Ch. 2 Research Methods
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Prefrontal Lobotomy
Surgical procedure that severs fibres connecting the frontal lobes of the brain from the underlying thalamus.
Facilitated Communication
A technique that involves a facilitator physically supporting the hand, arm, or wrist of a person with communication difficulties to help them type messages on a keyboard, letter board, or other communication device.
Heuristic
A mental shortcut that allows people to make decisions and solve problems quickly and efficiently, often based on past experiences.
Naturalistic Observation
Watching behaviour in real-world settings without trying to manipulate the situation.
External Validity
Extent to which we can generalize findings to real-world settings.
Case Study
Research design that examines one person or a small number of people in depth, often over an extended time period.
Existence Proof
Demonstration that a given psychological phenomenon can occur.
Survey
a quantitative and qualitative research method that collects data from a group of people to learn about their opinions, attitudes, and behaviours — usually through questionnaires or interviews.
Random Selection
Procedure that ensures every person in a population has an equal chance of being chosen to participate.
Reliability
The consistency of a measure, indicating that it produces stable and consistent results over time.
Inter-rater Reliability
the degree of agreement among different observers assessing the same phenomenon.
Validity
Extent to which a measure assesses what it purports to measure.
Response Set
Tendency of research participants to distort their responses to questionnaire items.
Correlational Design
Research design that examines the extent to which two variables are associated.
Positive Correlation
A relationship between two variables where an increase in one variable corresponds to an increase in the other variable.
Negative Correlation
A relationship between two variables where an increase in one variable corresponds to a decrease in the other variable.
No (Zero) Correlation
A relationship between two variables where changes in one variable do not predict changes in the other variable.
Confirmation Bias
the tendency to search for, interpret, favor and recall information in a way that confirms or supports one's prior beliefs or values.
Scatterplot
Grouping of points on a two-dimensional graph in which each dot represents a single person's data.
Illusionary Correlation
Perception of a statistical association between two variables where none exists.
Experiment Group
Research design characterized by random assignment of participants to conditions and manipulation.
Control Group
In an experiment, the group of participants that doesn't receive the manipulation.
Independent Variable
Variable that an experimenter manipulates.
Dependent Variable
Variable that an experimenter measures to see whether the manipulation has an effect.
Operational Definition
A working definition of what a researcher is measuring.
Placebo Effect
Improvement resulting from the mere expectation of improvement.
Blind Study
Unaware of whether one is in the experimental group or control group.
Experimenter Expectancy Effect
Phenomenon in which researchers' hypotheses lead them to unintentionally bias the outcome of a study.
Double-Blind Study
When neither researchers nor participants are aware of who's in the experimental or control group.
between-subjects design
different groups are assigned to control or experimental conditions.
Demand Characteristics
Cues that participants pick up from a study that allow them to generate guesses regarding the researcher's hypothesis.
Informed Consent
Informing research participants of what is involved in a study before asking them to participate.
Statistics
Application of mathematics to describing and analyzing data.
Descriptive Statistics
Numerical characterizations that describe data.
Central Tendency
Measure of the "central" scores in a data set, or where the group tends to cluster.
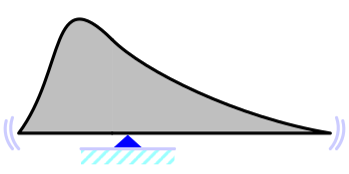
Mean
Average; a measure of central tendency
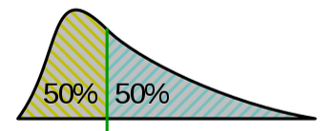
Median
Middle score in a data set; a measure of central tendency
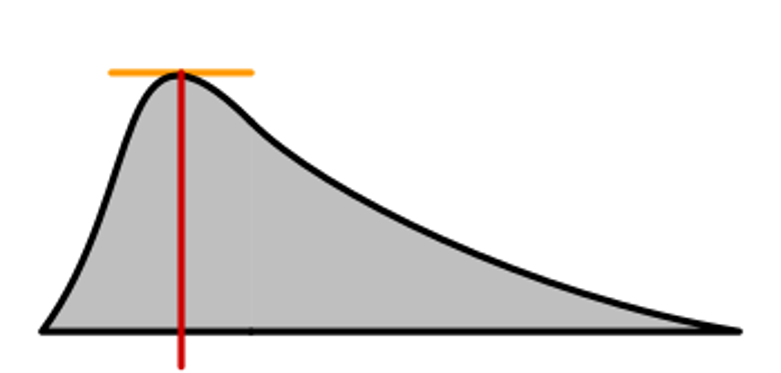
Mode
Most frequent score in a data set; a measure of central tendency
Variability
Measure of how loosely or tightly bunched scores are.
