EXAM VI (QUIZ REVIEW)
4.5(2)
4.5(2)
Card Sorting
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
1
New cards
What will happen when additional reactant is added to a system at equilibrium?
a) more products will form
2
New cards
At chemical equilibrium. which of the following is always true of the concentration of reactants and products?
a) they are constant
3
New cards
The statement “Equilibrium lies to the right” meant that at equilibrium
a)product concentrations are much greater than reactant concentrations.
4
New cards
When equilibrium lies to the right, Keq is
c) much greater than 1
5
New cards
What is equilibrium constant for the general equation aA + bB ⇄ cC +dD?
K =\[C\]c\[D\]d/\[A\]a\[B\]b,
6
New cards
A heterogeneous equilibrium is one in which the substances are
d) in different states
7
New cards
Chemical equilibrium exists when
d) two opposing processes occur at the same right
8
New cards
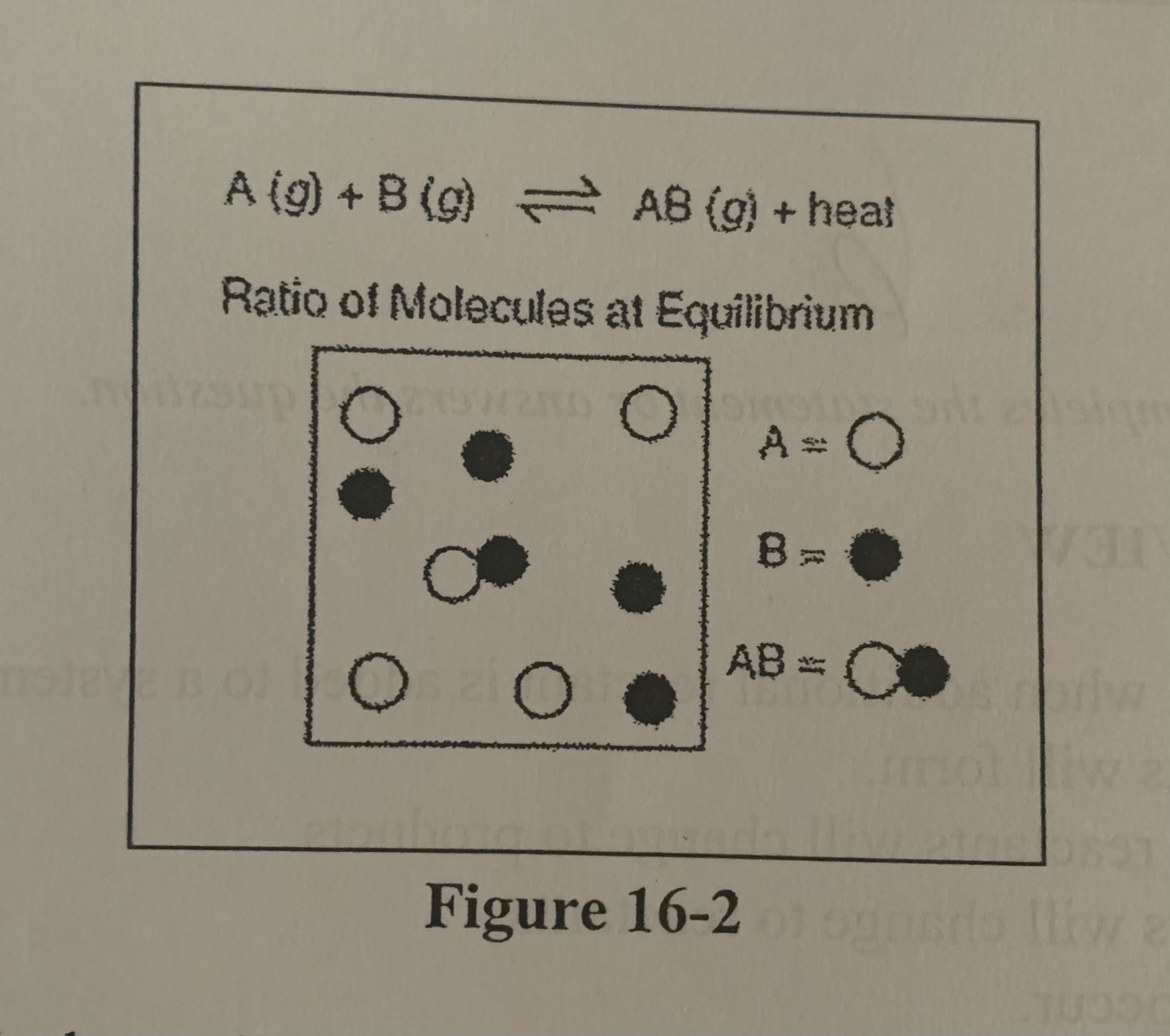
Refer to Figure 16-2. What is the equilibrium constant for the system?
