Unit 4-7
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/201
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 4-7 (inc)
Last updated 2:26 PM on 4/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
202 Terms
1
New cards
Internal resources
* When organizing internal continuing education programs, local resources available from the health care community should be considered.
2
New cards
External resources
can also be presented by topic experts;
* proficiency testing services
* manufacturers
* scientific societies
* World Health Organization
* United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
* nongovernmental organizations.
* proficiency testing services
* manufacturers
* scientific societies
* World Health Organization
* United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
* nongovernmental organizations.
3
New cards
Job Enlargements
Is the process of increasing job **scope**.
Or a system of job rotation may be initiated, so that workers move from one job to a completely different one.
Or a system of job rotation may be initiated, so that workers move from one job to a completely different one.
4
New cards
Motivation
is a general term applying to drives, desires, needs and wishes of an individual in order to perform
It involves a chain reaction starting out with felt needs, resulting in wants or goals sought which gives rise to tensions (that is unfulfilled desires),
It involves a chain reaction starting out with felt needs, resulting in wants or goals sought which gives rise to tensions (that is unfulfilled desires),
5
New cards
CPD
* is an educational program that brings employees up- to-date in a particular area of knowledge or skills
6
New cards
Training
* is a process to provide and develop knowledge, skills, and behaviors to meet requirements
* is linked to the job description and competency assessment
* is linked to the job description and competency assessment
7
New cards
Promotion
Is the advancement of an employee to better job in terms of greater responsibility, more prestige, or “status”, greater skill, and especially increase rate of pay salary.
8
New cards
Discipline & Dismissal
Requires documented facts sufficient to support the contemplated action or the kind of case the employee committed.
9
New cards
Personnel Record
Provides a ready references to an employee, job description, education, experience, qualifications, length of employment, job references, written reprimands, comments and personal list
* **Larger laboratory maintains summary and analysis records.** This is to keep the director up to date on vacancies, personnel turnover, retirements, staffing patterns, recruiting services, and other vital data to maintain a good staff.
* Records should be **centralized with accessibility limits** to appropriate **supervisor and employee** in order to maintain confidentiality of information.
* Where: within the laboratory, HRD
* **Larger laboratory maintains summary and analysis records.** This is to keep the director up to date on vacancies, personnel turnover, retirements, staffing patterns, recruiting services, and other vital data to maintain a good staff.
* Records should be **centralized with accessibility limits** to appropriate **supervisor and employee** in order to maintain confidentiality of information.
* Where: within the laboratory, HRD
10
New cards
Personnel Evaluation
Consists of periodic written reports on employees’ performance
11
New cards
Orientation (9)
1. Briefing history etc
2. Introduction people, position function
3. Description dutires responsibilities
4. Introduction faci service
5. Briefing on mechanism of setting problems
6. Briefing on opportunities
7. Briefing on sick leave, overtime, place receiving pay
8. Try-out / probation
9. Another meeting before dismissal of work
12
New cards
It is a good policy to have a period of probation -usually about __ months
3
13
New cards
Personnel Orientation
Is the introduction of the employee to this new environment.
14
New cards
T/F: Generally, the person who work for financial reasons is likely to be a more stable employee than is the person who is economically independent.
True
15
New cards
An applicant who has held 3 to 4 jobs within the past five years is a _____. Chances are this person is a _.
high risk; job hopper
16
New cards
Recent emotional crises in an individual may lead to __for a period of time.
emotional instability
17
New cards
If the writing is sloppy, it may indicate a generally __ attitude or nanswered items in the application form indicate __.
careless attitude; forgetfulness or evasiveness
18
New cards
3 things about impressions
1. close to truth
2. dangerous
3. based on limited information
19
New cards
Personnel Interview (3)
1. Setting the stage in advance so the interview will be in control & not be interrupted by other visitors
2. Asking general questions to set the applicant at ease
3. Respecting the applicant’s individuality
4. Getting the applicant to talk revealingly.
\
Note: final action “do not jump into conclusion”.
20
New cards
_____ interview by the manager is necessary in order to increase the accuracy of prediction on the applicant.
Pre-employment interview
21
New cards
Types of interview
planned and patterned interview
Non-directive interviews
depth interviews
group interviews
Non-directive interviews
depth interviews
group interviews
22
New cards
Steps in Selection Process (10)
1. Posting or advertising job vacancies
2. Reception of applications either in person or in writing
3. Preliminary interview
4. The applicant is interviewed by the personnel manager. It could be used to determine what type of personality the applicant possesses.
5. Applicant reports to the personnel manager or his assistant who briefs him on opportunities in the organization.
6. Investigation of applicant’s background
7. Introduction of the qualified applicant to his immediate boss
8. Selection from among qualified applicants
9. Medical examinatin
10. Induction and placement of the new employee
23
New cards
T/F: Job applicant who fall short of the required qualifications for the job in question or who may be overqualified maybe rejected
True
24
New cards
Source of Labor
1. Internal Source
2. External Source
25
New cards
Internal Source
* refer to the employees actively working in the laboratory
* not difficult to accept employees being recommended by other employees or anyone that is known by someone in the organization
* Job applicant who fall short of the required qualifications for the job in question or who may be overqualified maybe rejected
* not difficult to accept employees being recommended by other employees or anyone that is known by someone in the organization
* Job applicant who fall short of the required qualifications for the job in question or who may be overqualified maybe rejected
26
New cards
External Source
● include persons who apply in person, who answer advertisements and who are recommended by schools.
