CIE IGCSE Biology Unit 1: Characteristics and Classification of Living Organisms
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Movement
Action by an organism or part of an organism causing a change of position or place

Respiration
Chemical reactions in cells that break down nutrient molecules and release energy for metabolism

Sensitivity
The ability to detect or sense STIMULI in the internal or external environment and to make appropriate responses
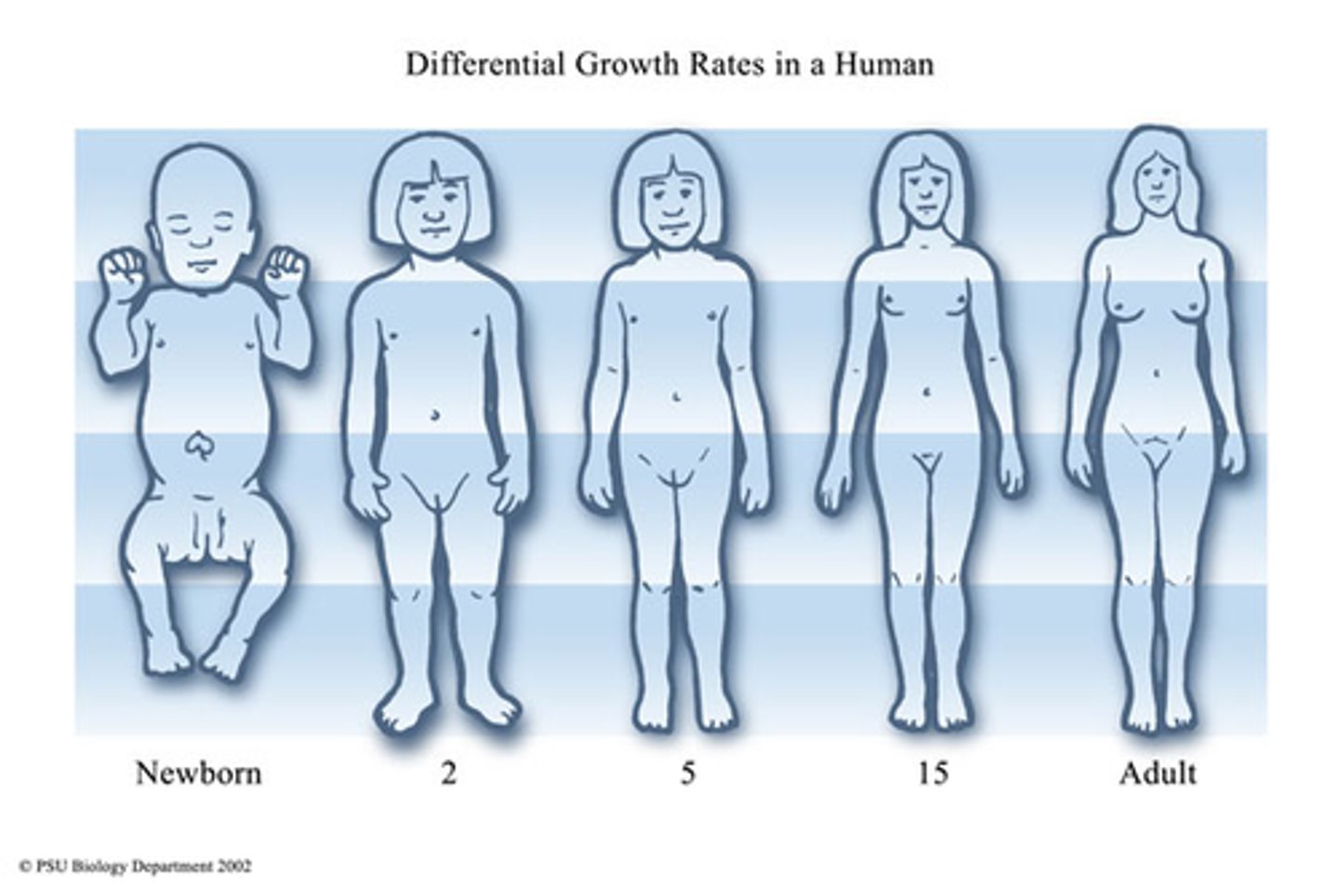
Growth
A permanent increase in size and dry mass by an increase in cell number or cell size or both
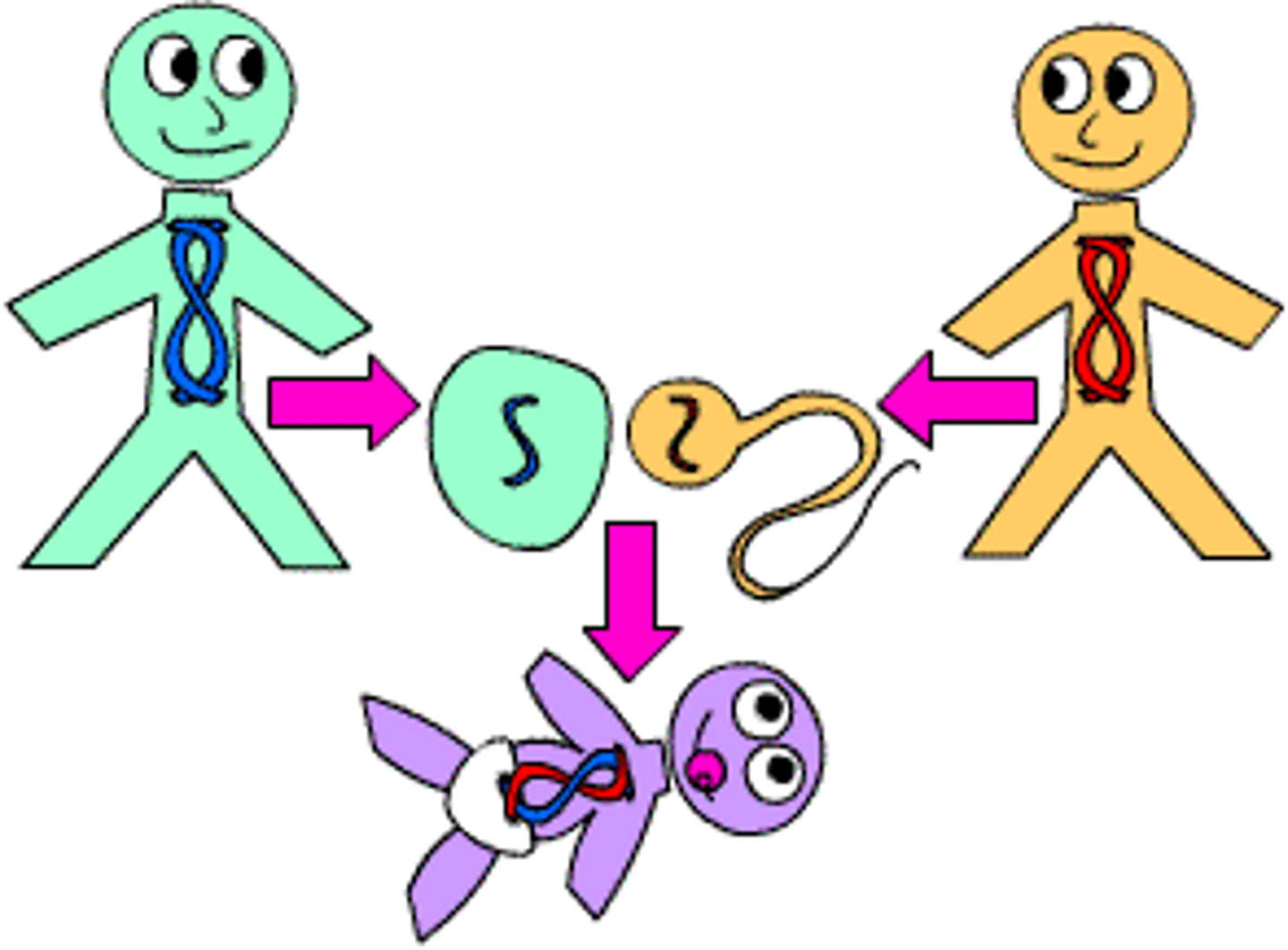
Reproduction
Processes that make more of the same kind of organism
Excretion
Removal of the waste products of METABOLISM, toxic materials, and substances in excess of
requirements
Nurtrition
Taking in of materials for energy, growth and development; plants require light, carbon dioxide, water and ions; animals need organic compounds and ions and usually need water
Species
A group of organisms that can reproduce to produce fertile offspring