d) \[AB\]/ \[A\] \[B\]
9
New cards
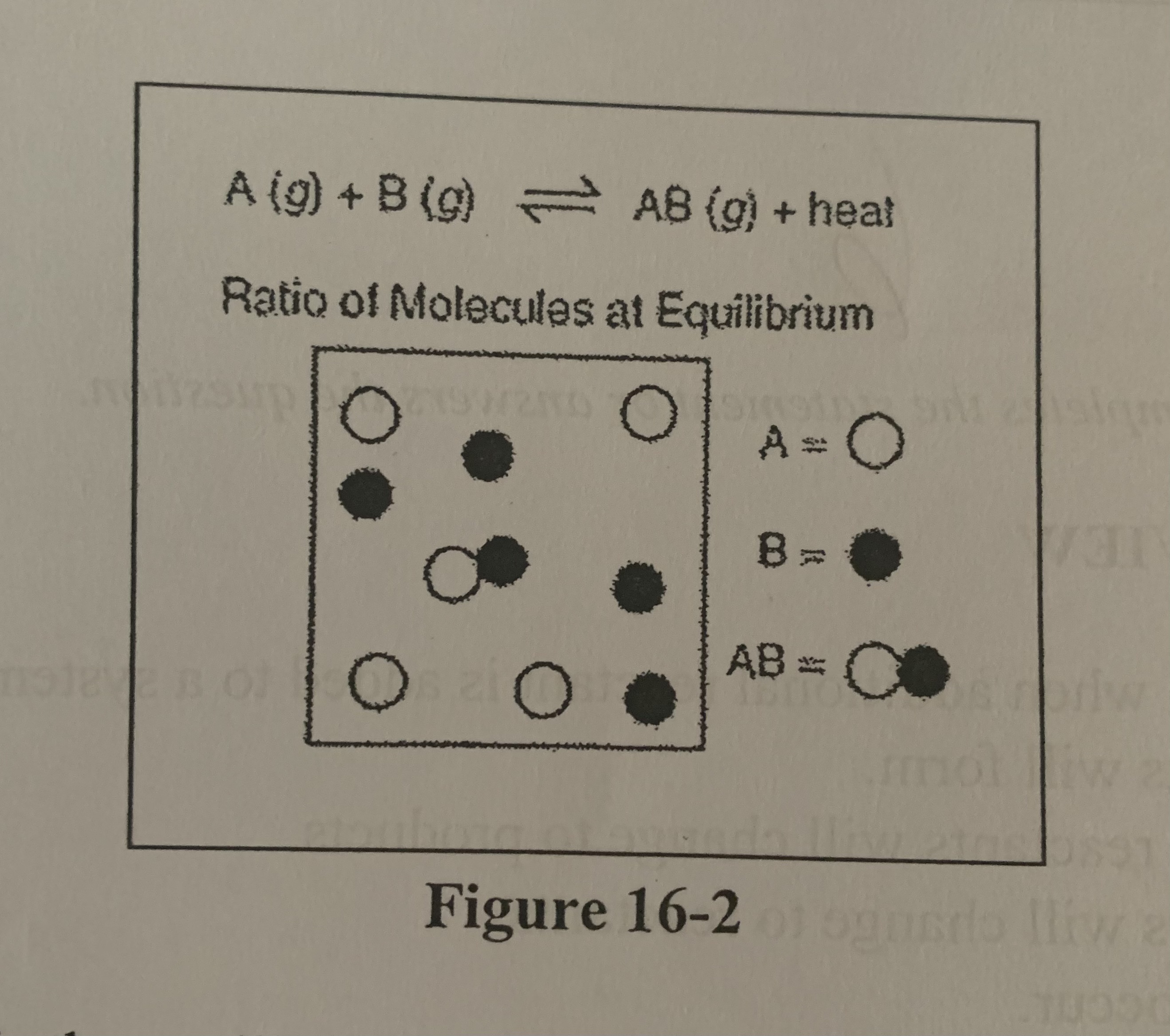
How would a reduction in volume of the container in the figure above affect the concentration of AB, assuming the other conditions are kept constant?
A) \[AB\] would increase.
10
New cards
How would an increase in temperature affect the concentration of AB, assuming the other conditions are kept constant?
