Biochem Amino Acids Functions
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
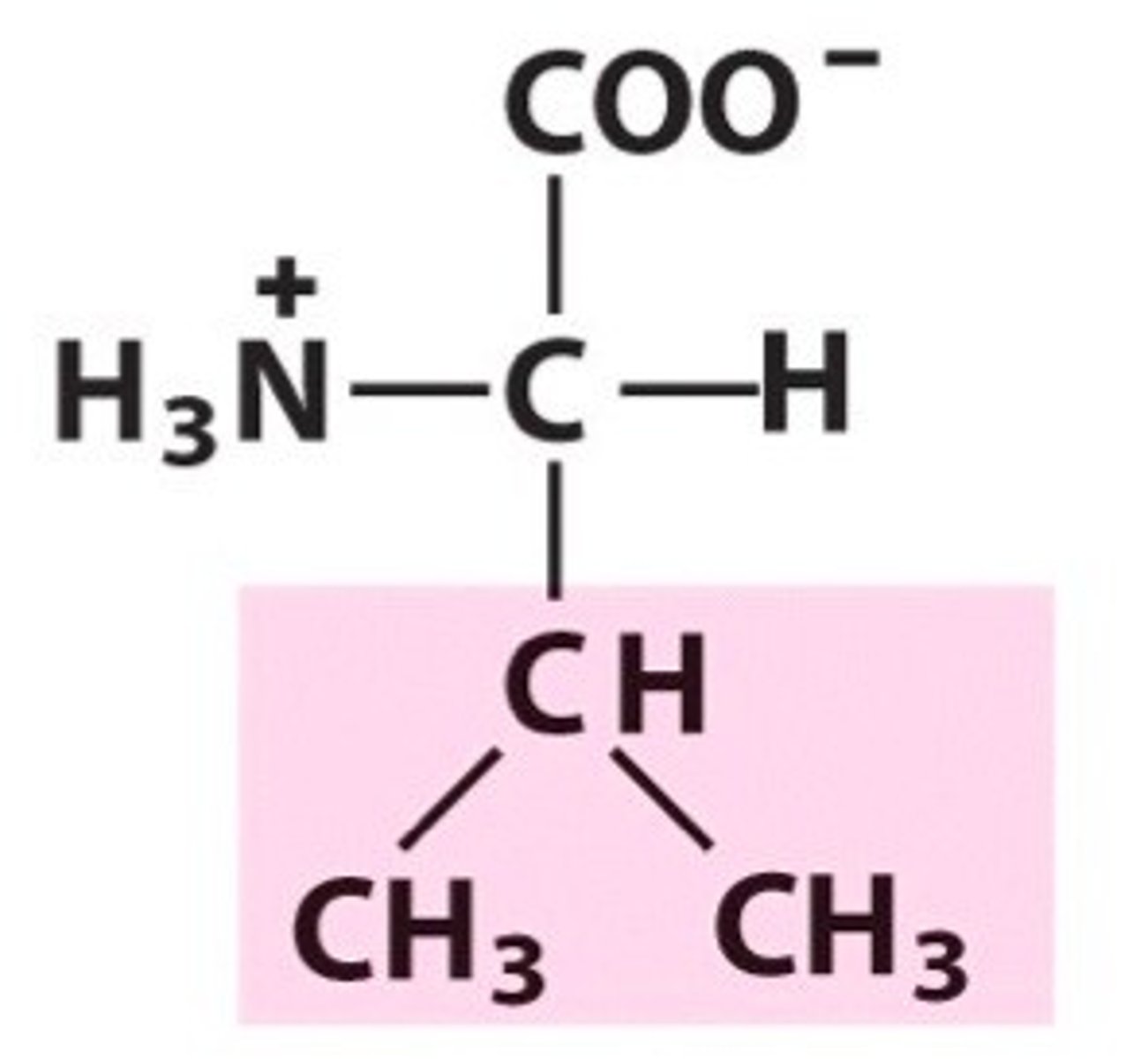
Alanine, Ala, A
Mother of all amino acids.
Plays a major role in the transfer of nitrogen from peripheral tissue to the liver
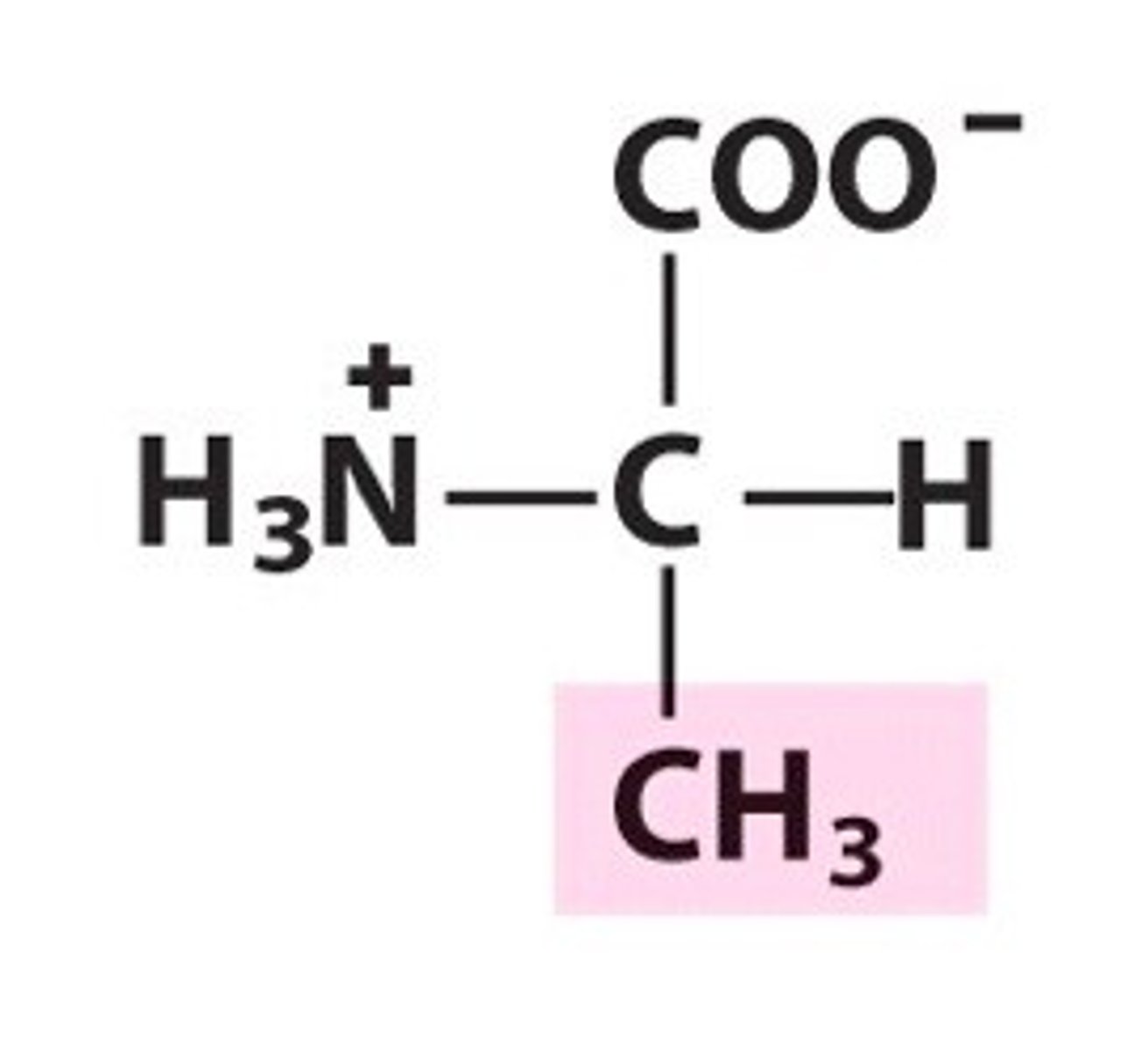
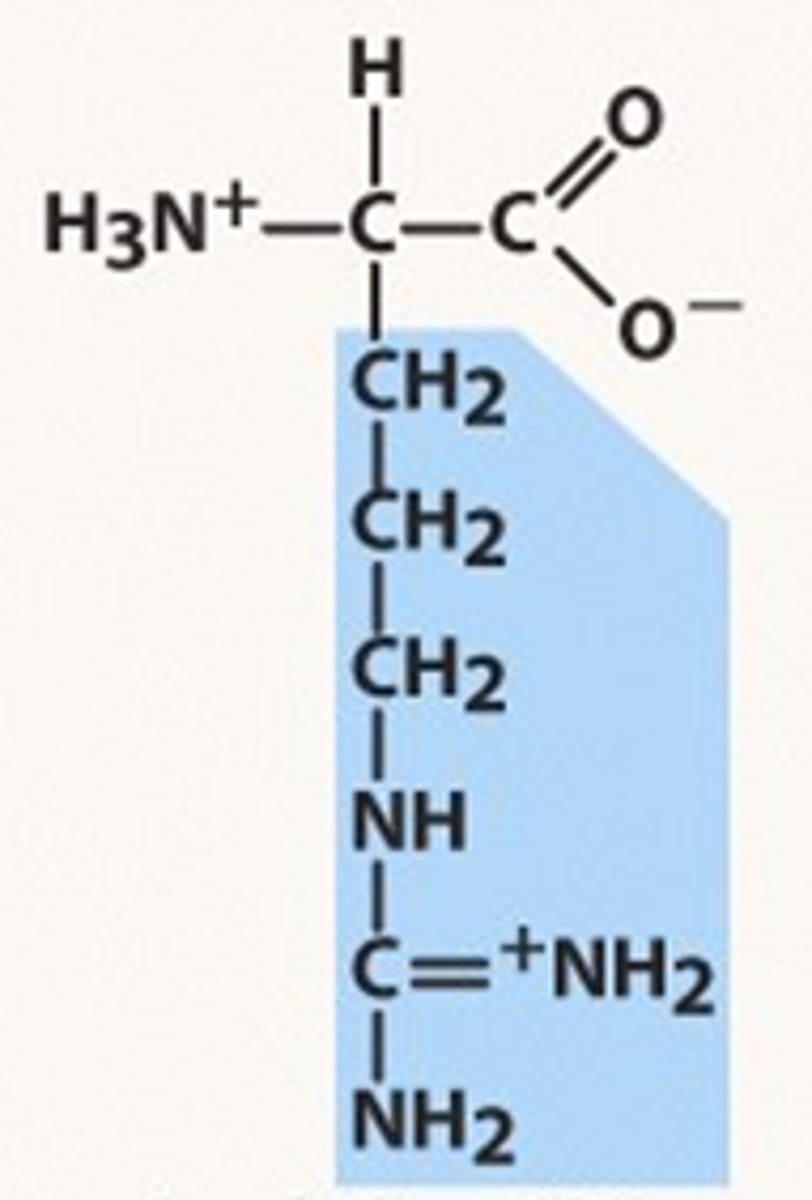
Arginine, Arg, R
Increases the size and activity of the thymus gland
Treats sterility in men by increasing sperm count and blood flow to the penis
Major component of collagen
Aids in stimulating the pancreas to secrete insulin
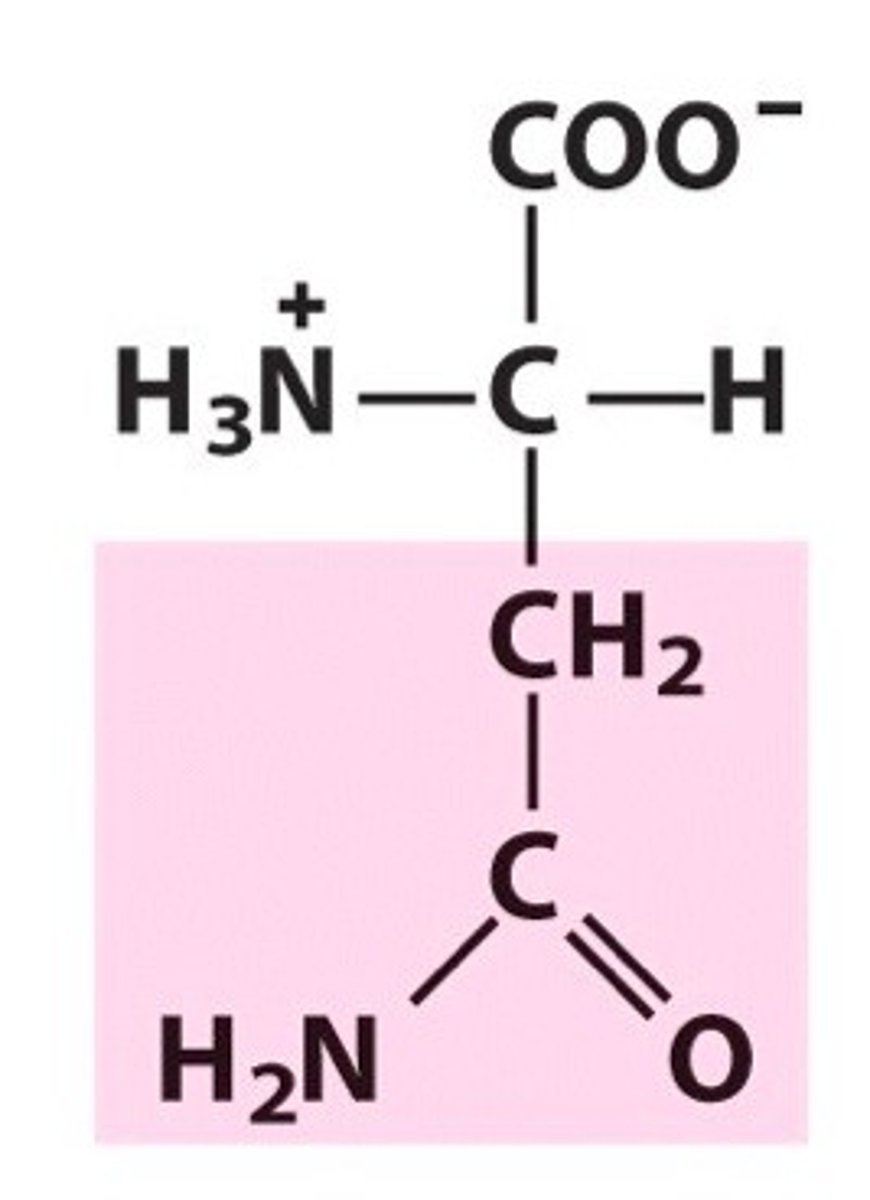
Asparagine, Asn, N
