Anatomy Final Reproductive System
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
reproductive system is composed of
primary sex organs
accessory reproductive organs
primary sex organs
testes and ovaries
-produce sex cells (gametes)
-secrete steroid sex hormones
—> androgens (males): testosterone, dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and androstenedione (precursor)
—> estrogens and progesterone (females)
gametes
sperm
oocytes (eggs)
steroid sex hormones androgens
males
testosterone, dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and androstenedione (precursor)
dihydrotestosterone (DHT) steroid sex hromone
most active
steroid sex hormones female
estrogen
progesterone
accessory reproductive hormones
ducts, glands, and external genitalia
testosterone —>
DHT
testes
-are located in the scrotum
-hang outside the body
testes function
produce sperm
sperm is best produced
in cooler temperatures (<37 degrees)
scrotum
layer of smooth muscle called dartos muscle
dartos muscle
if too cold: muscle contracts
if too hot: muscle relaxes
sperm are delivered to exterior through a
system of ducts
path of sperm delivery to exterior
epididymis —> ductus (vas) deferens —> ejaculatory duct —> urethra
vasectomy
cuts the vas deferens to inhibit sperm from leaving
spongy tissue of the penis
-corpus cavernosum
-corpus spongiosum
prepuce
foreskin
the testes are surrounded by 2 tunics
-tunica vaginalis
-tunica albuginea
seminiferous tubules
site of sperm production (in the walls)
sperm passes through ____ in the testes
-seminiferous tubules
-rete testis
-efferent ductules
-epididymis
interstitial (leydig) cells
-outside the seminiferous tubules
-produce androgens (EX: testosterone)
testosterone is converted to
more active form DHT by 5-alpha reductase
functions of testosterone
-facilitates spermatogenesis
-stimulate libido and development of secondary sex characteristics (hair growth in axillary anf pubic regions, deeper voice, facial hair)
spermatic cells
give rise to sperm
meosis are
primary for spermatic cells
mitosis
spermatogonia form spermatocytes
meiosis
spermatocytes form spermatids
spermatogenesis
-spermatids become sperm (spermatozoa)
-haploid (n)
—> sex chromosome is either X or Y
major regions of the sperm
-head
-midpiece
-tail
head of sperm
1) nucleus
2) acrosome
acromosome head of sperm
containing enzymes that enable sperm to penetrate the egg
midpiece of sperm
produce mitochondira
tail of sperm
flagellum (microtubules)
sustentacular (sertoli) cells
present in testicles
• Provide nutrients and signals to dividing cells throughout
spermatogenesis
• Dispose of excess cytoplasm sloughed off during
spermiogenesis
• Produce chemical mediators to regulate spermatogenesis
—>• ABP – promotes spermatogenesis
—>• Inhibin – inhibits spermatogenesis
• Forms blood-testis barrier
ABP
chemical mediator that promotes spermatogenesis
inihibin
chemical mediator that inhibits spermatogenesis
accessory sex glands produce
the remaining components of semen
accessory sex glands
-seminal vesicles
-prostate
-bulbourethral
semen consists of secretions from
-seminal glands
-prostate glan
-bulbourethral glands
seminal glands (70%)
Secretions are alkaline which neutralizes vagina acidity
• Fructose nourishes sperm (only place fructose is produced; can be
used in rape kit)
• Prostaglandins promote widening of external os of cervix
why can fructose be used in a rape kit
it is th only place in the body fructose is produced (seminal glands)
fructose
nourishes sperm
prostaglandins
promote widening of external os of cervix
prostate gland
secretes milky fluid containing:
-citric acid
-seminalplasmin
-PSA
citric acid prostate gland
nutrient for sperm health
seminalplasmin prostate gland
antibiotic that combats urinary tract infection; may also prevent female immune system from attacking sperm
PSA prostate gland
enzyme to liquefy semen
-prostate specific antigen
bulbourethral glands
produce pre-ejaculatory fluid (pre-cum)
pre-ejaculatory fluid
-lubrication of urethra and tip of penis
-neutralization of acidity in urethra
-clearing the urethra of urine or debris
The hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis
anterior pituitary
1. Hypothalamus releases gonadotropin-
releasing hormone (GnRH)
—>. Massive increase Begins during puberty
2. GnRH stimulates the anterior pituitary
to secrete FSH and LH
3. FSH causes Sertoli cells cells to release
androgen-binding protein (ABP), which
makes spermatogenic cells receptive
to testosterone
4. LH stimulates Leydig (Interstitial) cells
to release testosterone
FSH
follicle stimulating hormone
