Covalent Bonding Models: Hybrid Orbitals, σ and π Bonds, and Molecular Polarity
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What determines the number of hybrid orbitals in covalent bonding?
The number of hybrid orbitals equals the number of atomic orbitals.
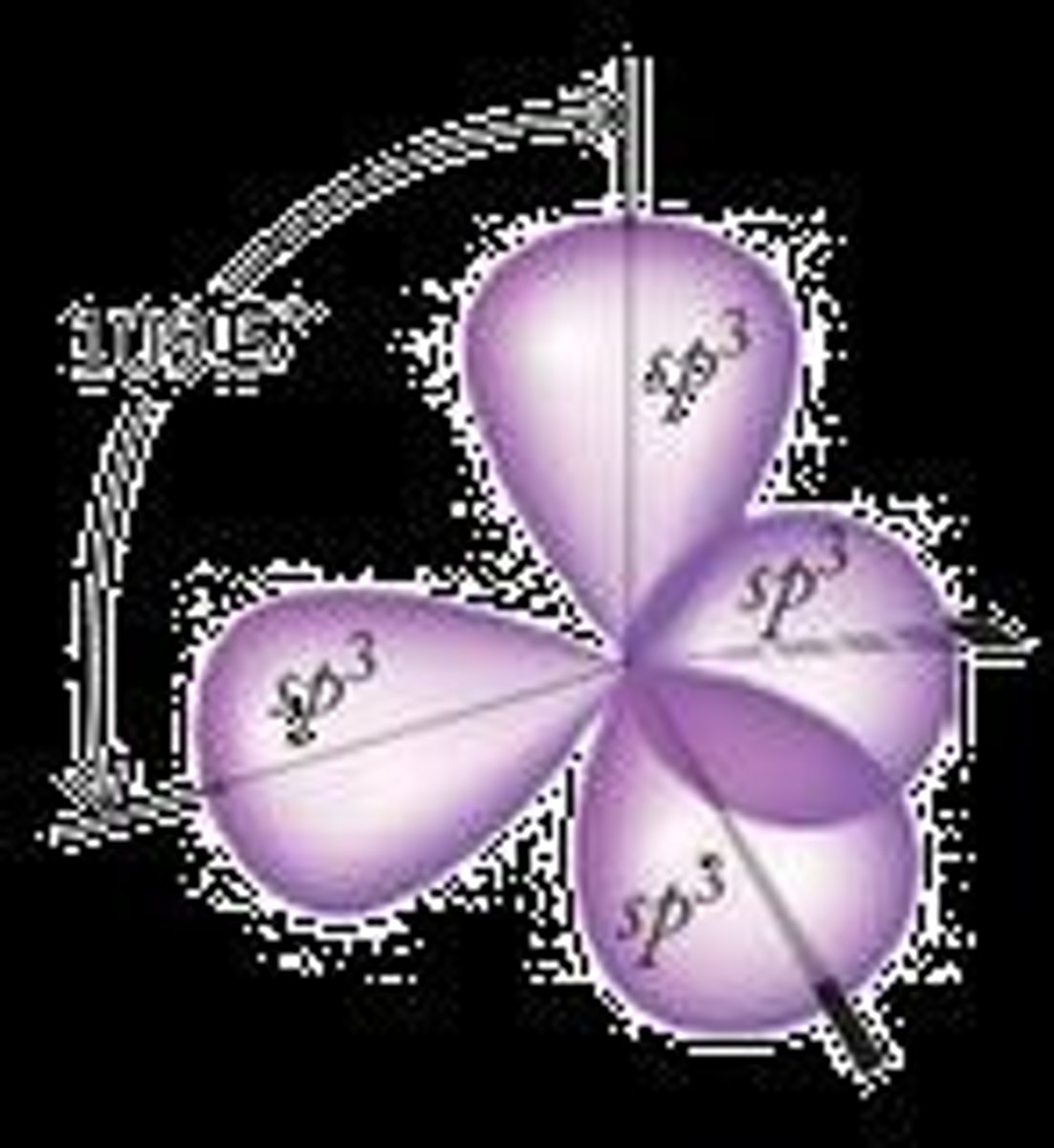
What is the type of hybrid orbital formed by one s and three p orbitals?