● both recommendation or advertisements, as long as they go through the proper HR process – then we can rely on that.
● both recommendation or advertisements, as long as they go through the proper HR process – then we can rely on that.
27
New cards
Functions of Personnel Manager
1. Recruit and interview job applicant
2. Administer employment tests to job applicants
3. Indoctrinate new employees on laboratory history, objectives, policies and rules
4. Introduce the new employees to his supervisor, the officers of the organization, his associates and subordinates
5. Motivate employees to do better
6. Keep employment records of all employees
7. Assist in transferring, promoting, demoting, discharging or retiring employee.
8. Handle complaint: grievances and disciplinary action cases.
9. Negotiate with the labor unions or union officials
10. Provide personnel services, medical, social and recreational.
28
New cards
**Recruitment**, selection, and planning
* Minimum qualifications required in prospective employees
* The sources from where labour supply will be available
* Selection tests
* The sources from where labour supply will be available
* Selection tests
29
New cards
Promotion policy & Training policy
* Induction
* Types of training
* Training of executives
* Types of training
* Training of executives
30
New cards
**Wage policy** includes
* Minimum wages
* Non-financial incentives
* Incentive plans
* Bonus, profit sharing etc.
* Non-financial incentives
* Incentive plans
* Bonus, profit sharing etc.
31
New cards
I**ntegration policy** consist of
* (a) Processing of grievances
* (b) Recognition of unions
* (c) Workers participation in management.
* (b) Recognition of unions
* (c) Workers participation in management.
32
New cards
**Salary** and wage administration
* how the company or organization is basing their salary and must be properly oriented to personnel
* some common issues in salary
* some common issues in salary
33
New cards
Changes in work assignment and hours
* This must be discussed among employees because in the laboratory, especially hospital-based, it is also clear that the hours of duties and work assignment must be property managed.
34
New cards
Employees’ health and safety
* Insurances must also be covered to personnel
* Safety guidelines must be familiarized because in the laboratory we are more exposed to many kind of risks
* Safety guidelines must be familiarized because in the laboratory we are more exposed to many kind of risks
35
New cards
Employees’ participation and work problems
* Also one thing that we need to be cleared about
36
New cards
Personnel Policies (10)
1. **Recruitment**, selection, and planning
2. Employee **induction** and training
3. Employee rating and **promotion**
4. **Transfer**, downgrading and lay-off
5. **Disciplining** and discharge
6. **Salary** and wage administration
7. **Changes** in work assignments and hours
8. Services for employees
9. Employees’ **health and safety**
10. Employees’ participation and work **problems**
37
New cards
Personnel Policies
* is the statement of intention
* commits the laboratory manager
* general course of action
* to accomplish a specific purpose
* commits the laboratory manager
* general course of action
* to accomplish a specific purpose
38
New cards
Personel Program
* consists of series of activities
* personnel policies of the laboratory
* purpose of realizing objectives of the organization
* personnel policies of the laboratory
* purpose of realizing objectives of the organization
39
New cards
PERSONNEL MANAGEMENT
was called before as human resource management/personnel administration
40
New cards
Documents
written information about policies, processes and procedures
41
New cards
Records
collected information produced by the laboratory
42
New cards
Policy
**what to do**
* a documented statement of overall intentions and direction defined by those in the organization and endorsed by management
* gives broad and general direction to the quality system
* include a statement of the organizational mission, goals and purpose
* serve as the framework for the quality system, and should always be specified in the quality manual
* a documented statement of overall intentions and direction defined by those in the organization and endorsed by management
* gives broad and general direction to the quality system
* include a statement of the organizational mission, goals and purpose
* serve as the framework for the quality system, and should always be specified in the quality manual
43
New cards
Processes
**how it happens**
* are the steps involved in carrying out quality policies
* set of interrelated or interacting activities that transform inputs into outputs
* Inputs: test requests, samples, requests for information
* Outputs: laboratory data, reports of results
* are the steps involved in carrying out quality policies
* set of interrelated or interacting activities that transform inputs into outputs
* Inputs: test requests, samples, requests for information
* Outputs: laboratory data, reports of results
44
New cards
Procedure
**how to do it**
* are the specific activities of a process
* performance of a test
* shows the step-by-step instructions that laboratory staff should meticulously follow for each activity
* are the specific activities of a process
* performance of a test
* shows the step-by-step instructions that laboratory staff should meticulously follow for each activity
45
New cards
Quality Manual
the overall guiding document for the quality system and provides the framework for its design and implementation
46
New cards
SOPs
contain step-by-step written instructions for each procedure performed in the laboratory
