Biopsychology Exam 1
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
biospychology
scientific study for the biology of behavior
The Organization of Behavior (1949)
Hebb’s book, a key factor in the development of neuroscientific discipline
Ultimate challenge for the human brain
Does our brain have the capacity to understand something as complex as itself?
Three dimensions of biopsychological research
human vs. non-human subjects
experimental vs. non-experimental studies
applied vs. pure research
Advantages of human subjects
they can follow directions
they can report subjective experiences
they are often less expensive
they have a human brian
advantages of nonhuman subjects
they have simpler nervous systems
studying various species makes it possible to use the comparative approach
they are fewer ethical constraints
experiments
cause-effect relationships
between-subject design
a different group of subjects tested under each treatment condition of an experiment
within-subject design
same group of subjects can be tested under multiple treatment conditions
independent variable
set or manipulated by the experimenter, produce different treatment conditions in an experiment
dependent variables
reflect the subject’s behavior, what the experimenter measures
confounded variables
unintended differences between conditions that can influence the depended variable
quasiexperimental design
researchers examine subjects in real-world situations who have self-selected in specific conditions, cannot control potential confounding variables
case studies
single subject, the extent to which their results tell us something about the general population is unknown
pure research
motivated primarily by the curiosity of the researcher to find out how things work, building blocks or basic concepts that may provide information salient in many problems
applied research
motivated by an attempt to directly use the building blocks of basic research to answer specific questions
physiological psychology
direct manipulation of the nervous system in controlled lab settings
typically lab animals
pure research
psychopharmacology
nervous system manipulated pharmacologically
drug effects on behavior and how changes are mediated by changes in neural activities
neuropsychology
behavioral effects of brain damage in humans, typically cortical damage
focus on case studies and quasiexperimental studies
psychophysiology
relationship between physiological and psychological processes in human subjects
EEG
cognitive neuroscience
newest division of biopsychology
focuses on neural bases of cognitive processes like learning/memory, atteniton and perceptual focus
comparative psychology
biology of behavior
comparative and functional approaches
evoluutionary psyching and behavioral genetics
converging operations
compensating for the shortcomings of other fields and used to solve the same problems
empirical method
answering questions by direct observation
nature-nurture
debate on whether behavior is inherited through genetics or learned through experience
based on the premise that genetic factors and environmental factors combine in an additive fashion
psychological or physiological thinking
over simplistic and false
model of the biology of behavior
behaviors are best viewed as the product of genetic potential interacting with past experience and current situational factors
heritability estimates
a statistical value that represents the proportion of variation in a trait within a specific population that is due to inherited genetic factors, ranges from 40-80 percent
cns/central nervous system
bony skull and vertebral column, brain and spinal cord
pns/peripheral nervous system
somatic and autonomic nerves
somatic
interacts with external environment
autonomic
interacts with the internal environment
efferent
escape/exit, away motor commands away from the CNS
afferent
bring sensory information into the CNS
sympathetic nerves
PNS, activates an organism, indicates arousal in target organ
parasympathetic nerves
PNS, acts to conserve energy, activates relaxation in target organ
cranial nerves
leave the CNS from the brain through the skull rather than the spinal cord. specific sensor and/or motor functions
meninges
membranes that protect the brain and spinal cord.