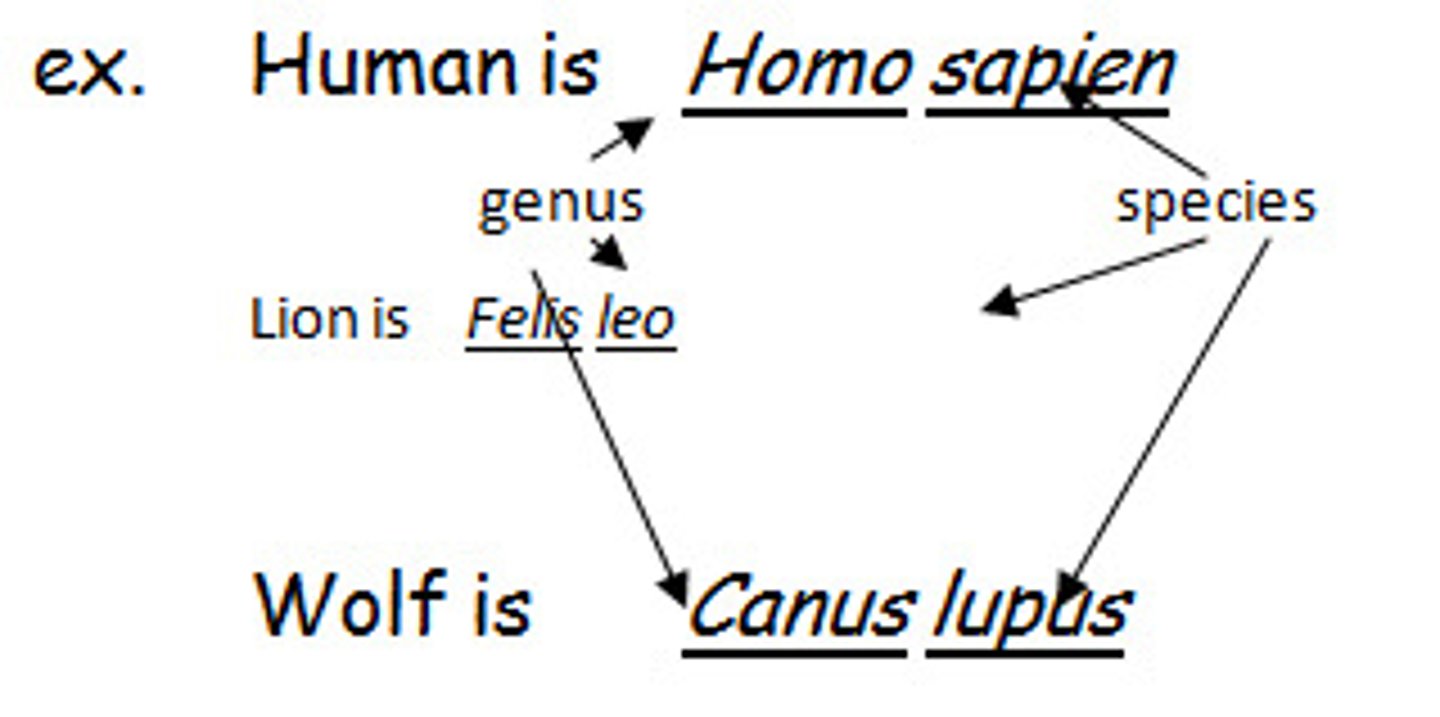
Binomial System
An internationally agreed system in which the scientific name of an organism is made up of two parts showing the genus and species (trivial)
Difference between Excretion & Egestion
Excretion is the removal of toxic, metabolic waste while Egestion is the removal of undigested and unabsorbed materials.
Difference between Respiration & Breathing
Respiration is the chemical reactions in cells that break down nutrient molecules and release energy for metabolism while Breathing is the gases exchange in the lungs.
Difference between Excretion & Secretion
Excretion is the removal of toxic, metabolic waste while Secretion is the release of substances by cells
Classification
The sorting out of the vast array of living organisms into groups.
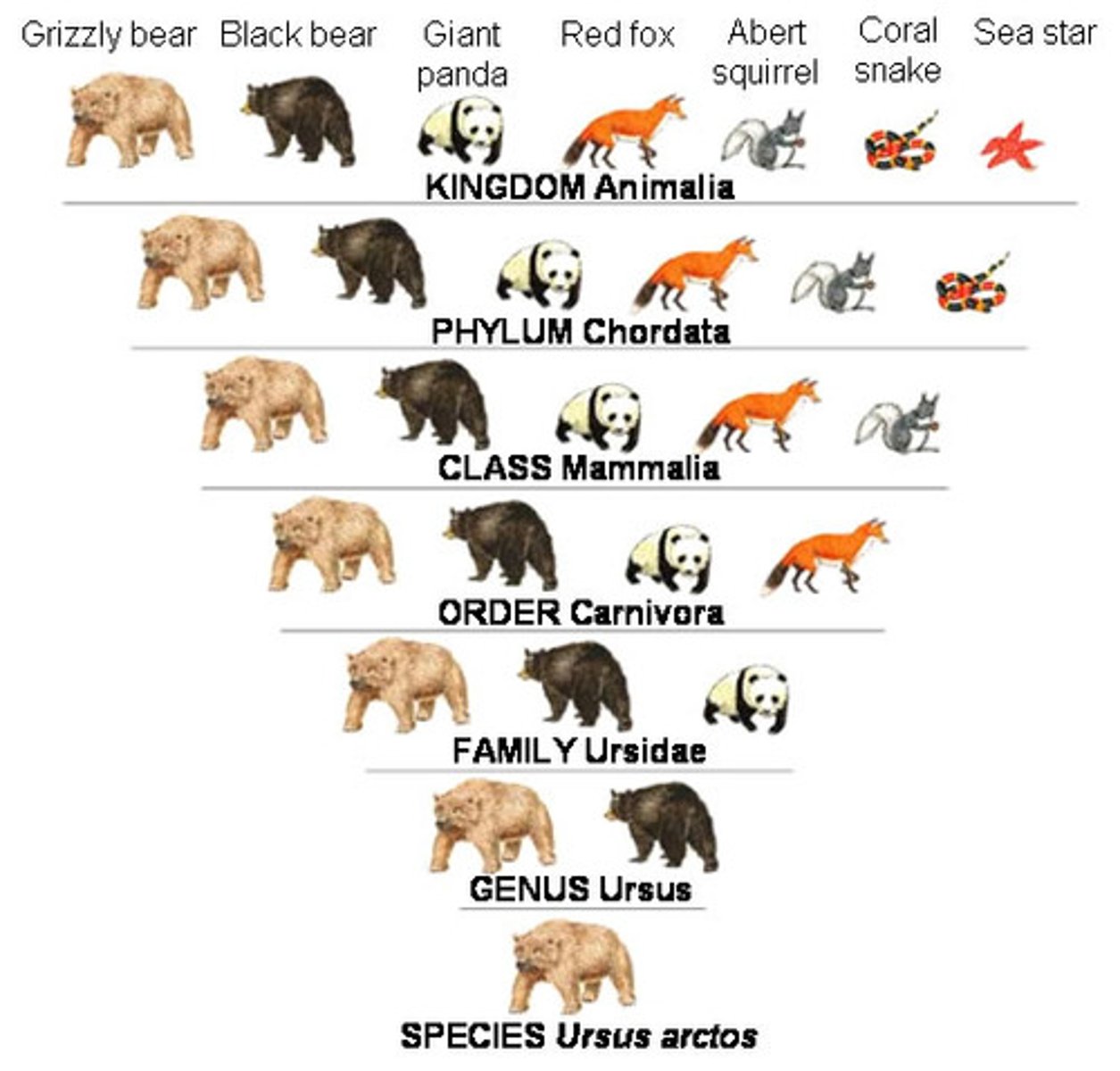
Traditional Method of Classification
Study and compare the MORPHOLOGY and ANATOMY of organisms and compare to fossil records. The more similarities between two organism, the more closely related and likely to have evolved along the same lines.
Accurate Method of Classification
Study and compare sequences of bases in DNA and of amino acids in proteins. The more similarities between two organism, the more closely related.
Morphology
The outward appearance of an organism

