1.11 Near vision effectivity
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is near vision effectivity error and its effect on pts
The prescription you get in the consulting room may not have the same effective power at near when made up in a different lens form
Pt may have near vis difficulties/have to accommodate more in the final spectacles compared to your trial case lenses eg high hypermetropes
How is back vertex power if a lens determind (ray diagram)
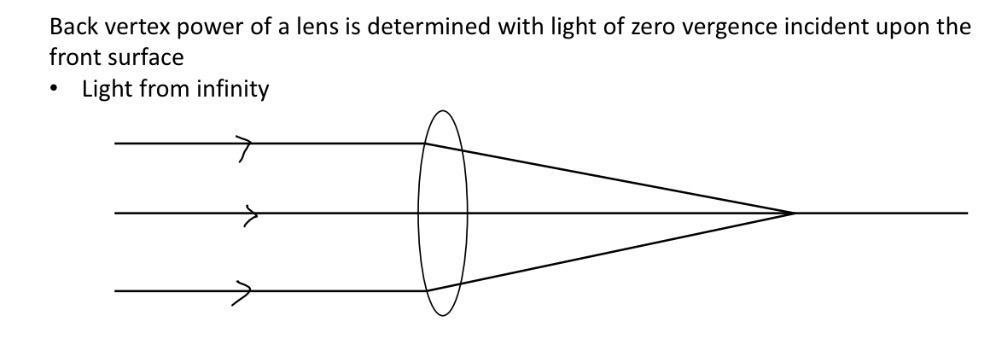
When might the back vertex power not give a true reflection of the lens performance
When the source of light is coming from a near object ie. not infinity
What does lens performance depend on when the object is at near
Incident vergence
Lens form (front surface power)
Lens thickness
Refractive index
What is incident vergence (L2) altered/modulated by
Lens form
Lens thickness
Refractive index
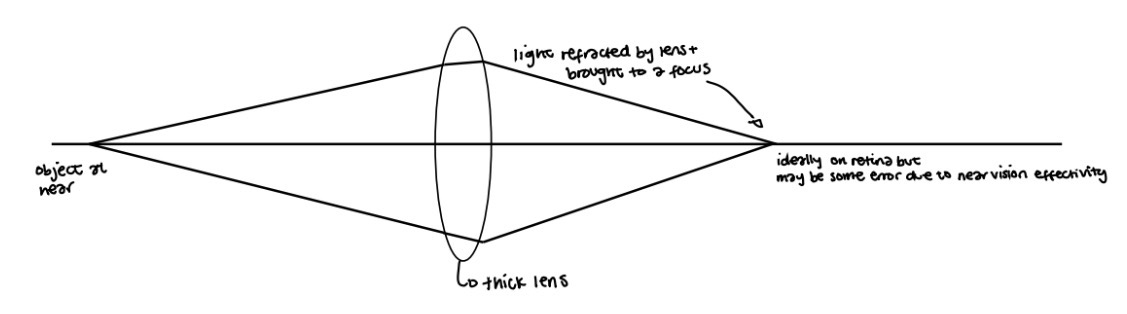
How can we quantify the nvee (2 ways)
Quantifying the actual error in relation to the trial lenses we have used to refract the pt
Comparing the emergent vergence obtained with a given thick lens to the theoretical emergent vergence that we would obtain with a thin lens of the same back vertex power
