metabolic processes
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Substrate level phosphorylation
The direct addition of a phosphate to an ADP from something else to make ATP or the removal of a phosphate
Oxidation phosphorylation
The synthesis of ATP through the transfer of elections in a series of chemical reactions
Ex.
Redox reactions
A chemical reaction involving the transfer of one or more electrons from one reactant to nether
Oil Rig
Oxidation is loss
Reduction is gain
Example of redox reactions
Combustion
Cellular respiration
A series of redox reaction to create energy in the form of ATP
What is NADH
Nicotinamide Adenosine dinuelectide + hydrogen
FADH2
Flavin Adenosine Dinucleotide + 2 hydrogen
The structure of the mitochondria
Inner membrane (Cristae)
folded in on itself
Matrix - liquid inside the cristae
outer membrane
Mitochondria function
Site for cellular respiration and photosynthesis
Two phases of cell respiration
Anaerobic - in the absence of oxygen - glycolysis taking place in the cytoplasm
Aerobic - in the presence of oxygen - all the other steps
4 main steps of cell respiration
Glycolysis
Pyruvate Oxidation
Kreb cycle
Electron Transport Chain
Glycolysis
Glucose is broke down to release 2 pyruvate and energy in the form of ATP
takes places in the cytoplasm
Step 1 of glycolysis
Hexose kinase converts glucose into glucose-6- phosphate by removing a phosphate from ATP to form ADP
Step 2 of glycolysis
The enzyme phosphogincoisomerase reacts with glucose-6- phosphate to make its isomer fructose-6-phosphate
Step 3 of glycolysis
Phosphofructokinase converts fructose-6-phosphate into fructose 1,6 bisphosphate by removing a phosphate from ATP
Step of glycolysis
Aldolase cuts fructose 1,6 bisphosphate in half to form Glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate (G3P) and dihydroxyacetone phosphate.
Step 5 of glycolysis
The enzyme aldolase quickly turns dihydroxyacetone into GP3
Step 6 of glycolysis
Triode phosphate dehydrogenase oxidizes G3P into bisphosphocglycerate (BPG) by removing electrons/H+ from NAD+ to form NADH (x2)
Step 7 of glycolysis
Phosphoglycerkinase removes a phosphate from BPG to form 3-phosphoglycerate and puts the phosphate on ADP to for ATP (x2)
Step 8 of glycolysis
Phosphoglyceromutase relocates the phosphate on 3-phosphoglycerste to form 2-phosphoglycerste (x2)
Step 9 of glycolysis
A water molecule is removed from each 2-phosphoglycerate by enolase to form phosphoenol pyruvate (x2)
Step 10 of glycolysis
The last phosphate is removed from each phosphoenol pyruvate and added to ADP to form ATP by pyruvate Kinase. Resulting in 2 by pyruvates (x2)
At the end of glycolysis there is?
2 pyruvate
2 ATP
2 NADH
2 water molecules
Pyruvate oxidation
At the end of glycolysis, the two pyruvate molecules move into the mitochondria. There, one carbon is removed from each pyruvate and released as carbon dioxide. The hydrogen from that carbon is used to turn NAD⁺ into NADH with the help of an enzyme called pyruvate dehydrogenase. The remaining two-carbon part joins with Coenzyme A (CoA) to form Acetyl-CoA
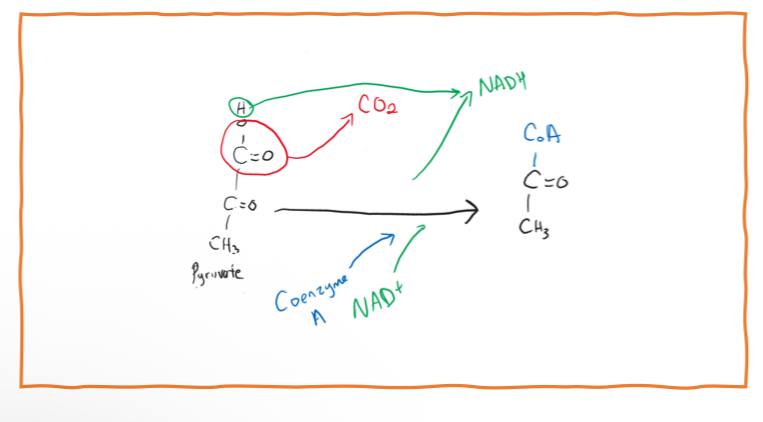