Anatomy
The internal structure of an organism
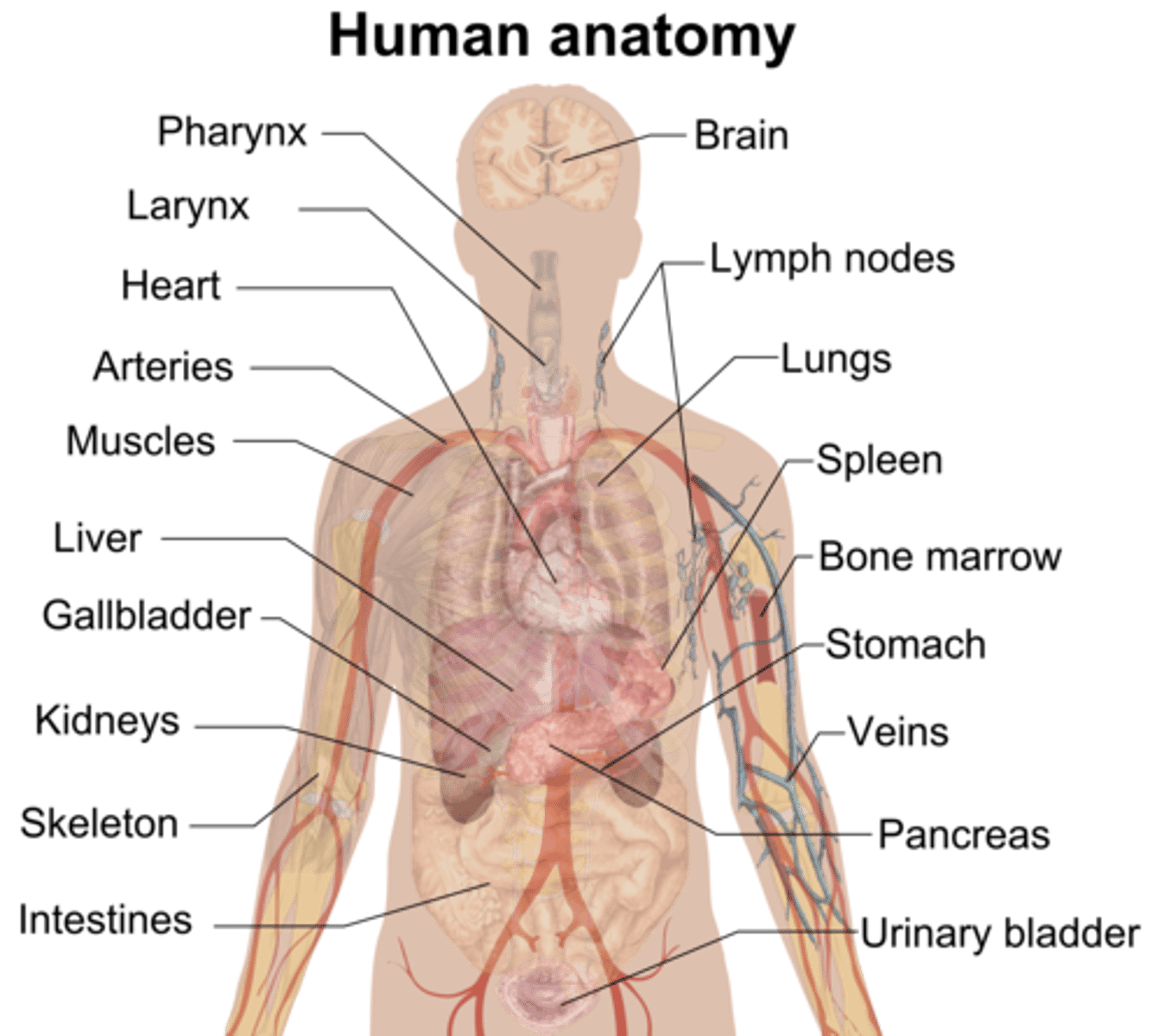
Cells
Basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. Contains cell membrane, cytoplasm, dna, and ribosomes.
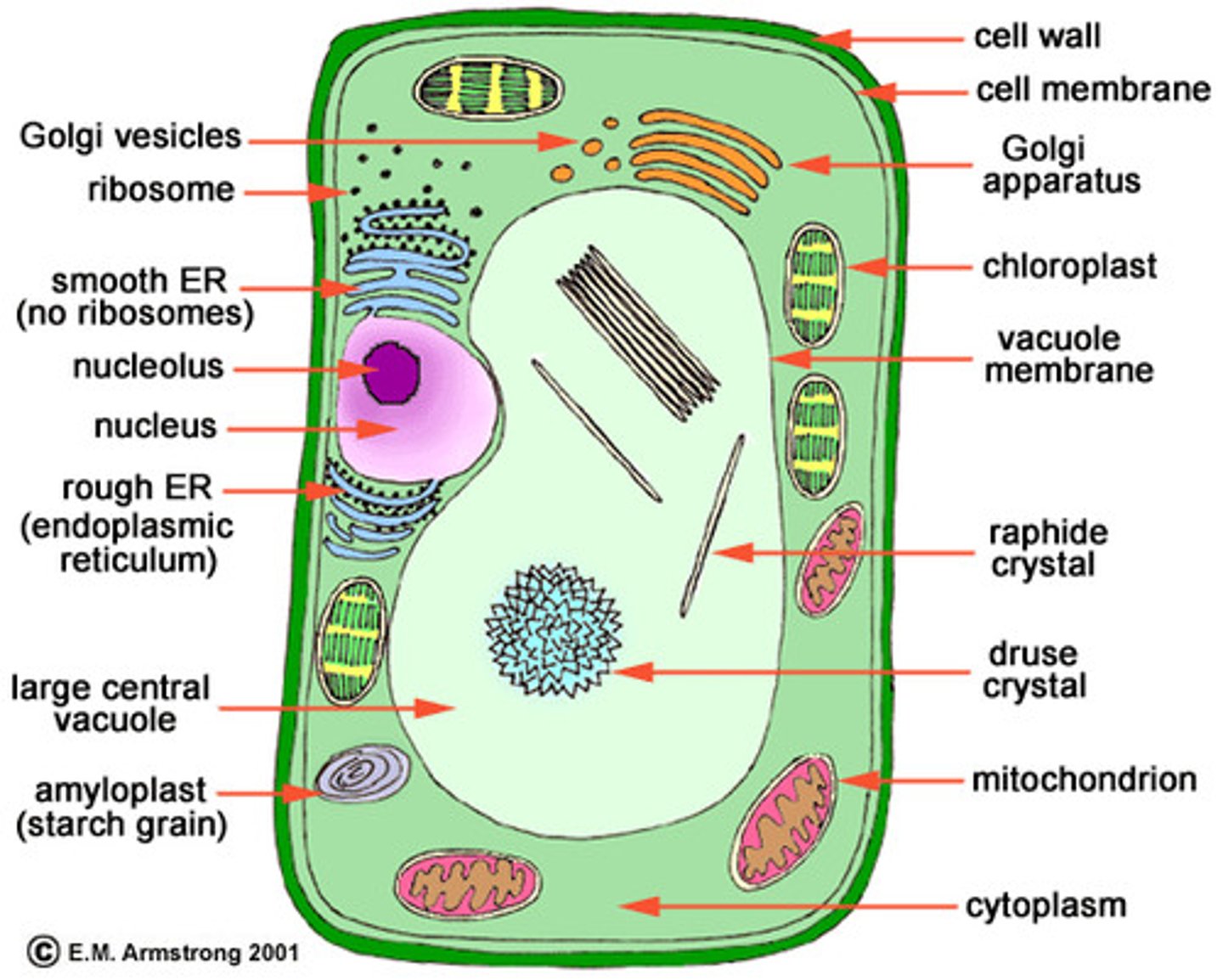
The Five Kingdoms
Plant, Animal, Prokaryote, Protoctist, and Fungi
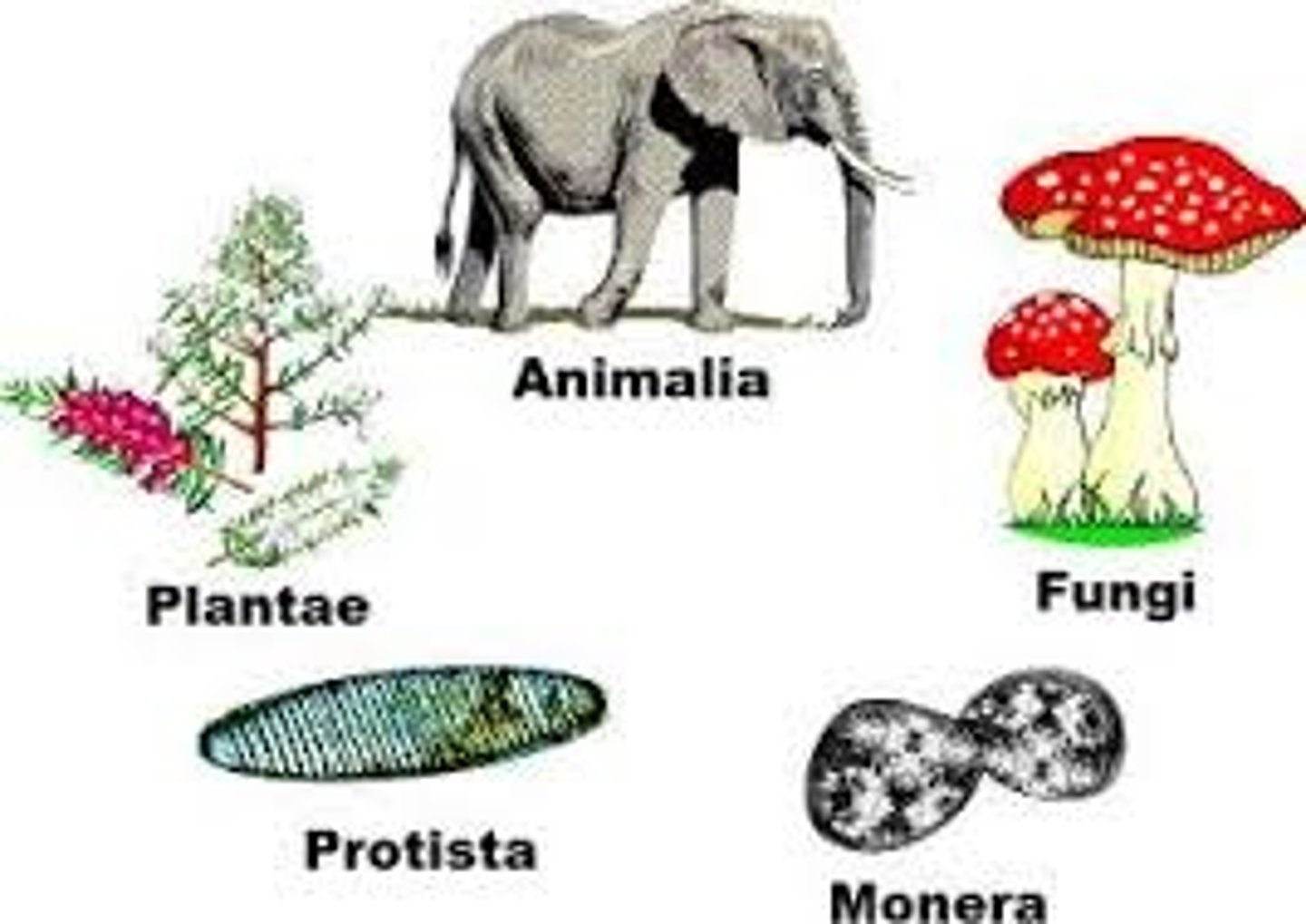
Plant Kingdom
- Multicellular organisms
- Contain cell wall
- Contain chlorophyll
- Photosynthesis for nutrients

