Lec 11 - November 14 2025
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
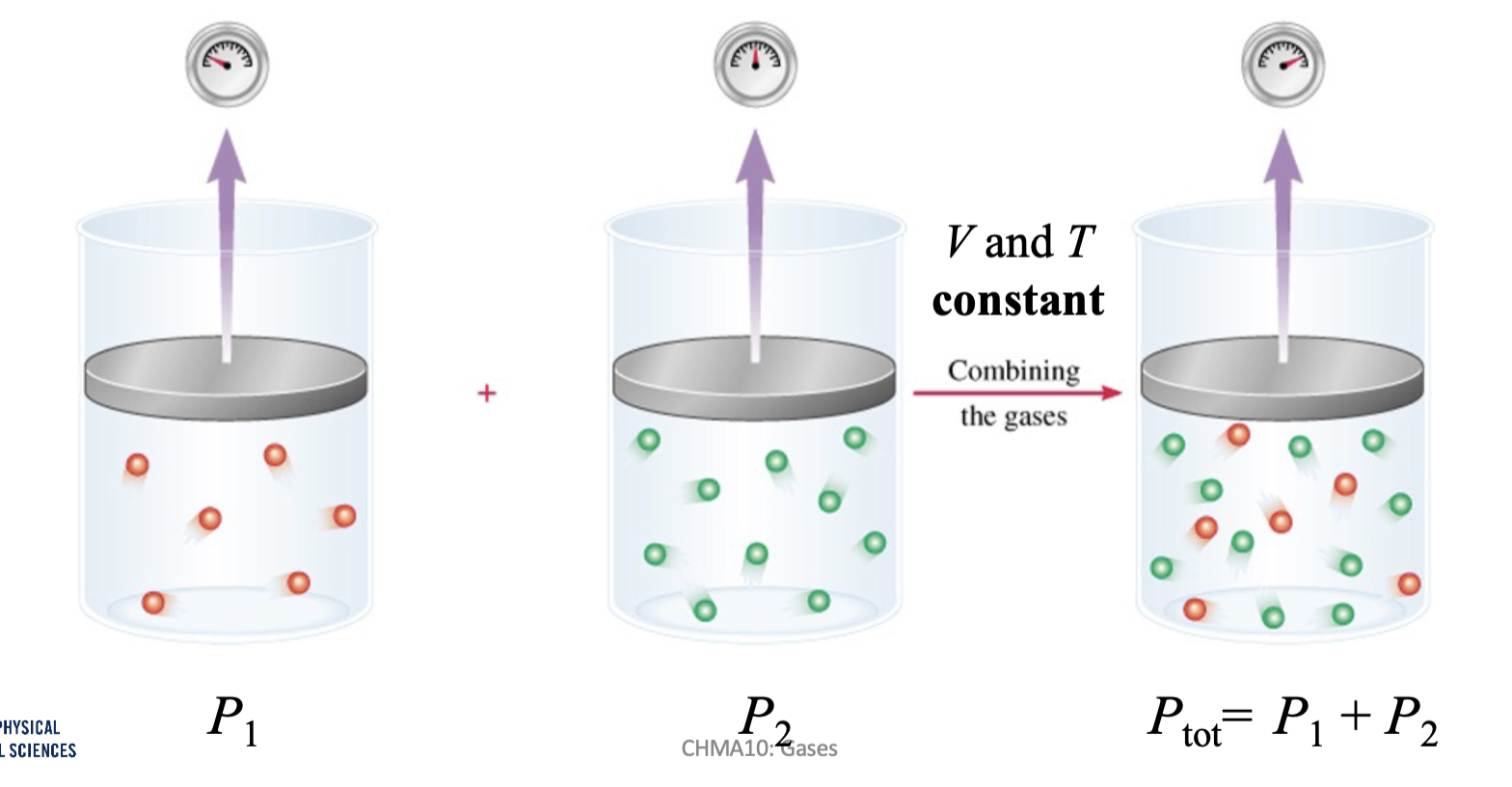
Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures
The total pressure of a mixture of gases is the sum to the partial pressures of the mixture
Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressure Equation
The total pressure is the sum of partial ones
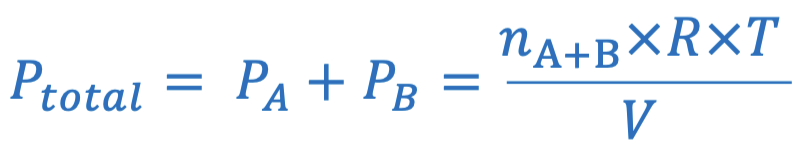
If the temperature and volume of the mixture of 2 gases are the same, we can use this equation
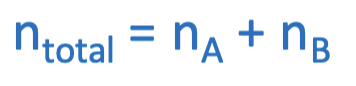
Mole fraction, X
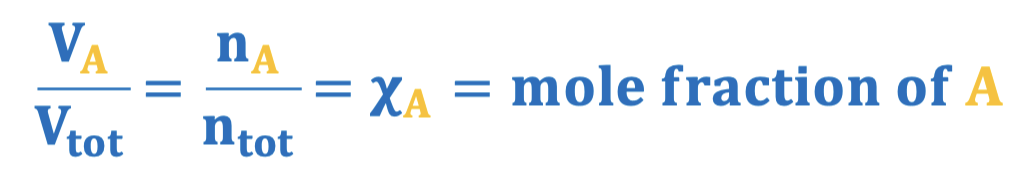
Partial pressure of a gas equation using mole fractions

What happens when a gas is collected over water?
