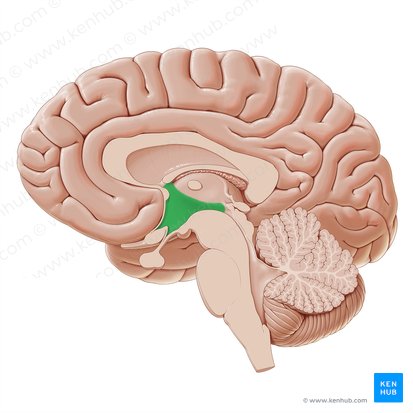
17
New cards
hypothalamus purpose
responsible for keeping body in a stable state: homeostasis
18
New cards
white matter
parts of CNS that contain neurons covered in myelin
where axons are connecting diff parts of grey matter to eachother
where axons are connecting diff parts of grey matter to eachother
19
New cards
grey matter
parts w/ mainly cell bodies, dendrites + synaptic terminals
where the “thinking” occurs
where the “thinking” occurs
20
New cards
motor neurons
carry signals from CNS to effectors
21
New cards
effectors
muscle cells/glands
put messages into effect
put messages into effect
22
New cards
sensory neurons
carry signals from cells in sense organs to CNS
e.g. pain receptors in neck
e.g. pain receptors in neck
23
New cards
interneurons
link sensory neurons directly to motor neurons
only make connections with other neurons
only make connections with other neurons
24
New cards
axon
carries signal away from cell body to axon terminals
25
New cards
dendrite location
attached to cell body
26
New cards
dendrite
sensitive branches that receive info as electrical signals from nerves near it
27
New cards
myelin sheath
fatty layer covering axon
helps speed up nerve impulse
protects impulse from “crossing wires”
helps speed up nerve impulse
protects impulse from “crossing wires”
28
New cards
cell body
contains a nucleus
29
New cards
axon terminal
bulb at end of axon
where electrical msg is passed across synapse to next dendrite
where electrical msg is passed across synapse to next dendrite
30
New cards
synapse
small gap between neurons
31
New cards
role of sense receptor
detects change in environment
e.g. photoreceptors detecting light
e.g. photoreceptors detecting light
32
New cards
stimuli
change in environment
33
New cards
positive feedback loop
enhances or amplifies changes
34
New cards
negative feedback loop
dampens or buffers changes
35
New cards
components of feedback loops
receptor (sensor), the control centre, and effectors.
36
New cards
importance of spinal reflex
helps prevent damage and injuries to the body
37
New cards
spinal reflex (reflex arc) sequence
1. stimulus
2. sensory receptor detect change
3. sensory neuron carries signal from receptor to spinal cord
4. interneuron relays signal from sensory neuron to motor neuron
5. motor neuron carries signal to effector cells
6. effector cell causes response
38
New cards
reaction sequence
1. stimulus
2. sensory receptor detects change
3. sensory neuron carries signal from receptor to CNS
4. CNS processes info, makes decision
5. motor neuron carries response signal to effector cells
6. effector cells cause response
39
New cards
reactions
slower, more complex reactions to stimuli
involves brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerves
involves brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerves
40
New cards
reflexes
fast, simple, automatic, involuntary responses to stimuli
involves peripheral nerves, often spinal cord (not brain)
involves peripheral nerves, often spinal cord (not brain)
41
New cards
alzheimers
caused by gradual dmg to neurons in brain
affects ability to remember + carry out normal activities
affects ability to remember + carry out normal activities
42
New cards
increase in blood sugar
1. pancreas receptors detect inc. blood sugar lvl
2. pancreas stimulates, secretes insulin in blood
3. insulin travels to insulin receptors on muscle + liver cells
4. muscle + liver cells remove excess glucose from blood, stored as glucagon
5. blood sugar lvls dec.
43
New cards
decrease in blood sugar
1. pancreas receptors detect dec. blood sugar lvl
2. pancreas stimulated to secrete glucagon into blood
3. glucagon travels to glucagon receptors on muscle + liver cells (target cells)
4. these cells release glucose into blood
5. blood sugar lvls inc.