b) \[AB\] would decrease
11
New cards
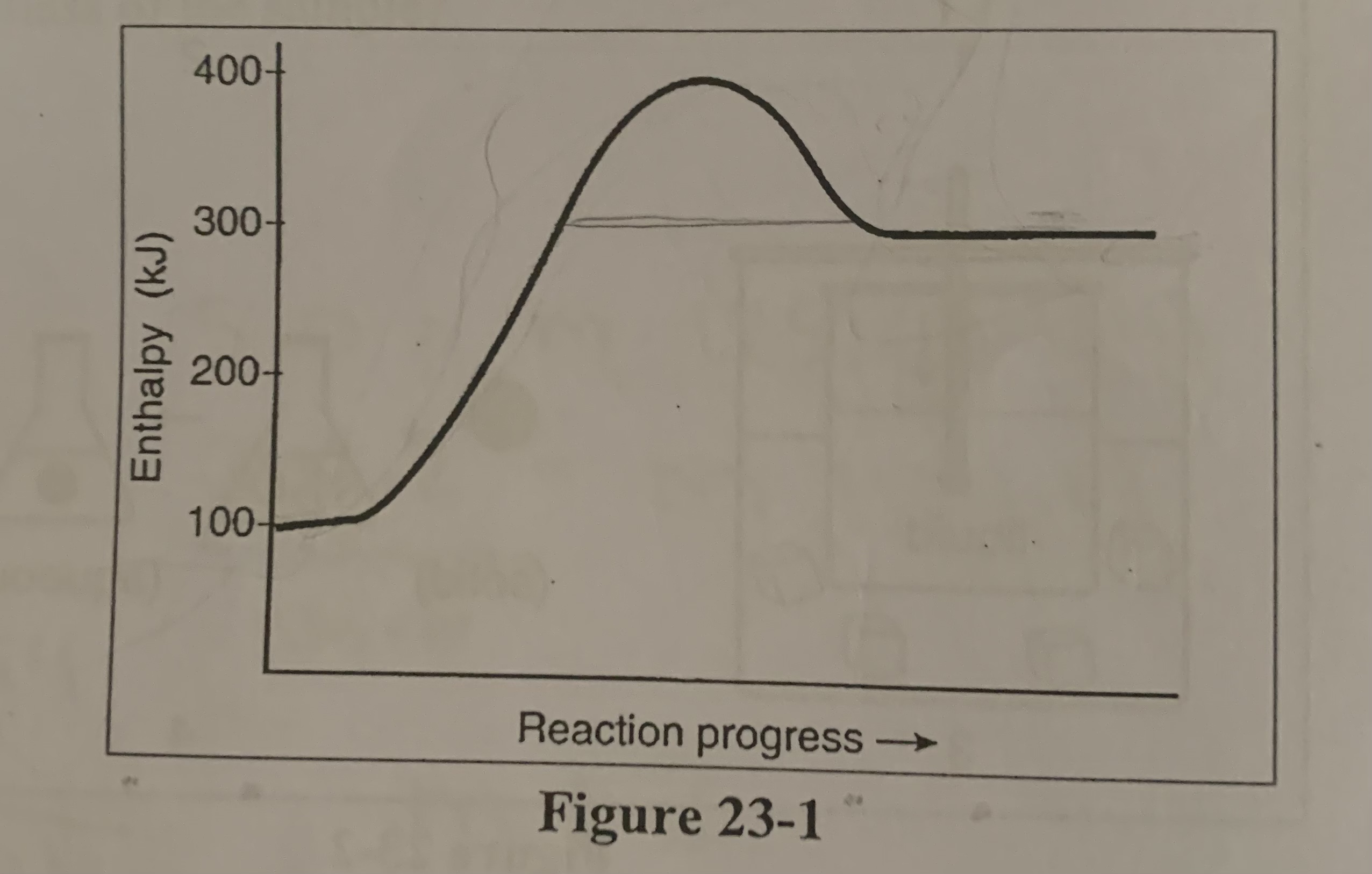
In the figure is the forward reaction exothermic and endothermic?
b) the forward is endothermic
12
New cards
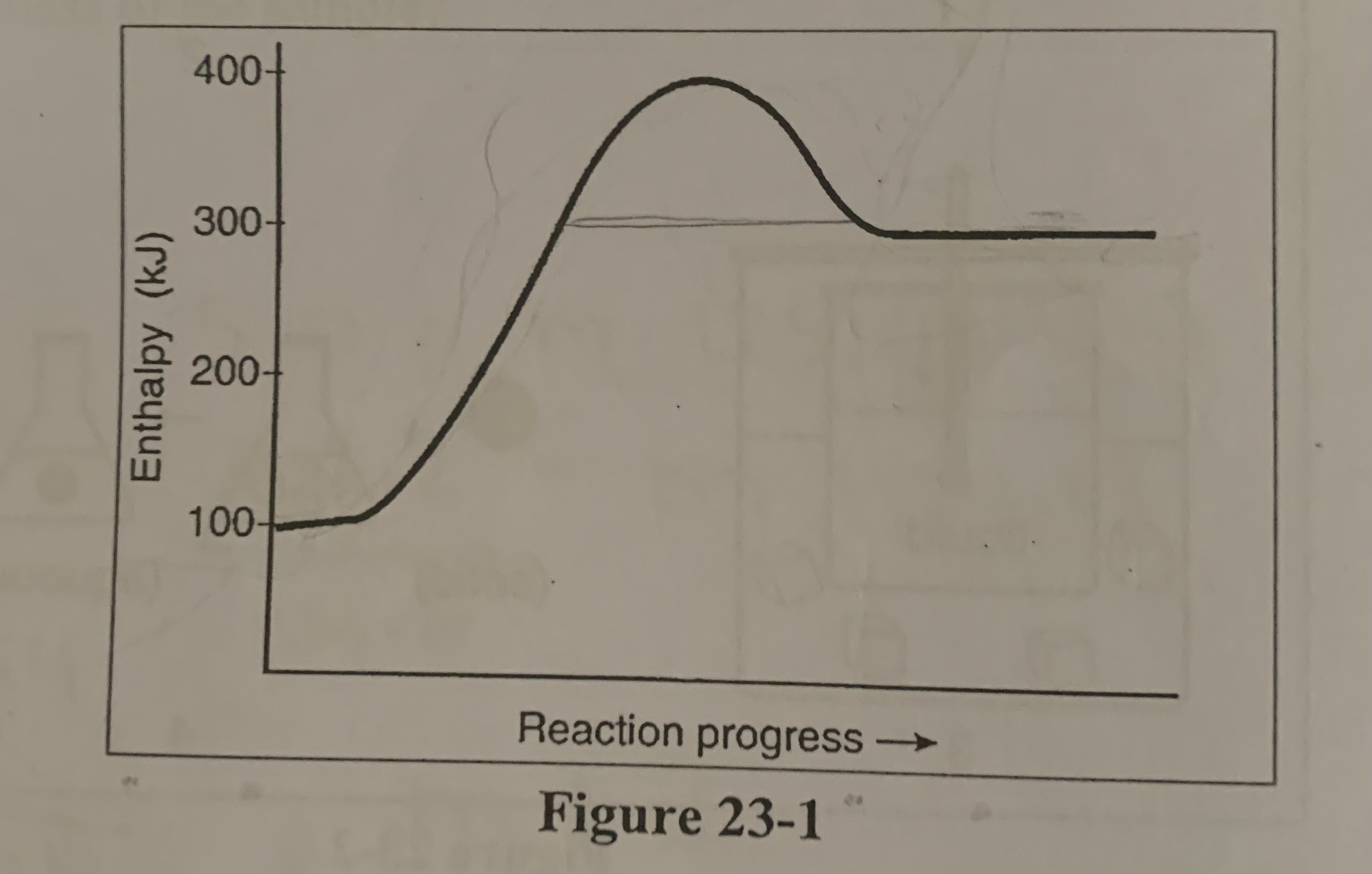
In the figure is the reverse reactions exothermic or endothermic?
