Carbonyl and Polar Functional Groups
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key terminology related to carbonyl and polar functional groups in organic chemistry.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
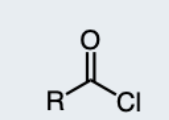
Ester
formed from the reaction of an alcohol and a carboxylic acid, characterized by the functional group -COO-.
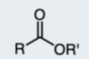
Acid Chloride
A reactive functional group containing a carbonyl and a chlorine.
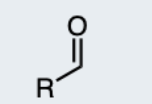
Aldehyde
A carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to at least one hydrogen.
Ketone
A carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to two carbon atoms.
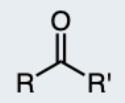
Carboxylic Acid
A functional group containing a carbonyl (C=O) and a hydroxyl group (–OH) attached to the same carbon atom.
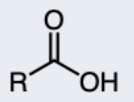
Imine
A functional group containing a carbon-nitrogen double bond, derived from a ketone or an aldehyde.
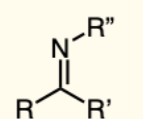
Anhydride
two carbonyl groups (C=O) bonded to the same oxygen atom.
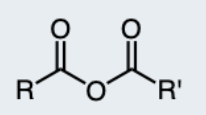
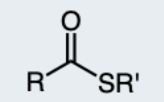
Thioester
An ester with a sulfur atom in place of the oxygen.
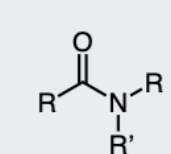
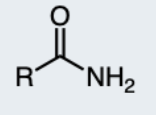
1-Amide
a carbonyl group (C=O) directly attached to a nitrogen atom and two hydrogen atoms
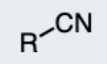
Nitrile
A compound containing the cyanide group (-C≡N).
Alkyl Halide
A carbon atom bonded to a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I).
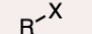
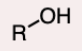
Alcohol
A compound containing one or more hydroxyl (-OH) groups.
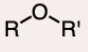
Ether
an oxygen atom connected to two R groups
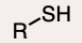
Thiol
A compound with a sulfhydryl (-SH) group.
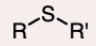
Thioether
An ether in which the oxygen is replaced by sulfur.
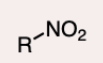
Nitro Group
A functional group consisting of a nitrogen atom bonded to two oxygen atoms.
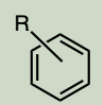
Arene
A hydrocarbon containing at least one aromatic ring.
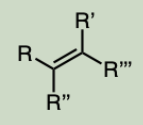
Alkene
carbon-carbon double bond.
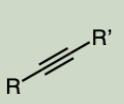
Alkyne
a carbon-carbon triple bond.
1º-Amine
the nitrogen atom is bonded to one R group and two hydrogen atoms.
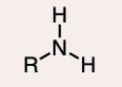
2º-Amine
the nitrogen atom is bonded to two R groups and one hydrogen atom.
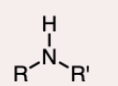
3º-Amine
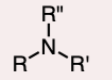
the nitrogen atom is bonded to three R groups
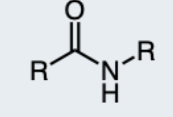
2-amide
carbonyl attached to a nitrogen and 1 hydrogen
3-amide
carbonyl attached to a nitrogen and 2 R groups