EXAM THREE BLUEPRINT
1/155
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
156 Terms
how many cranial bones does the head have?
eight
what is the most important cranial bone?
frontal bone
what is the function of the frontal bone?
protect and reinforce brain tissue and give facial appearance
where is the frontal bone located?
forehead
where is the parietal bone located?
top of the head
which cranial bones has two of them?
parietal and temporal
where is the temporal bone located?
near the sides of the ears
where is the occipital bone located?
back of the neck (kitchen)
where is the ethmoid bone located?
deep inside the middle of the nose
where is the sphenoid bone located?
the base of the skull, towards the front of the head, and behind the eyes.
how many bones are in the adult skull
22
what are immovable joints called?
sutures
how many facial bones are there?
14
what is a temporal artery
an artery that branches from the external carotid artery and has palpable pulse
what does the temporomandibular joint do?
allows the jaw to move forward, side to side and backwards
what is the function of the parotid glands
secretes saliva into the mouth
what glands has the largest salivary glands?
parotid
what does the submandibular glands do?
drains saliva through the wharton’s ducts
what is wharton’s ducts
major salivary ducts located on the floor of the mouth that carries saliva from the submandibular gland to the mouth.
what is the function of the sinuses?
decreases the weight of the skull and gives resonance to voice during speech
what do the sinuses surrounds?
the nasal cavity
what are the four paranasal sinuses?
frontal, ethmoid, sphenoids and maxillary
where is the frontal sinus located?
above the eyes in the center of the forehead
where is the ethmoid paranasal sinus located?
between the eyes but not palpable
where is the sphenoids paranasal sinus located?
behind the nasal cavity but cannot touch
where is the maxillary paranasal sinus located?
in the cheekbones below the eyes (largest)
what is the primary function of the nose?
smell, breathe, moisten and filter the air
what are nose turbinates?
bony structures covers by soft mucosa that cleanses, moistens and warms the air as it passes the nostrils to the lungs
what are nose adenoids?
clusters of lymphatic tissue and apart of the immune system
what is the mouth?
the first portion of alimentary canal for ingestion and digestion of food
what are the soft palates of the mouth used for?
responsible for closing off the nasal passages during the act of swallowingwh
where are the hard palates?
roof of the mouth
what is the jaw bone (mandible)
strongest and largest bone of the face
what are the three salivary glands that secrete saliva to start the process of digestion and moisten the throat?
parotid, submandibular and sublingual
what are the stensen’s ducts
the route saliva flows from the parotid gland into the mouth
what are the functions of teeth?
chewing and breaking down food
where is the tongue located and its function?
muscle located on the floor of the mouth and organ of the taste
what is the word used for throat?
pharynx
what is the trachea?
the windpipe that connects the voice box (larynx) to the lungs.
what is the function of the trachea?
carries air to and from the lungs during breathing.
what is the epiglottis?
a flap that separates the trachea from the esophagus
what is the function of the epiglottis
prevents aspiration of food and fluids
what are tonsils and where are they located?
lymphatic tissue located in the back of the pharynx
what is the function of the tonsils?
part of the body’s immune system
what is dysphagia and who is referred to for this condition?
difficulty swallowing and a speech language pathologist
what are the signs of dysphagia?
coughing during meals and drooling of saliva
name the different types of headaches
migraines, tensions, clusters and sinuses
what does a migraine headache consist of?
pulsating intense pain that lasts for a few hours to 3 days and has sensitivity to light, noise and smells
what does a tension headache consist of?
feeling pressure in the front or sides of the head
what does a cluster headache look like?
stabbing constant pain on one side of the face
what does a sinus headache look like?
throbbing pain in the front of the face (nasal congestion)
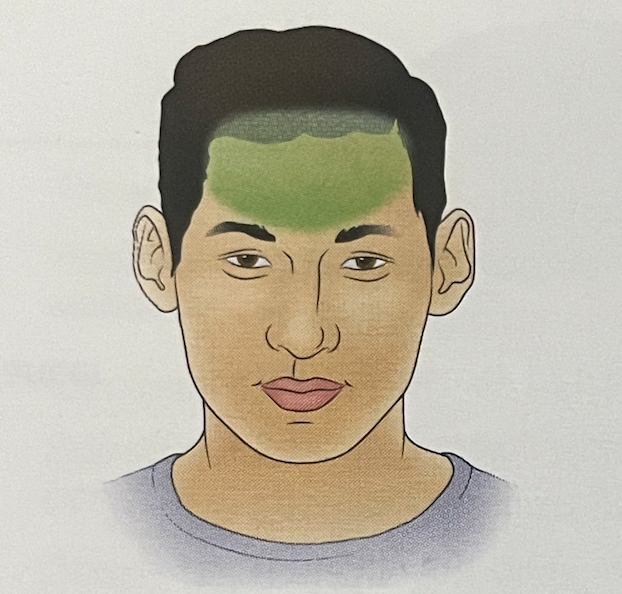
what headache is this?