dura mater
tough mother, outside layer of meninges
arachnoid layer
spidery mother, middle layer of meninges
pia mater
gentle mother, inside layer of meninges
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
manufactured by the choroid plexus,
circulates through the ventricular system of the brain, the central canal of the spinal cord, and the subarachnoid space, and absorbed into large channels called sinuses
when the flow of CSF is blocked, hydrocephalus results
choroid plexuses
capillary networks that protrude into the ventricles
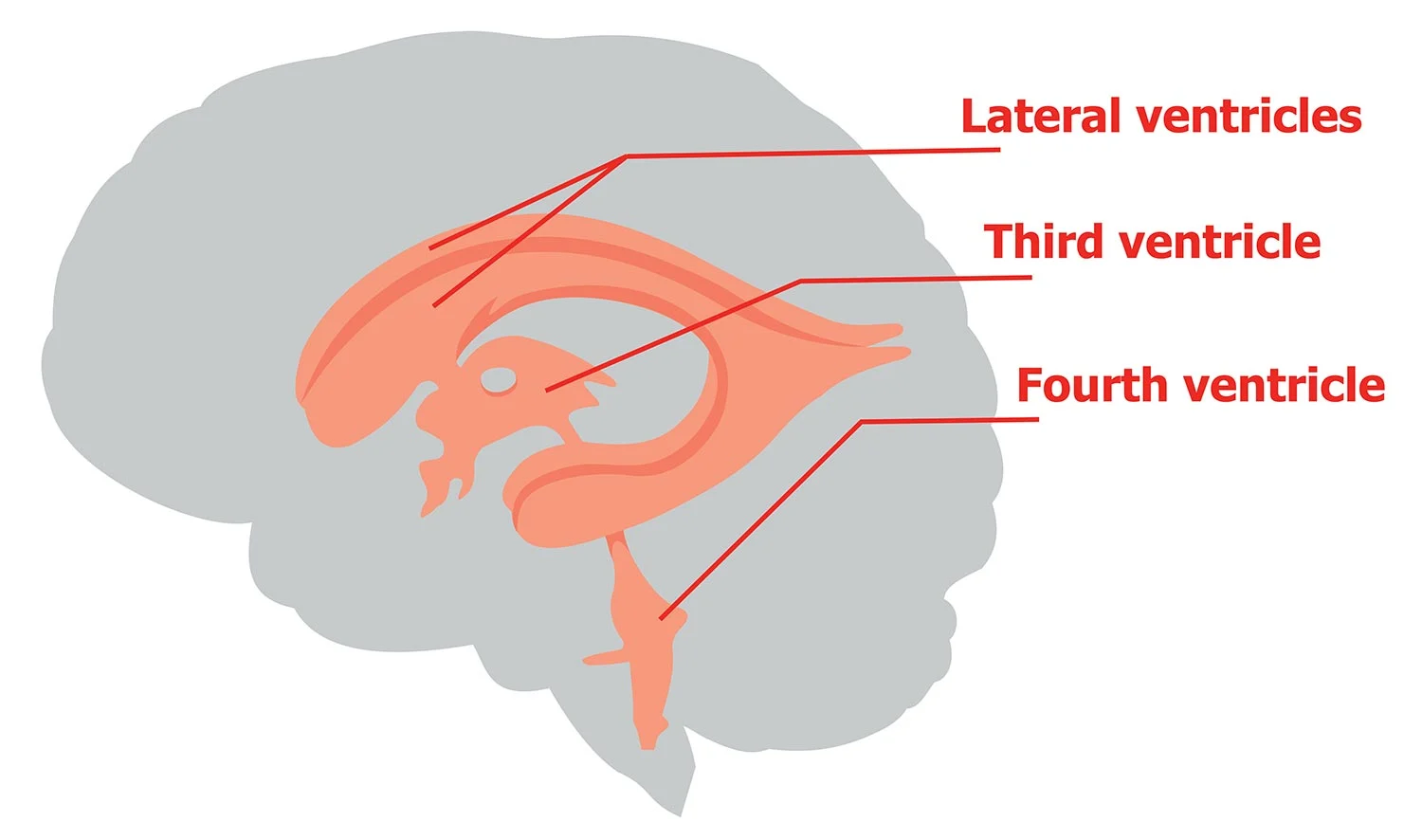
ventricles
A fluid-filled cavity in the heart or brain
blood-brain barrier
A network of blood vessels and tissue that is made up of closely spaced cells and helps keep harmful substances from reaching the brain
dendrite
shorters processes that emanate from the cell body and receive input from synaptic contacts with other neurons
axon
projects away from the cell body
axon hillock
the junction between cell body and axon, conveyance of electrical signals of the neuron
myelin sheaths
formed by oligodendroglia in the CNS and Schwann cells in the PNS
insulate the axon and assist in the conduction of electrical signals
nodes of ranvier
small spaces between adjacent myelin sheaths
buttons
branched endings of the axon that release chemicals that allow the neuron to communicate with other cells
synapses
points of communication between the neuron and other cells
multipolar neuron
multiple dendrites and an axon extending from the soma, more than two processes extending from its cell body
bipolar neuron
single axon and single dendrite, two processes extending from its cell body
unipolar neuron
one process that combines both axon and dendrites
