Both CB and G lab
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/127
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
1
New cards
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic acids
The Four classes of macro molecules
2
New cards
Monosaccharide
Carbohydrate monomer
3
New cards
Polymers
Lipids do not form
4
New cards
Fatty acid
lipid monomer
5
New cards
amino acid
Protein monomer
6
New cards
Creates bond and produces water as a product
Dehydration reaction
7
New cards
Uses water to break bond
Hydrolysis
8
New cards
CnH2nOn
General Glucose structure
9
New cards
Philic Head: Carboxyl group, Phobic tail: hydrocarbon chain
Parts of fatty acid
10
New cards
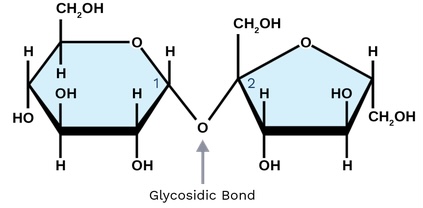
\
Draw glycosidic bond
11
New cards
1 = Monosaccharide, 2 = Disaccharide, 3-10 = Oligosaccharide, Many = polysaccharide
\# of sugars = ??????
12
New cards
Cellulose, Chitin, Starch
Three examples of a polysaccharides
13
New cards
Has both a hydrophobic and hydrophilic region
Amphipathic
14
New cards
Strach, Cellulose, and Chitin
Examples of Polysaccharides
15
New cards
Unsaturated has a C=C bond known as a kink
Saturated vs Unsaturated
16
New cards
A-T: 2
G-C: 3
G-C: 3
\# of hydrogen bonds between A-T and G-C
17
New cards
Purine
Double ring nucleotide =
18
New cards
Pyrimidine
Single ring nucleotide
19
New cards
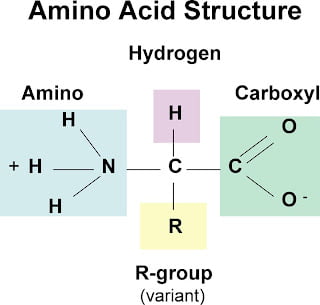
\
Draw an amino acid
20
New cards
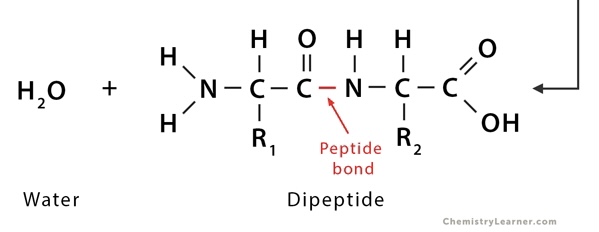
\
Draw a peptide bond
21
New cards
0\.5-10, 1-20
P10 and P20 volume range
22
New cards
20-200, 200-1000
P200 and P1000 volume range
23
New cards
D = M/V
Density equation
24
New cards
Not expressed in mRNA
Intron
25
New cards
expressed and codes for protein
Exon
26
New cards
Does not code for proteins but does regulate gene expression
Noncoding DNA
27
New cards
Codes for protein
Coding DNA
28
New cards
short repetitive interspersed elements
SINE
29
New cards
Alu 1 restriction enzyme recognition site
Alu name comes from
30
New cards
C16 pv92 and 300bps long
Alu location and bp size
31
New cards
Has - chalex beads that grab metal ions like Mg2+ that are required as cofactors for enzyme like DNase (in Lysosome) which breaks down DNA.
PV92: Instagene’s purpose
32
New cards
In vitro, Amplyfies section of DNA
PCR is a ______ technique that ______
33
New cards
Kary Miulus
PCR was invented by?
34
New cards
Forward primer
PCR: 5’ to 3’
35
New cards
Reverse primer
PCR: 3’ to 5’
36
New cards
Denaturation: 1 min at 90-95 C, separates DNA strands
Annealing: 45 seconds at 50-55 C primers attach and make complementary strands
Extension: 2 minutes at 75 and DNA polymerase adds dNTP’s to the strand
Annealing: 45 seconds at 50-55 C primers attach and make complementary strands
Extension: 2 minutes at 75 and DNA polymerase adds dNTP’s to the strand
Three steps of PCR and simple explaination
37
New cards
Taq, Yellowstone, *Thermus aquatics*
PCR: DNA polymerase is known as _________ and is acquired from?
38
New cards
Size only
Agarose Gel Electrophoresis differentiates using __________. In DNA
39
New cards
Cathode
DNA is attracted to which part of the electrophoresis machine
40
New cards
Fred Sanger
Sanger Sequencing was invented by ________
41
New cards
with colored ddNTP’s which lack a free 3’ OH
How are things labeled
42
New cards
Target DNA, 2 Primers, DNA polymerase, nucleotides (dNTP’s), Mg 2. 5 Total
Ingredients of PCR
43
New cards
TBE: High capacity but slow migration and lower than 2kb, TAE: fast migration and higher than 2kb but low capacity.