Four sp3 orbitals.
What is the hybridization of carbon in ethene (C2H4)?
sp2 hybridization.
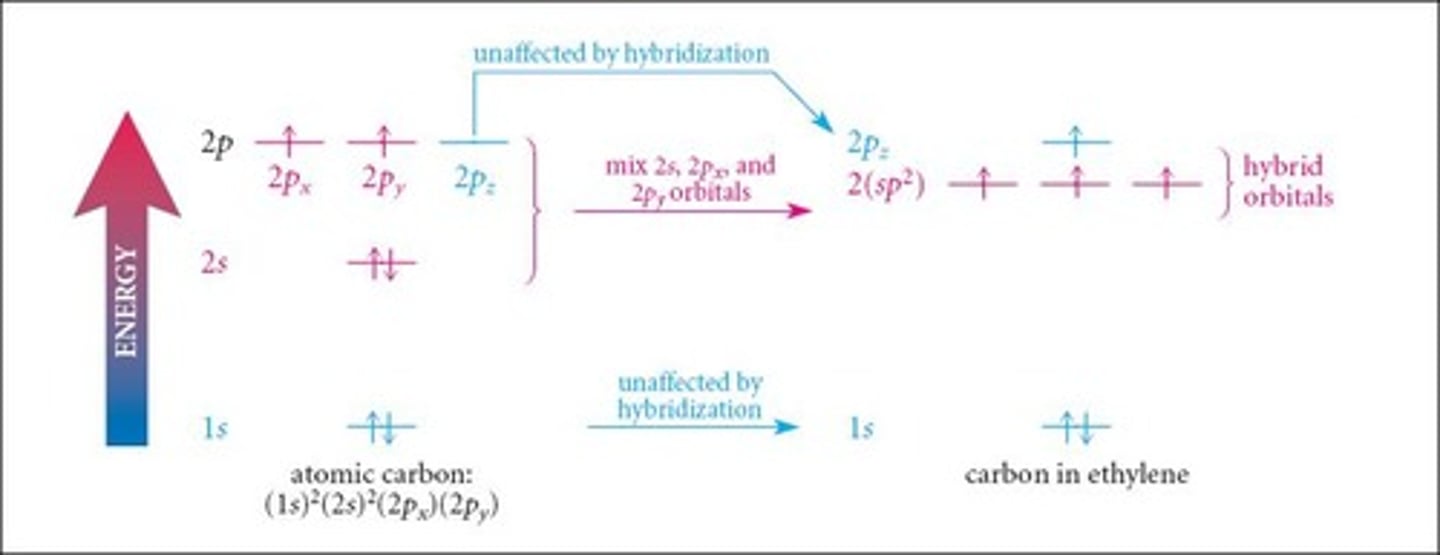
What is the geometry of each carbon atom in ethene?
Trigonal planar.
How many equivalent bonding orbitals are required for ethene?
Three equivalent bonding orbitals.
What type of bond is formed in addition to the sigma bond in a double bond?
A pi bond.