Result of pyruvate oxidation
2 NADH
On the Carpet In the Kitchen Sally C Saw Five Mice
Oxaloacetate
Citrate Synthase
Isocitrate
a-Ketoglutarate
Succinyl - CoA
Succinate
Fumarate
Malate
Step 1 of the kreb cycle
Acetyl-CoA is binded to oxaloacetate by citrate synthase to create citrate
Citrate in converted to isocitrate by aconitase
Step 2 kreb cycle
Isocitrate is oxidized removing cabon dioxide and a H+ to reduce NAD+ to NADH due to isocitrate dehydrogenase resulting in a-ketogluterate
Step 3 of kreb cycle
A-ketogluterate is oxidized by removing carbon dioxide, NAD+ is reduced to NADH and CoA is bonded to form succinyl -CoA due ketoglutate dehydrogenase
Step 4 of kreb cycle
Water and succinyl-CoA reacts to produce CoA ATP and succinate due to succinyl CoA synthase
Step 5 of kreb cycle
Succincte reacts with FAD to produce FADH2 and fumerate due to succinate dehydrogenase
Step 6 of kreb cycle
Fumerate produces water and malate due to fumerase
Step 7 of the kreb cycle
Malate is oxidized by NAD to form oxaloacetate and NADH+ due to malate dehydrogenase
Result of kreb cycle
6 NADH
2 ATP
2 FADH
Sugar metabolism
Penrose and hexose is modified into glucose or fructose to enter glycolysis
Triose is converted to G3P or dehydroxyaetone phosphate to enter glycolysis
Metabolism of starch and glycogen
Hydrolysis (addition of water) breaks alpha 1-4 and 1-6 bonds to leave the sugars to enter glycolysis
Metabolism of fats
Triglycerides split into fatty acids and glycerol
Glycerol - converted to glucose due to “glucogenisis” or G3P to enter glycolysis
Fatty acids - are brought to the matrix where it undergoes B- oxidation
B-oxidation
The process splitting a molecule into 2 carbon acetyl groups starting with the carboxyl end
Turning into acetyl-CoA breaking down 1 ATP and tuning the resulting NADH and FADH into ATP
Metabolism of proteins
Undergoes deamination removing the amp group and turns it into ammonia
Other reactions converts the different side chains into different products in glycolysis and krebs cycle
Examples of protein metabolism
Leucine → acetyl-CoA
Alanine → pyruvate
Proline→ a-ketogluterate
Anaerobic respiration
Oxygen is only made at the end of the ETC and it receives the electrons from NADH and FADH2
without oxygen the electrons can't go anywhere resulting in NADH and FADH2 to not get oxidized
Results of a lack of oxygen
Kreb need NAD+ and FAD not NADH and FADH+ so this will stop the whole kreb cycle (shuts down mitochandria)
glycolysis keeps going producing 2 ATP and 2 NADH because its anaerobic but a pathway needs to be made
Fermentation
The process when NADH is oxidized by breaking pyruvate into another product
Types of fermentation
Alcohol fermentation
lactic acid fermentation
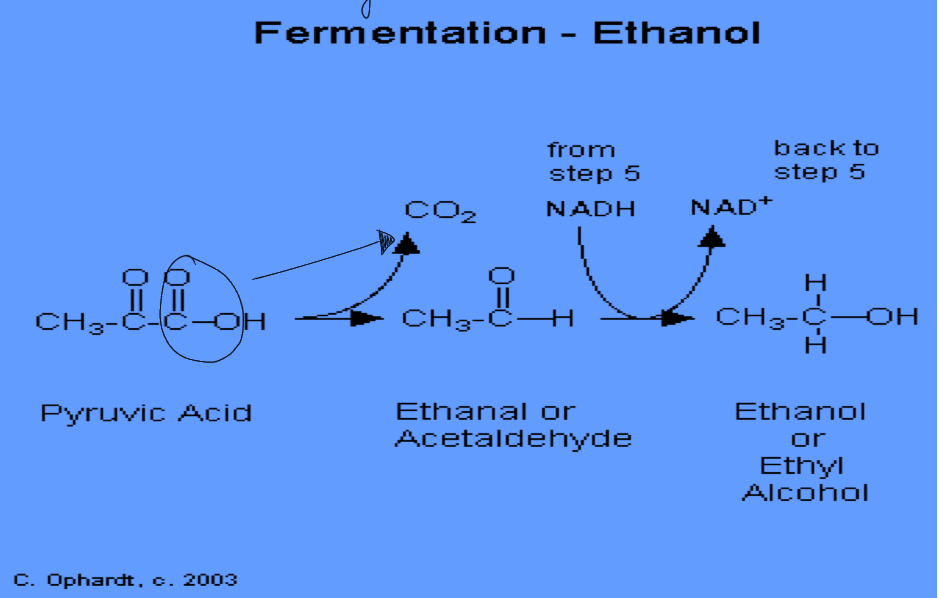
Alcohol fermentation
Done by yeast and bacteria
Pyruvate loses a CO2 and turns into acetaldehyde
NADH gives an H+ to reduce acetaldehyde into ethanol
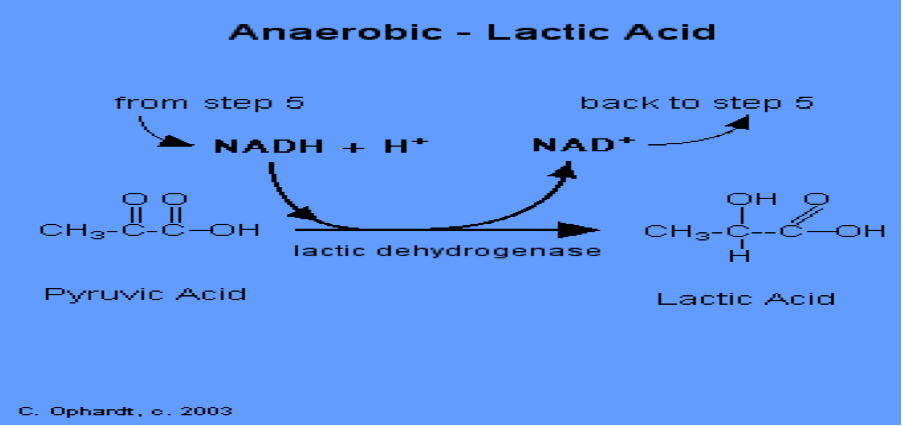
Latin acid fermentation
Done in all living organisms that anaerobically respire
pyruvate is converted to lactic acid by removing H+ from pyruvate.