c) the reverse exothermic
13
New cards
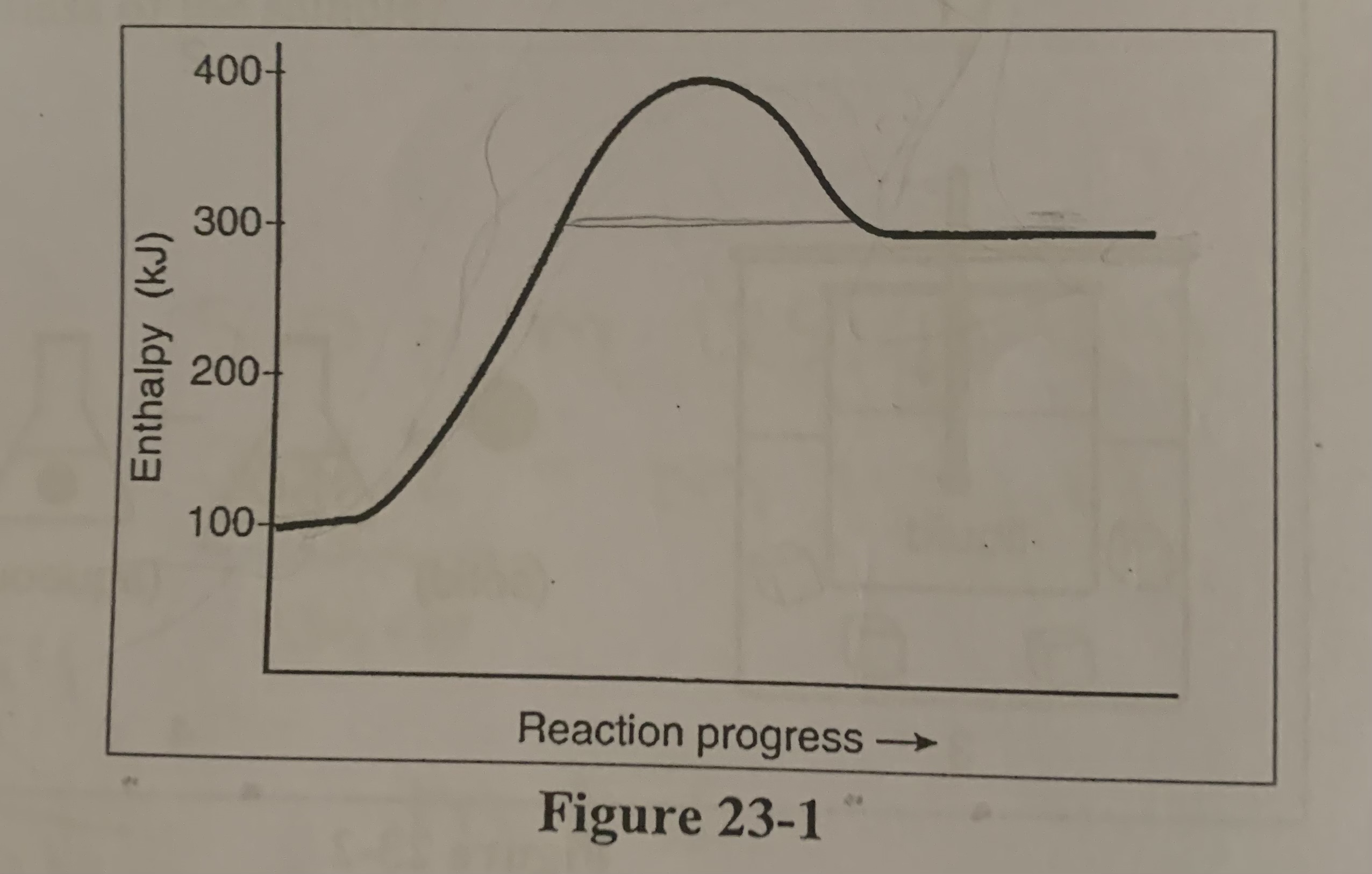
What is the value of ΔH for the reverse reaction in the figure?
