THE MALARIAL PARASITES
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
PROTOZOA
First animals
inner (endoplasm) and outer later of cytoplasm (ectoplasm)
PROTOZOA Contains an
cytostomes
mouth like opening
use to ingest food
sexually and asexually
PROTOZOA Reproduce
trophozoite (active and motile form);
cyst (resting stage)
PROTOZOA
2 forms:
active and motile form
resting stage
FEMALE Anopheles MOSQUITO
Plasmodium spp. Grows by sexual reproduction in the
aghe
intermitent fever
marsh fever
fever
MALARIA aka
malaria
Plasmodium spp. Causative agent of
female Anopheles mosquito
MALARIA It is transmitted by the
Plamodium vivax
Benign Tertian Malaria
Plasmodium falciparum
Malignant Tertian Malaria
Plasmodium malariae
Benign Quartan Malaria
Plasmodium ovale
Benign Tertian Malaria
P. vivax, P. ovale
infect young RBCs
P. malariae:
infects old RBs
P. falciparum:
infects all age groups
P. falciparum, P. ovale, and P. vivax
Cycle repeats every 48 hours in
P. malariae
Cycle repeats every 72 hours in
9-14 days
P. falciparum
incubation period
8-17 days
P. vivax
incubation period
16-18 days
P. ovale
incubation period
18-40 days
P. Malariae
Incubation Period
Schüffner dots
Small red dots
Plasmodium vivax
Blood Smear
stippling
Plasmodium vivax
Has the widest distribution, Preferentially penetrates reticulocytes , Ring stage is large, usually single, prominent thicker chromatin
12-24 irregular grape-like clusters
Plasmodium vivax
Number of merozoite
spherical or globular
Plasmodium vivax
Gametocytes
Maurer’s cleft
Large red spots
Plasmodium falciparum
Blood Smear
stippling
Plasmodium falciparum
Most severe form of malaria,
Ring stage is delicate and small with double chromatin and multiple rings
crescent
banana shape
Plasmodium falciparum
Gametocytes
Plasmodium malariae
Blood Smear
stippling
Ziemann’s Stippling
few tiny dots
Plasmodium malariae
Ring stage is similar to P. vivax but thicker,
Schizont nearly fills red cell
Plasmodium malariae
Gametocytes
spherical or globular
Plasmodium ovale
Blood Smear
stippling
James dots
numerous small red dots
Plasmodium ovale
Schizont fils three quarters,
Merozoites 6-14 fills three quarters
spherical or globular
Plasmodium ovale
Gametocytes
Febrile paroxysm
Anemia
Splenomegaly
CLINICAL FEATURES
The typical picture of malaria consists of
lasts for 15-60 minutes (intense cold and shivering)
FEBRILE PAROXYSM
Cold Stage min.
lasts for 2-6 hours
FEBRILE PAROXYSM
Hot stage hrs.
FEBRILE PAROXYSM
Sweating Stage
fever ends by crisis accompanied by profuse sweating
ANEMIA
Causes of anemia in malaria
Destruction of large number of RBCs by complement mediated and autoimmune hemolysis
Suppression of erythropoiesis in the bone marrow
Antimalarial therapy in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficient patients.
SPLENOMEGALY
Enlargement of SPLEEN
CEREBRAL MALARIA
• This is the most common cause of death in malignant tertian malaria
It is manifested by headache, hyperpyrexia, coma or confusion, and paralysis
ALGID MALARIA
• It resemble surgical shock with cold clammy skin, peripheral circulatory failure and profound shock. Patient may also develop vomiting and diarrhea or dysentery.
SEPTICEMIC MALARIA
It is characterized by a high degree of prostration, there is high continuous fever with involvement of various organs.
BLACK WATER FEVER
Patients with G6PD deficiency may develop this condition after taking oxidant drugs, even in the absence of malaria.
blood smear
The most common diagnostic test for malaria is the??
Thick
Blood smear
is used for detecting, most importantly in early cases where there are less parasites.
Thin
Blood smear
is used for identifying which specific specie is the cause of the disease.
Thin Film
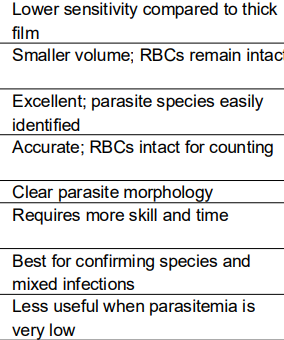
Thick Film
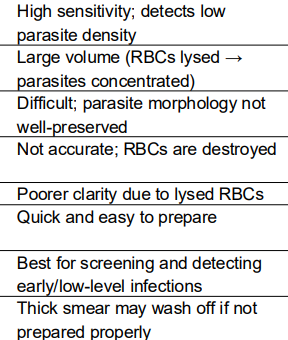
Chloroquine
OLD DRUG OF CHOICE
Uncomplicated malaria P. falciparum
Atovaquone + Proguanil
Arthemeter + Lumefrantine
OLD DRUG OF CHOICE
With chloroquine resistance:
Blood stage: Chloroquine
Liver stage (hypnozoite): Primaquine
OLD DRUG OF CHOICE
P. vivax and P. ovale
Blood stage:
Liver stage (hypnozoite):
Arthemeter + Lumefrantine
DOH Revised Guideline on the Tx of Malaria 2009
First line for confirmed uncomplicated and severe P. falciparum
Quinine + Tetracycline
Doxycycline
Clindamycin
DOH Revised Guideline on the Tx of Malaria 2009
If ALL combination is not available, whether the patient is conscious or unconscious Treatment failure 2nd line Treatment
Artesunate suppository
DOH Revised Guideline on the Tx of Malaria 2009
Severe Malaria, Patient is unconscious Facility: no capacity to manage the px
Artermisinin-based combination therapy
DOH Revised Guideline on the Tx of Malaria 2009
For all Plasmodium species and mixed infections
Chloroquine
PROPYLAXIS
ATORVAquine
PROQUANIL
Chloroquine
if not sensitive here we use
MEFLOQUINE
IF traveles
we give