44
New cards
hormones
chemical messengers used to carry info
45
New cards
endocrine system glands purpose
glands secrete hormones
46
New cards
endocrine system purpose
responsible for growth, repair, digestion, sexual reproduction, homeostasis
47
New cards
what is the hypothalamus made of
nerve tissues
48
New cards
hypothalamus target + main effect
pituitary gland
links nervous system to endocrine
links nervous system to endocrine
49
New cards
pituitary gland hormones
thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
growth hormone
growth hormone
50
New cards
thyroid stimulating hormone purpose
controls rate of thyroxin released
51
New cards
growth hormone purpose
stimulates muscle growth + bone size
52
New cards
adrenaline purpose
prepares body for “flight or fight” response
causes immediate release of energy
causes immediate release of energy
53
New cards
estrogen + progesterone functions
female sexual development, maintenance of pregnancy
54
New cards
testosterone functions
male sexual development + activity (sperm)
55
New cards
thyroid gland hormone
thyroxine
56
New cards
thyroxine purpose
regulation of chemical reactions in cells e.g. respiration (metabolism)
57
New cards
pancreas hormones
insulin
glucagon
glucagon
58
New cards
insulin + glucagon functions
control blood sugar levels
59
New cards
relationship between hypothalamus and pituitary gland
hypothal. constantly checks internal environment. if the conditions change, it responds by secreting hormones to the pituitary gland, which then responds to the information by secreting other hormones or producing fewer.
60
New cards
internal environment
conditions within tissues, organs and systems
61
New cards
type 1 diabetes
pancreas progressively decreases insulin produced until there’s none at all
62
New cards
type 2 diabetes
pancreas makes insulin but cells don’t respond to it as they should (insulin resistance)
63
New cards
1st line of defence + purpose
physical barriers
prevents pathogens from entering body
prevents pathogens from entering body
64
New cards
physical barriers
skin, saliva, eyes (tears), mucus membrane (trap), acid (stomach), reflexes
65
New cards
second line of defence
innate immune response
66
New cards
innate immune response
1. broad response
2. wbc get involved
67
New cards
1. broad response
blood clotting, inflammation, fever
68
New cards
blood clotting
prevents pathogens entering through damaged skin
69
New cards
inflammation
increased no. of wbc reaching infected area (becomes red, hot)
70
New cards
fever
destroys weaker pathogens that can’t handle the heat
71
New cards
2. wbc get involved
* neutrophils
* macrophages
* macrophages
72
New cards
phagocytosis
wbc arrive in blood, eat any foreign substances
73
New cards
neutrophils
phagocytosis, die, become pus
74
New cards
macrophages
phagocytosis, present particles to next defence line
75
New cards
3rd line of defence
adaptive immune response
76
New cards
adaptive immune response purpose
wbc in this line are made to target __specific__ pathogens
77
New cards
wbc in adaptive immune response
* b-cells
* t-cells
* t-cells
78
New cards
b-cells
* produce antibodies
* antibodies fit exactly on specific ptg to prevent spreading + help t-cells
* antibodies fit exactly on specific ptg to prevent spreading + help t-cells
79
New cards
t-cells
attack + destroy specific, recognised pathogens
80
New cards
main pathogens that cause disease
* bacteria
* virus
* parasites
* fungi
* virus
* parasites
* fungi
81
New cards
bacteria
* single celled, living organisms
* some killable w/ antibiotics
* e.g. necrotising faciitis (flesh eating disease)
* some killable w/ antibiotics
* e.g. necrotising faciitis (flesh eating disease)
82
New cards
virus
* much smaller than bacteria, non-living
* insert selves into cells, use body’s DNA to replicate + spread
* e.g. ebola, covid
* insert selves into cells, use body’s DNA to replicate + spread
* e.g. ebola, covid
83
New cards
parasite
* organism, lives on another host organism
* benefits from nutrients causing harm to host organism
* e.g. malaria
* benefits from nutrients causing harm to host organism
* e.g. malaria
84
New cards
fungi
* caused by fungus
* feed off a protein in skin, nails, hair etc
* red + itchy skin
* most harmless, easily treated
* e.g. ringworm
* feed off a protein in skin, nails, hair etc
* red + itchy skin
* most harmless, easily treated
* e.g. ringworm
85
New cards
how are vaccinations made?
made with killed/weakened versions of the disease-causing germs/parts of germs (antigens)
86
New cards
how do vaccinations work?
each pathogen has a specific antibody that acts on it
1st time we’re exposed, our body is slow to make antibodies to fight it
2nd time, antibodies are made much faster + pathogen destroyed because you’re immune
1st time we’re exposed, our body is slow to make antibodies to fight it
2nd time, antibodies are made much faster + pathogen destroyed because you’re immune
87
New cards
memory cells
* adaptive defence has memory b&t-cells made especially for the disease
* cells remember disease if it enters our body again + kills it very quickly
* cells remember disease if it enters our body again + kills it very quickly
88
New cards
pathogens
disease causing micro-organisms
89
New cards
disease
anything that causes your body to stop working properly
90
New cards
infectious diseases
diseases that can be spread
91
New cards
contagious diseases
diseases easily spread
→ passed by touching infected person/items touched by them
→ passed by touching infected person/items touched by them