COMPLEXATION TITRATIONScx
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
145 Terms
Complexation Methods
These are class of reactions that deal with complex formation.
Complexation Methods
Current method of choice for the determination of metal ions except
Group 1A metals
Because monovalent metal ions yield relatively weak or unstable complex
monovalent
Because _ metal ions yield relatively weak or unstable complex
Al3+, Bi3+, Ca2+, Cu2+, Hg2+, Mg2+, and Zn2+
the complex formation is rapid and quantitative with polyvalent metal ions such as:
polyvalent metal ions
the complex formation is rapid and quantitative with _ such
metal ions
Complexation Methods - Current method of choice for the determination of _ except Group 1A metals
equivalence point
During titration, metal ion reacts with a suitable ligand to form a complex, and the _ is determined by an indicator or appropriate instrumental method
metal ion
During titration, _ reacts with a suitable ligand to form a complex, and the equivalence point is determined by an indicator or appropriate instrumental method
indicator or appropriate instrumental method
During titration, metal ion reacts with a suitable ligand to form a complex, and the equivalence point is determined by an _
when a metal ion combines with a molecule then donates electron
how does a complex form?
Ligand
species that has a molecule with at least one pair of unshared electron
Ligand
an electron donor, while a metal is an electron acceptor
Ligand
based on lewis theory
Complex
If a ligand contains 2 or more molecules or groups that can donate electron. The resulting complex is called chelate.
molecules/groups that can also donate electrons
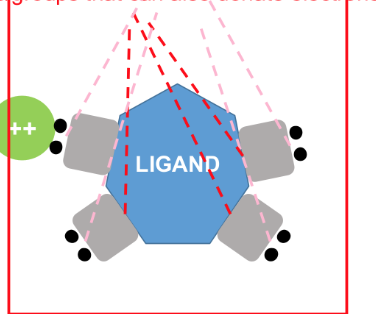
chelate
If a ligand contains 2 or more molecules or groups that can donate electron. The resulting complex is called _.
metal +
ligand nucleophilic (excess e-) ?
monovalent metal ions
yield relatively weak or unstable complex
electron donor
a ligand is an _; while metal is an electron acceptor
complex
a _ is formed because of sharing of electrons: metal being positive, will accept electrons, while ligand (having unshared electrons), will donate electrons. this follows the principle of lewis acid-base theory
metal
a complex is formed because of sharing of electrons: _ being positive, will accept electrons, while ligand (having unshared electrons), will donate electrons. this follows the principle of lewis acid-base theory
ligand
a complex is formed because of sharing of electrons: metal being positive, will accept electrons, while _ (having unshared electrons), will donate electrons. this follows the principle of lewis acid-base theory
lewis acid-base
a complex is formed because of sharing of electrons: metal being positive, will accept electrons, while ligand (having unshared electrons), will donate electrons. this follows the principle of _ theory
electron acceptor
a ligand is an electron donor; while metal is an _
Al3+, Bi3+, Ca2+, Cu2+, Hg2+, Mg2+, Zn2+
examples of metals
Al3+
astringent
Bi3+
hyperacidity
Ca2+
bone, homeostasis, vit d, 2nd most abundant extracellular
Cu2+
antiseptic
disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetate (Na2EDTA)
the most commonly used analytical reagent for complexation reaction is the
unshared electrons
groups that contain _ and therefore can be accepted by the metal analyte
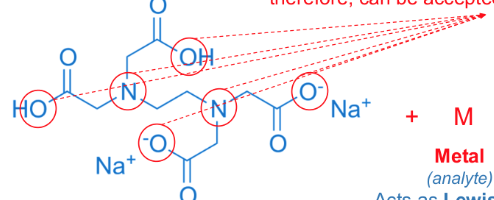
multidentate (“many toothed”) or a chelating agent
essentially, a ligand that attaches to a metal ion through more than one ligand atom is said to be _ 3
chelate effect
is the ability of a ligands to form more stable metal complexed
stable
If there are more molecules/atoms in a ligand that can form a bond (making additional ring in the complex)
with the metal ion, it is considered more _. Therefore:
Stability of ligands:
MULTIDENTATE LIGANDS >> MONODENTATE LIGANDS
>>
If there are more molecules/atoms in a ligand that can form a bond (making additional ring in the complex)
with the metal ion, it is considered more stable. Therefore:
Stability of ligands:
MULTIDENTATE LIGANDS_ MONODENTATE LIGANDS
pKn value or (Kn)
the dissociation constant of a chemical reaction
opposite
if we do the _ (decrease H+/increase the pH of the soln), the rxn proceeds forward, producing the product species
product
if we do the opposite (decrease H+/increase the pH of the soln), the rxn proceeds forward, producing the _ species
pK
higher _, low K
1
note that 1 mole of edetate reacts 1 mole of metal producing a complex, therefore:
the factor used in all complexometric titrations using EDTA is _
formation constant, Kf, stability constant
the equilibrium constant for the reaction of a metal with a ligand is called the _ 3
↑
_Kf of a complex, ↓pH at which the complexation titration can be run.