Required by the nervous system because it maintains balance in the brain and nervous system
Detoxifies ammonia from the body
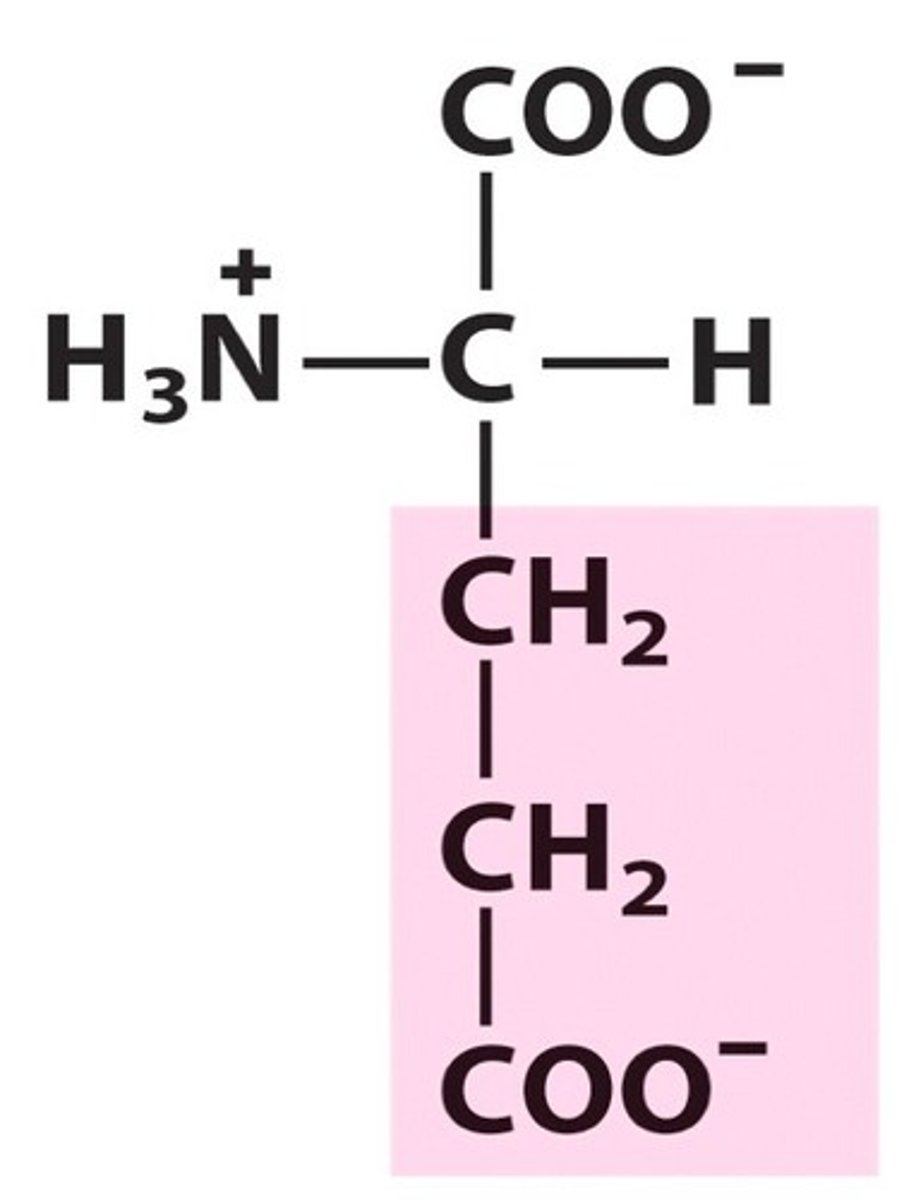
Aspartic Acid, Asp, D
Major excitatory neurotransmitter
Increases stamina and helps with chronic fatigue and depression
Protects the liver via the expulsion of ammonia
Combines with other amino acids to absorb toxins and remove them from the body
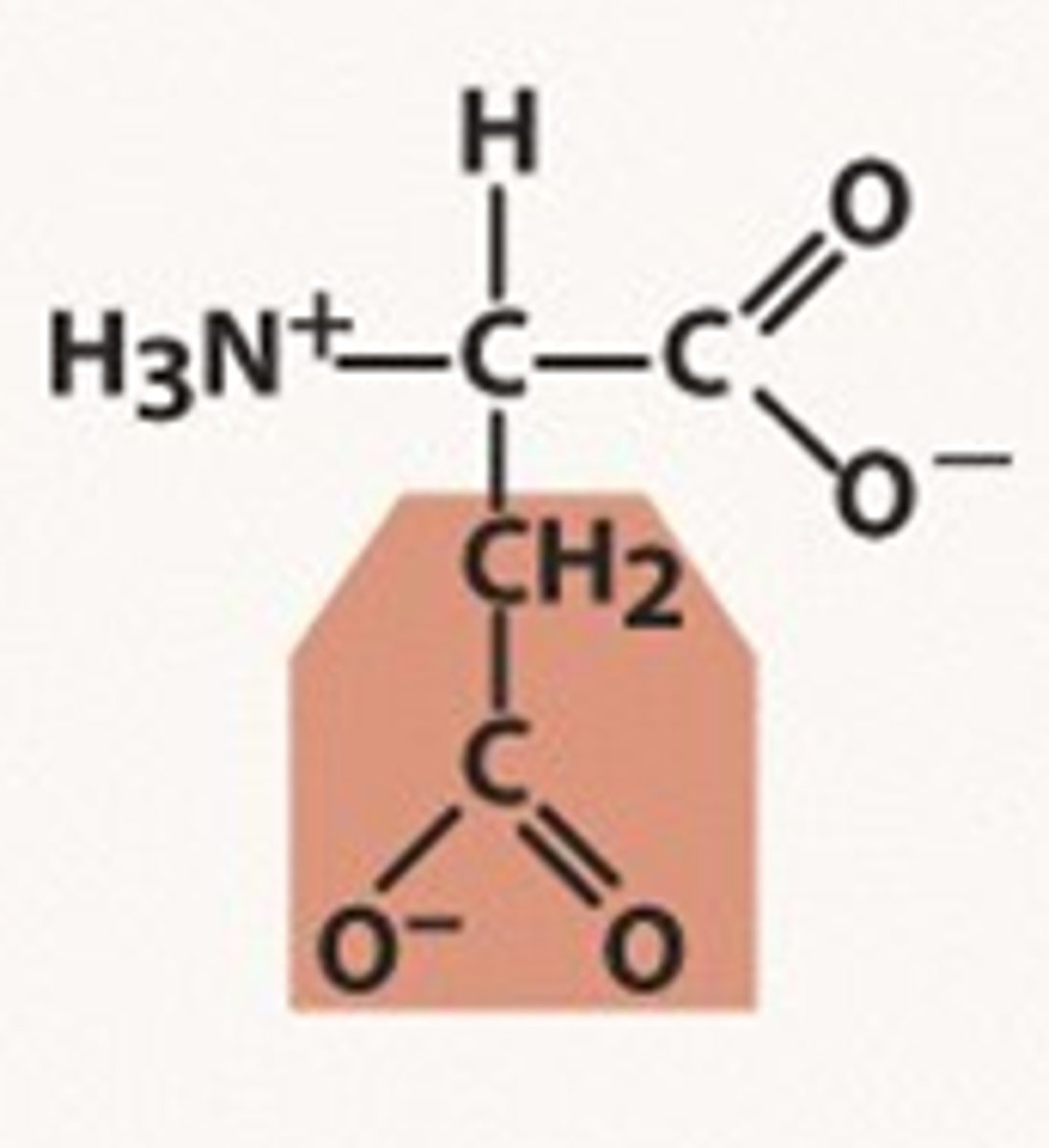
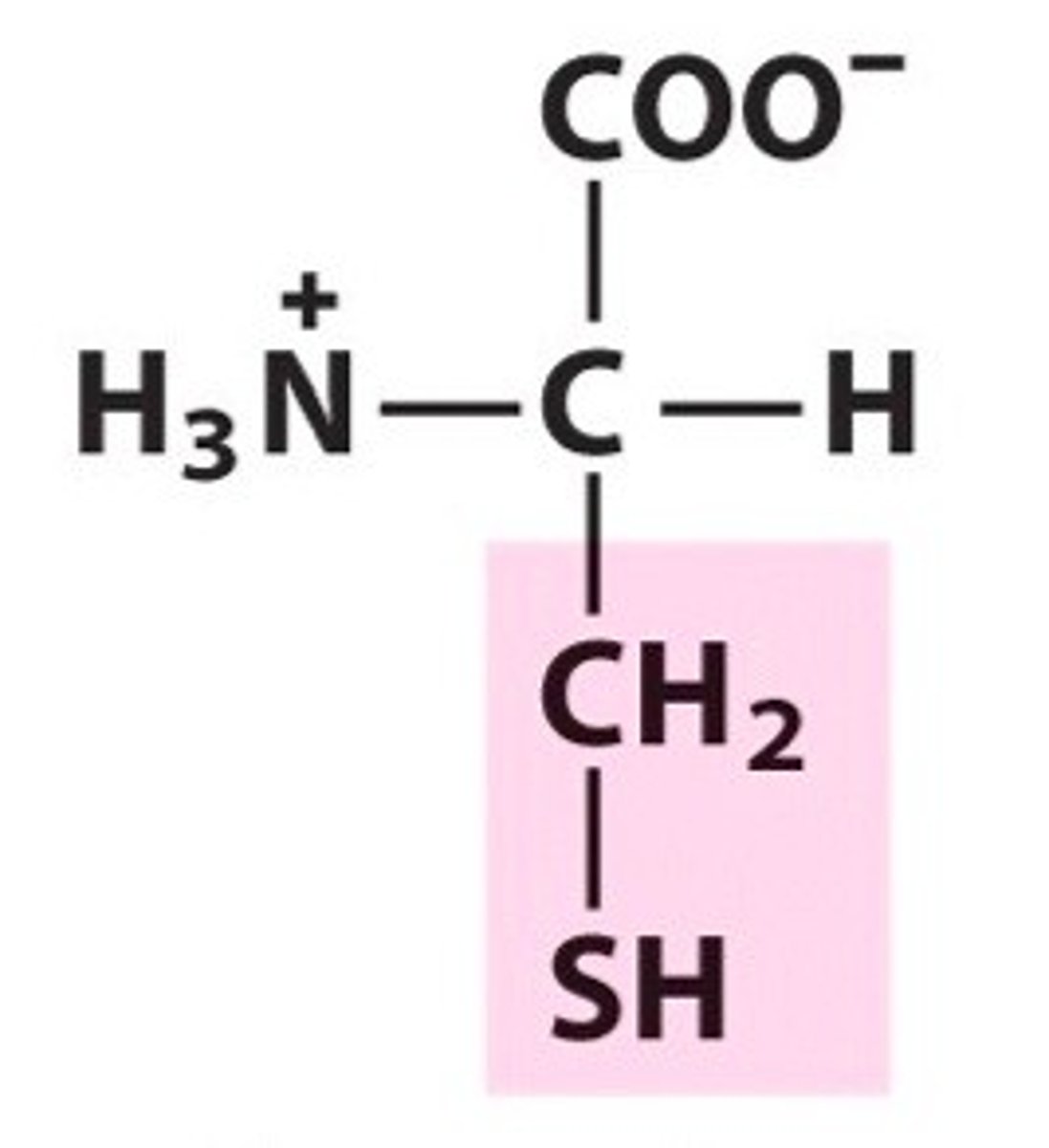
Cysteine, Cys, C
Functions as a powerful antioxidant in detoxifying toxic substances
Slows down the aging process
Promotes healing from severe burns and surgery