TENSION
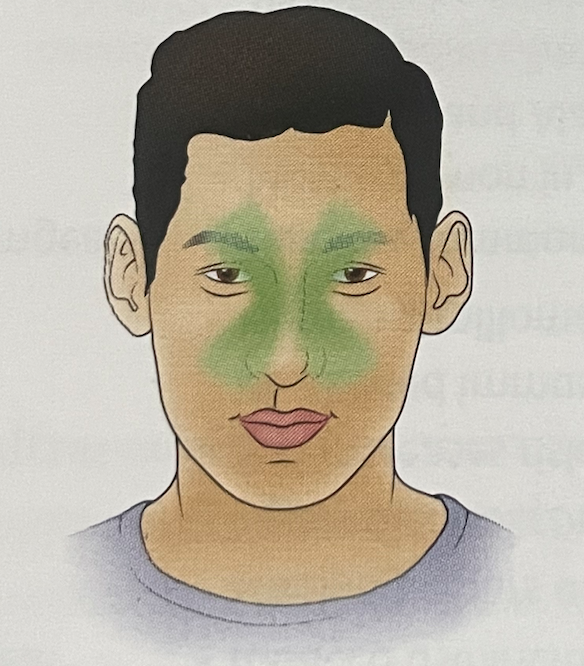
what headache is this?
SINUS
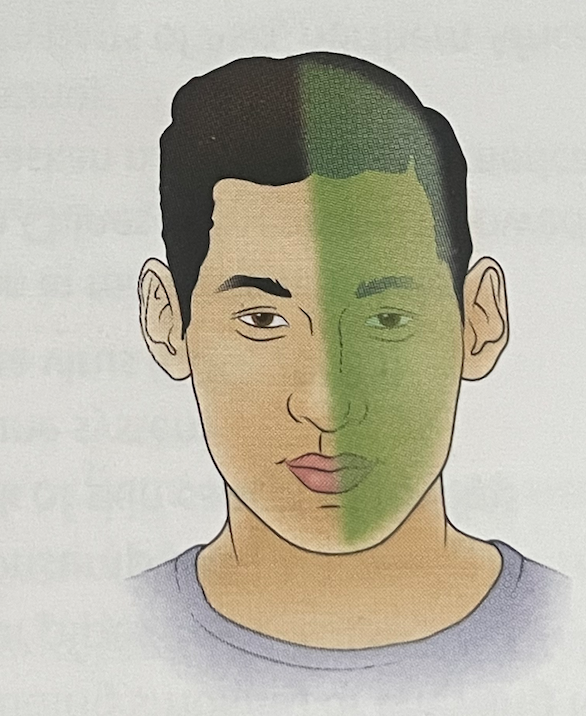
what headache is this?
MIGRAINE
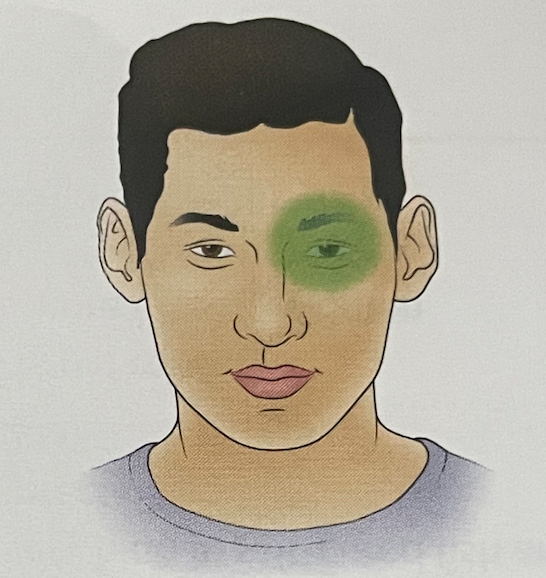
what headache is this?
