Psychodynamics
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Central techniques of psychoanalytic treatment
Free Association
Transference Analysis
Resistance
Dream interpretation
Primary process
“Pleasure–unpleasure” principle.
We seek immediate release of tension by wish fulfillment.
This energy is mobile and allows for displacement and condensation (emerging ideas).
It’s dominant in dreams and symptoms
Secondary process
Dominant, rational, planned actions.
Psychic Determinism
Every mental process is not spontaneous but determined by unconscious or preexisting mental complexes. Nothing is without a reason.
Pleasure principle
based on the constancy principle which states the unconscious is governed by the need to immediately respond to excitatory stimulus, lowering tension.
Homeostasis= pleasure.
Heightened tension = unpleasantness/pain (anxiety)
Reality principle
the limitations and demands of reality.
Child – omnipotent. Neurotic patients wish for an object that does not exist/is not accessible.
Repetition Compulsion
There are many repetitions in life.
Things which are repressed come in dreams, symptoms, and in reliving past experiences.
We have a compulsion to repeat — not measurable or necessarily pleasurable.
Dream Formation
An event stirs up an unexpressed wish- Extra strong if similar to childhood wish.
The two sources for the wish push the mind.
Reality prevents wish fulfillment.
The energy goes to hallucinatory wish fulfillment.
The scenarios imagined need to be easy to digest.
This process uses condensation, displacement, etc.
Rules of Dream Interpretation
Rules of Dream Interpretation
You can’t interpret everything.
You can't see things “as they are” and interpret according to that.
The dreamer must interpret the dream.
You can’t deeply understand a dream early in analysis.
You gather the patient’s associations before/after.
Dream interpretation shouldn’t overshadow therapy.
Not every dream must be interpreted.
Reporting dreams can also be resistance.
The analyst appearing in dreams isnt a bad sign
Changes in dreams = progress in therapy; some dreams mark termination of therapy.
Dream Work- definition and what it consists of
The ego operations that turn the wishes+thoughts+ “day residue” into dream content.
Consists of:
condensation
Displacement
Symbolism
Secondary revision
Condensation
fusion of objects/concepts.
Happens in Dreams, Jokes, and parapraxes. In jokes and parapraxes, it is more of a compromise between censorship and fantasies.
Displacement’s four types of subconscious shifts
Ideational displacement – changing ideas
Relational displacement – changing object of feeling
Affective displacement- changing the situation to which an emotion was regarded
Temporal displacement – changing timing of the emotion
Secondary revision
Mental process that ”tidies up” a dream to turn it into a coherent story
Symbolism
The symbol is concrete; the symbolized is abstract.
Dreams in pairs
two dreams in one night are steps in wish fulfillment. They are interwined.
Dreams of convenience
Fulfill basic bodily needs.
Therapy Termination dreams
termination signal- appears before a decision to end the sessions has been made. The patient dreams of cleaning attic, finishing tasks, or assesing the patients progress
Termination phase dream - Appear after the decision to end the sessions. These dreams show the patient’s symptoms in a better state, and the analyst is involved. Also rebirth/ coming out of a tunnel
Parapraxes definition
Para- “beside”, Praxis- “action”
Parapraxes are unintentional actions (mistakes) that have hidden motives.
Freud: occurs when conflict exists between conscious intention and unconscious wish.
Types of Parapraxes
Slip of tongue
Slips of the pen
Slips in reading/hearing
Forgetting - protects from distressing memories
Losing/misplacing objects – unconscious wish to reject or punish oneself
Mistaken actions – there are no mistakes, everything is driven by forces.
We express inner feelings or thoughts that contradict conscious intention
General information about Jokes
Aesthetic pleasure from weakening repression and releasing energy
The form of the story is more important than content
Uses condensation, displacement, reversal, instinct fusion (fusion of sexual and destructive instincts, for example)
Jokes disguise inner aims; we fulfill wishes through jokes
Types of jokes
Fear of uncanny- black/morbid,
Fear of otherness- racist
Routine- knock knock jokes
Sexual jokes
Weakness - impotence, laziness, addictions
Self-depreceting jokes
Defense Mechanisms
Regression
Isolation
Projection
Repression
Undoing
Sublimation
Turning against the self
Reaction formation
Rules of defense mechanisms
Aim to reduce anxiety
Operate unconsciously
Rooted in childhood
Some emerge at specific developmental stages
Some defenses are permanent, others situational
Important for structure formation and ego functioning
Any activity can be used as a defense
Some are specific to psychopathological symptoms (Conversion- hysteria, undoing- obsessional neurosis)
Some are more “ego”, others more “id”
Mature defenses are different from primitive ones.
Why are they called “primitive defences”?
Developmental context: They come early in the development, when there’s less ego organization.
Motivation context: They come to protect from more primal threats, like the threat of self-consistency.