Skin and hair are made of 10-14% cystine (Found abundantly in natural curly hair)
Glutamic acid, Glu, E
Excitatory neurotransmitter for the CNS, brain, and spinal cord
Aids in the transport of Potassium into spinal fluid
Helps correct personality disorders and is used in the treatment of epilepsy, mental retardation, muscular dystrophy, and ulcers
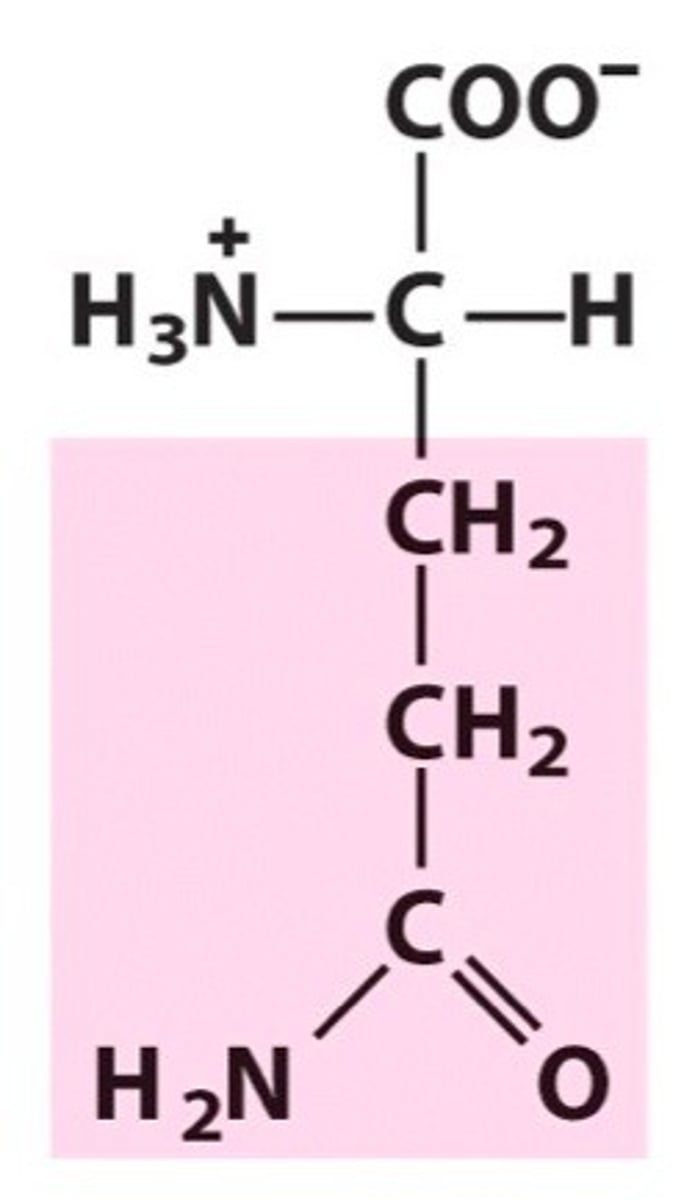
Glutamine, Gln, Q
Commonly found in muscles
Helps and maintains muscle tissue
Considered "brain fuel" as it increases brain function and mental activity
Assists in maintaining the proper acid/alkaline balance in the body
Glycine, Gly, G
Simplest amino acid