Edetate disodium
_ may contain trace of moisture, so it must
be dried at 80oC to obtain the required hydrates
(C10H14N2Na2O8.2H2O)
13
Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) alkalinizes the solution to a pH of about _,
so that the Ca-EDTA complex would be stable and any magnesium
which might be present as a contaminant would not react. Magnesium
can form complex with EDTA at pH 10.
we use an indicator
how do we determine the endpoint?
Organic dyes
_which form colored chelates with many metal ions. The resultant color of the
metal-indicator complex is distinctly different from that of the dye itself.
sharpened
The endpoint may be _ by the addition of a nonchelating screening dye that is
complementary to the color observed either just before or just after the endpoint is reached.
Metallochromic indicators
_ are also affected by pH, since they are also acid-base indicators.
10-100x
Metal-dye complex should be _ less stable than the corresponding metal-EDTA complex
metal ions
If the metal-indicator complex color is similar to the free indicator color, the color change occurs when one or more hydrogen ions are replaced by _. Therefore, indicator is sensitive to change in pH and also concentration of metal ions.
complexometric
Chelometric means _. So chelometric calcium
carbonate is used as primary standard for complexometric
titration. (In this case, as the analyte for the standardization
of Na2EDTA VS)
↓
↑Kf of a complex, _pH at which the complexation titration can be run.
8
For successful titrations with EDTA, the Kf (as log) of the
complex formed must be greater than _.
complexometric titrations
_ require pH control at which metals are being analyzed
Hg2+
antiseptic, preservatives
Mg2+
2nd most abundant cation; antacid; laxative
Zn2+
astringent; antiseptic
Titrant (Chelating Agent/Complexing Agent/complexone)
most commonly used analytical reagent for complexation; disodium, ethylediamine
Titrant
(Chelating Agent/Complexing Agent/complexone)
Na2EDTA
acts as Lewis base
Metal (analyte)
acts as lewis base
groups containing unshared electrons
monodentate
bidentate
tridentate
tetradentate
hexadentate
heptadentate
octadentate
nonadentate
etc
If a ligand binds to a metal ion through only 1 atom, the ligand is said to be:
multidentate
A ligand attached to a metal ion through 1 or more ligand atom is said to be_ (many tooth)
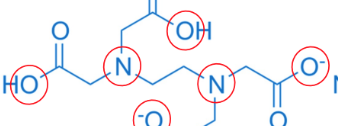
hexadentate
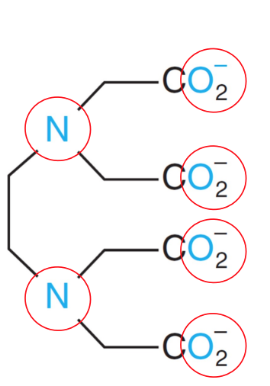
Na2EDTA
Acts as Lewis Base
monodentate
How many dentate/s does the following ligand contain?
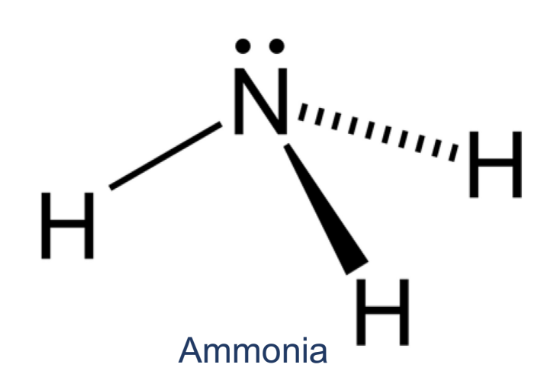
monodentate
How many dentate/s does the following ligand contain?