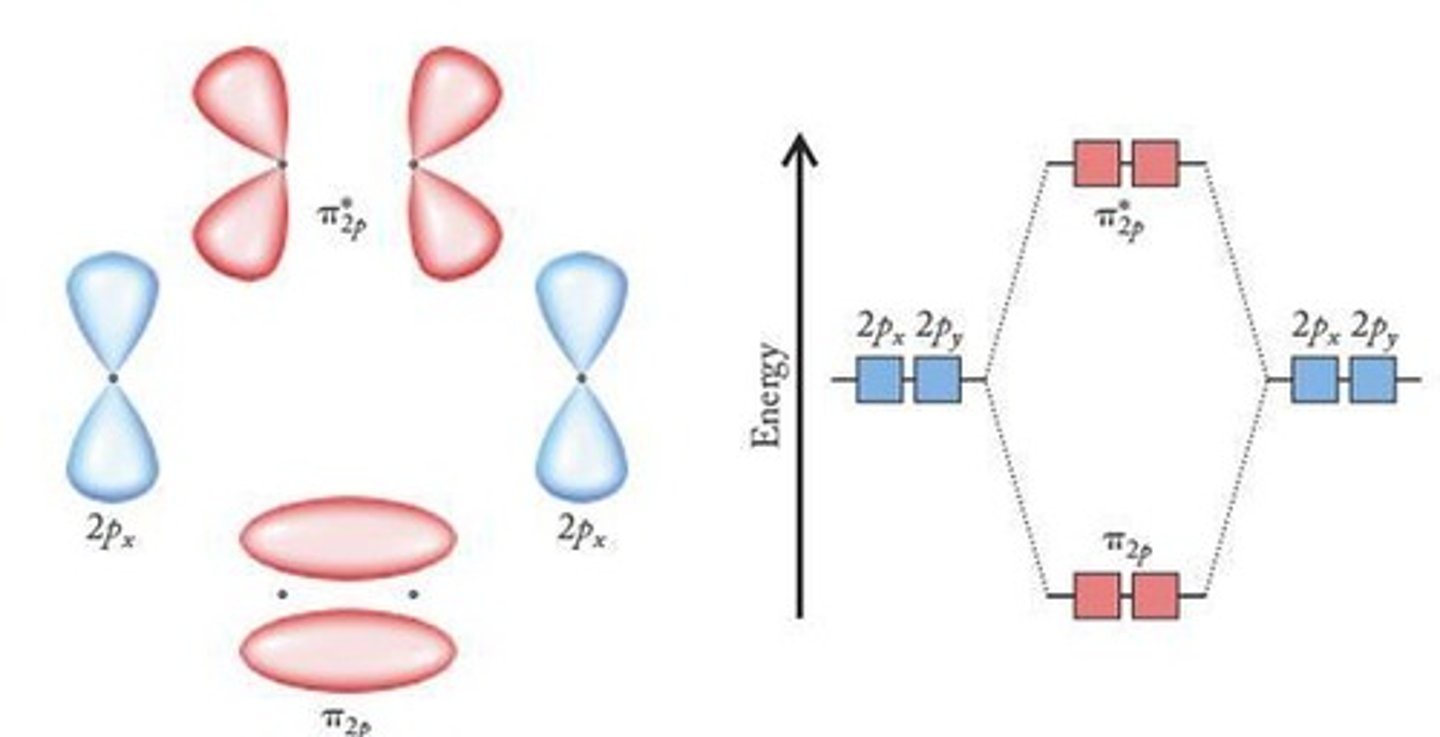
What is the overlap type for sigma bonds?
Head-to-head overlap.
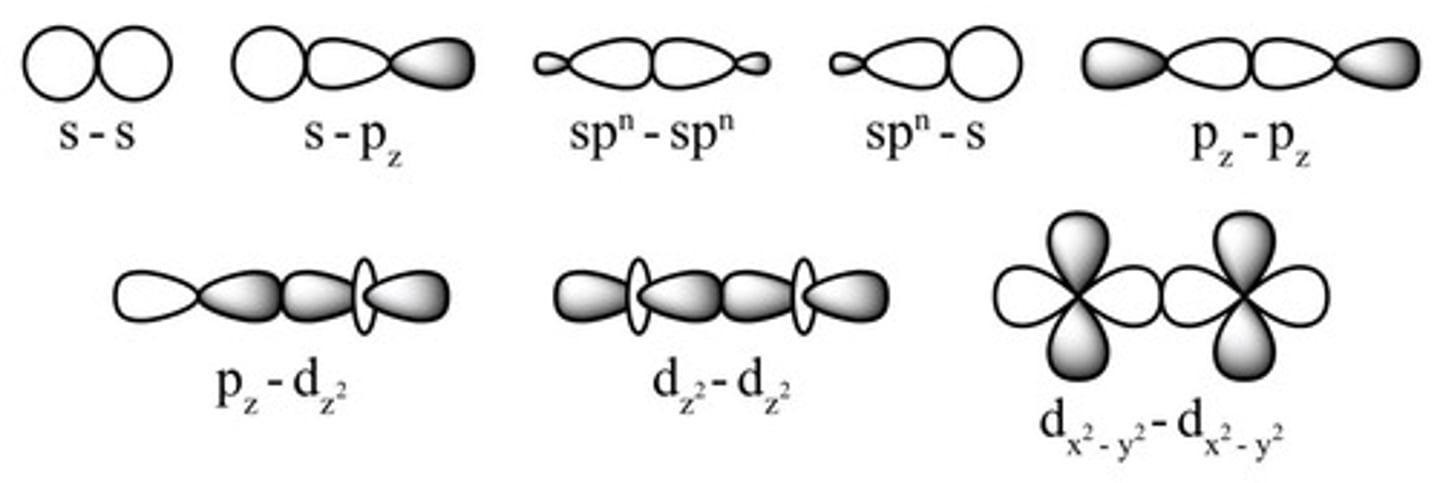
What is the overlap type for pi bonds?