Optically inactive because of the a lack of an asmetrical alpha-carbon
"Stops" muscle degeneration
Promotes healthy prostate, central nervous system, and immune system
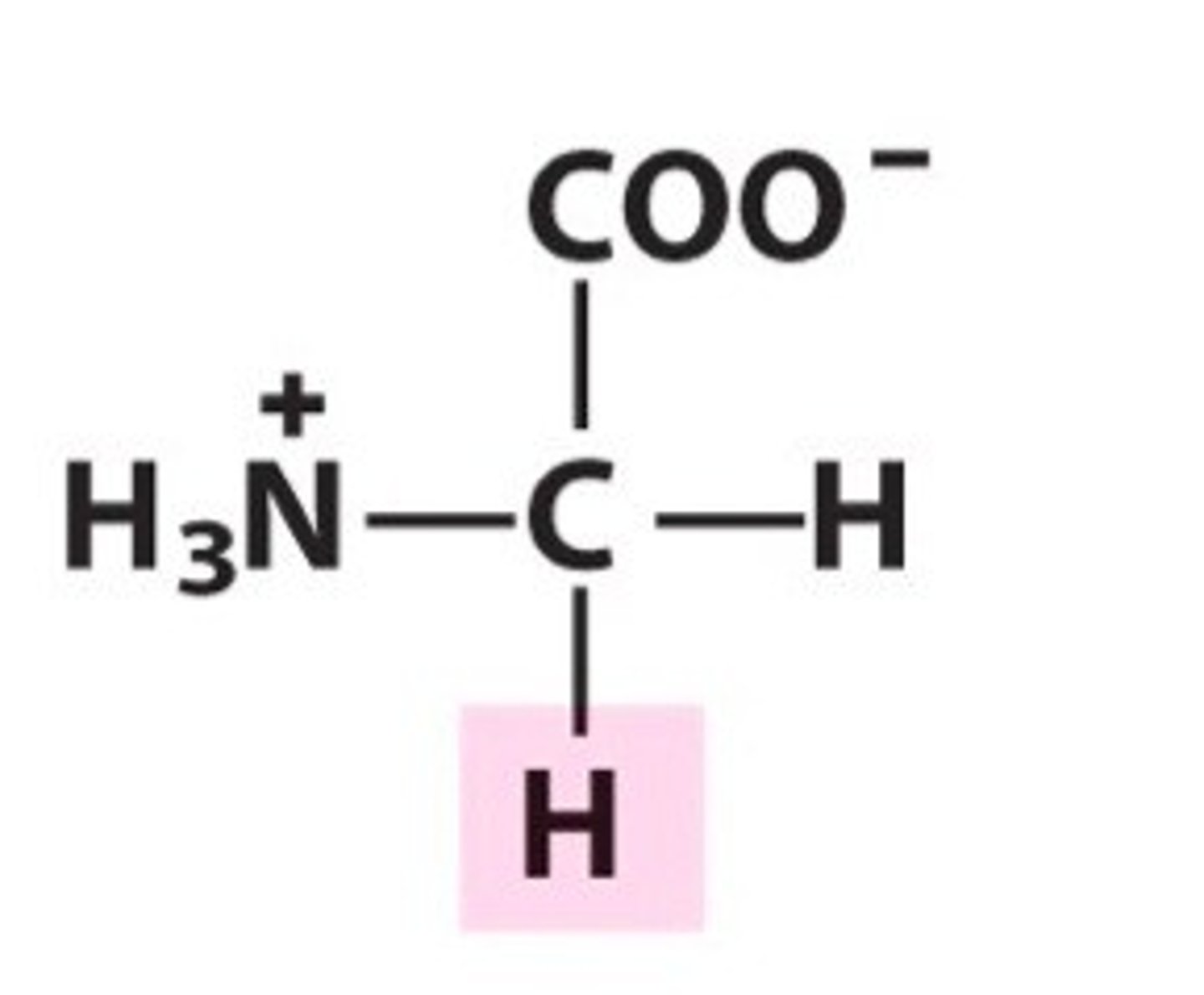
Histidine, His, H
Only amino acid being able to buffer pH levels
Found abundantly in hemoglobin
Important for the maintainance of myelin sheaths, protecting nerve cells
Causes vasodilation from the decarboxylation of histadine and causes the symptoms most associated with fevers and allergies
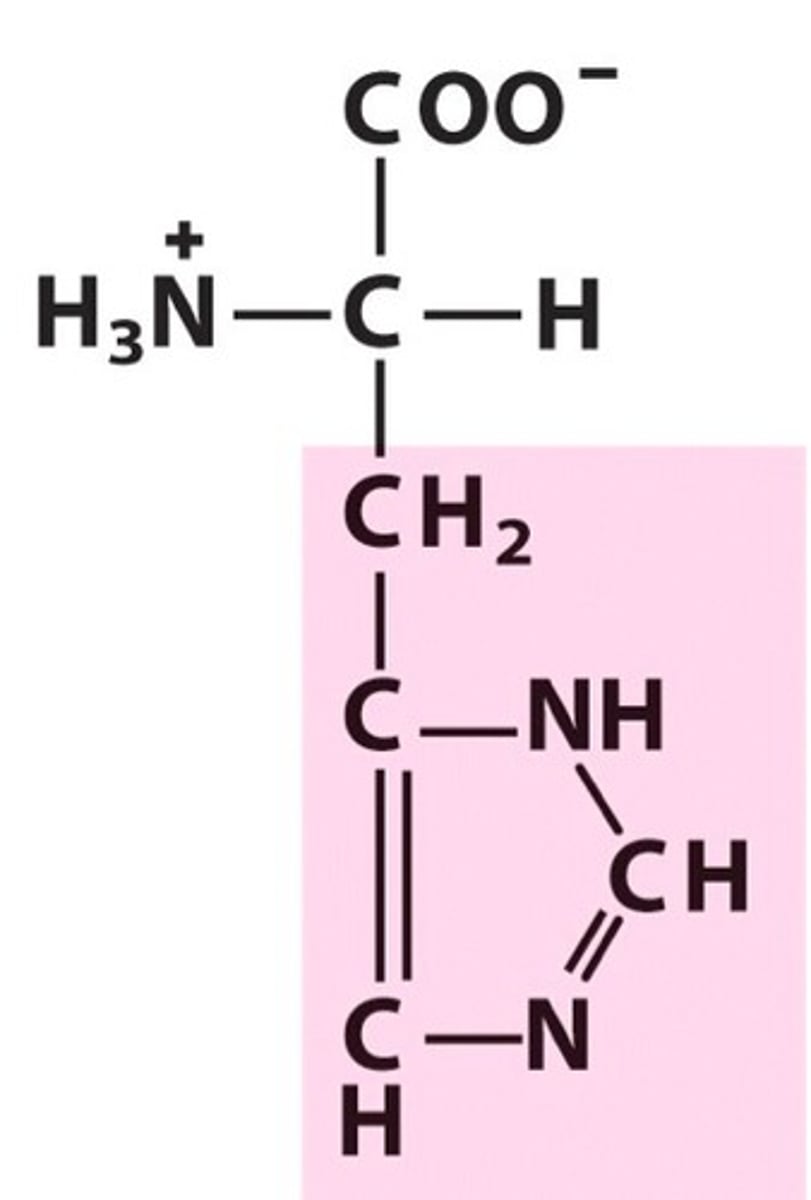
Isoleucine, Ile, I
Needed for the formation of hemoglobin
Balances blood energy and sugar levels
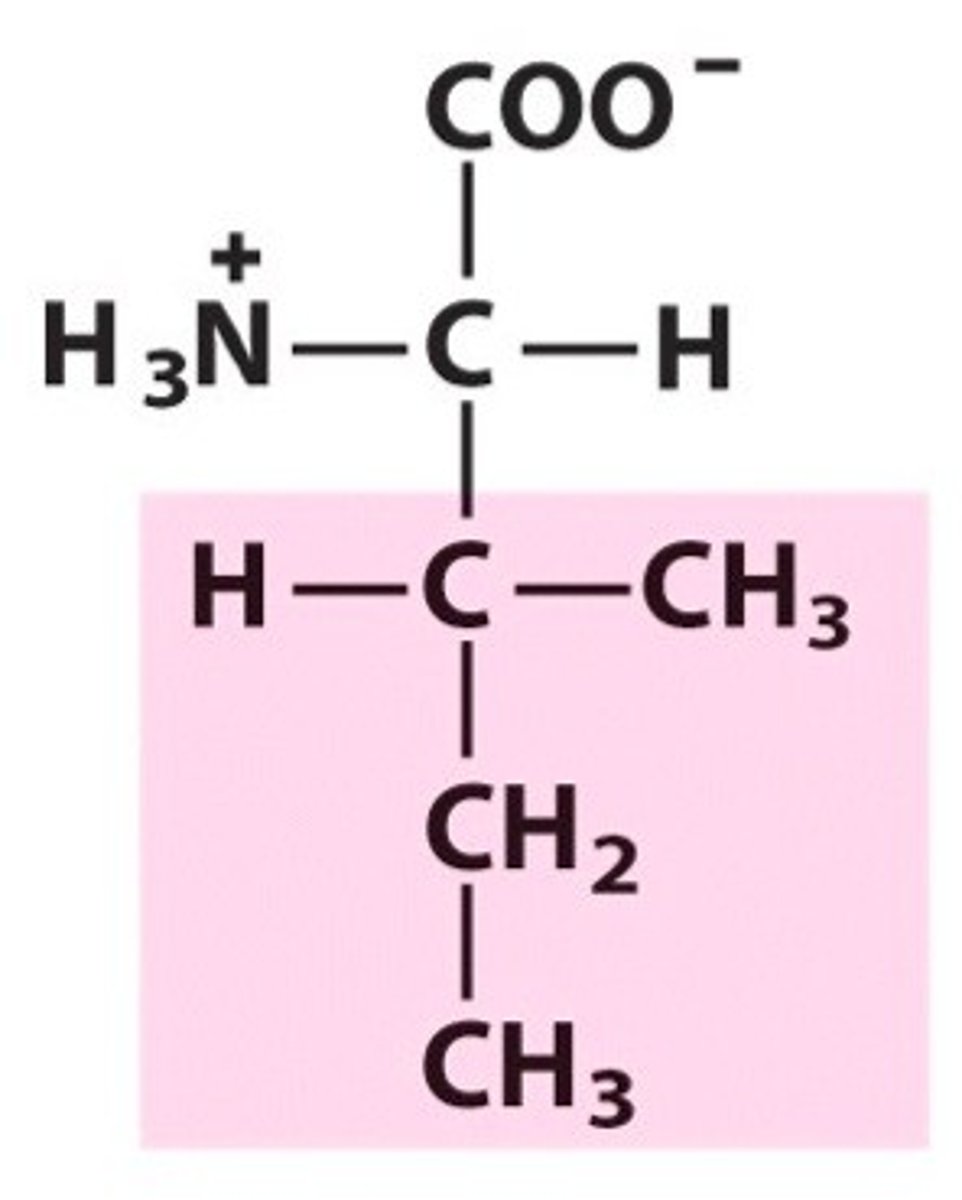