c) -200 KJ
14
New cards
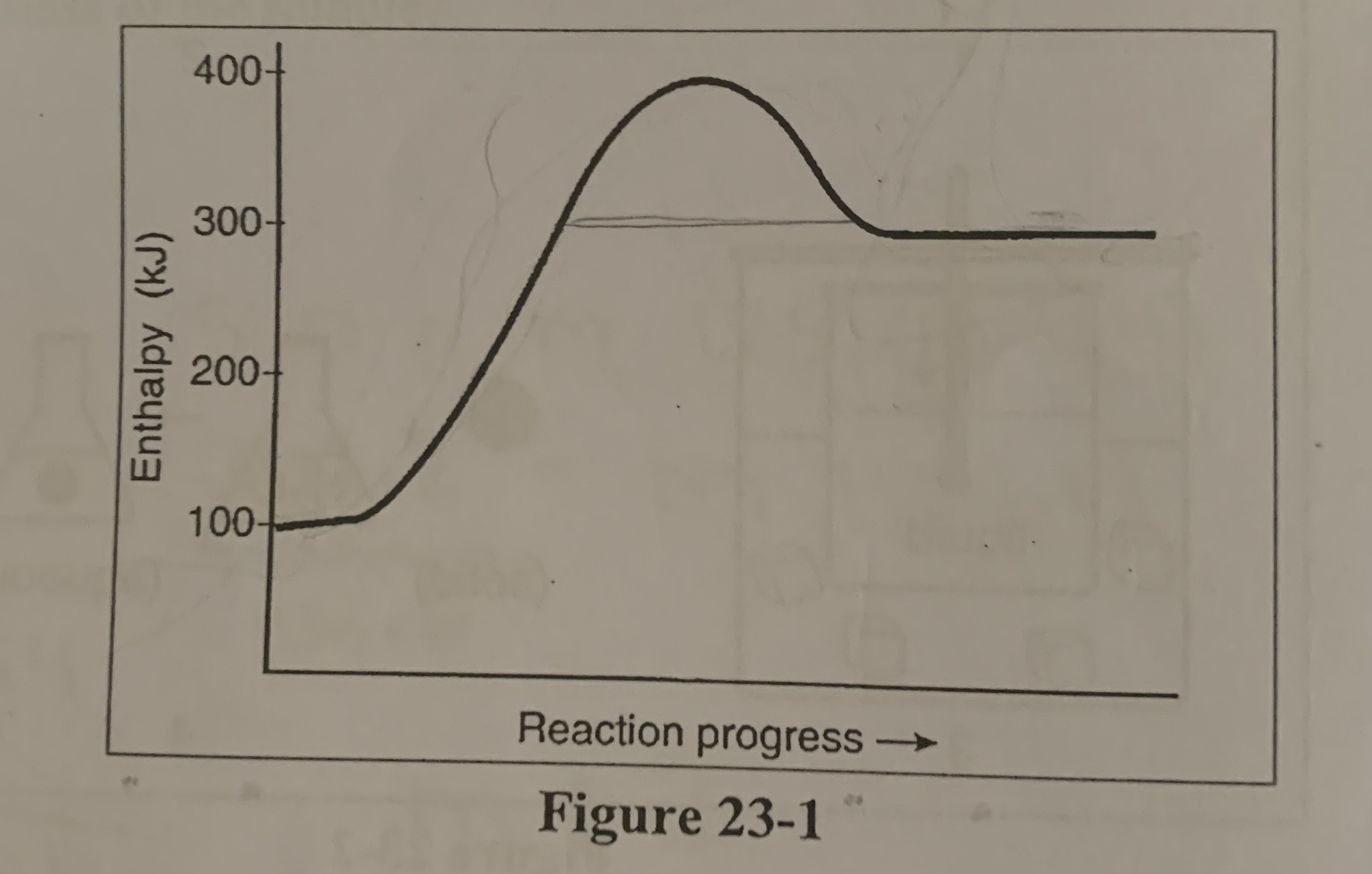
Where would the kilojoules of heat be placed for the reversed thermochemical reaction in the figure?