there is a water vapour present (PH2O)
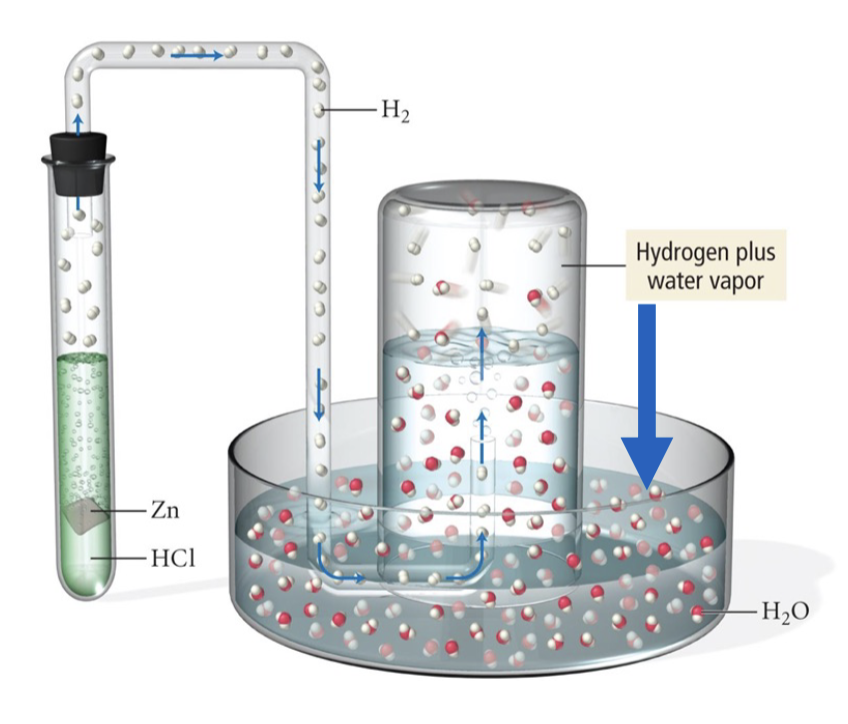
PH2O equation for Ptotal
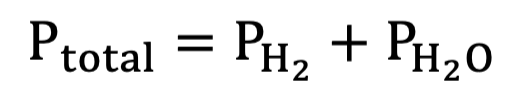
PH2O equation for PH2
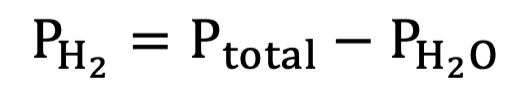
T/F Vapour pressure of water is constant
False
T/F: Vapour pressure of water varies with the temperature
True
Kinetic molecular theory
Average kinetic energy (1/2mv²) of the particles is proportional to the temperature in K
Boyle: At constant temperature and moles
Pressure is inversely proportional to volume
volume increases, pressure decreases, collisions decrease
Charles: At constant pressure and moles
Volume is proportional to Temperature
Temperature increases, volume increases, collisions increase
Avogadro: At constant pressure and moles
Volume is proportional to moles
moles increase, volume increases, collisions increase
Dalton: At constant volume and temperature
Ptot= Pa + Pb + … Pn
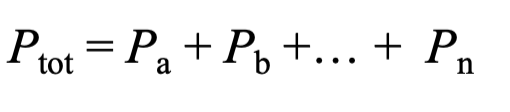
Average kinetic energy of gas particles is proportional to the ___________
gas temperature
gas particles have the same average kinetic energy at the ________
same temperature
Kinetic energy of a single molecule equation

If gas particles have the same kinetic energy but different masses, then they must also have:
different velocities
Root mean square velocity (urms)
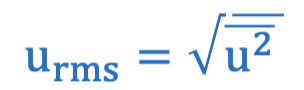
Average kinetic energy equation in terms of root mean square velocity
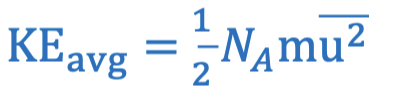
Average kinetic energy equation in terms of temperature
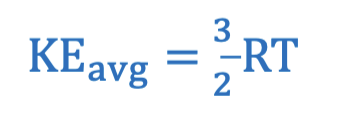
root mean square velocity equation using gas constant
this equation is proportional to molar mass and temperature
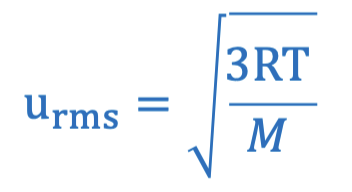
Diffusion
migration of molecules due to random molecular motion
Rate of diffusion is proportional to:
average molecular speed