Leucine, Leu, L
Associated with digestive enzymes
Works together with Isoleucine and Valine to promote the healing of muscle, skin, and bone tissue
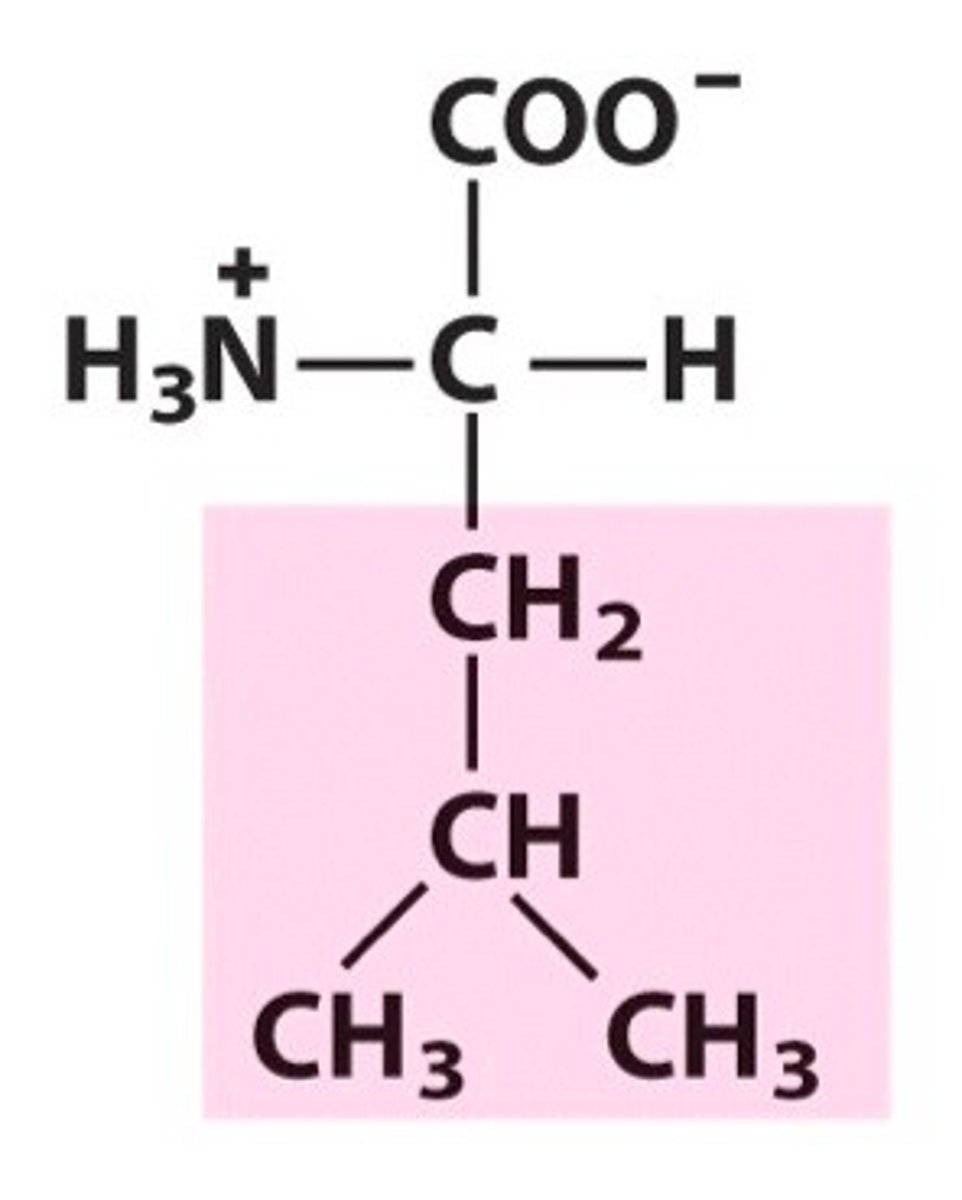
Lysine, Lys, K
Found in collagen
Aids in the assimilation of other amino acids
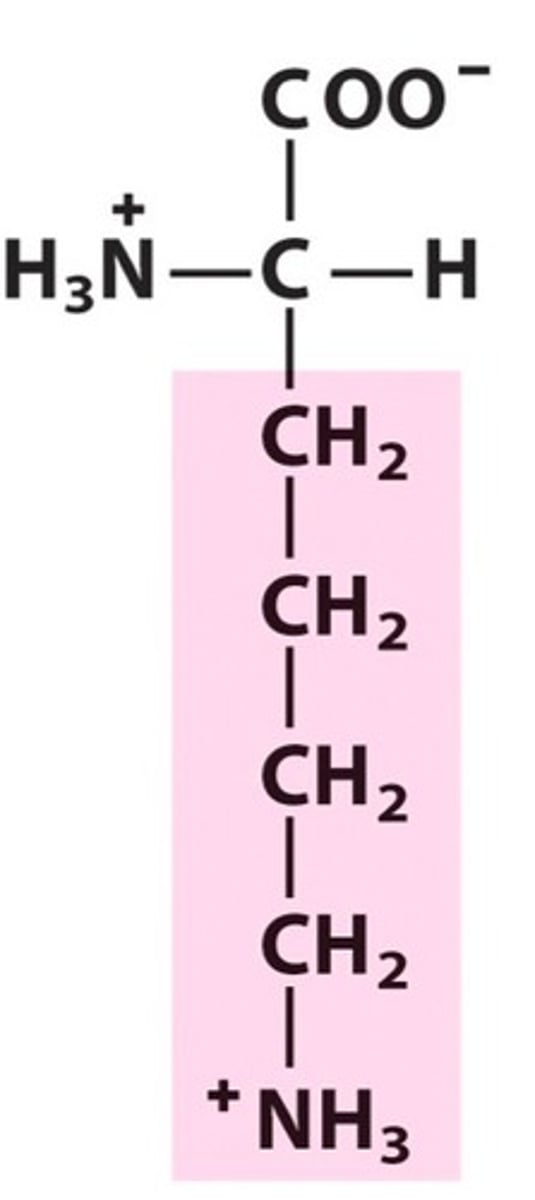
Methionine, Met, M
Initiates protein synthesis
Powerful oxidant and source of sulfur, which can prevent disorders in the hair, skin, and nails
Reduces the levels of histamine in the body which can cause the brain to relay wrong messages
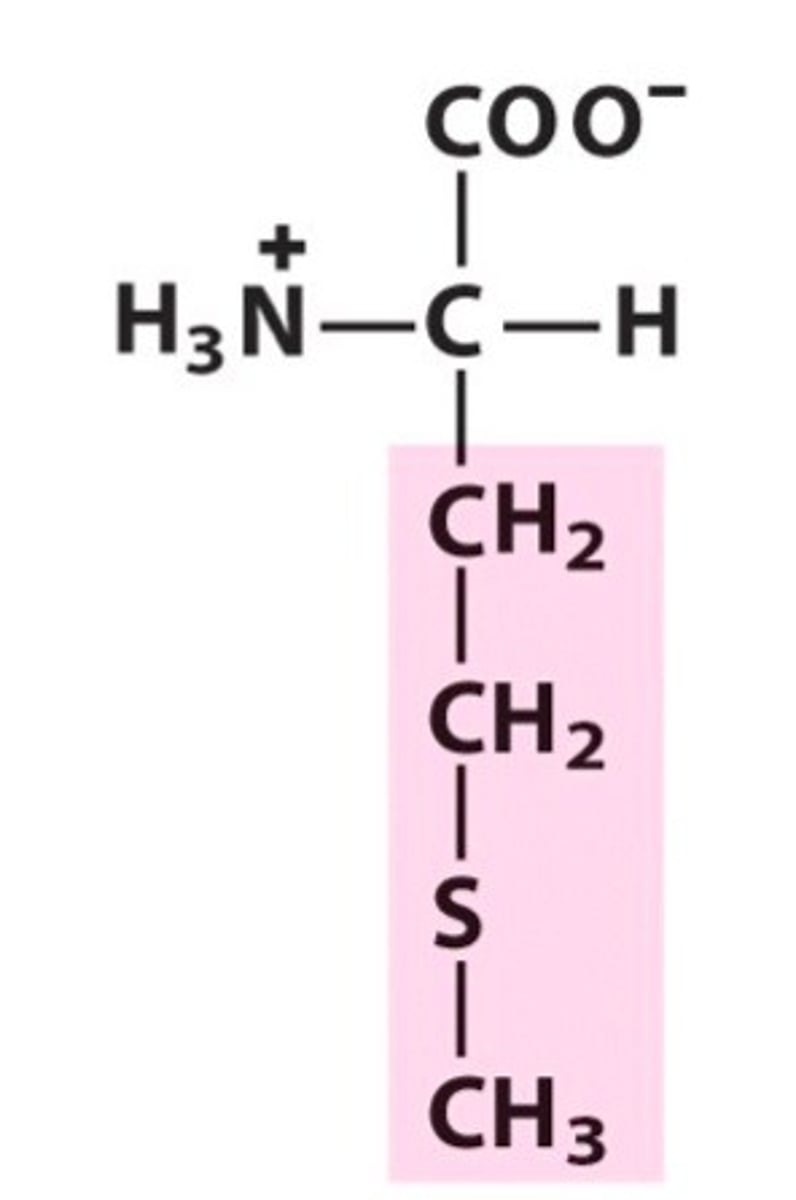
Phenylalanine, Phe, F
Utilization of Vitamin C