nuclei
clusters of cell bodies in the central nervous system
ganglia
clusters of cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system
glia
cells that provide physical and functional support to neurons
microglia
responsibilities in the brain and play a role in the regulation of cell death, synapse formation, and synapse elimination
astroglia
largest of glail cells
support and provide nourishment for neurons and form part of the blood brain barrier
help send chemical signals between neurons and establish and maintain connections between neurons
golgi stain
permitted individual neurons to be studied for the first time
nissl stain
highlights cell bodies of all neurons, allowed estimation of cell density in tissue
electron microscopy
allows visualization of neuronal ultrastructure
neuroanatomical tracing techniques
highlights individual axons
may be retrograde (trace back from terminal fields) or anterograde 9trace from soma and terminal fields)
anterior/posterior
toward the nose or front/toward the tail or back
dorsal/ventral
toward the surface of the back or top of the head/indicates the surface of the chest or bottom of the head
medial/lateral
toward the midline of the body/outside or away from the midline
gray matter
cell bodies
white matter
myelinated axons
dorsal horns
upper (dorsal; posterior) wings of the butterfly spinal cord
ventral horns
lower (ventral; anterior) wings of the butterfly spinal cord
dorsal roots
sensory axons, cell bodies lie just outside the the spinal cord in the dorsal root ganglia
ventral roots
motor axons, cell bodies lie inside the ventral horns
medulla