Animal Kingdom
- Multicellular organisms
- Does not contain cell wall
- Ingest other plants or animals for nutrients
- Have nervous system to respond to stimuli and movement

Prokaryote Kingdom
- Unicellular organisms
- No nucleus ( Just loop of DNA )
- Do not have chloroplast or mitochondria
Protoctist Kingdom
- Unicellular and multicellular
- Have nuclei
- May contain chloroplast
Fungi Kingdom
- Made up of thread like hyphae
- Contain many nuclei throughout cytoplasm
- Some species are parasites
- Some are saprotrophs ( feed on dead or decaying matter )

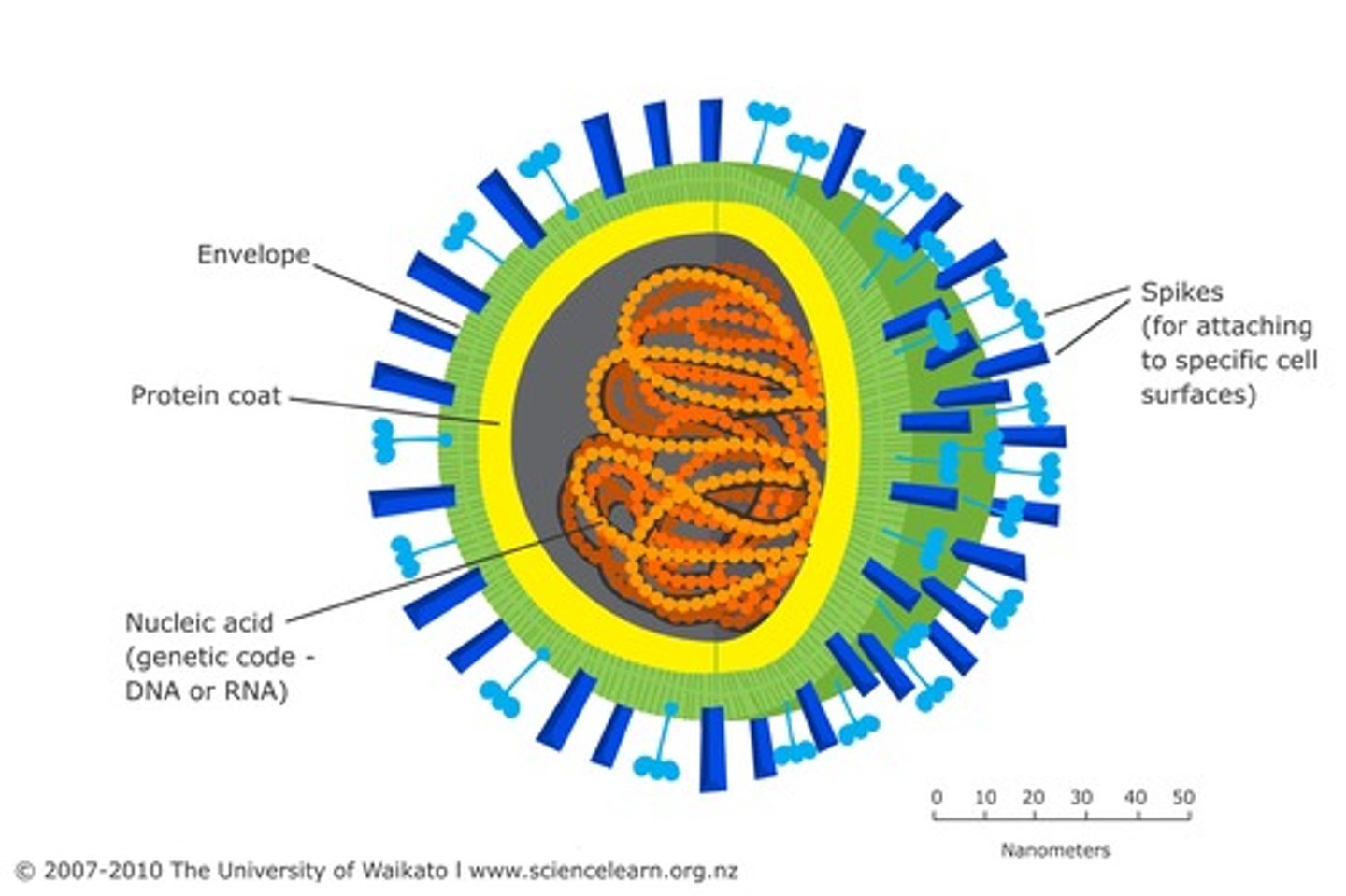
Viruses
- Not cells
- Surrounded by protein coat
- Made up of genetic material (DNA or RNA)
- Are parasites
Verterbrates
Have a vertebral column
Example: mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish

Anthropods
Has segmented bodies and exoskeleton
Example: myriapods, insects, arachnids, crustaceans