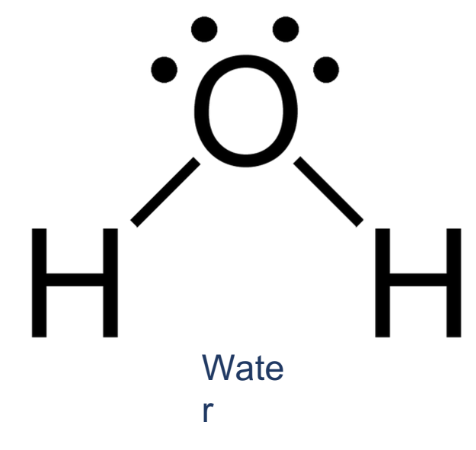
electron pairs, just the atom (depends parin)
In identifying the # of dentate/s dont look at the ___
monodentate
How many dentate/s does the following ligand contain?
bidentate
(carbonyl grp not kasama bcs stable bond w/carbon atom)
How many dentate/s does the following ligand contain?
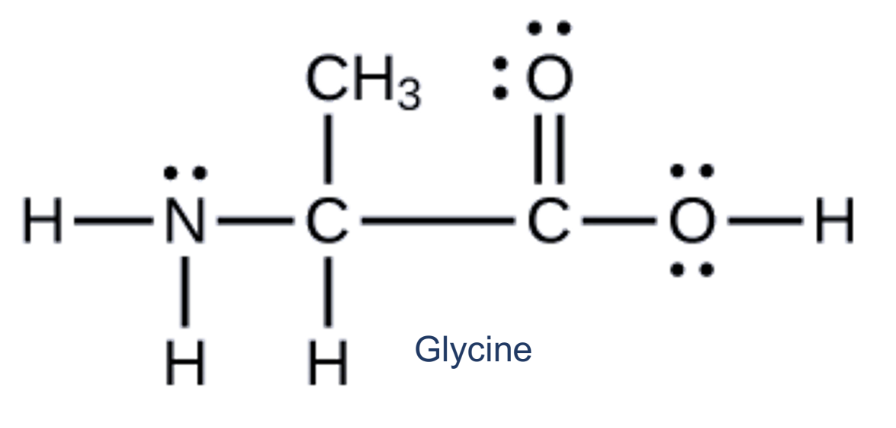
bidentate
How many dentate/s does the following ligand contain?
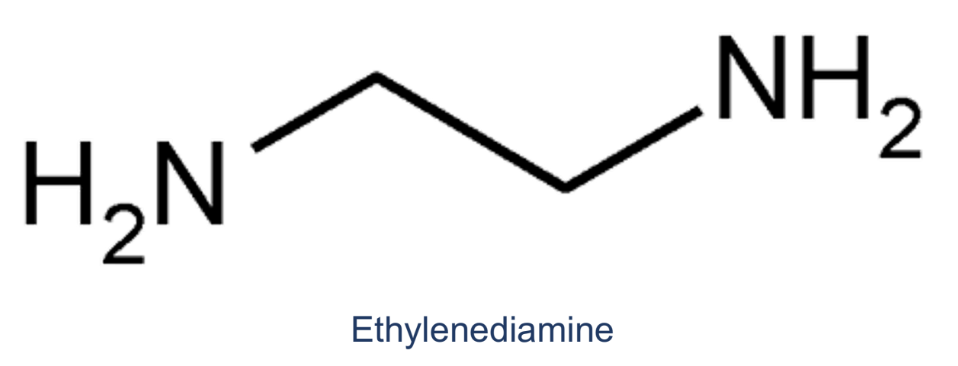
tetradentate (oxygen not included)
How many dentate/s does the following ligand contain?