Diagnostic context- Less “character organization”, like in psychoses, causes the use of more primitive defense mechanisms
Mature defense mechanisms
suppression
altruism
sublimation- לצייר במקום להרביץ
humor
anticipation- תכנון
Primary repression
something wasn’t allowed to enter consciousness
Repression proper
Something is pushed from consciousness to unconsciousness .
General facts about repression
Its strength depends on the strength of desire and the power of suppression
It requires constant mental energy
It’s the base of all defenses
Conversion
The energy attached to a repressed idea is transformed into somatic symptoms
emotional energy → somatic symptoms.
Somatization
similar to conversion, but its not neurological and it’s with multiple body symptoms
Reaction formation - what it is and similar concepts
turning unacceptable wishes (feelings) into the opposite.
Similar concepts:
Undoing- short, momentary impulse that changes. a person tries to cancel out or remove an unhealthy, destructive or otherwise threatening thought or action by engaging in contrary behavior.
Displacement – object changes, not wish. Same feelings, different person
Sublimation - You change the outcome, not the emotion.
Polymorph perverse sexuality
The child is satisfied by different erotogenic zones in different stages. These zones serve as a source of pleasure.
Fixation
happens when a child is unsatisfied in one of the stages.
freud’s stages
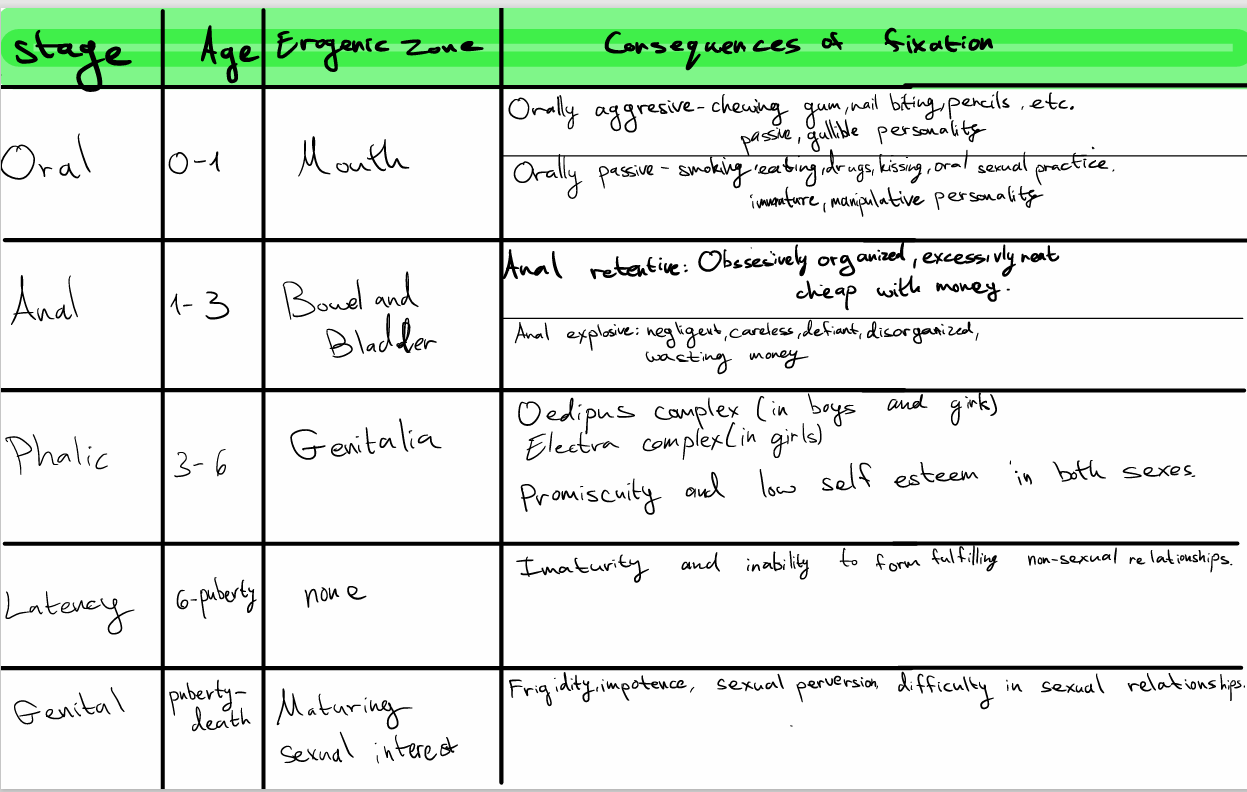
Oral (0–1)-
The mouth is the erogenous zone
Passive/oral fixation → dependency, gullible
Aggressive → nail biting, chewing, sarcasmAnal (1–3)
The butthole is the erogenous zone
Retentive → organized, stingy
Expulsive → messy, careless, wastefulPhallic (3–6)
The Genitals are the erogenous zones
Oedipus/Electra complex
Fixation → promiscuity, low self-esteemLatency (6–puberty)
Fixation →immaturity, unstable relationshipsGenital
Mature sexuality
Fixation → frigidity, impotence, sexual perversion, difficulty in sexual relationships
Four Psychologies
Drive psychology- Freud. Focus is on instincts, tension reduction. This is no longer the central theory. What is the wish?