Range
Difference between the highest and lowest scores; a measure of variability.
Standard Deviation
Measure of variability that takes into account how far each data point is from the mean.
Inferential Statistics
Mathematical methods that allow us to determine whether we can generalize findings from our sample to the full population.
base rate
How common a characteristic or behaviour is in the general population
Cognitive biases
Systematic patterns of deviation from norm or rationality in judgment, often affecting decision-making.
Hindsight Bias
The tendency to see events as having been predictable after they have already happened, leading to overconfidence in one's ability to predict outcomes.
Overconfidence
The tendency to overestimate one's own abilities, particularly in making accurate predictions or judgments.
Random assignment
Randomly sorting participants into groups
within-subject design
each participant acts as his or her own control
Extrasensory perception
Perception of events outside the known channels of sensation
Scientific method
A systematic approach used in psychology and other sciences to formulate hypotheses, conduct experiments, and analyze data to draw conclusions and advance knowledge.
meta-analysis
A statistical technique that combines the results of multiple studies to identify patterns, trends, or overall effects across a body of research.
Nocebo Effect
Harm resulting from the mere expectation of harm.
Hawthorne Effect
The alteration of behaviour by study participants due to their awareness of being observed.
Covert Observation
Observation in which the observer's presence or purpose is kept secret from those being observed
malingering
Deliberate faking of a physical or psychological disorder motivated by gain
Self-report measure
A method in which participants provide subjective data about their own thoughts, feelings, or behaviours, often through questionnaires or interviews.
Practical significance
The importance or relevance of a research finding in real-world applications
Statistical significance
applies that the results are not likely due to chance
Social Desirability Bias
the tendency of survey respondents to answer questions in a manner that will be viewed favourably by others, often leading to distorted or inaccurate self-reports.
Participant Observation
A qualitative research method where the researcher immerses themselves in a group or community to observe behaviours and interactions in their natural context.
Structured Observation
A research method where observers record specific behaviours in a predetermined manner, often using checklists or coding systems.
Analytical Thinking
A cognitive process that involves breaking down complex information into smaller parts to understand and evaluate it systematically.
Intuitive Thinking
A cognitive process that relies on instinctive judgments and immediate perceptions rather than systematic reasoning. It often involves quick decision-making based on prior experiences and feelings.
Conceptual Definition
Explains the meaning of a concept or construct in abstract, theoretical terms. ie. happiness, driving performance
leading questions
items are presented in an unbalanced way that can be overtly or subtly suggest that one viewpoint or response is preferable to another
loaded questions
items that contain emotionally charged words that suggest one viewpoint or response is preferable to another, or they contain assumptions with which the option to disagree is not provides
double-barrelled question
items that ask about two issues within one question, forcing respondents to combine potentially different opinions into one judgment
double negatives
items whose phrasing contains two negative words
Experimental Design
a structured process for conducting experiments to test hypotheses and establish cause-and-effect relationships
Ethics
represents a system of moral principles and standards
Internal Validity
the extent to which a research study establishes a trustworthy cause-and-effect relationship.
representative heuristic
a mental shortcut or rule of thumb that people use to estimate the probability of an event by comparing it to an existing prototype or stereotype in their mind, rather than using statistical data
availability heuristic
a mental shortcut where people estimate the likelihood or frequency of an event based on how easily examples or instances of it come to mind