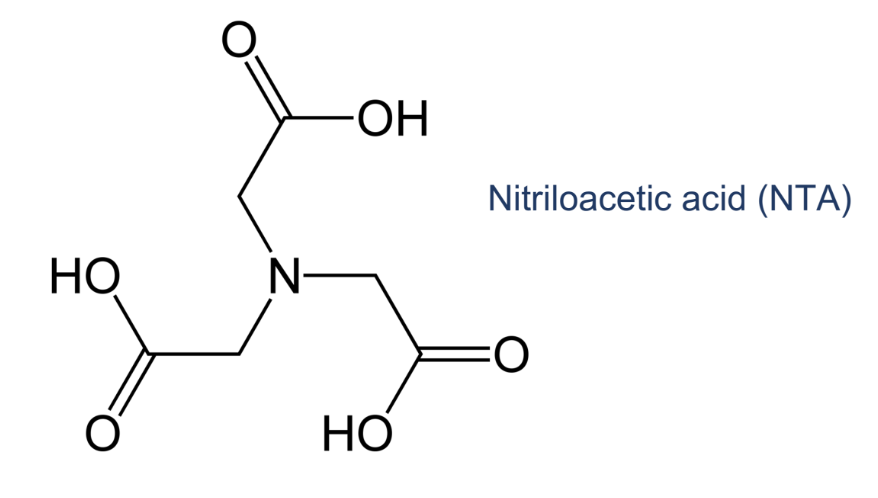
hexadentate
How many dentate/s does the following ligand contain?
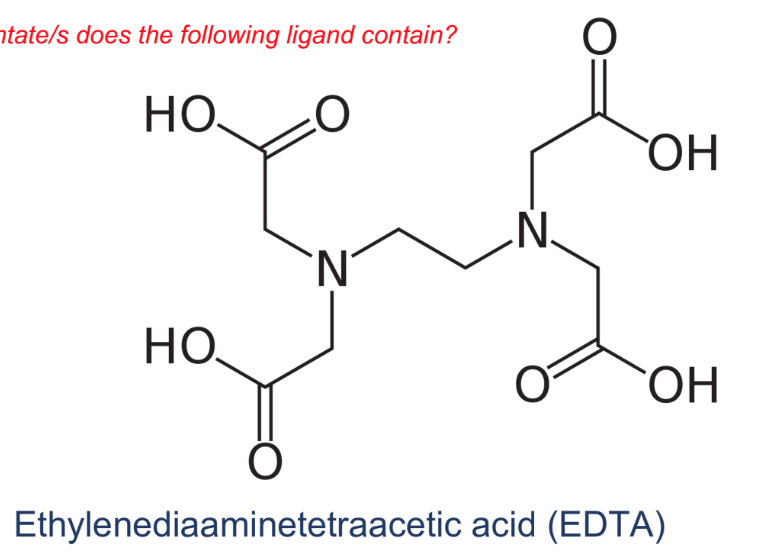
hexadentate (mahirap magshare to other e-; delocalize)
How many dentate/s does the following ligand contain?
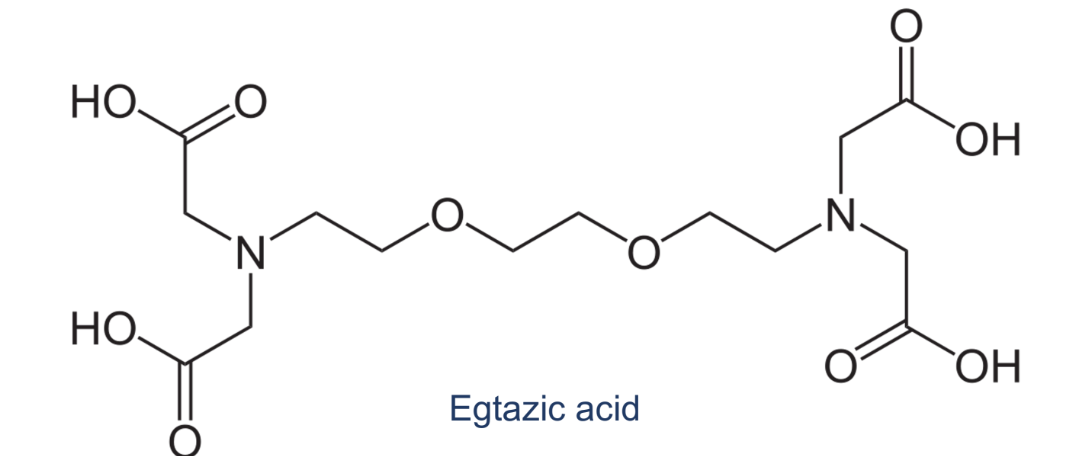
octadentate
How many dentate/s does the following ligand contain?