Ego psychology - Anna Freud, Hartman. Focus is on defense mechanisms, reality testing. What defense is at work?
Object relations psychology - Klein, Winnicott. Focus is on internalized relationships, primary caregiver, and early relational trauma. What relationship is being played out?
Self psychology - Kohut. Focus on self-esteem, empathy, needs, narcissistic vulnerability. How coherent is the sense of self? Is the self valued?
Psychosis definition
Severe disturbance of reality testing:
Delusions, hallucinations, disorganized thinking, disruption of identity and self-experience.
Psychiatric diagnoses that include psychosis
Schizophrenia
schizoaffective
acute psychosis
persistent delusions
Depression/mania with psychotic features
Organic or substance-induced psychosis
Structural Levels of Personality Organization:
Neurotic – stable personality, anxiety disorders
Perverse – sexual disorders, narcissism, antisocial traits
Borderline – unstable self, intense emotions, primitive defenses
Psychotic – loss of reality testing, fragmentation

Anxiety in psychosis vs. neurosis
Neurosis → fear of loss, guilt, rejection
Psychosis → annihilation, disintegration, persecution
Primitive defences in psychosis
There’s massive denial of reality. “This does not exist.” “I’m not ill, you are”.
There’s a need for omnipotent control or a sense of grandiosity.
Their boundaries of external-internal are broken, causing inner fantasies to appear as external reality, and external events to be experienced as personal messages.
Freud’s take on psychosis
Neurotic conflict comes from id vs. ego vs. super ego
Psychotic conflict is more severe and primitive and comes from fusion vs. separation, good vs. bad internal objects, trust in society vs. hostility.
The psychotic conflict might be too unbearable, causing the ego to withdraw and reality to be replaced with delusions
Freud believed severe deprivation in the very early stages (especially oral) causes psychosis. Stress→regression to this level→psychosis
Klein’s take on psychosis
Paranoid schizoid position
Early in life the world is split into good and bad objects
Dominant defences: Splitting, projective identification
Dominant anxiety : persecutory
Psychosis causes a regression to this Paranoid schizoid level
The next level is the depressive position, in which there is an understanding that the object can be both good and bad. This causes guilt, concern, and the development of empathy, symbolization, and an ability to tolerate ambivalence.
Winnicott’s take on psychosis
Talked about the “good enough mother” and “holding”- the capacity of the environment to contain and support the infants experience.
In psychosis there’s a failure of holding, which causes a development of a false self
Under stress, the false self collapses
Winnicott emphasized how therapy must provide holding and safety.
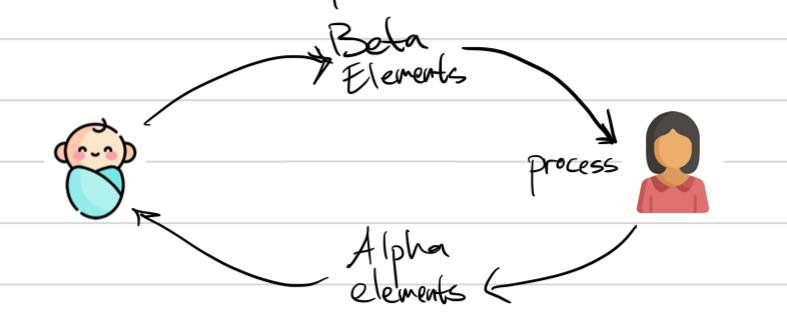
Bion’s take on psychosis
Containment and thinking
The infant has raw, unprocessed emotional experiences- Beta elements
The mother acts as a container - receives, processes, and transforms these experiences into a tolerable form, then returns them to the baby- Alpha elements.
If the containment fails, the experiences remain unprocessed or unthinkable
This creates an inability to think and symbolize emotional experiences
Thoughts become indistinguishable from reality
This causes projective identification
psychotic parts of the personality control the individual’s thoughts, his link between self and others, and links between past, present and future.
Kohut’s take on psychosis
Self psychology and psychosis
Kohut said that for the development of the self we need Self-object (caregiver)
Actions needed from the caregiver:
mirroring- “ you see and value me” warm reflection on the childs experiences
idealization- A powerful, calm, reliable adult to deolize
twinship - Alter ego experience. “I am like you. I belong.” Part of a group, connected.
If the self-object fails → fragmentation of the self, and in sever cases→ psychosis.
Guidelines for Therapy With Psychotic Patients
Provide stability, predictability
Containment of anxiety
Support reality testing
Slow pace
Minimal interpretation
Strengthen self
Focus on the here-and-now