TBE vs TAE
44
New cards
encodes for green fluorescent protein
pGLO component: GFP
45
New cards
Origin of replication
pGLO component: ori
46
New cards
β-lactamase which breaks down ampicillin
pGLO component: bla
47
New cards
Promotes RNA polymerase when bound to AraC-arabinose
pGLO component: pBAD promoter
48
New cards
codes for protein that binds to pBAD promoter which additionally need arabinose and then expressed GFP
pGLO component: *araC*
49
New cards
taking genetic material from the environment
transformation
50
New cards
Foreign genetic material given by a virus or viral vector
transduction
51
New cards
genetic material transfer from bacteria to bacteria through direct contact
conjugation
52
New cards
foreign DNA introduce to eu.by physical and chemical means in a lab
transfection
53
New cards
growing using phenotype to distinguish
Screening
54
New cards
Allows growth only for selected bacteria
Selection
55
New cards
Remove alkaline environment allowing plasmid renaturation
What is the purpose of the neutralization buffer?
56
New cards
260
DNA absorbs light at which wavelength?
57
New cards
ampicillin
To ensure that only the bacteria transformed with the plasmid grew in the culture media, the bacteria were grown in the presence of ____________
58
New cards
beer lamberts law that concentration is directly linked to concentration
The principle of Nanodrop is
59
New cards
destabilizing proteins and nucleic acids
What is the purpose of lysis buffer during plasmid isolation
60
New cards
Attract target DNA
What is the purpose of the silica column?
61
New cards
Identification/characterization of gene causing a mutant phenotype observes the phenotype first and is unbiased.
forward genetics
62
New cards
observation of phenotype by purposefully disrupting a gene
reverse genetic
63
New cards
calcium chloride treatment causing plasmid to attach to the cell wall, heating in a water bath to open pores to allow entry
pGLO transfer process
64
New cards
Gel red
What chemical is used in lab to visualize the DNA in an agarose gel under UV light?
65
New cards
Differentiate between G- and G+ microbes
Principle of a gram stain
66
New cards
Lps, Outer membrane, thin peptioglycan layer, inner membrane
G- Bacteria Structure
67
New cards
pink
G- color after stain
68
New cards
Thick peptidoglycan layer and plasmas membrane
G+ Bacteria structure
69
New cards
Purple
G+ color
70
New cards
stains them purple, 30-60 sec
Crystal Violet
71
New cards
Attaches the crystal violet to cell wall, 30-60 sec
Iodine
72
New cards
Washes stain from G- walls, 3 sec
Decolorizor
73
New cards
stains g- pinks, 30 seconds
safranin
74
New cards
Maintaining pure culture + isolating from a mixed culture
Principle of Bacterial Streaking
75
New cards
Dillutuion of the \# microbes within a volume
Principle of Serial Dilution
76
New cards
1/10
1 mL into 9 mL dilution factor?
77
New cards
1/6
5 mL into 25 mL dilution factor?
78
New cards
1/400
Current Dilution factor: 1/4 Previous Dilution factors: 1/2, 1/5/ 1/10 What is the final dilution factor?
79
New cards
Salt contamination, 1.8 for DNA and 2.0 for RNA
Nanodrop: 260/230 ratio meaning and ideal value(s)
80
New cards
Protein contamination, ~2.0 lower than 1.8 is heavy contamination
Nanodrop: 260/280 ratio meaning and ideal value(s)
81
New cards
A sequence that is read the same backwards as forwards
What is a palindromic sequence
82
New cards
Enzyme that does not produce a overhang
Restriction Digestion: Blunt
83
New cards
double stranded DNA
Restriction enzymes only cut ________
84
New cards
A natural defense in bacteria against bacteriophages
Restriction enzyme acts as?
85
New cards
Annex V: stains Phosphatidylserine (PS) which is located in the cytosolic part of the membrane
Propidium Iodide: stains DNA and can only enter if the membrane integrity is low
Propidium Iodide: stains DNA and can only enter if the membrane integrity is low
FC: Apoptosis Staining
86
New cards
Necrosis
FC: Apoptosis Staining PI only
87
New cards
Early Apoptosis
FC: Apoptosis Staining Annex V only
88
New cards
Late Apoptosis
Flow Cytometry: Apoptosis Staining both
89
New cards
Three, Fluidics, Optics, Electronics
Flow cytometer is composed of **[A]** main subsystems. These are **[B]**, **[C]** and **[D]**.
90
New cards
0\.2-50 µm
What is the range of size of cells of particles that is suitable for flow cytometric analysis?
91
New cards
Route the laser beams to the flow cell for interrogation
FC: The purpose of the excitation optics is to:
92
New cards
Decrease the flow rate or the sample pressure
FC:What can be done to improve data resolution?
93
New cards
Maintain the sample core in the center of the sheath fluid
FC: Hydrodynamic focusing is used to
94
New cards
sample Core
FC: What is the name given to the portion of the fluid stream where the cells are located?
95
New cards
places them in a single file line
FC: The purpose of the fluidics system in a flow cytometer is?
96
New cards
Sample core, Fluidics
FC: The particle suspension is injected into _________________ within the _________________.
97
New cards
light
FC: When fluorescent compounds absorb light energy and then release excess energy, they emit ____________________.
98
New cards
Cell Size
FC: FSC is proportional to:
99
New cards
complexity or granularity
FC: SSC is proportional to the ___________ or _____________ of the cell
100
New cards
Forward, Inside
FC: Correlated measurements of both _______________ and _____________ can allow differentiation of cells types in a heterogeneous cell population.