average molecular speed is proportional to:
molecular weight
Effusion
the escape of molecules through a tiny hole
Rate of effusion is inversely proportional to:
molecular mass
Graham’s Law definition
the rate of effusion is inversely proportional to molecular mass
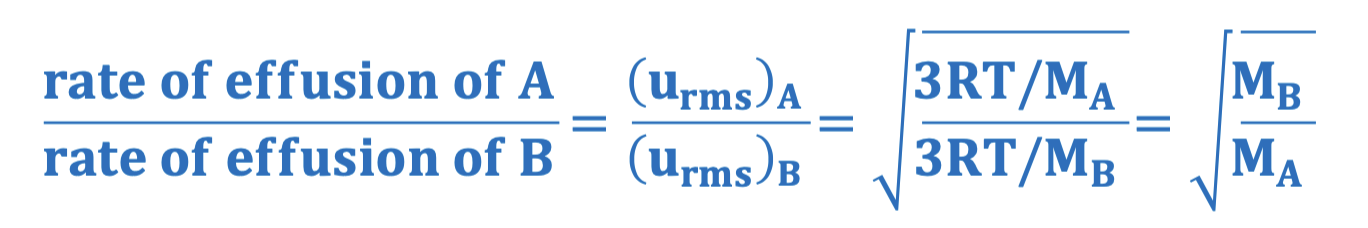
Graham’s Law equation

In Graham’s Law, how do you determine which effusion rate for a gas goes in the numerator and which goes in the denominator
The lighter gas (molar mass) goes on top and the heavier gas goes on the bottom
Non-Ideal gases
gases that deviate from the gas laws
At high pressure and low temperature, the ideal gas model fails. Why might this be?
two assumptions are violated
volume of gas is negligible
there are no forces interacting on particles
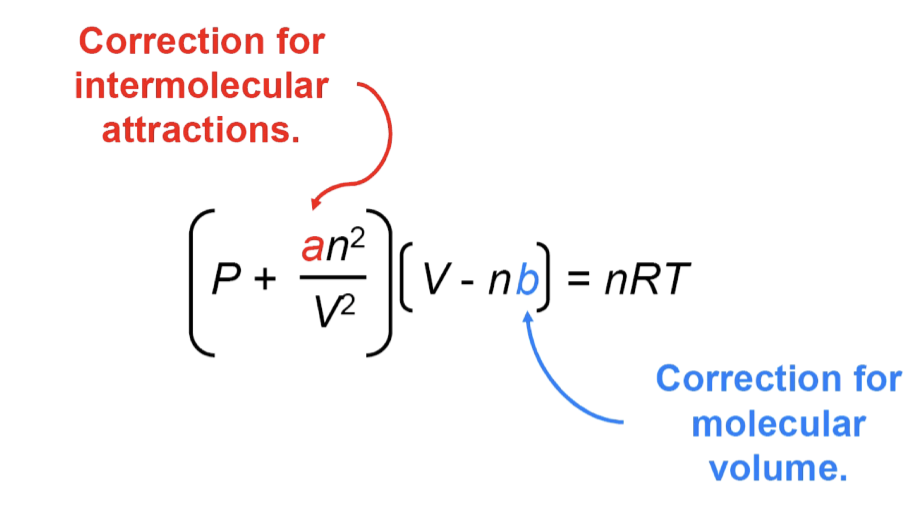
Volume corrections
ideal gas law assumes gases take up zero volume
need to account for the actual volume gas occupies
the more gas, the more subtraction needed
the larger the gas molecules, the more volume will be occupied
Volume correction calculation
V-nb
When is the volume correction between ideal gases and real gases most needed?
at high pressures, small volumes, or near the condensation point
Pressure corrections
ideal gas law assumes gases don’t interact
need to include factor that accounts for intermolecular forces
real gas exerts less pressure than an ideal gas at low pressure
at high pressure repulsive forces are dominant
the more gas, the more adding is required
When is the pressure correction between ideal and real gases most needed?
at low pressures or near the condensation point
Pressure correction calculation
P + an²/V²
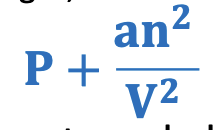
Van Der Waals equation
Polar species have a _____ value of a (from equation) since they are more “sticky”
higher
Species with a _______ volume have a _______ volume of b
larger, larger