Fish
-slimy scales
-lays egg
-cold blooded
-use gills to breathe

Amphibian
-moist permeable skin
-carries out external fertilization
-breathes through skin in water
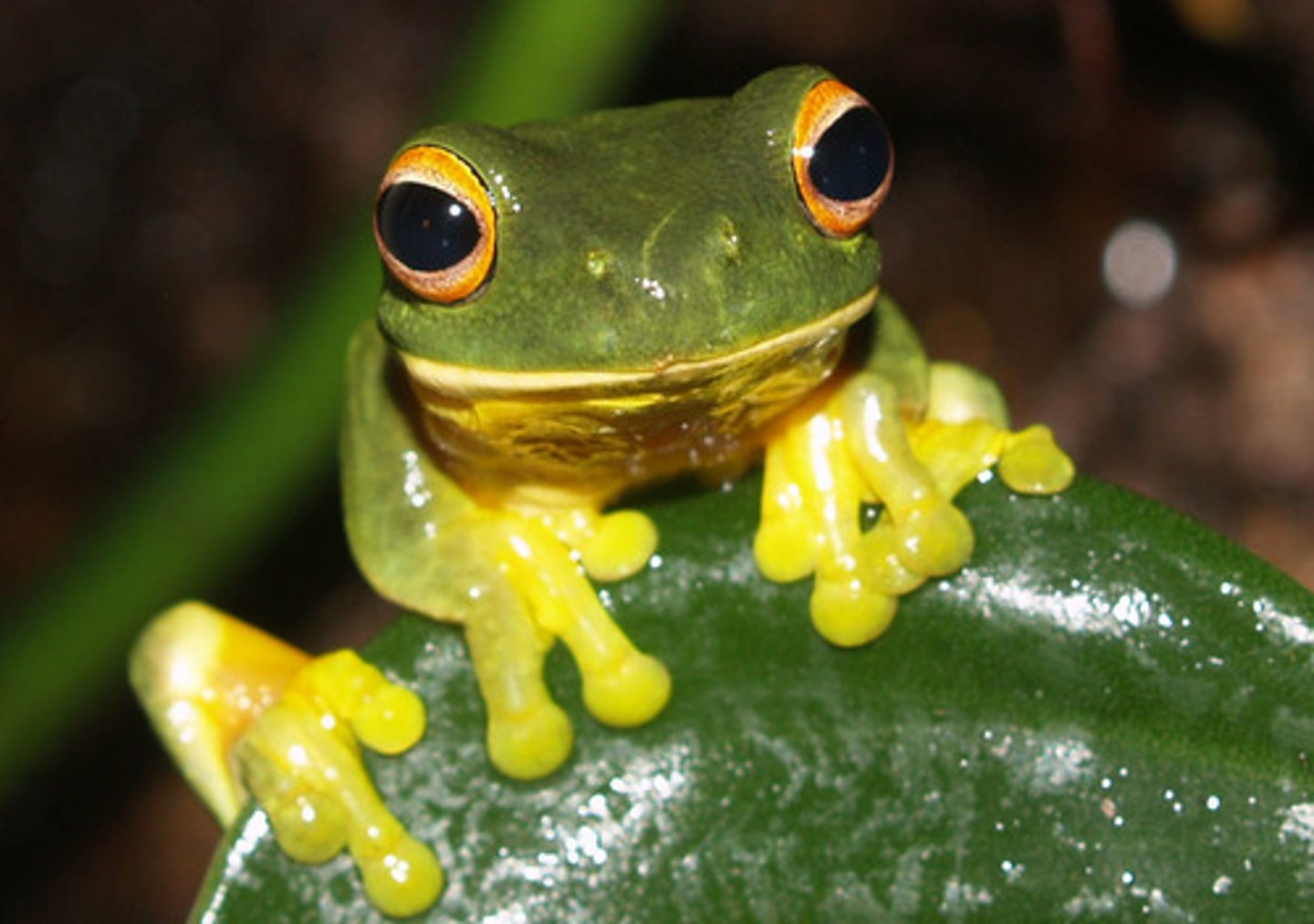

Reptiles
-dry scaly skin
-lays soft shelled eggs
-cold blooded
Birds
-have feathers
-lays hard shell eggs
-warm blooded
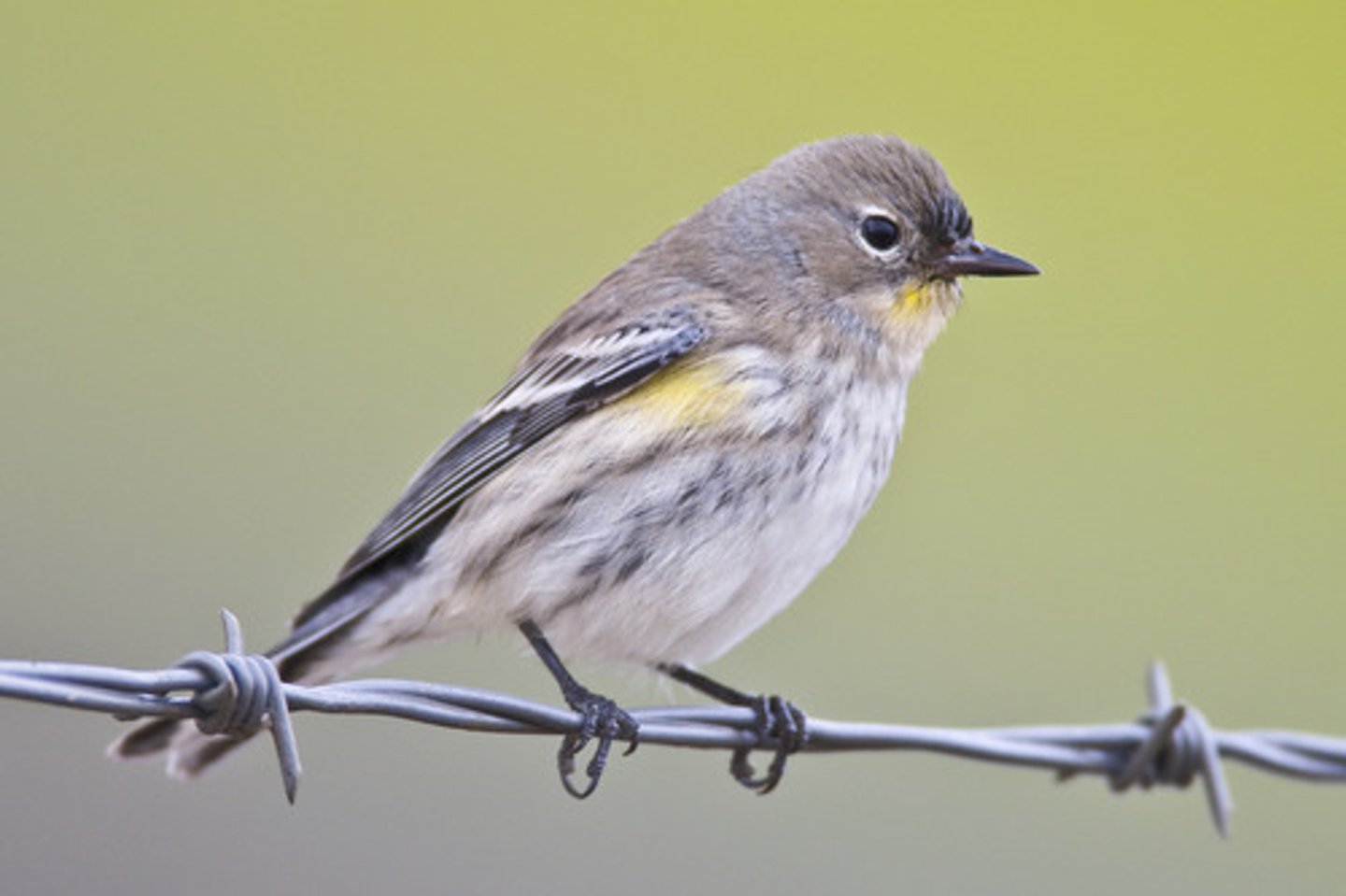