Converted into thyroxine (Tyr, T)
When people lack an enzyme to convert this into thyroxine, it undergoes an alternative metabolic pathway producing phenylpyruvic acid
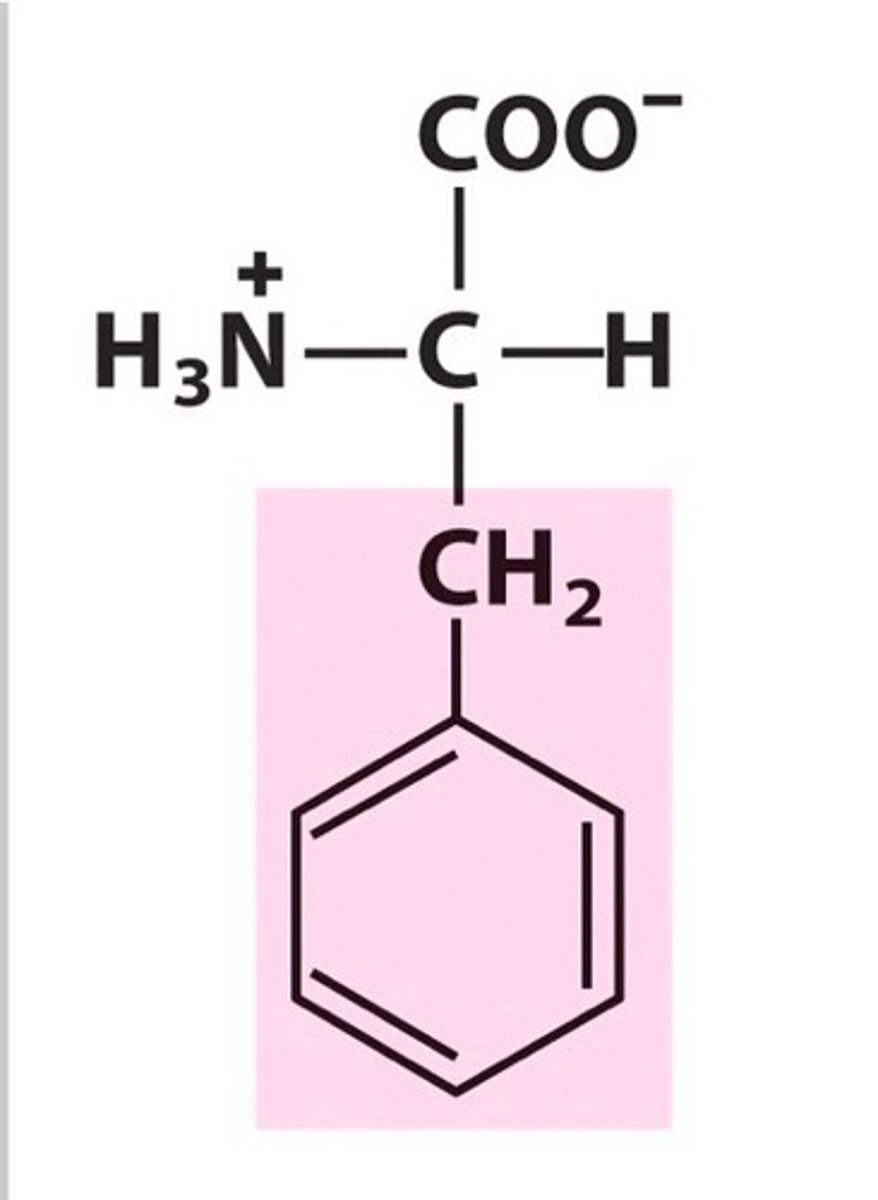
Phenylpyruvic acid
Produced when Phenylalinine (Phe, F) undergoes an alternative metabolic pathway
Causes pku disease or phenylketonuria (mental retardation in infants that are lacking in the enzyme that converts Phe into Tyr, this disease cannot be cured. but can be managed by restricting foods rich in Phe such as meat)
Proline, Pro, P
Called "imino acid" or "alpha-helix breaker" as it disrupts and inhibits the formation of an alpha-helix of -COOH.