47
New cards
==Retention==**:** Blood bank deferred donor records
Indefinite
48
New cards
Retention: Cytogenetic reports/images
20 years
49
New cards
Retention: Urine
24 hrs
50
New cards
Retention: Serum/CSF/Body Fluids
48 hrs
51
New cards
Retention: Wet tissue
2 weeks
52
New cards
Retention: Blood/fluid smears
7 days
53
New cards
Retention: Microbiology stained slides
7 days
54
New cards
Retention: Blood bank QC records
5 years
55
New cards
Retention: Cytology slides
5 years
56
New cards
Retention: Requisitions
2 years
57
New cards
Retention: Accession logs
2 years
58
New cards
Retention: Maintenance/instrument logs
2 years
59
New cards
Retention: Quality control records
2 years
60
New cards
Retention: Clinical pathology test records
2 years
61
New cards
Retention: Retired laboratory procedures
2 years
62
New cards
Retention: Blood bank donor/receipt records
10 years
63
New cards
Retention:Blood bank patient records
10 years
64
New cards
Retention: Blood bank employee signatures/initials
10 years
65
New cards
Retention: Surgical pathology (bone marrow) slides
10 years
66
New cards
Retention: Paraffin blocks/slides
10 years
67
New cards
Retention: FNA slides
10 years
68
New cards
Retention: Reports (surgical/cytology/nonfore nsic)
10 years
69
New cards
Retention:Flow cytometry plots/histograms
10 years
70
New cards
VERTICAL COMMUNICATION
1. Upward
2. Downward
71
New cards
UPWARD COMMUNICATION
When subordinate communicates directly to his supervisor or superiors
It is for providing suggestions, complaints and the like to superiors.
It is not directive in nature
It is for providing suggestions, complaints and the like to superiors.
It is not directive in nature
72
New cards
DOWNWARD COMMUNICATION
When a superior or supervisor communicates directly to his subordinates.
Top level management used this kind of communication in informing employees about their decisions, policies, procedures, and sending of memos.
Top level management used this kind of communication in informing employees about their decisions, policies, procedures, and sending of memos.
73
New cards
HORIZONTAL COMMUNICATION
flow of information between colleagues and peers.
74
New cards
DIAGONAL COMMUNICATION
between positions that are on different lateral planes and activities of the organizational structure
occurs between laboratory personnel and the human resources department; or between laboratory management and nonmanagerial members of other departments
occurs between laboratory personnel and the human resources department; or between laboratory management and nonmanagerial members of other departments
75
New cards
FOUR PERSPECTIVES IN A BALANCED SCORECARD
1. Financial Performance
2. Customer Service
3. Internal Business Processes
4. Potential for Learning and Growth
76
New cards
BALANCED SCORECARD
a comprehensive management control system that balances traditional financial measures with measures of customer service, internal business processes, and the organization’s capacity for learning and growth
77
New cards
INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
system that incorporates all the processes needed for effectively managing data – both incoming and outgoing patient information
paper-based, computer-based, or a combination
paper-based, computer-based, or a combination
78
New cards
COMMUNICATION
the process in human relations of passing information and understanding from one person to another
79
New cards
Interdepartmental
the transmission of information **between or among** departments
80
New cards
Intradepartamental
the transmission of information **within** the department
81
New cards
capital budget
budget that plans and reports investments in major assets to be depreciated over several years
82
New cards
cash budget
estimates receipts and expenditures of money on a daily or weekly basis to ensure that an organizations has sufficient cash to meet its obligations
83
New cards
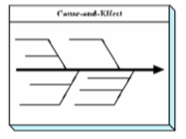
CAUSE-AND-EFFECT (CE) DIAGRAM
the problem itself, the effect, which is placed on the right side of the diagram;fleshes out the various potential causes of the problem
\
fishbone analogy
\
fishbone analogy
84
New cards
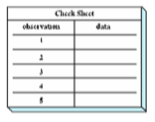
CHECK SHEETS
data collection done, which are put in a tabular list representing collected data about the process
85
New cards
A RESPONSIBILITY CENTER
as any organizational department or unit under the supervision of a single person who is responsible for its activity
86
New cards
expense budget
revenue budget lists forecasted and actual revenues of the organization
87
New cards
revenue budget
lists forecasted and actual revenues of the organization
88
New cards
Directing
Wide
89
New cards
Supervising
Narrow
90
New cards
Directing
includes motivation, communication, supervision, training, & leadership
91
New cards
Supervising
only one of the elements of direction
92
New cards
Directing
generally at top level; formulates polices and takes important decision
93
New cards
Supervising
restricted to the lower level management; for implementation
94
New cards
Directing
related to supervision which is the intermediate link between the workers and management
95
New cards
Supervising
deal, guide and lead workers directly under commands
96
New cards
Directing
Financial & non financial incentives
97
New cards
Supervising
cannot provide incentives but it can only recommend rewards in special case
98
New cards
Directing
Leads the efforts of medium and lower Level executives
99
New cards
Supervising
Efforts of employee under his commands
100
New cards
Level 1 - Individual
**Capable**
contributes talent, skills, knowledge
contributes talent, skills, knowledge