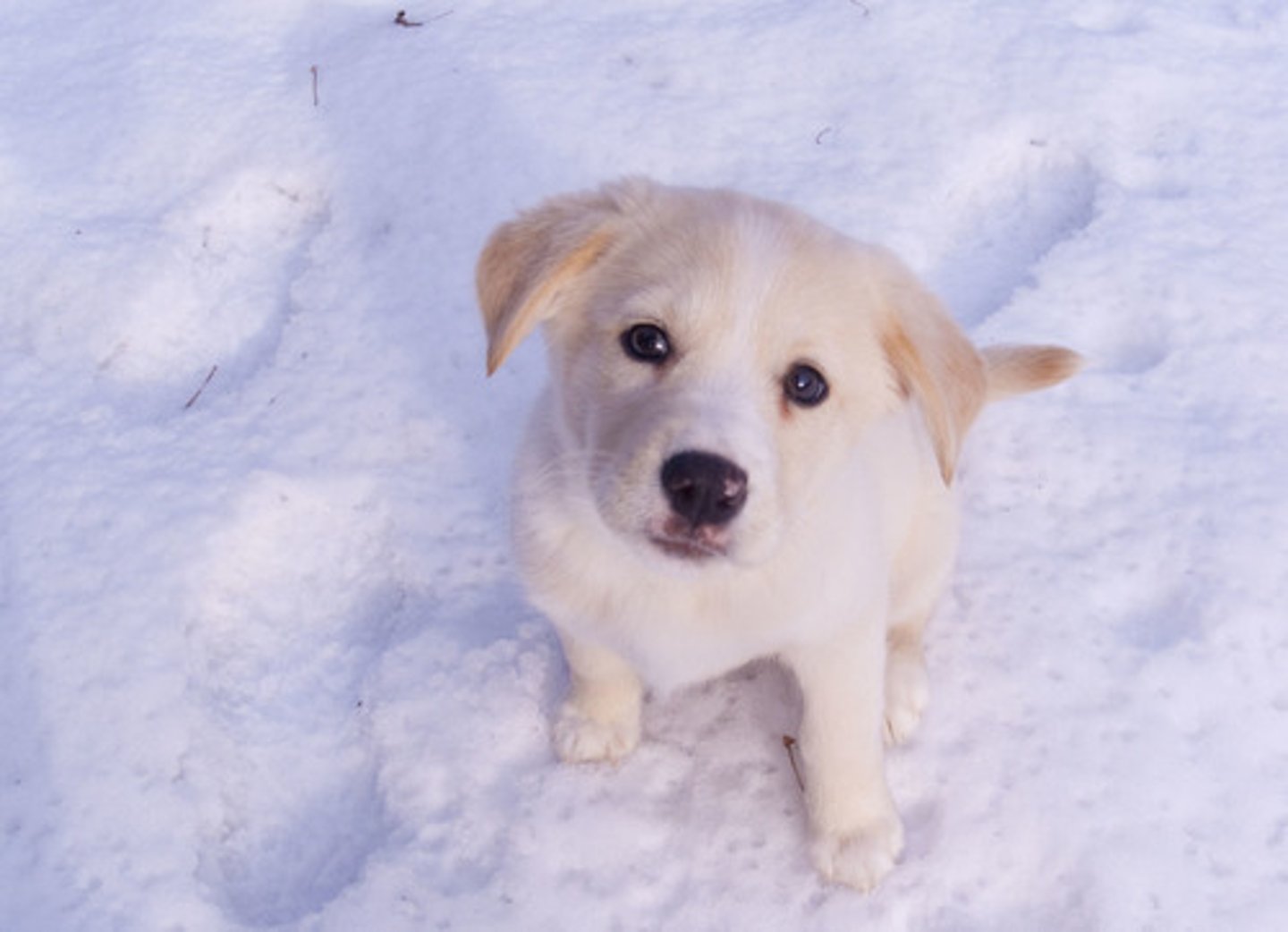
Mammals
-homeothermic
-has hair
-internal fertilization

Crustacean
-hard exoskeleton
-compound eyes
-jointed limbs
-body divided into 2 segments : cephalothorax (head-thorax), and abdomen
Myriapods
-hard exoskeleton
-long segmented body (not divided into separate regions)
-pairs of legs on each body segment
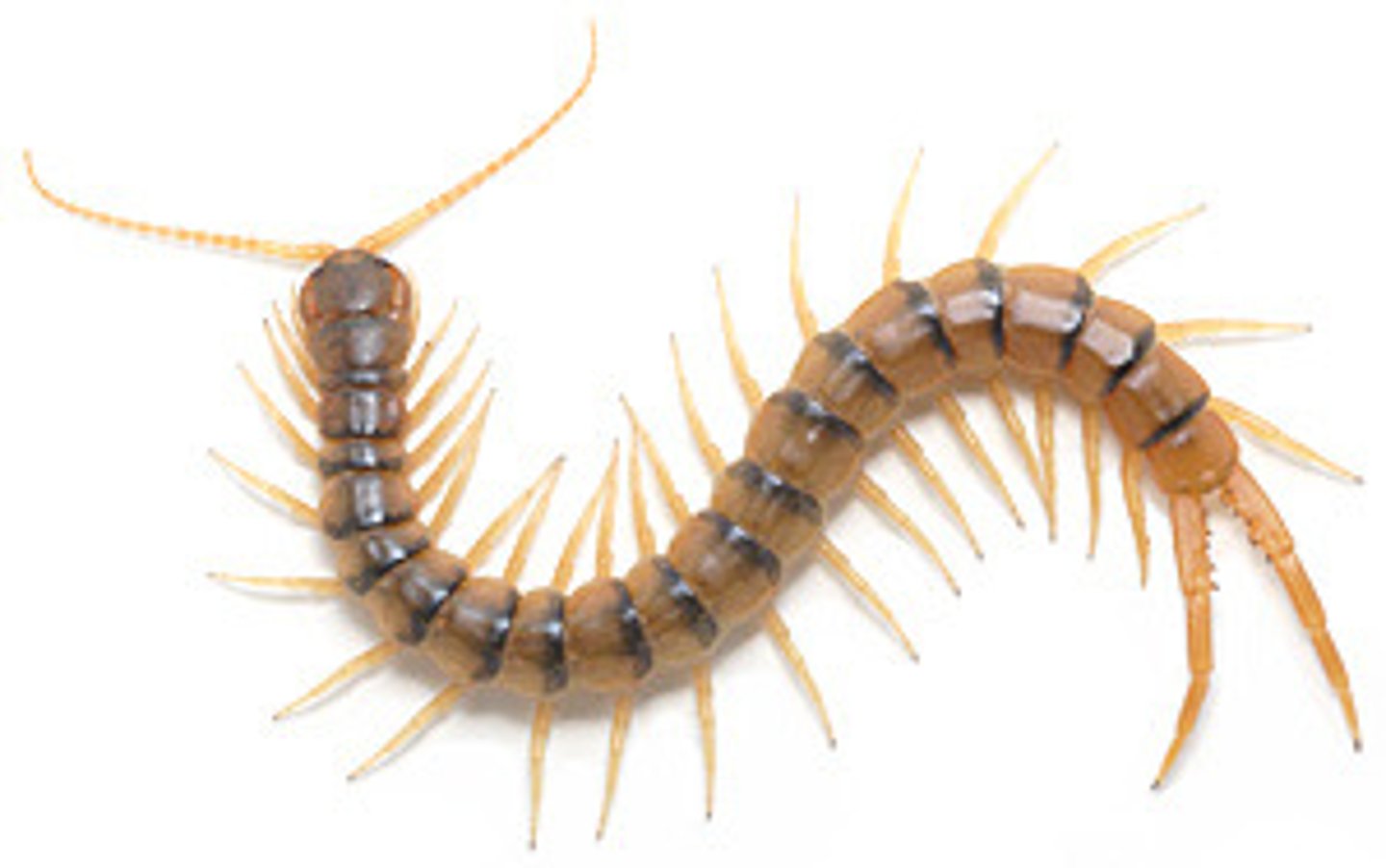

Insects
-3 pair of legs
-body separated into 3 segments : head, thorax, and abdomen
-have antennae
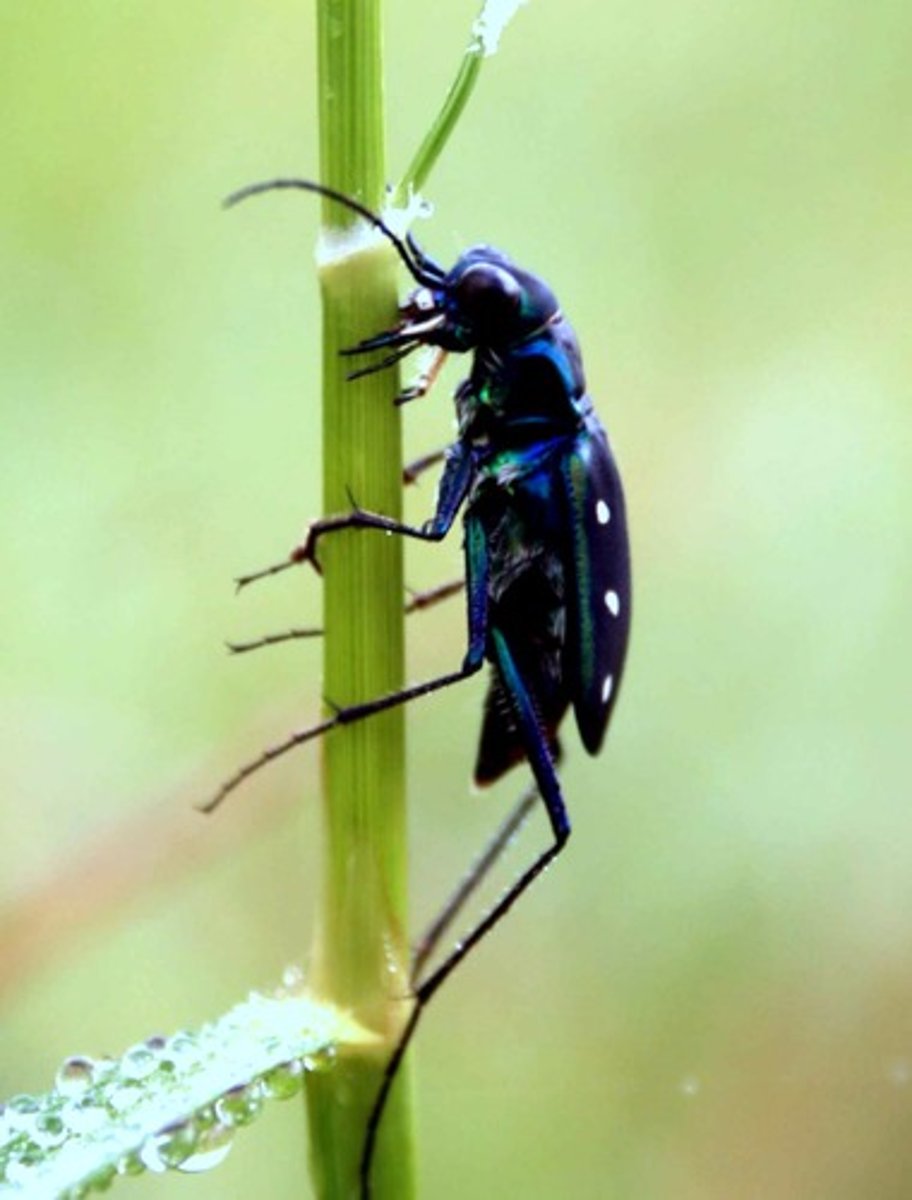