Sideways overlap.
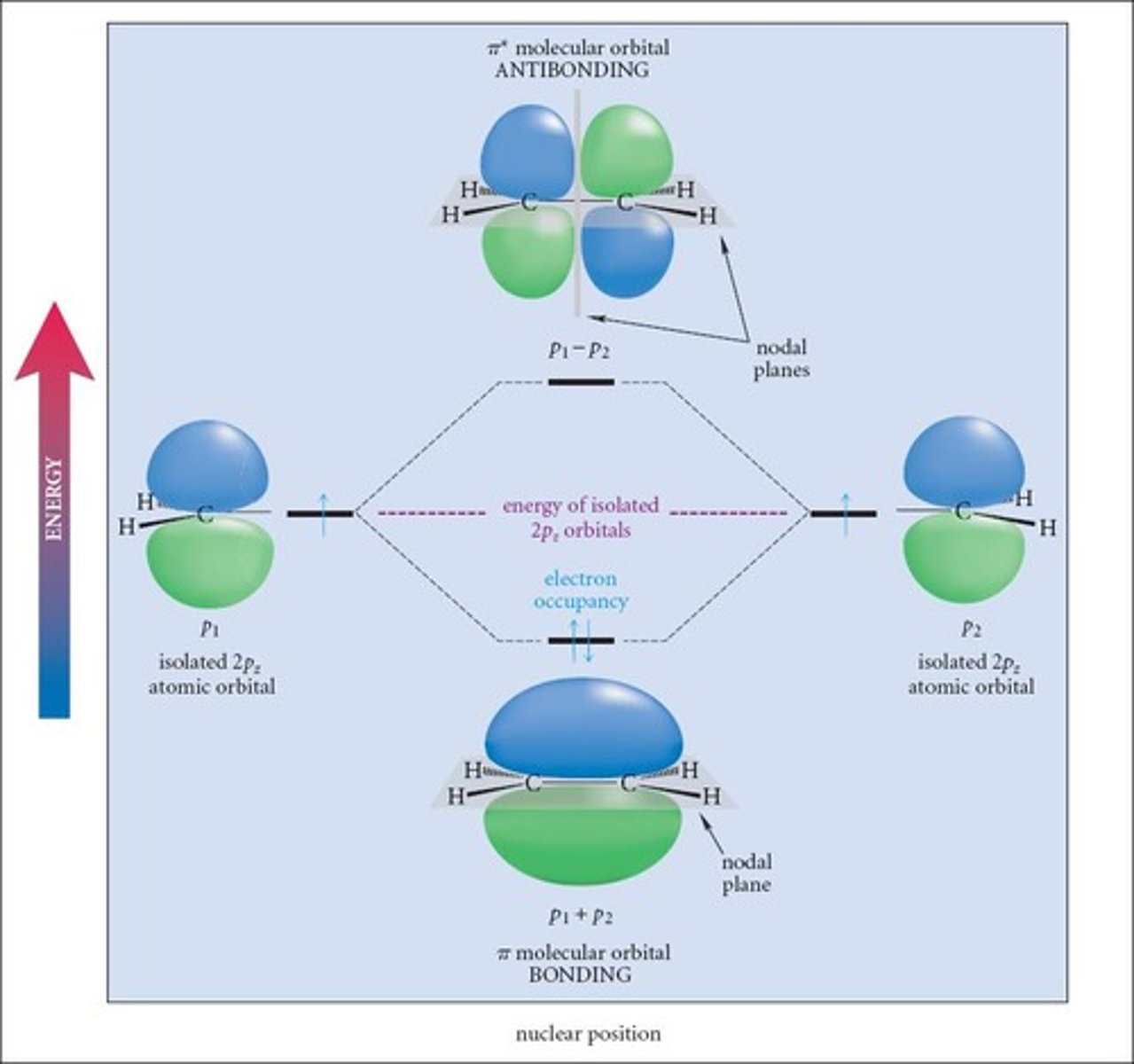
How many bonds constitute a double bond?