a) with products
15
New cards
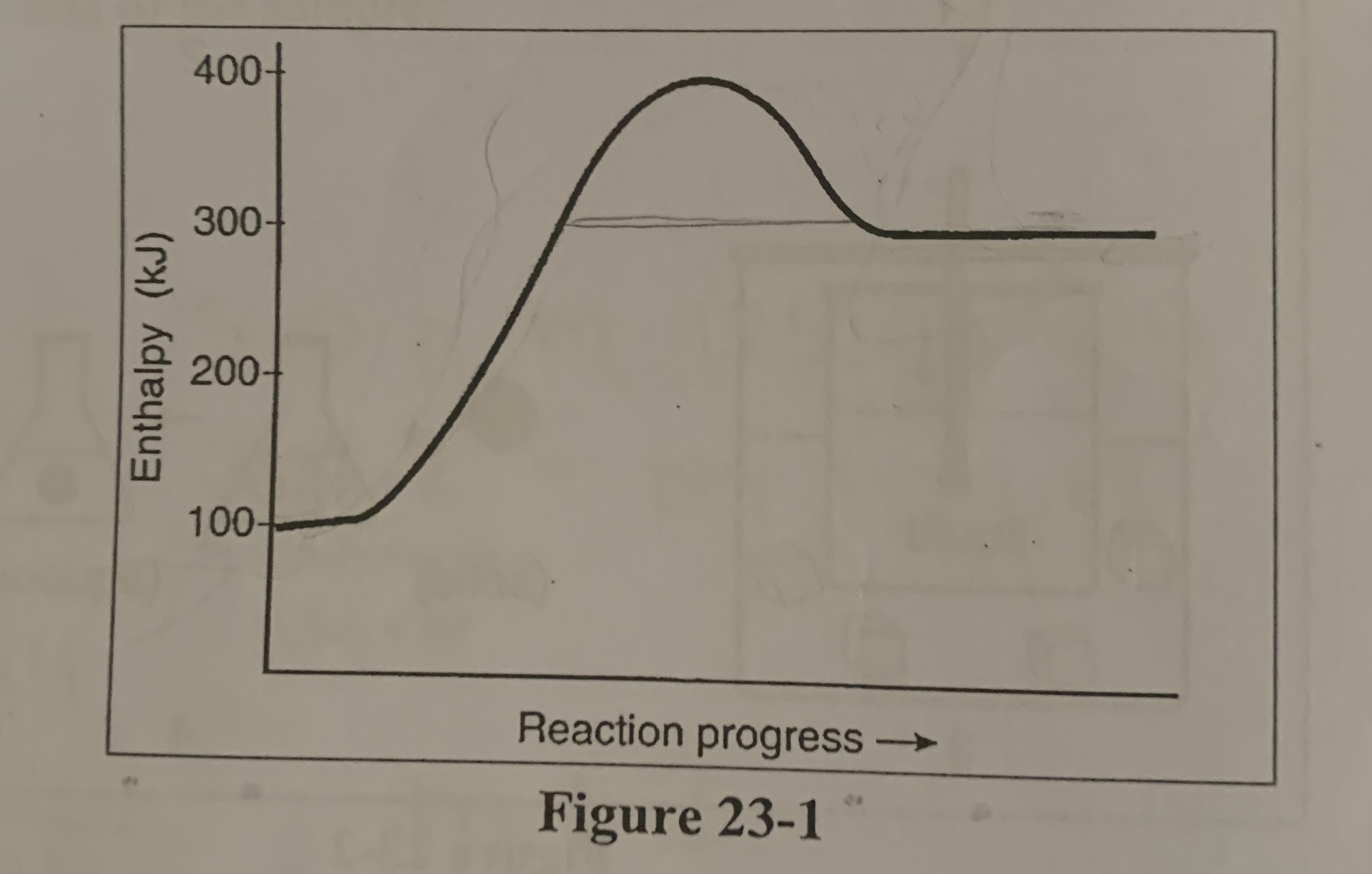
What is the activation energy for the forward reaction in the figure?
d) +300 KJ
16
New cards
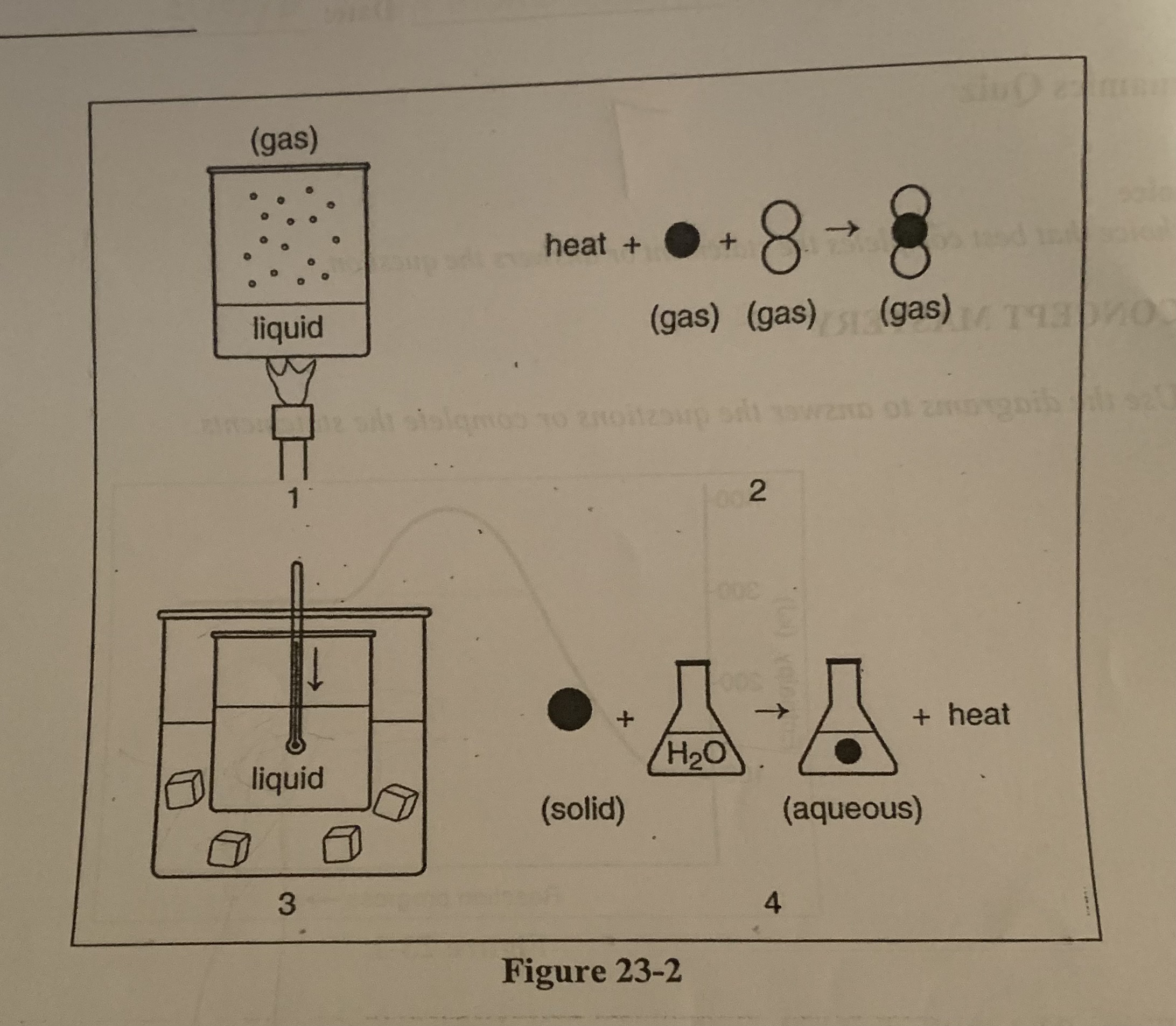
What is happening to the enthalpy of `the` ice in diagram 3?