composed of major ascending and descending tracts and network of small nuclei involved in sleep, attention, muscle tone, cardiac function, and respiration
hindbrain subcortical structure
reticular formation/reticular activating system
core network of nuclei
composes the core of the hindbrain and midbrain
thought to be an arousal system
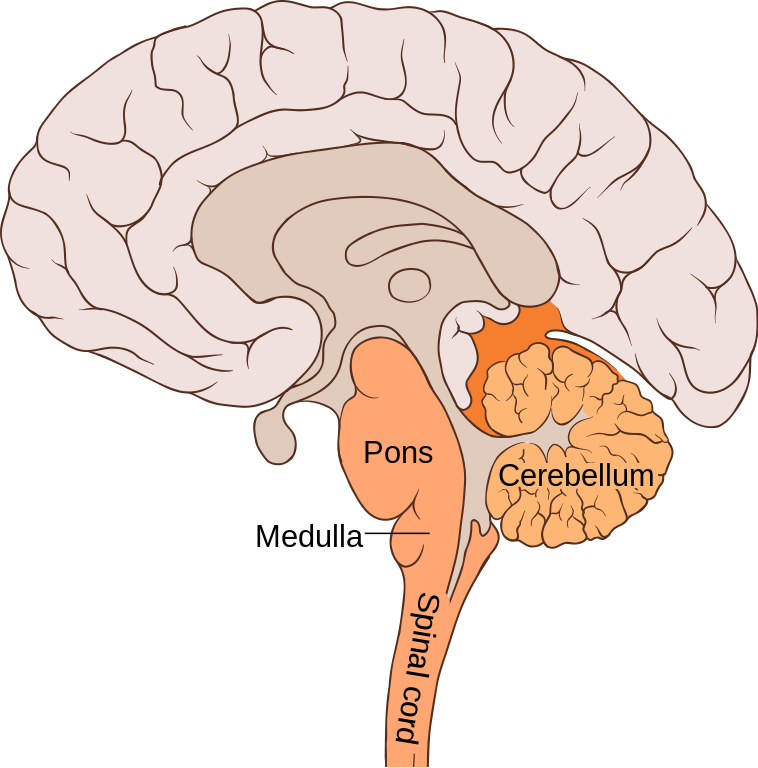
cerebellum (little brain) and pons (bridge)
sensorimotor and cognitive functions. pons is visible as swelling on the inferior surface and also contains the reticular formation
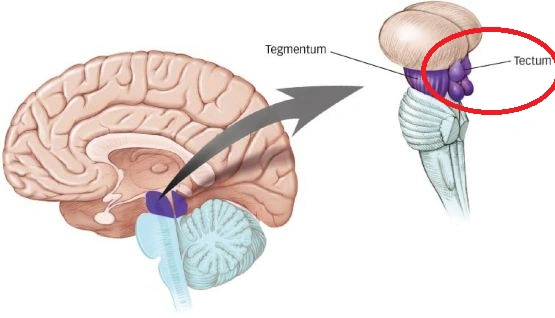
midbrain
tectum and tegmentum
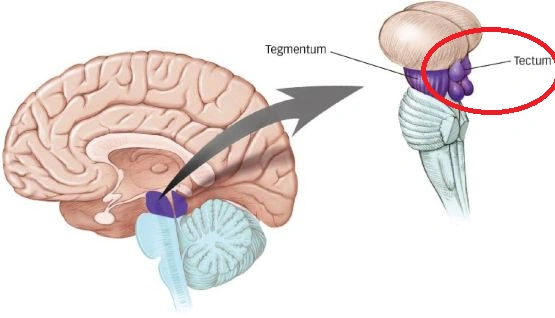
tectum
superior colliculi (visual relay)
inferior colliculi (auditory relay)
in lower vertebrates, simple one optic tectum
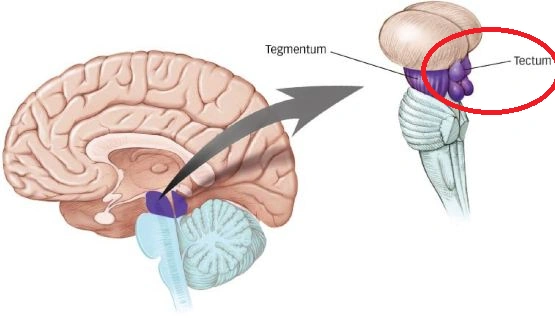
tegmentum
relays reticular formation
red nucleus (sensorimotor)
substantia nigra (sensorimotor cell bodies die here in patients with parkinson’s)
periaqueductal grey (mediates analgesia)
forebrain subcortical structures
thalamus and hypothalamus
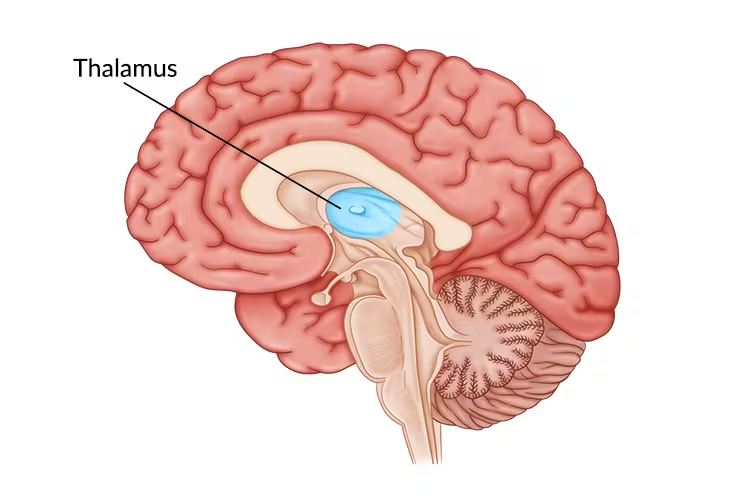
thalamus
top of the brain stem, comprised of many different nuclei
sensory relay nuclei (lateral geniculate nuclei, vision; medial geniculate nuclei, audition; ventral posterior nuclei, touch)
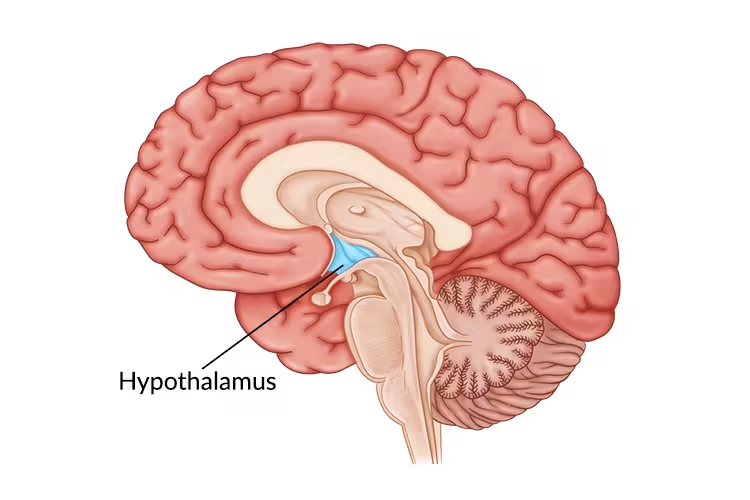
hypothalamus
below the thalamus and pituitary gland (snot gland) is suspended from the hypothalamus
key roles in endocrine function and motivated behaviors
mammillary bodies are two small bumps visible on the inferior surface
optic chaism is the X-shaped part of the optic nerve that lies in front of pituitary
cerebral cortex/cerebral hemispheres
characterized by the cortex with many convolutions, like gyri and fissures.