One sigma bond and one pi bond.
What is the molecular orbital (MO) model used for in covalent bonding?
To show electron distribution in the pi system.
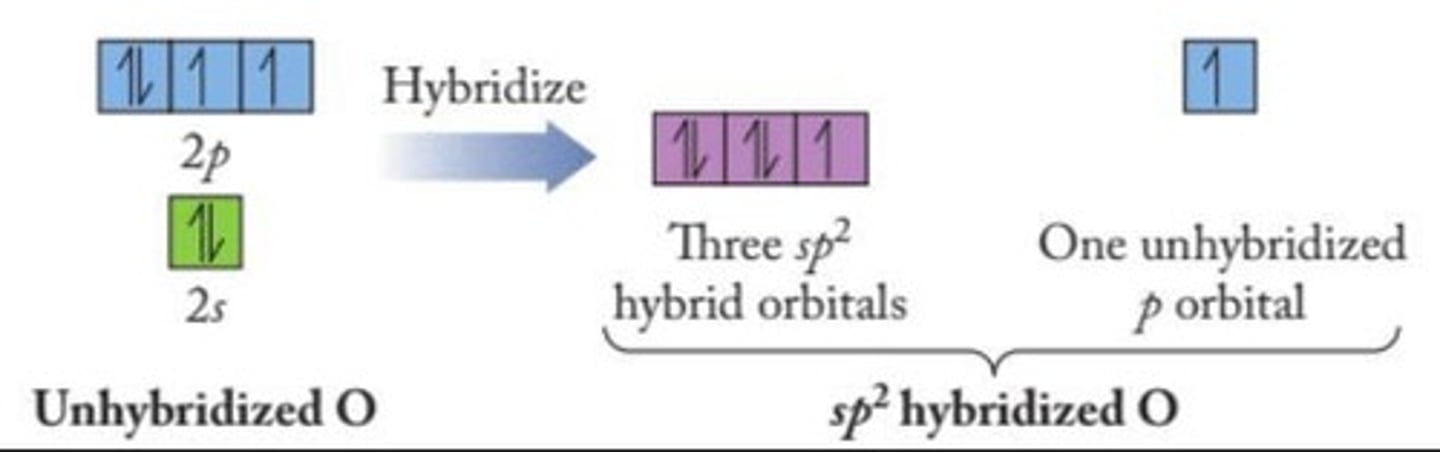
What is the hybridization and geometry of carbon in formaldehyde (CH2O)?
sp2 hybridized and trigonal planar.