b) there is an increase in entalphy
17
New cards
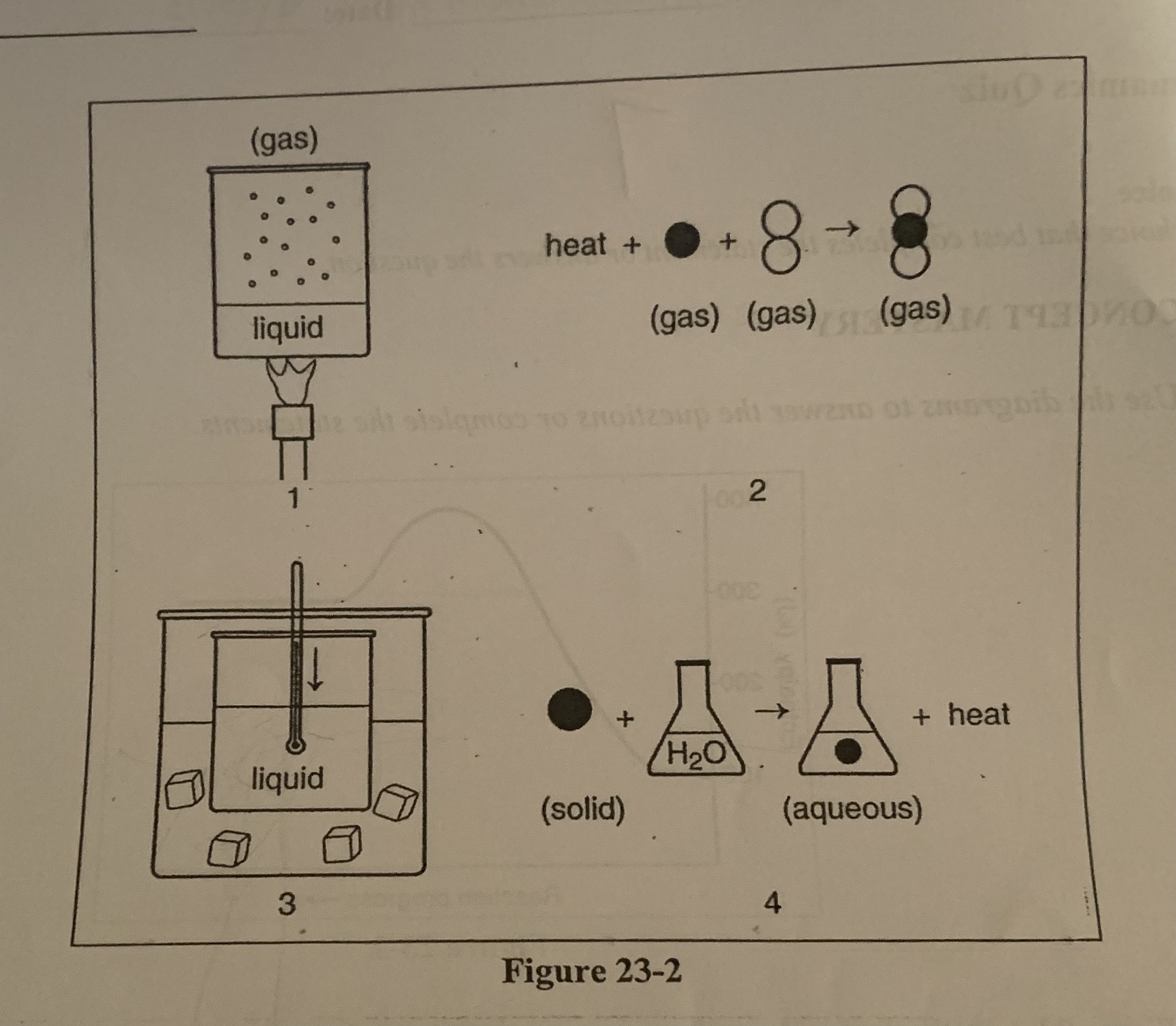
What is happening to the enthalpy of the liquid substance in diagram 1?