large division of the brain
90% is the neocortex, comprised of six layers of pyramidal cells and stellate cells
four lobes
gyri
like hills
fissures
like valleys
commissures
large tracts that connect two hemispheres
corpus callosum is the largest
telencephalon
in cerebral cortex, mediates most complex cognitive functions
four lobes
frontal lobe
temporal lobe
parietal lobe
occipital lobe
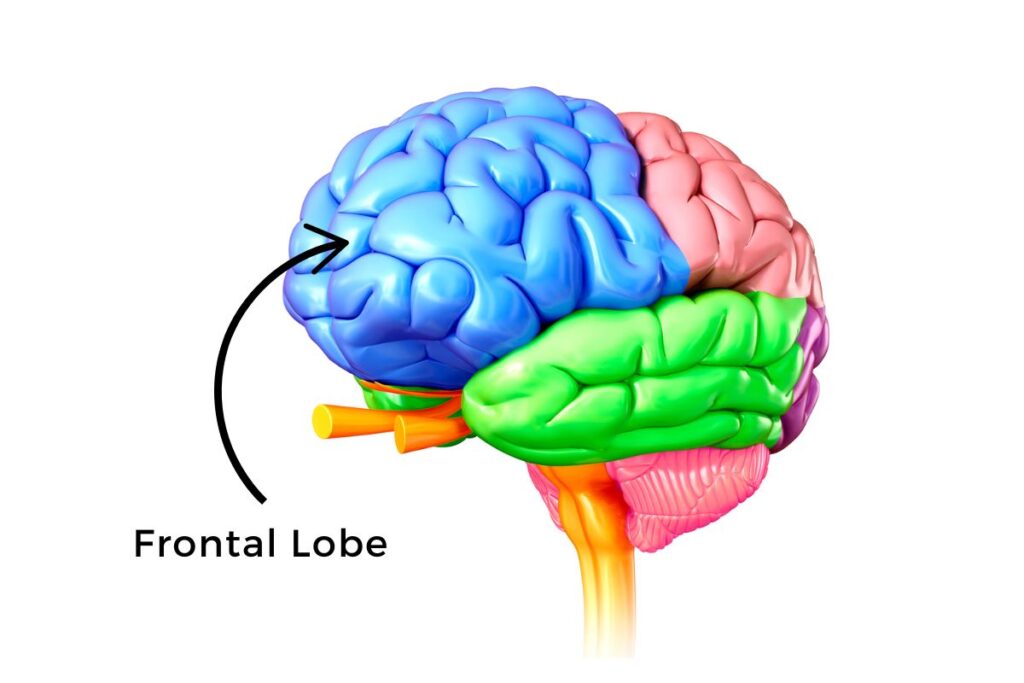
frontal lobe
superior to lateral fissure and anterior to central fissure
cognitive, motor, and emotional functions
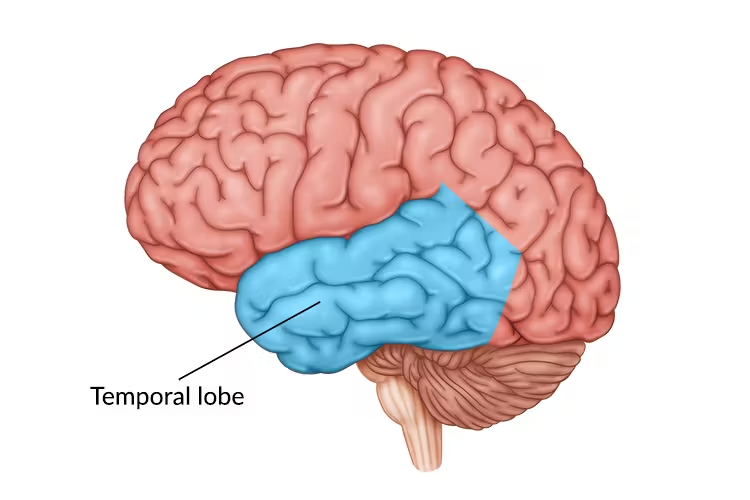
temporal lobe
inferior to lateral fissure
interpreting sounds from the ears and plays a significant role in recognizing and using language
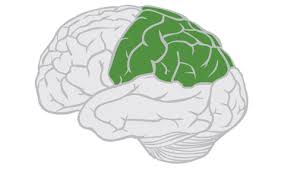
parietal lobe
posterior to central fissure