Arachnids
-four pair of legs
-simple non compound eyes
-body separated into: cephalothorax( head-thorax ), and abdomen
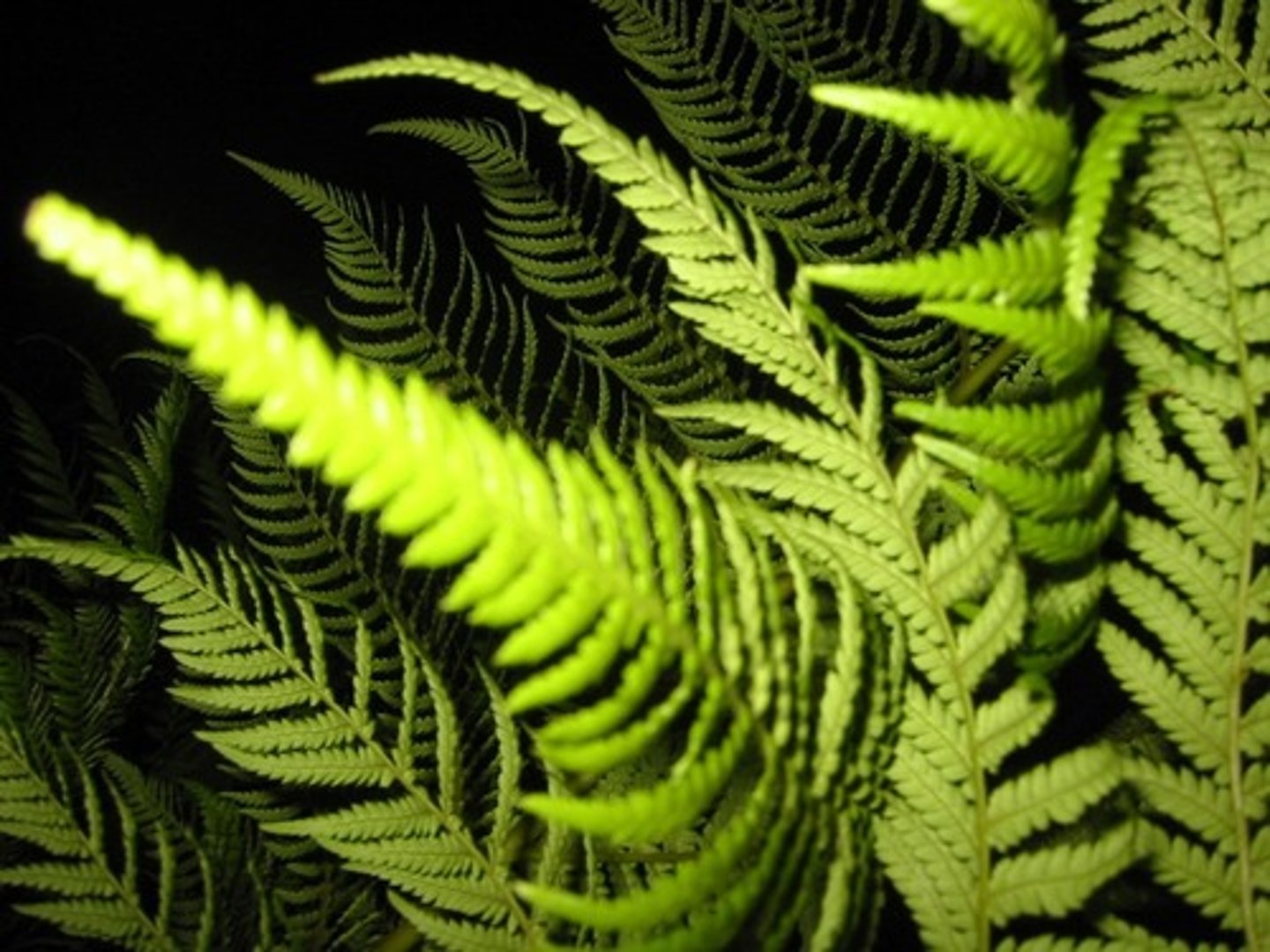
Ferns
-produce spores
-wind polinated