Back vertex power formula
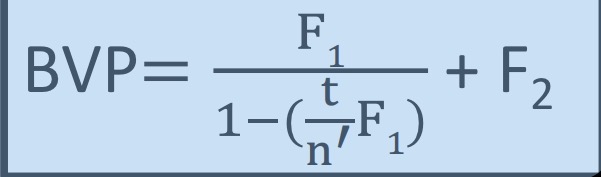
When do we use the back vertex formula
To calculate vergence leaving the back surface of a thick lens when light is coming from infinity
Variation of BVP formula when light is coming from near
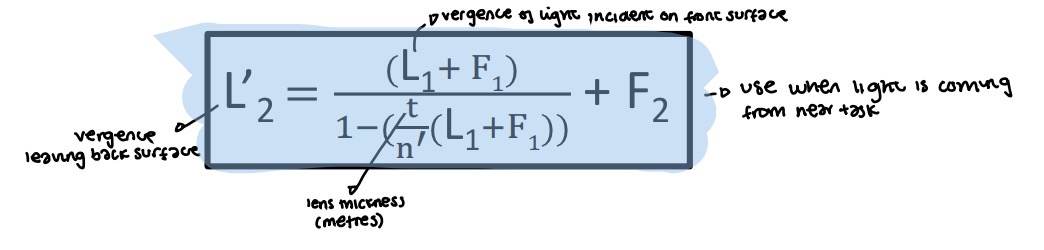
How to calculate theoretical thin lens power
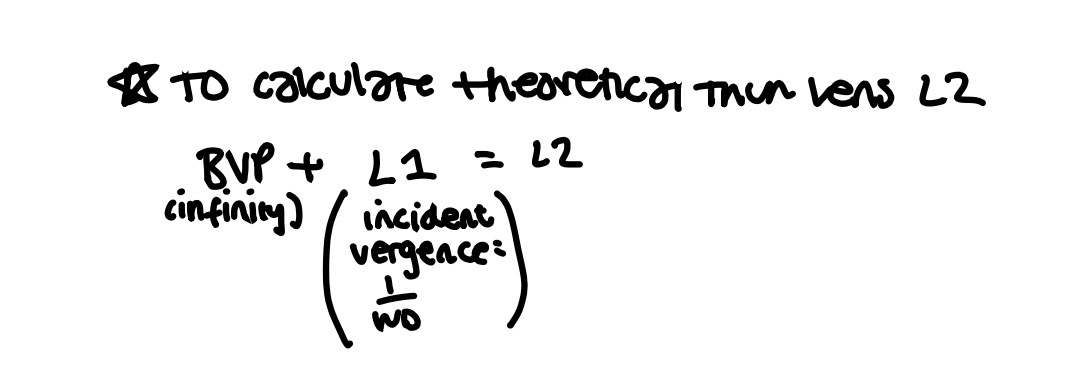
Lens:
F1 = +17.00 DS
F2 = -3.18 DS
t = 10mm
Calculate the vergence of light leaving the back surface of the lens when light is coming from
Infinity
Near task of 33cms
Comment on NVEE


Comment in the nvee
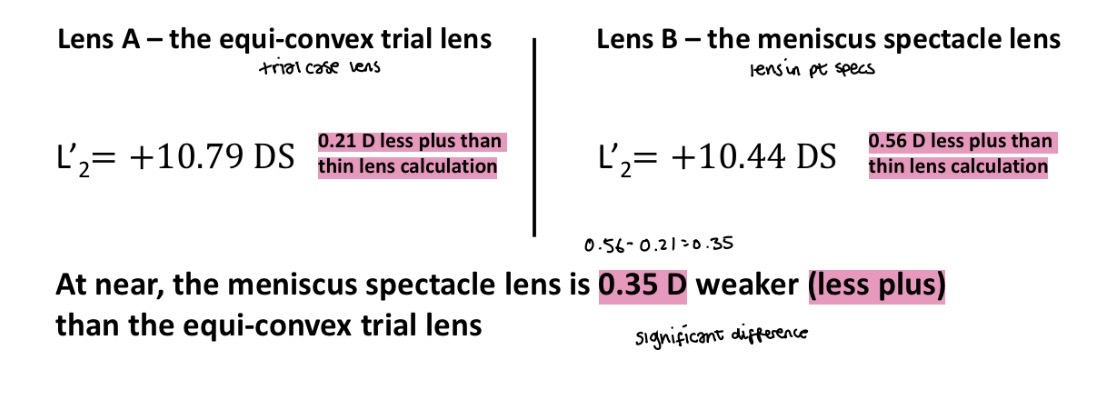
Does nvee affect myopes
No
The lens performs almost the same whether its a low or high powered lens
The nvee is not significant
Equation which gives an approximation of the NVEE

Steps to ray trace through a thick lens - how do we calculate
Incident vergence
Vergence after F1
Incident vergence at F2
Vergence after F2
Incident vergence on F1= 1/distance (eg 1/33cms = -3.00)
Vergence after F1 = incident vergence on F1+ surface power of F1
Incident vergence at F2 = n / ( (n/vergence after F1) - centre thickness in metres)
Vergence after F2 = incident vergence at F2 + surface power of F2