processes sensory information like touch, pain, and temperature
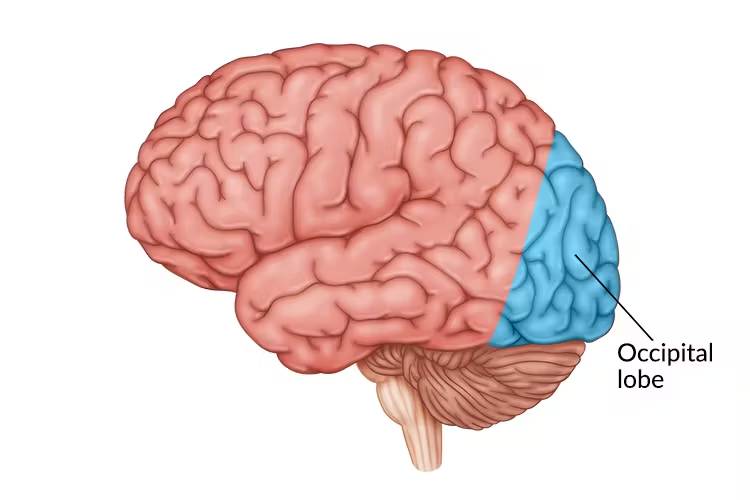
occipital lobe
posterior to temporal love and to parietal lobe
processing visual information
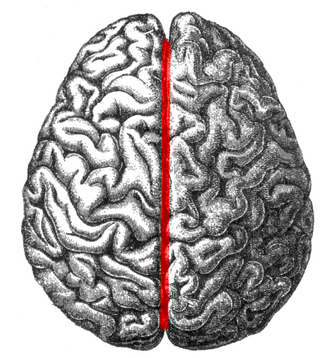
longitudinal fissure
between hemispheres
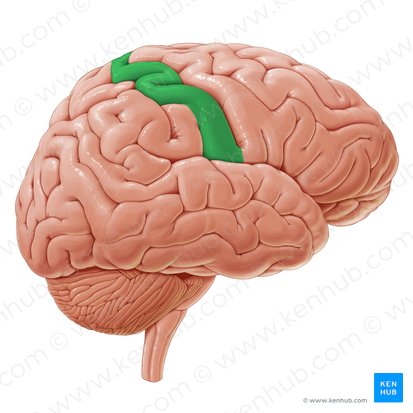
postcentral gyri
in parietal lobe; primary somatosensory cortex
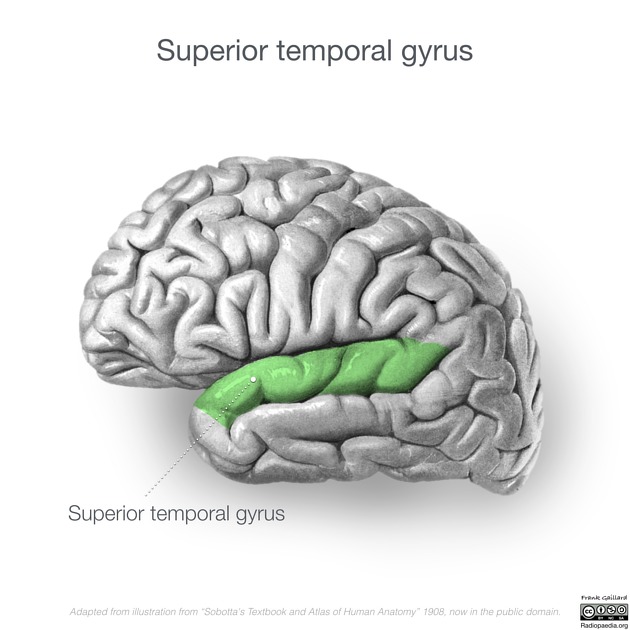
superior temporal gyri
auditory cortex
prefrontal cortex
nonmotor portion of the frontal lobe
limbic system
regulation of motivated behaviors (four Fs)
mammillary bodies, hippocampus, amygdala, fornix, cingulate, cortex, and septum
hippocampus
responsible for your memory and learning
amygdala
processing emotions, particularly fear and anxiety
basal ganglia
involved in movement
amygdala, caudate and putamen, globus pallidus