Electron transport chain
A series of proteins that are found in the cristae. Each protien accepts electrons . and pumps protons into the intermentrane space
Etc process
NADH and Fadh2 release their electrons in the protiens to move across the chain. As the electrons move from protein to protien protons into the intermembrane space.
What causes pH drop?
The increase of H+ cause the pH to drop making the the intermembrane space more acidic
Electrochemical gradient
The gradient that forms form the intermenbrane space and the matrix this remains consistent as the charge of the protons make them unable to diffuse
Final electron acceptor
Oxygen accepts the electrons from complex 4 resulting in water
What pumps H+?
The energy evenly released during the oxidation of each protein is enough to pump the H+ from the matrix to the intermembrane space
ATP synthase function
To synthesize ATP
Pumps H+ back into the matrix and uses that energy to fuse an inorganic phosphate to ADP (H+ serves as a battery)
How much ATP is made per FADH2 and NADH
NADH →3 ATP
FADH2 → 2 ATP
How much ATP is made at the end of aerobic respiration?
36 ATP is made (theoretical yield)
Why is it not exactly 36?
H + is not completely impermeable to the membrane so some are lost
NADH from glycolysis need to be actively transport into the mitochondria losing 1 ATP per NADH
Types of glucose formation
Photosynthesis → use light
Chemosynthesis → uses hydrogen sulfide and extreme temperature
Photosynthesis equation
Sunlight + 6CO2 + H2O → C6HI2 + 6O2
Where does photosynthesis the place?
The thylokids in the mitochondrial matrix
Pigments
The molecules just absorb light energy efficiently
Photons
Tiny bundles of light energy
Chlorophyll a
Is a long hydrocarbon chain attended to an 8 ring structure (Porphyrin) and a methyl group
Essential for photosynthesiS
Chlorophyll B
Is a long hydrocarbon chain attended to an 8 ring structure (Porphyrin) and an aldehyde
Electromagnetic radiation
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation
it has particle duality - sometime its a wave and others it can be a particle
How do we see color?
Each color has its own type of photon wavelength. When light strikes pigment molecules the color that is seen is reflected while what's not is absorbed
Have are the main stages of photosynthesis
Light dependant reaction
light independent reaction
Light dependent reaction
Absorbs light energy and converts it into chemical
occurs in the thylakoids
photosynthetic reaction centres (PRCs)
The series of protiers on the thylakoids membrane
made of photosystems (1 and 2) that absorb light
Light independent reaction intro
ATP and NADPH are now found in the stroma of chloroplast are used to power this reaction
Stage #1 of the light independent reaction
3 CO2 + 3 ribulose bisphosphate (3RuBP) = 6 Phosphoglycerate (PGA)
Using the enzyme ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase
Stage #2 of light independent reaction
6 ATP +6 phosphoglycerate →6 bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)
6 NADPH + 6 BPG → glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate + NADP+
Stage #3 of the light independent reaction
2G3P → glucose (most do 2 cycles to get 2 G3P)
5 G3P → 3 ribulose-5 - phosphate molecules
3ATP + 3 ribulose -5-phosphate → ribulose bisphosphate
The restarts
C3 cycle
The Calvin cycle because the first stable molecule is 3 carbons long (RuBP)
C4 Cylce
C4 photosynthesis or CAM when the first stable molecule is 4 carbons long (RuBP+CO2)
Alternate mechanisms of carbon fixation
The Calvin cycle thrives in cooler climate so hotter/dryer cause water loss when the stomata opens to get CO2
Photorespiration
Photosynthesis continue to consume CO2 and H2O and producing O2 causing an increase in O2 stoping stage 1 of the Calvin cycle
Reaction: O2 + RuBP + phosphoglycerate + phosphglycate
Bad takes a lot of energy
C4 photosynthesis
Co2 is bonded to a phospheonol pyruvate to make oxaloacetate
And is transported into a bundle sheath (made of wax). The CO2 is put into the Calvin cycle where C4 and C3 happen of the same time in different placeses
Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM)
Co2 is stored as crassulalean acid before it's brought into the bundle sheath. CAM or a form of C4 happen at night and the CO2 is entered into the stomata. During the day the Calvin cycle happens