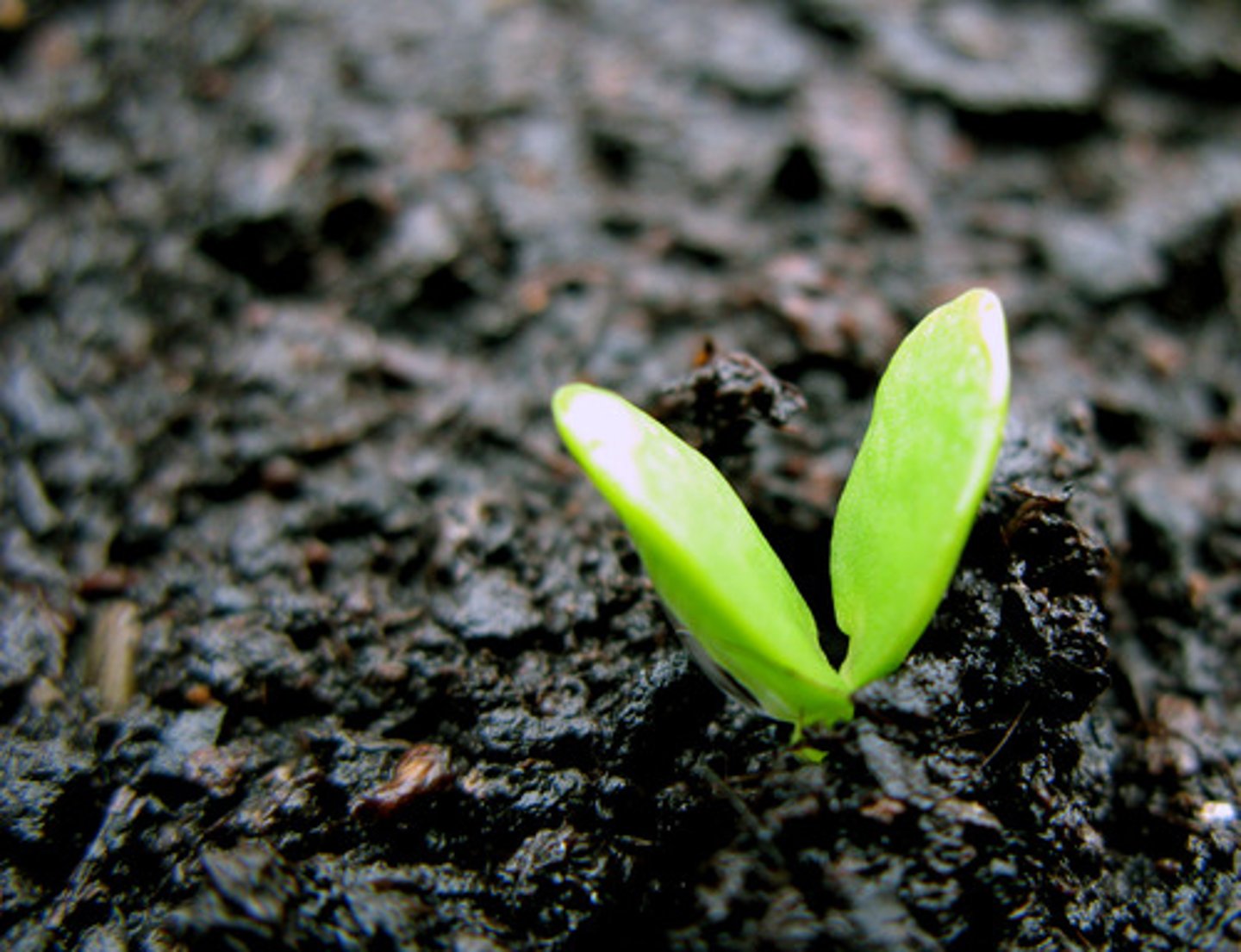
Monocotyledons
- Narrow leaves with parallel veins
- Flower petals are in multiples of three
- Have one seed leaf (cotyledons)
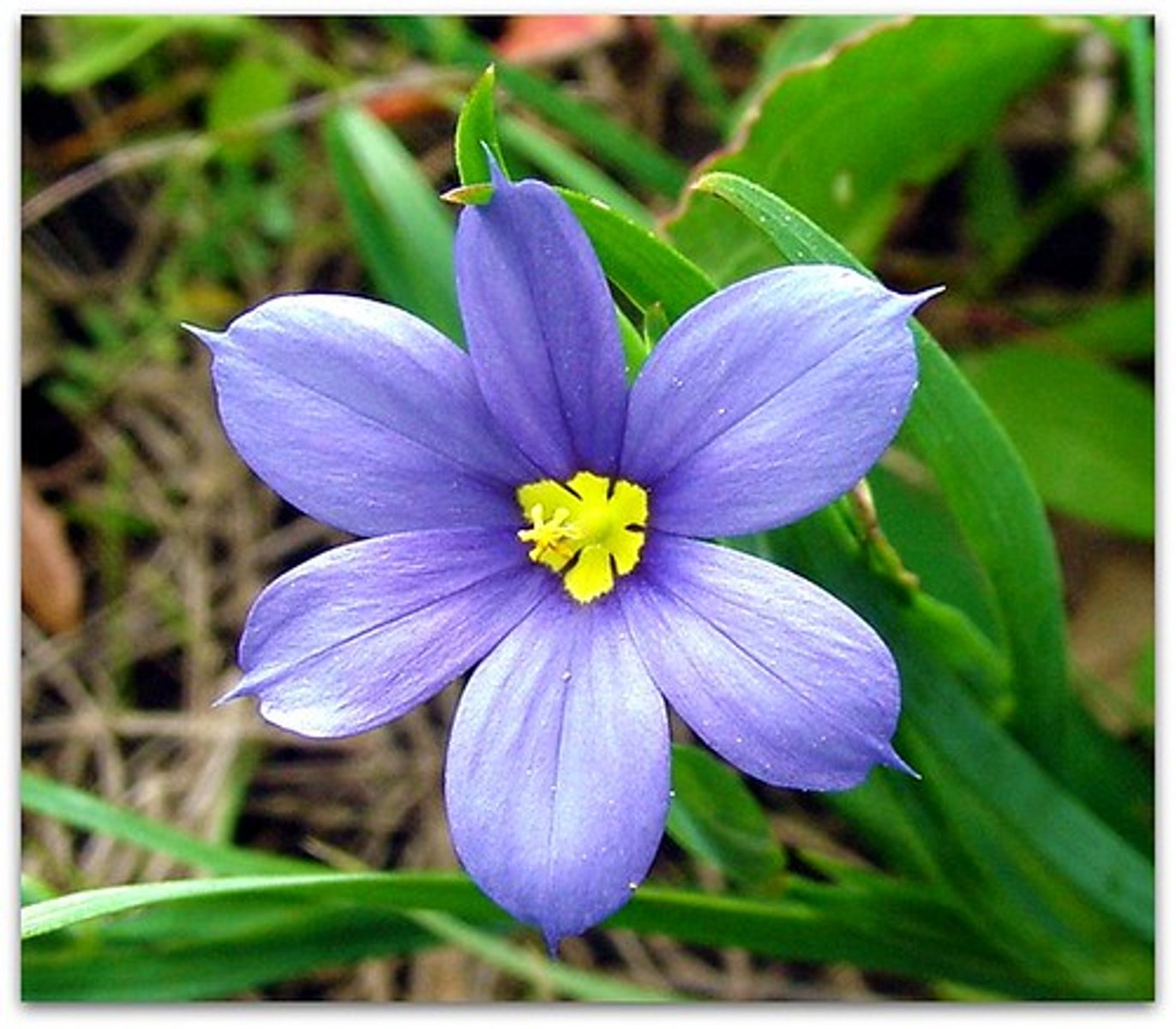

Dicotyledons
- Broad leaves with network of branching veins
- Flower petals are in multiples of four/five
- Have two seed leaves (cotyledons)

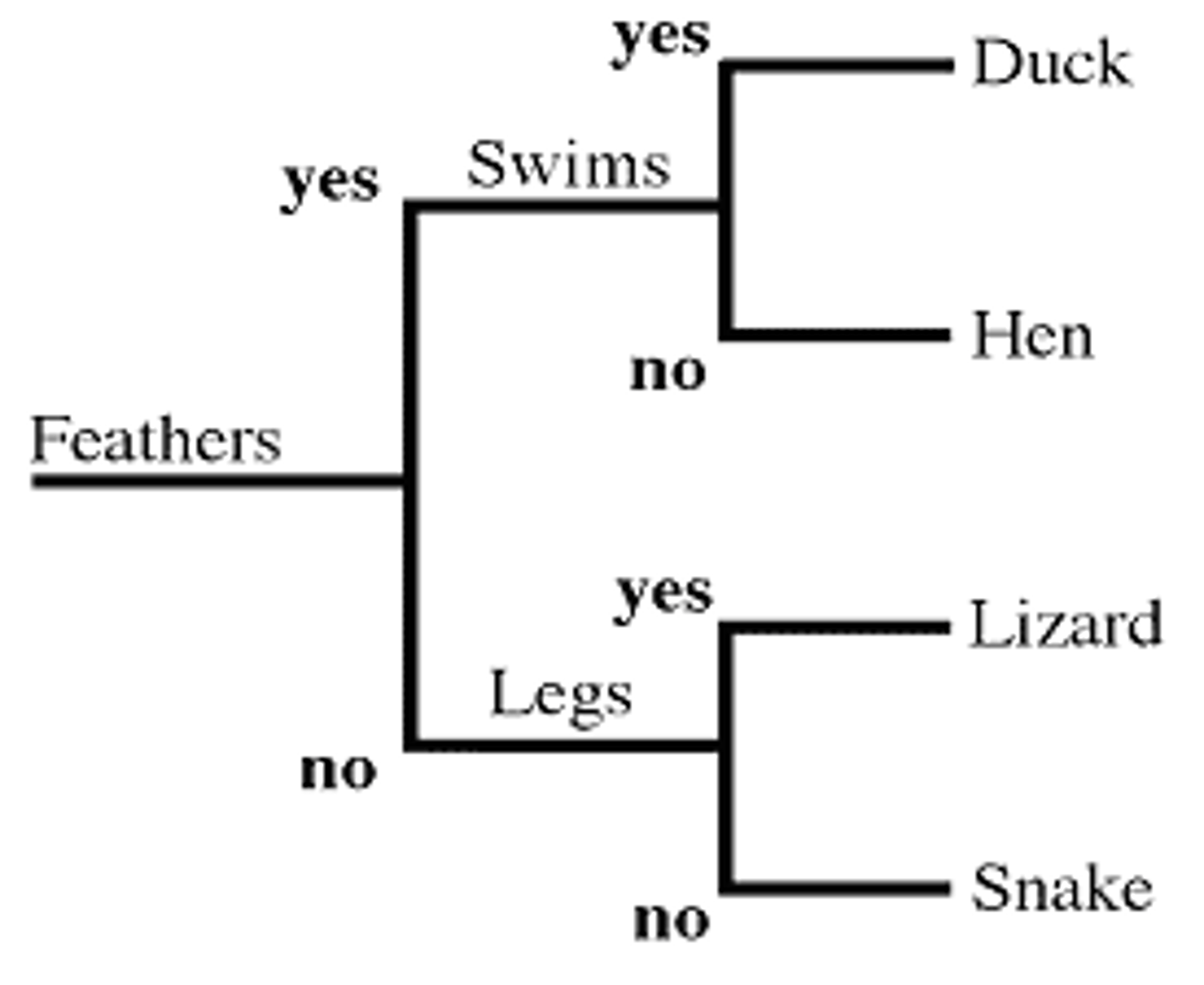
Dichotomous Key
Used to identify organisms by using a series of paired statement or questions which lead to an identification