d) There is an increase in enthalpy
18
New cards
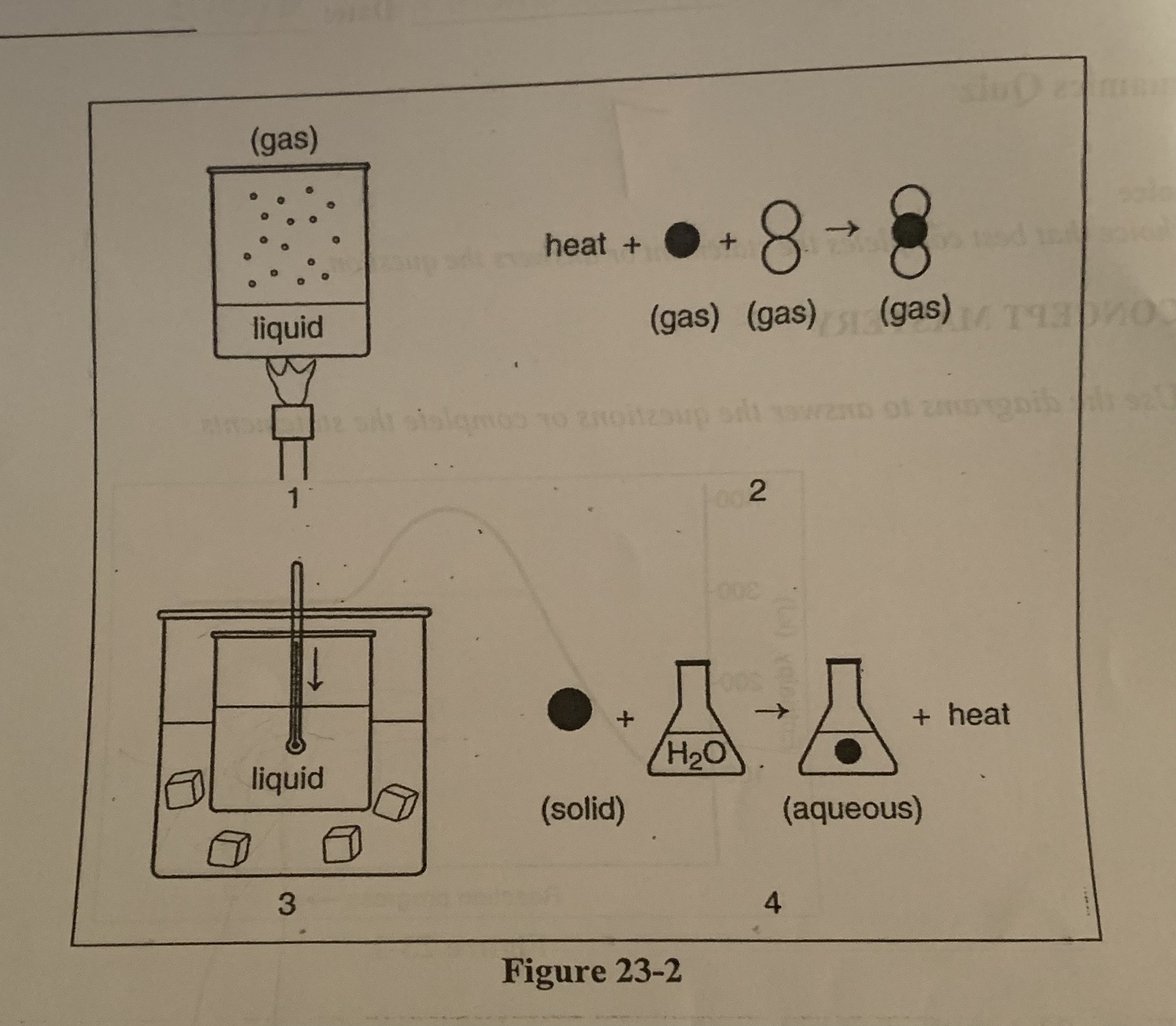
What is happening to the enthalpy of the liquid substance in diagram 3?
c) there is a decrease in enthalpy
19
New cards
If 335g water at 22.5 C loses 9750 J of heat, what is the final temperature of the water.
c) 18.5 C
20
New cards
The temperature of a sample of water increases from 25.0 C to 50.0 C as it absorbs 50.0 calories of energy. What is the mass of the sample.
2\.0 g
21
New cards
According to the collision theory
d) both molecular orientation and energy level must be right for a reaction to occur
22
New cards
What is the general relationship between concentration and reaction rate?
a) the higher concentration, the higher the reaction rate
23
New cards
The symbol used to represent concentration is
d. \[ \]
24
New cards
Activation energy equals the
b) difference between the peak energy and the energy of the reactants
25
New cards
the symbol used to represent “change in” is
c) **Δ**
26
New cards
What is the general relationship between temperature and reaction rate?
a) The higher the temperature, the higher the reaction rate
27
New cards
Chemical kinetics is mainly concerned with
a) reaction rate
28
New cards
reaction rate is the change in
d) concentration per unit time
29
New cards
In order for molecules to react with one another, they must
c) collide
30
New cards
What factors account for the fact that powdered sugar dissolve more quickly than granulated sugar under the same conditions?
d) surface are