Biology ✿ Inheritance, variation and evolution
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
meiosis
a type of cell division which forms gametes which are genetically different from parent cells
gametes
sex cells
sexual reproduction
mixing of genetic information (from a mother and father) which leads to variety in the offspring (meiosis)
asexual reproduction
involves only one parent and no mixing of genetic information causing them to produce to genetically identical offspring (mitosis)
what are the stages in meiosis? [3]
DNA replicate to make copies of genenetic information
cell divides twice to form 4 cells
this produces gametes which are haploids and are all genetically different
why are gametes genetically different?
they receive different combinations of chromosomes
why do gametes only contain half the set of chromosomes? (23)
so that at fertilisation, when two gametes fuse they’ll have a full set of chromosomes
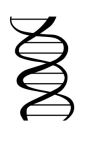
DNA
polymer made up of two strands forming a double helix and stores genetic code
gene
small section of DNA that codes for a protein
genome
the entire genetic code in an organism
genotype
the organisms specific genetic code
phenotype
how the genetic code is expressed in physical characteristics
state 3 advantages of understanding the human genome sequence
can search for genes which cause diseases
helps understanding and treatment of inherited disorders
can trace human migration patterns from the past
chromosome
long molecule of DNA that contains genes
allele
different versions of the same gene
homozygous
2 same alleles e.g. bb or BB
heterozygous
2 different alleles e.g. Bb or bB
what is Polydactyly?
what causes this disease?
having extra fingers/ toes
caused by one parent passing on the dominant allele
what is Cystic fibrosis?
what causes this disease?
a disorder of cell membranes which causes build up of mucus in the lungs
caused by two parents (carriers) who both pass on recessive alleles
embryo screening
before an embryo is implanted in IVF, it is possible to remove cells to analyse the genes for inherited disorders
give 3 ethical reasons why embryo screen is seen as bad
selecting embryos goes against natural life and religious beliefs
some embryos are destroyed, which people are against as they believe is it killing a potential life
implies people with disorders are unwanted, leading to prejudice
sex chromosome for females
XX
sex chromosome for males
XY
variation
differences in the characteristics of an organism’s population
Embryos can be screened for the alleles that cause inherited disorders.
Give two advantages of embryo screening [2]
less people with disorders
parents can decide if they want to continue with pregnancy
![<p>Explain the<strong> process of evolution</strong> that could cause the trend in Figure 4. [6]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b3c69e07-7b33-4eff-9933-caa2d0978ed0.png)
Explain the process of evolution that could cause the trend in Figure 4. [6]
random mutations in genes causes variation of beak length
birds with longer beaks are at advantage as they can survive easily
they reproduce offspring
offspring inherit and pass on longer beak allele
allele frequency increase in each generation
mutation
changes in genes, which only very rarely will lead to a new phenotype and causes all new variants
evolution
the change of genes of a population over time which occurs through natural selection
what does the theory of evolution by natural selection state?
all species of living things have evolved from simple life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago
explain how evolution occurs through natural selection of variants that give rise to phenotypes best suited to their environment.
variation in a population is caused by mutations
there is competition between organisms to survive (food), the better adapted survive and reproduce offspring
offspring inherit better adapted alleles
over many generation, they cannot produce fertile offspring with other populations as a new species has been made
natural selection
the processes of organisms who are best adapted to environment survive and pass on their genes
selective breeding
the process of humans breeding plants or animals for specific genetic characteristics
give 4 examples of desired characteristics that people may want during selective breeding
gentle nature of domestic animals
animals which produce more milk or meat
large/ unusual flowers
disease resistant
Describe the steps of selective breeding [4]
choose parents with desirable characteristics
parents are bred
only offspring with desirable characteristics are bred
this is repeated over generations until the characteristic is fully developed
genetic engineering
the process of modifying an organisms genome by using another organisms genes to get a desired characteristic
Describe the steps of genetic engineering [4]
enzymes are used to isolate required gene
gene is inserted into a vector (e.g. plasmid) so that gene can be inserted into cell
gene is transferred into organism at an early stage of development so they fully develop with desired characteristic
what are 3 advantages of genetical engineering
GM usually involves transferring only one gene so it is precise
GM crops can produce toxins to kill insects
GM crops can be herbicide resistant making agriculture faster
what are 3 disadvantages of genetical engineering (in plants)
GM crops which are herbicide resistant may breed with weeds
limited research on how GM crops impact human health
can reduce biodiversity
give 3 causes of extinction
new predators
new diseases
natural disaster
how does a fossil form?
organism dies
layers of sediment form on top
lack of oxygen prevents decay of bones
eventually, the bones are mineralised
state 3 reasons why the fossil record is incomplete?
some fossils are destroyed by earthquakes or erosion
early forms of life were soft bodied so they decayed
dating older fossils is hard
state 3 ways to reduce the rate of development of antibiotic resistant strains
only prescribing antibiotics when needed
complete full course of antibiotics so no resistant bacteria is left
don’t prescribe antibiotics for viral infections as they only kill bacteria
Explain how the widespread use of antibiotics in farming is a threat to human life. [4]
antibiotic is spread into the environment by faeces
bacteria in land become antibiotic resistant
these bacteria are human pathogens
which cause human diseases which cannot be treated
who introduced the ‘three-domain system’?
Carl Woese
Carl Woese developed the ‘three-domain system’ of classification.
Describe the ‘three-domain system’ of classification.
the system is based on DNA evidence
Eukaryota → plants and animals
Bacteria → all true bacteria
Archaea → usually extremophiles
state the taxonomic hierarchy
Kingdom
phylum
class
order
family
genus
species
What is the naming system that Carl Linnaeus introduced?
binomial system
binomial name format
genus species
give 3 reasons why children look different
environmental factors
different combination of alleles
multiple genes determine appearance
Explain why sexual reproduction could produce a new variety [3]
fertilisation of gametes
leads to mixing of chromosomes
one copy of each allele is from each parent
how are new species caused by?
isolation of population
change of habitat
A gene codes for a particular sequence of __________ _______
amino acids