-causes sertoli cells to release anddrogen-binding protein (ABPT) which makes spermatogenic cells receptive to testosterone
LH
leutinizing hormone
-stimulates Leydig(interstital) cells to release testosterone
the penis consists of
-root
-shaft
-glans penis
-prepuce
-3 cylindrical bodies of erectile tissue
-urethral regioms
3 cylindrical bodies of erectile tissue
-corpus spongiosom
-corpora cavernosa
urethral regions of the penis
both urine and semen pass through
1)prostatic urthra (prostate)
2) membranous urethra
3) spongy (penile) urethra (outside body)
Male secual response consists of
-erection
-ejaculation
erection
– Parasympathetic
reflex promotes
release of nitric oxide
(NO) – a vasodilator
– NO causes erectile
tissue to fill with
blood
blood fills spongy tissue
ejaculation
– Sympathetic spinal
reflex causes
• Ducts and accessory
glands to contract
and empty their
contents
• Bladder sphincter
muscle to constrict,
preventing the
expulsion of urine
men with decreased testosterone levels in 50s
o Due to decreased number of interstitial (Leydig) cells
o Decline more gradually than women’s hormone drop
o Most men have few symptoms
o Some with mood swings, decreased sex drive, hot flashes
prostate elargement
o experienced by most men with age
o interferes with sexual and urinary functions
erectile dysfunction
o inability to achieve or maintain erection
o associated with aging, other risk fatcors
female gonads
ovaries
-produce female gametes (ova)
-secrete female sex hormones (estrogen and progesterone)
accessory ducts in female reproductive system
-uterine tubes
-uterus
-vagina
the ovaries are held in place by several ligaments
-ovarian ligament
-suspensory ligament
-broad ligament
-round ligament
follicle
oocyte surrounded by granulosa cells
stages of developement for follicle
– Primordial follicle
– Primary follicle
– Secondary follicle
– Late secondary follicle
graafian follicle
-fluid-filled antrum forms
ovulation
ejection of the oocyte
corpus luteum
develops from reptured follicle
female duct system
-uterine (fallopian) tubes
-uterus
-vagina
fallopian tubes
-ampulla
-isthmus
ampulla fallopian tubes
– Infundibulum - distal expansion
near ovary
– Usual site of fertilization
– Ciliated fimbriae of
infundibulum create currents to
move oocyte into uterine tube
Infundibulum ampulla
distal expansion near ovary
isthmus fallopian tubes
constricted region where tube joins uterus
oocyte is carried along by
peristalsis and ciliary action
uterus
cervix & uterine wall
cervix
narrow neck to vagina
– Cervical canal connected to
– Vagina via external os
– Uterine body via internal os
cervical glands
secrete mucus
blocks sperm entry except during midcycle
3 layers of the uterine wall
1) perimetrium
2) myometrium: smooth muscle
3) endometrium: mucosal lining
myometrium
: smooth muscle
contracts during labor to push the baby out
endometrium
: mucosal lining
grows during menstrual cycle; shed during menstruation
functions of the vagina
as birth canal,
recieves penis,
passageway for menstruation
vagina
thick-walled, fibromuscular tube
3 tunics of the vagina
-mucosa
-muscularis
-adventitia
mucosa tunic of vagina
o Nonkeratinized stratified
squamous epithelium
o Acidic secretions prevent
infection
o Form vascularized
membranous barrier, hymen
which covers part of external
vaginal opening
hymen
vascularized membranous barrier that covers part of external vaginal opening
female external genitalia
-labia majora
-labia minora
-greater vestibular glands
-clitoris
labia majora
outer fatty skin folds
labia minora
inner skin folds
-protect the vaginal and urethral openings from mechanical irritation, dryness and infections
greater vestibular glands
release mucus into the vestibule for lubrication
clitoris
-contains erectile tissue
-glans clitoris: exposed
glans clitoris
exposed
oogenesis —> production of female gametes
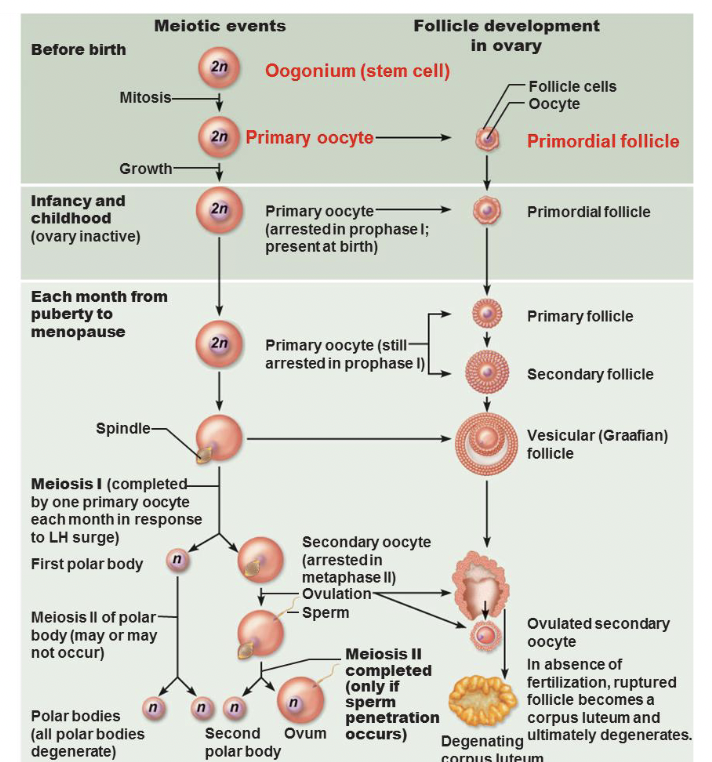
gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) female reproductive
– Secretion from hypothalamus begins to rise towards very
end of previous menstrual cycle
– Leads to the increase in production/secretion of FSH and
the production of LH
follicular stimulating hormone (FSH) female reproductive
-causes the development of the follicle
-causes granulosa cells fo the follicle to secrete estrogen
lutenizing hromone (LH) female reproductive
– Before day 10, it’s secretion is blocked by low levels of
estrogen (negative feedback)
– After day 10, it’s secretion is increased by high levels of
estrogen (positive feedback)
• This leads to ovulation
gonadotropin hormone levels female reproductive
-GnRH
-FSH
-LH
Ovsarian hormone levels
-estrogen
-progestogens