Organic Stereochemistry and Reaction Mechanisms: Chirality, SN1/SN2, and Alkene Stability
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Achiral
A molecule that is superimposable on its mirror image
Chiral
object that has non-superimposable mirror image
Plane of symmetry effect on chirality
The molecule is achiral if it has a plane of symmetry
How do you draw enantiomer?
Mirror or switch wedge and dash
how to name chiral centers
put chirality and C# in parentheses at start (ex. (1R, 3S)
Diastereomers
Stereoisomers w/ at least one matching chiral center and one differing chiral center
# of stereoisomers possible
2^n
n = # of chiral centers
meso compound
achiral molecule with chiral centers
Are meso compounds optically active?
no
Are racemic mixtures optically active?
no, the two components cancel out eachothers' effect on light
Are chiral molecules optically active?
yes they rotate plane polarized light
Horizontal line fischer
wedge
Vertical line fischer
dash
Chirality of Sn2
Inverts chiral center
SN2 rate law
rate = k[substrate][nucleophile]
SN1 rate law
rate = k[substrate]
SN1 rate determining step
loss of leaving group
SN2 solvent preference
polar aprotic
SN1 solvent preference
polar protic
Hammond’s postulate
the transition state is more similar in structure to the species to which it is more similar in energy
SN1 chirality
Produces racemic mix
How are carbocations stabilized?
inductive effect and hyperconjugation
hyperconjugation
spreading out charge by the overlap of an empty p orbital with an adjacent sigma bond
carbocation/radical stability high to low
3 benzyl > 3 allyl > 2 benzyl > 2 allyl > 3 > 1 benzyl > 1 allyl > 2 > 1 > methyl
β-Branching Sn2 Rate trend
Less beta branches -> faster rxn
Leaving group ranking good to bad
I- > Br- > Cl- > H2O >> F- > acetate- > OH- > CH3O- > NH2-
Convert the -OH into a better leaving group
Use tosycl chloride (Tscl) which replaces OH with OTs which is a good LG
Nucleophilicity trend across a period
Decreases left to right
Nucleophilicity trend down group in polar aprotic solvent
Decreases down
Nucleophilicity trend down group in polar protic
Increases down
Zaitsev
more substituted alkene
Hoffman
less substituted alkene
Alkene stability high to low
tetra > tri > trans > cis > mono
E1 substrate ranking
3 > 2 > 1 > Me
E2 substrate ranking
3 > 2 > 1 > Me
E2 base preference
strong base (negatively charged)
E2 LG and leaving H geometry
anit-periplanar
When do dehydration reactions take place?
Acid (Ex H2SO4), water and heat
If there is a bulky base reacting with a primary group, what rxn will proceed?
E2
Radical chemistry steps
Initiation, propagation, termination
What reagent for allylic bromination
NBS
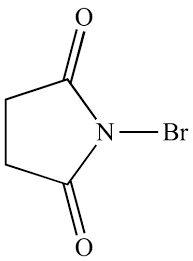
H2O Pka
15.7
H3O+ Pka
-1.7

Carboxylic acid pka
5
R-OH Pka
16-18
Ph-OH Pka
10
R-NH2 Pka
36-40
R-NH3+ Pka
9-11
H-C≡N Pka
9
R-C≡C-H Pka
25
NH3 Pka
35
H2 Pka
35
E1 rate law
rate = k[substrate]
E2 rate law
rate = k[base][substrate]