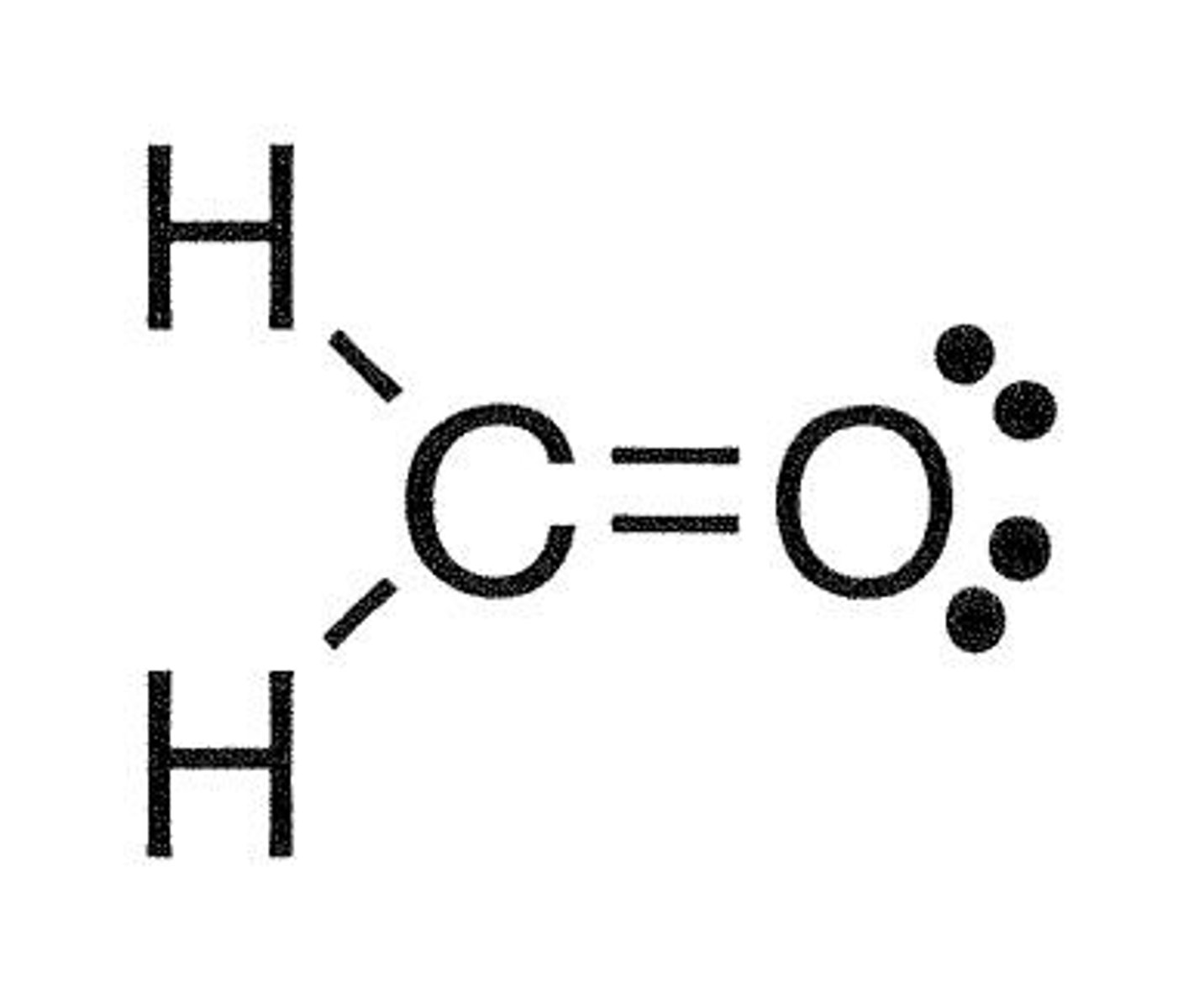
What type of overlap occurs when carbon bonds to oxygen in formaldehyde?
One sigma sp2-sp2 overlap and one pi p-p overlap.
How does bond strength relate to orbital energy?
Bond strength increases as orbital energy decreases.
What happens to effective electronegativity as s character increases?
Effective electronegativity increases.
What condition makes a covalent species polar?
An uneven distribution of electrons.
What is the dipole moment in a polar molecule represented by?
The overall molecular dipole moment, μ.
What does d+ and d- indicate in a polar molecule?
They indicate regions of partial positive and negative charge, but do not represent actual charges.