Contributes to better skin texture via collagen production and slower loss of collagen through aging
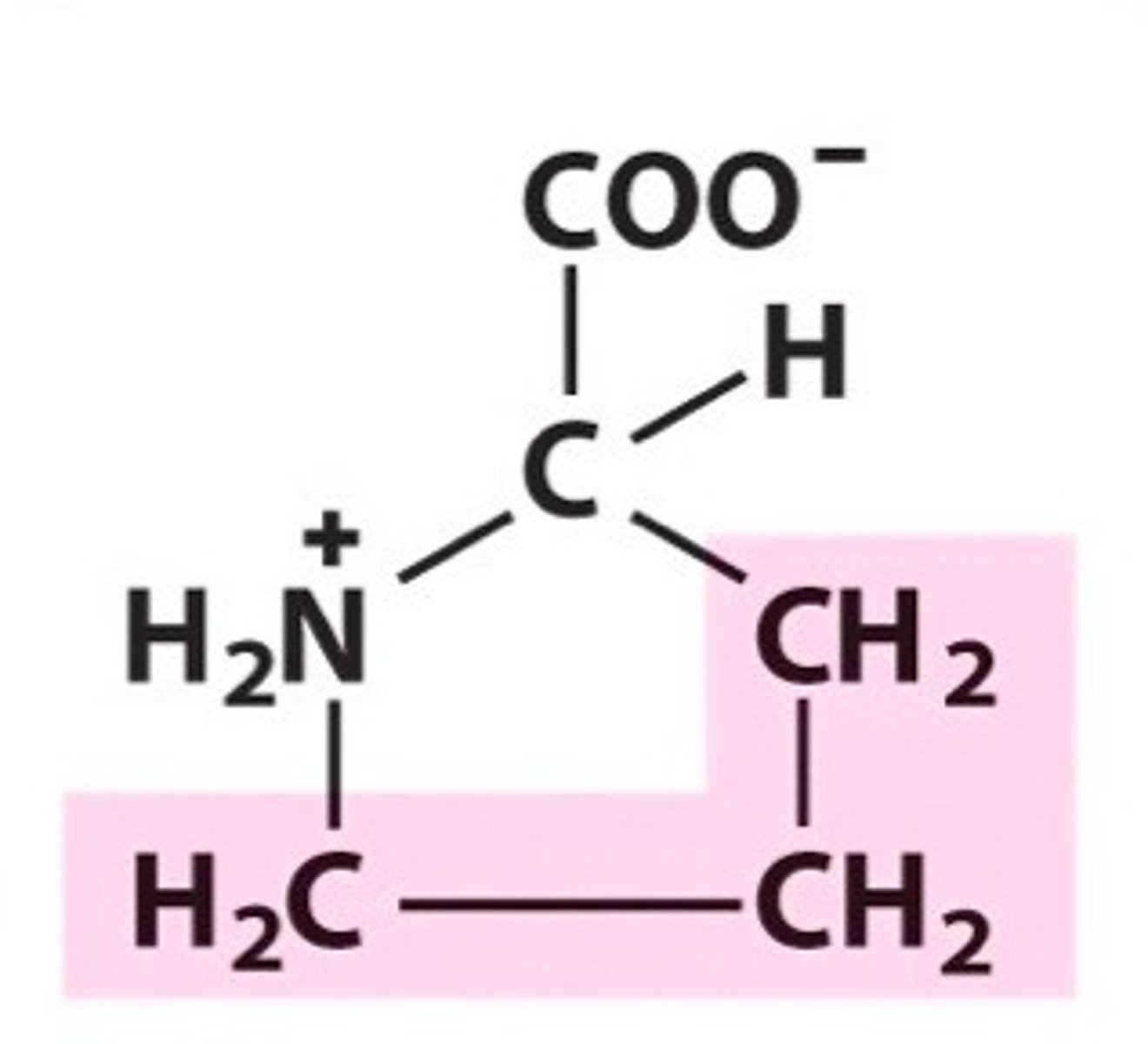
Serine, Ser, S
Part of phosphoprotein
Phosphate group is attached to this amino acid
Component of myelin sheaths that protect nerve fibers
Aids in the production of immunoglobins and antibodies
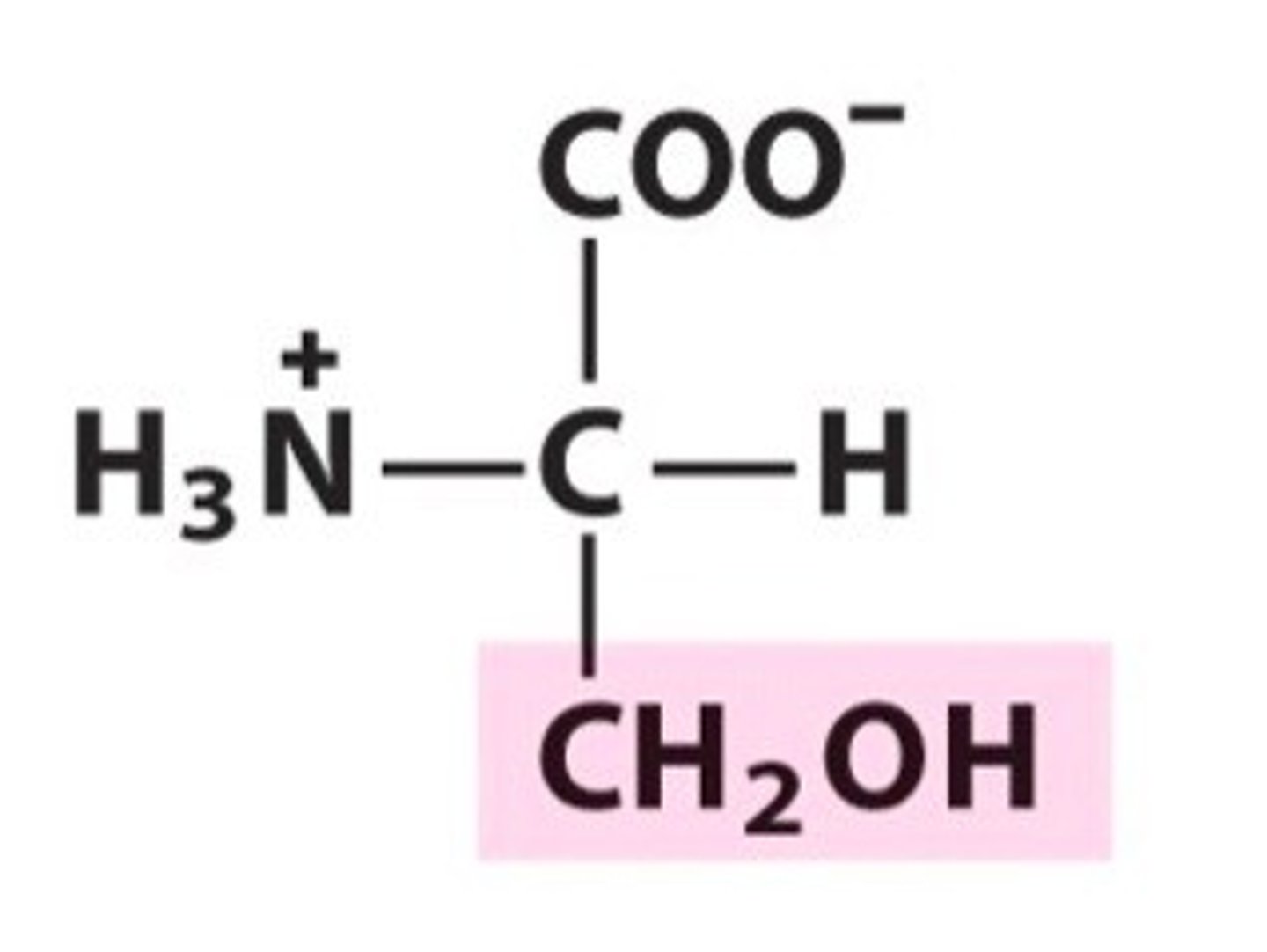
Threonine, Thr, T
Important in building tissue and utilzation of nutrients
Regulates protein balance in the body
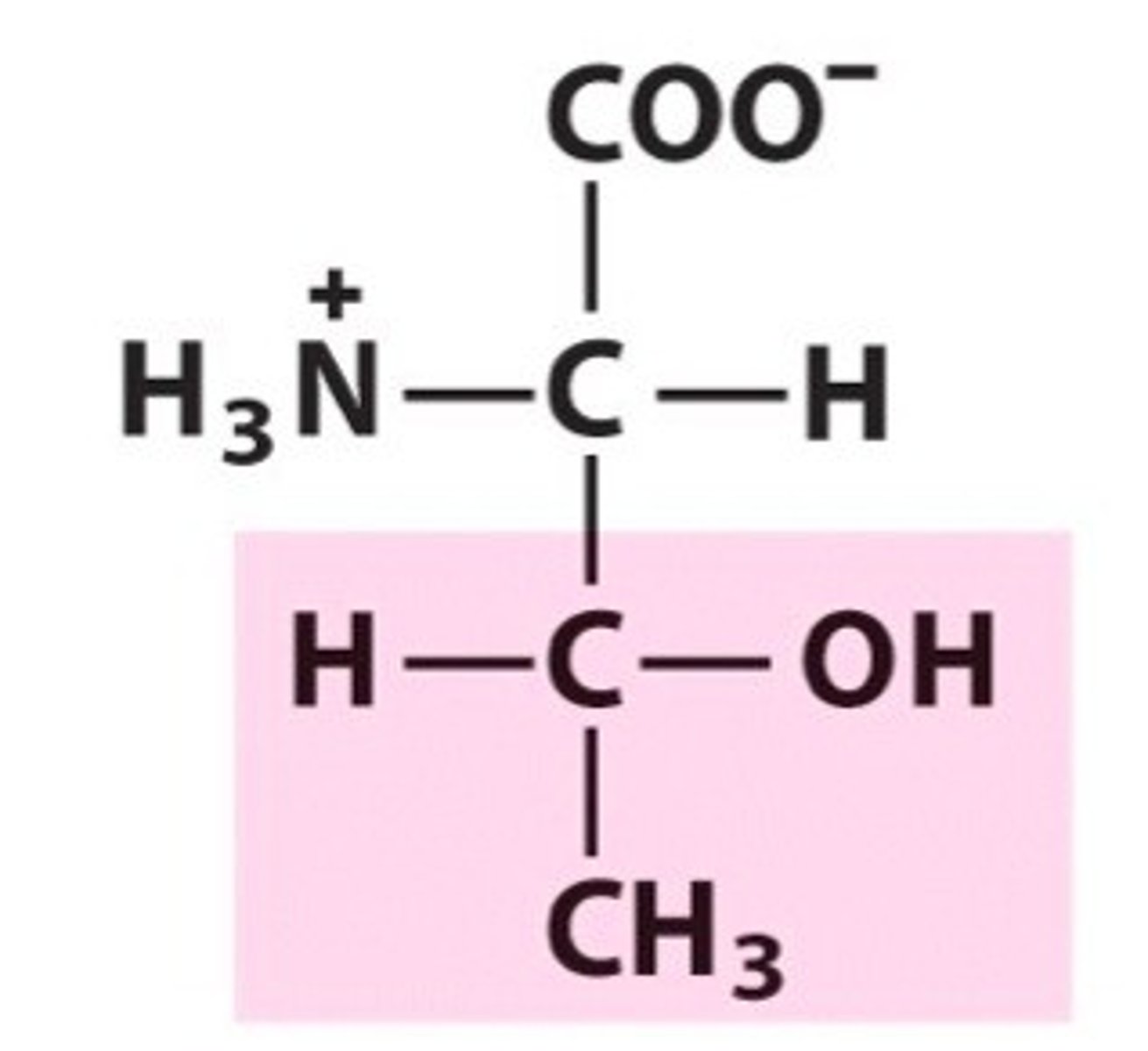
Tryptophan, Trp, W
Utilization of B-vitamins and the synthesis of neurotransmitters