CLUSTER
what is the neck’s function?
protects the nerves that carry sensory and motor impulses from the brain to the body
what are the major muscles that support the neck?
sternocleidomastoid and trapezuis
what is the hyoid bone and the function?
horseshoe shaped bone where the tongue rests and aids the tongue in moving and swallowing
what is the thyroid cartilage function
protects the vocal folds
what is the terminology for “adam’s apple”
thyroid cartilage
what is the cricoid cartilage function
forms the lower and back part of the cavity of the larynx
what is the larynx
the voice boxw
what is the thyroid’s function
plays a role in metabolism, iodine and hormone production
what do the carotid arteries do?
transports oxygenated blood supply to the brain
what do the jugular veins do?
transports deoxygenated blood from the brain, face and neck to the heart
when inspecting the pt’s head, what are you looking for?
size, shape, configuration and movement
what are the two things you must do together when assessing the head?
inspect and palpate
when looking at a pt’s head, what are some normal findings?
symmetric head, no involuntary movements, no pain, tenderness or masses during palpation and normocephalic
what is normocephalic?
a normal head shape for the age
what are the most common types of headaches?
tension
what are interventions a pt should use when dealing with a cluster headache?
rock in a sitting position, pace, and push their hands into the area of most pain
when inspecting a pt’s FACE, what are the normal findings?
symmetrical face, eye contact, no uncontrollable muscle movement, no edema and no pulsations
when palpating a pt’s face, what are the steps?
use the finger pads, palpate face for swelling and tenderness
place fingers in front of earlobes and corner of eyes and palpate temporal arteries
place fingertips in front of each ear and ask pt to open and close
when palpating a face, what are the normal findings?
no facial tenderness, nontender temporal arteries and mouth opens 1.4-2 inches
when inspecting the nose of a pt, where should you stand?
in front of the patient
when palpating the nose, what should you be palpating for?
tenderness
when inspecting and palpating the NOSE, what are the normal findings?
symmetrical nose, straight midline, no drainage and lesions and face and skin color are the same.
NOSEBLEEDS: why should the head be above the heart level?
to reduce the bleeding
NOSEBLEEDS: what does tilting the head forward?
drains the blood from the nares
what would be proper instructions for a pt dealing when a nosebleed?
the pt should hold pressure and breathing through their mouth and after 5 mins of pinching to check for bleeding.
how should a nurse palpate the frontal sinuses?
pressing up and under the eyebrows
how should the nurse palpate the maxillary sinuses?
place thumbs below the cheek bones
what are the normal findings of palpating of the sinuses?
no tenderness or pain
when inspecting the mouth, what is the proper way to assess?
assess the mouth from the front and work towards the back of the mouth.
when inspecting and or palpating the mouth, what type of gloves should the nurse wear and why?
clean gloves because you will be coming in contact with the pt’s saliva
when assessing the mouth, what should the nurse be looking for?
redness, tenderness, lesions or abnormalities
what should a female pt do before assessing of their lips?
remove their lipstick
when inspecting the lips, what are the five things the nurse should be looking at?
color, lesions, moisture, swelling and symmetry
what are normal findings of a pt’s lips?
upper lip everted, symmetrical lips, pink in color with no swelling, lesions or cracking
what is angioedema
swelling of the lips due to the allergic reaction
when inspecting the teeth, what should the nurse be looking for?
color, dentures, missing teeth or tooth decay
when inspecting the teeth, what should the nurse do?
ask pt to clench their teeth to assess
what are the normal findings of the teeth?
white to ivory color of teeth, clean debris, smooth edges and 32 or 28 teeth
what are the steps of assessing the buccal mucosa?
-have pt remove dentures
-inspect and palpate the buccal mucosa
-use the tongue depressor to hold the tongue out of the way to visually see the gums
what are the normal findings of the cheek?
pink, smooth, moist, no tenderness when touching
what are the normal findings of the tongue?
pink tongue and saliva present with no lumps and etc
what are the normal findings of the soft and hard palates?
stensens ducts are draining, pink to light red and moist
what are the steps of inspecting the tonsils?
-moisten the gauze with warm water
-ask pt to tilt head back and say ah
-use tongue depressor and ask pt to say ah to asses the throat
-touch the back of the pharynx to get a gag reflex
what are the normal findings of tonsils
pink in color
what does a +1 mean in terms of tonsils?
tonsils are visible and protruding