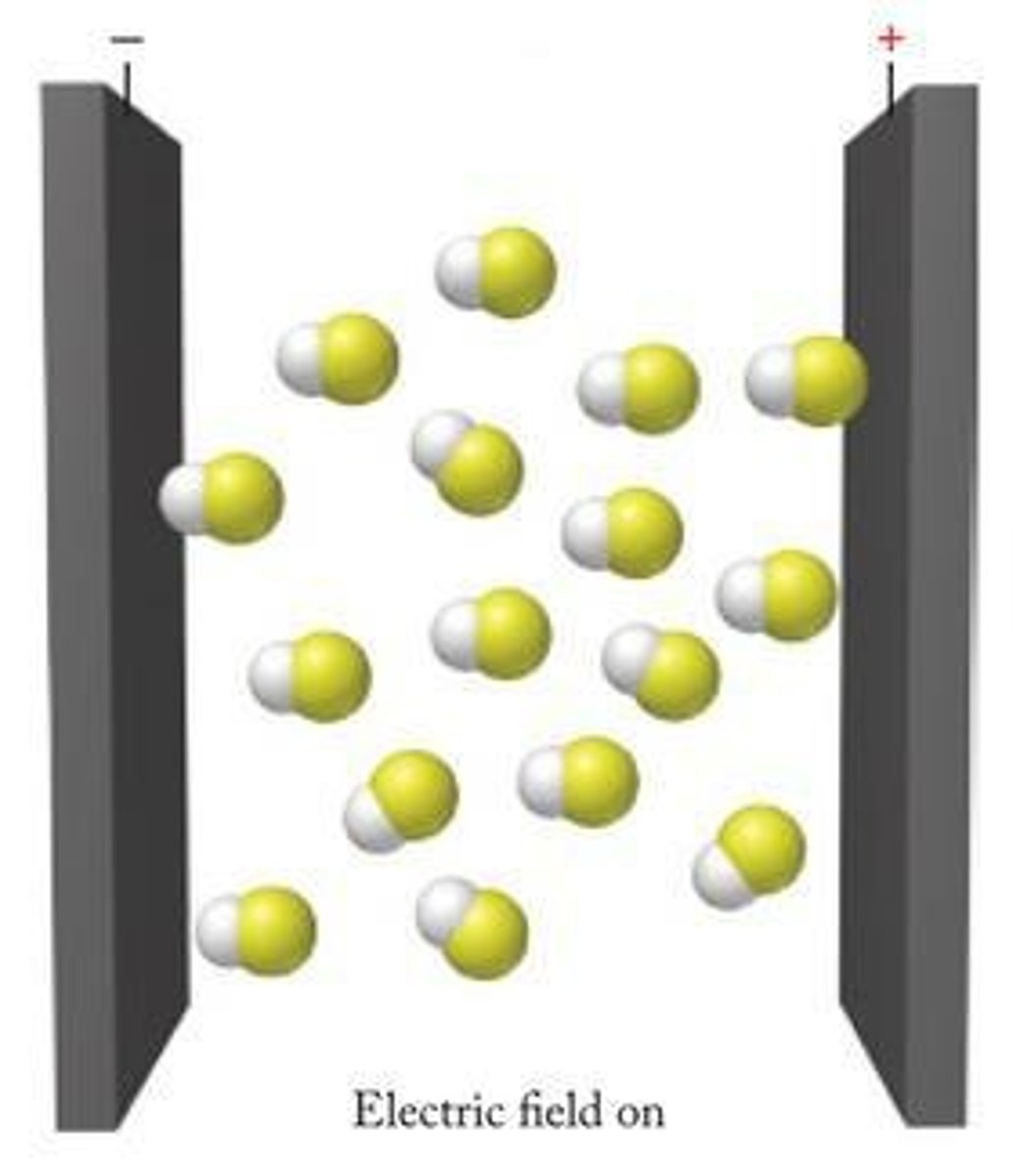
What occurs to molecules when an electric field is applied?
Molecules become oriented.
What is the significance of nonbonding orbitals in covalent bonding?
They indicate shared electrons are closer in energy to the more electronegative atom.
What is the relationship between electronegativity and electron distribution in a molecule?
Shared electrons are closer in energy to the more electronegative atom, affecting molecular polarity.