octadentate
most stable kasi 8 not most used in titration cuz its expensive
The CHELATE EFFECT
ability of a ligand to form more stable metal complexes
The CHELATE EFFECT
if more molecules/atoms in a ligand titration form a bond w/metal ions, more stable
>
Multidentate ligands ( _ ) monodentate ligands
chelating
multidentate ligands =
complexing
monodentate ligands =
chelating
stronger _ effect, more stable
bond breakage
high temp, high _
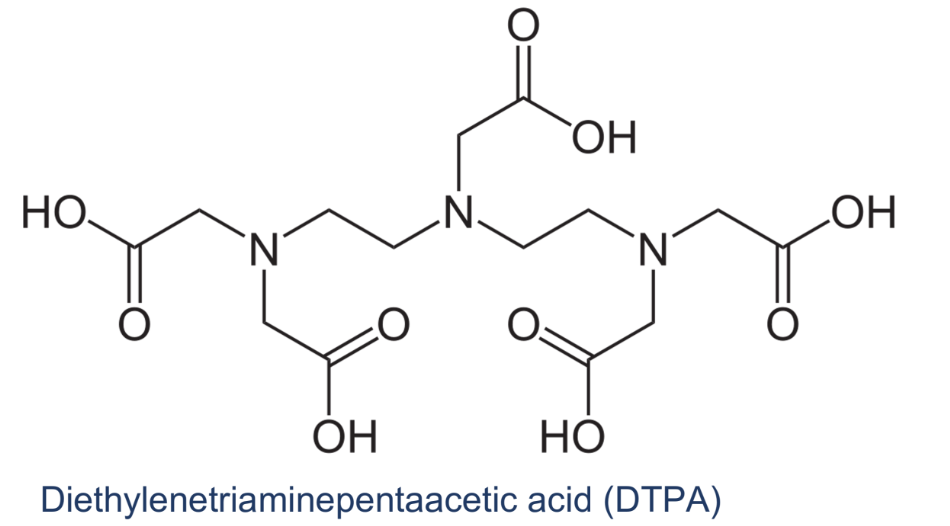
Octadentates
(such as DTPA) give more stable complexes than hexadentates (EDTA),
EDTA
_ has the
widest general application in the analysis because of its powerful complexing action and commercial
availability.
octadentates
DTPA
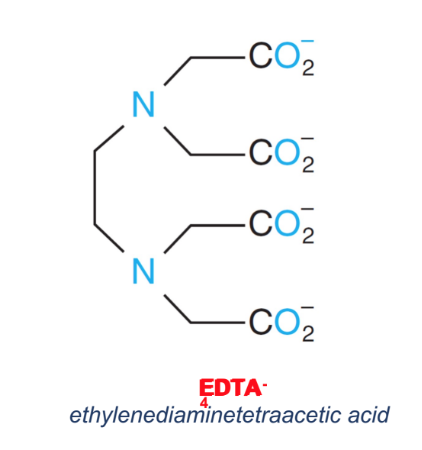
H4Y - 4 Hydrogens in EDTA
What are the factors that affect the stability of a complex?
Kn formula
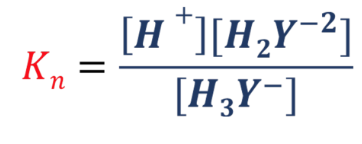
pKn formula
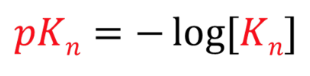
K2 formula
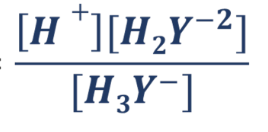
pH
The dissociation/reaction of
EDTA is dependent on _.
pH
Therefore, _ affects the
stability of complex formed
by EDTA during
complexation reaction.
unprotonated ligand
In EDTA titrations, the _, Y4-
, forms complexes
with metal ions.
greater than 8
For successful titrations with EDTA, the Kf (as log) of the
complex formed must be _
most stable

AlY-
Al3+ Complex [MY-4]
BiY-
Bi3+ Complex [MY-4]
CaY-2
Ca2+ Complex [MY-4]
CuY-2
Cu2+ Complex [MY-4]