Found in the charred portions of broiled fish and meat, which is responsible for cancer diseases
A natural relaxant that alleviates insomnia by inducing normal sleep
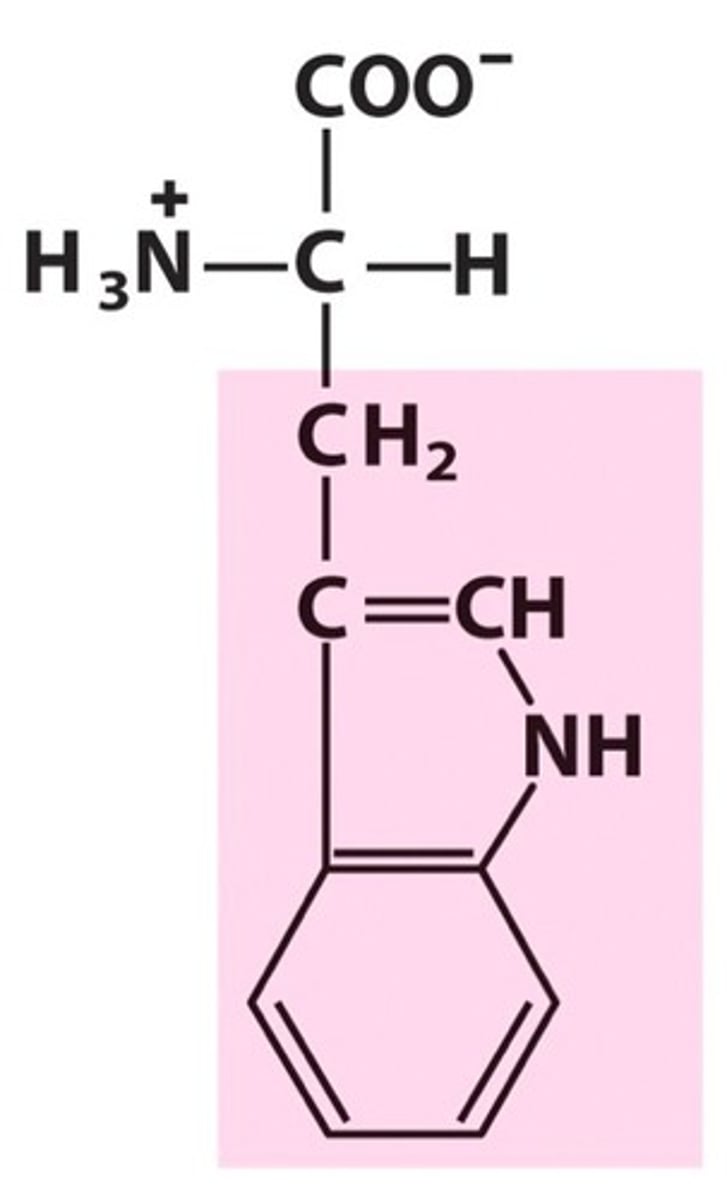
Tyrosine, Tyr, Y
Needed in the synthesis of some thyroid hormones
Important in overall metabolism
Precursor of adrenaline, norepinephrine, and dopamine, which regulate mood and stimulates metabolism in the nervous system
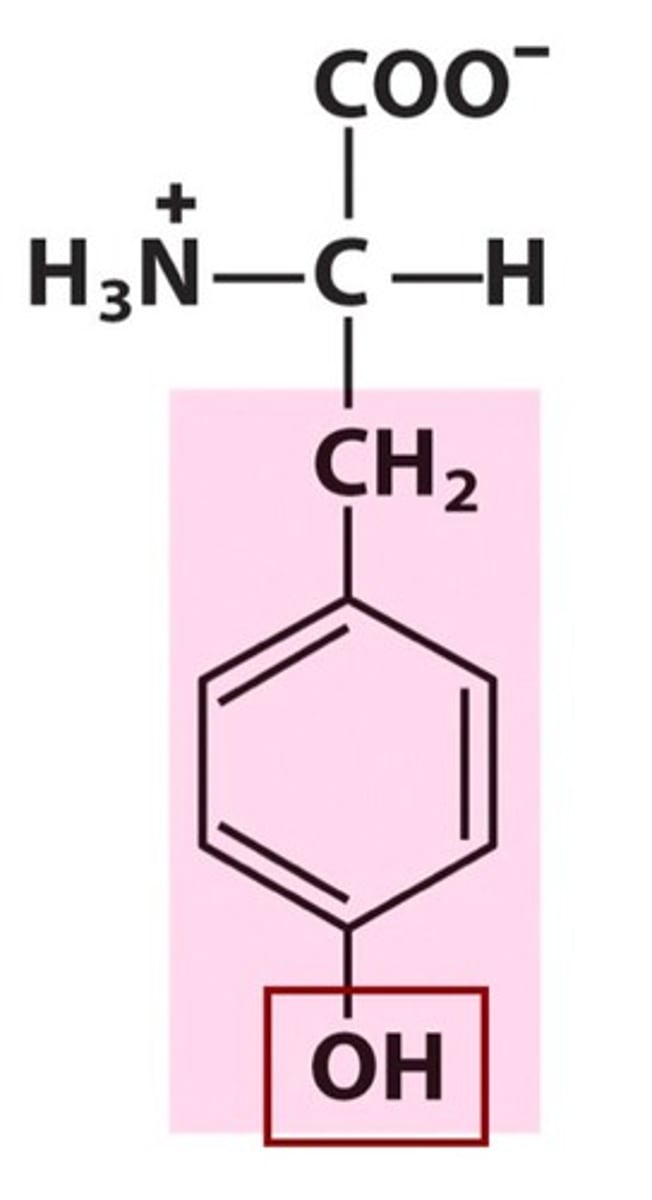
Valine, Val, V
Important for the functioning of the nervous system
Contributes to muscle and tissue repair
Ensures proper nitrogen levels in the body