A&B: Wiring Diagrams Up to 400MBH
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is a transformer and what are its key features?
AC device using mutual induction from two coils on the same core
Magnetic circuit made of low reluctance material with no air gaps
Two main purposes:
Change circuit voltage
Isolate circuits
Built from laminated silicon steel to reduce eddy currents
High voltage side usually marked "H", low voltage side "X"
Multi-winding transformers allow for flexible voltage stepping
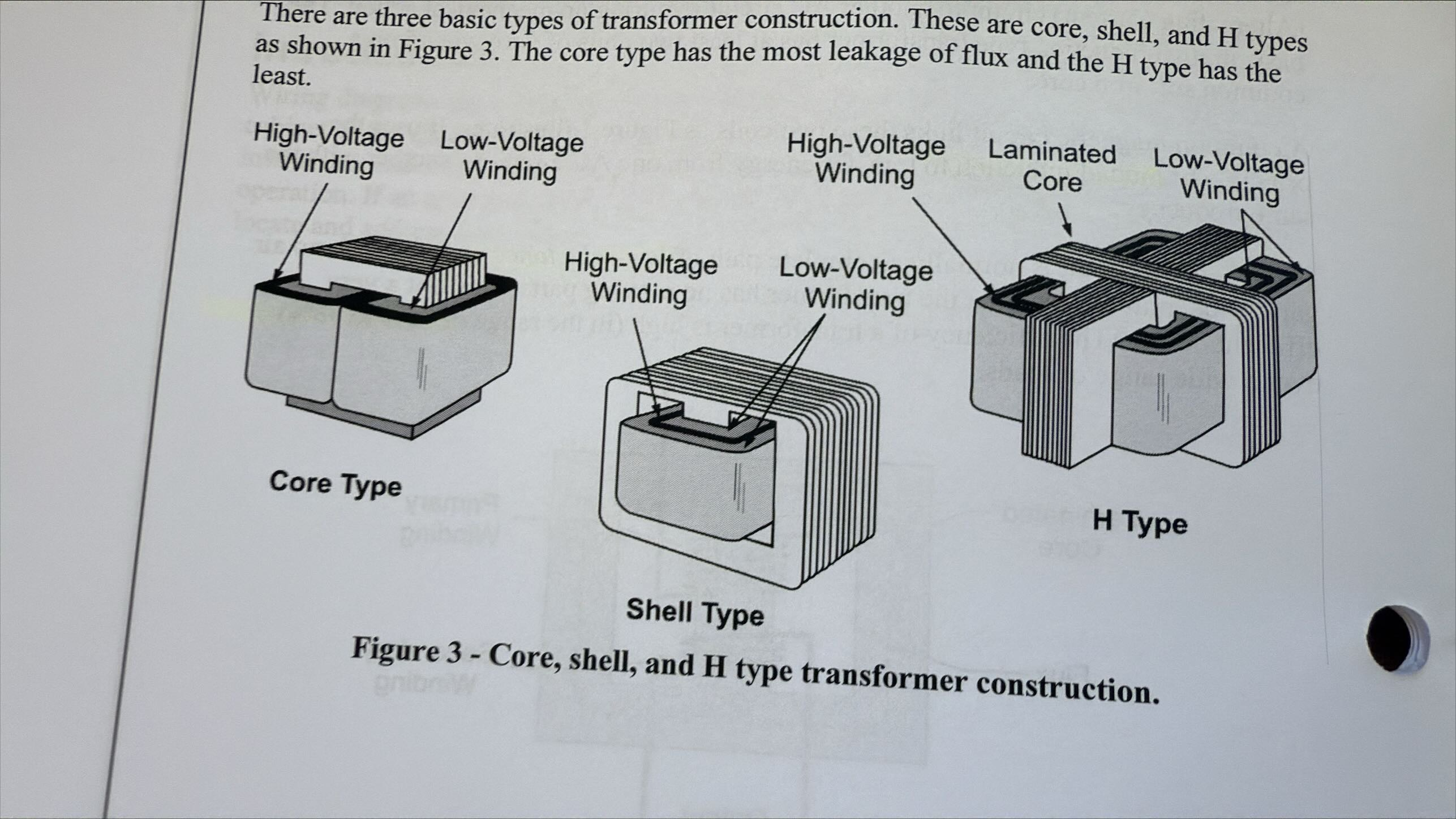
What are the main transformer construction types and their characteristics?
Core Type: most flux leakage
Shell Type: moderate flux leakage
H Type: least amount of flux leakage
What are typical efficiency levels of transformers and why?
95–98% efficient
No moving parts
Low reluctance path
Small flux leakage through the iron core may cause minor inefficiencies
What are common voltage applications for ignition and control transformers?
Step-up: 120V to 6000V (ignition transformers)
Step-down: 120VAC to 24VAC (control transformers)
How does an ideal transformer behave?
Voltage ratio equals turn ratio
No impedance or voltage drops
Example: 100 turns on primary with 100VAC = 1 VAC/turn
10-turn secondary = 10VAC output
How does a practical transformer differ from an ideal one?
Primary and secondary have resistance and reactance
Voltage drop exists due to excitation current or winding losses
Drops are minor but real in application
What is exciting (magnetizing) current and what does it do?
Flows continuously at 2–10% of rated current
Establishes magnetic flux for operation
Manages hysteresis and eddy current losses in iron core
What does Lenz’s Law state about transformer voltage?
Induced voltage opposes the change that caused it
Supply voltage and induced voltage are always in opposition
What happens in a transformer under no load vs. full load?
No Load: secondary voltage equals output primary flux cuts secondary winding
With Load: secondary current generates opposing flux
primary adjusts flux to maintain balance
What is transformer capacity rated in and what does it represent?
Measured in VA or kVA (apparent power)
Reflects full output power (not input)
1 VA = 1 Watt
Rating must account for power factor
Example: 20W load at 0.8 PF = 25 VA required
How do you calculate transformer voltage per turn and turn ratios?
Formula: a = Vprimary / Vsecondary = TurnsPrimary / TurnsSecondary
Example: 120VAC across 240 turns = 0.5V/turn
What happens when a transformer reaches saturation?
Flux no longer increases with current
Saturation typically occurs around 110% of rated voltage
Beyond this point, primary current rises rapidly and may cause burnout
Why is voltage rating dependent on iron content in the core?
More iron allows for more flux capacity
Helps avoid early saturation and maintain output under load
What are current limiting transformers and where are they used?
Small transformers with high internal impedance
Even a shorted secondary produces low current
CEC limits to 100VA (Class 2)
Common in gas control applications
How does the air gap in current limiting transformers affect performance?
Limits secondary current delivery by saturating core
Prevents increase in magnetic flux
Eliminates need for overcurrent protection
What information is required to size a control transformer?
Load voltage
Load amperage
Available line voltage
Likely power factor of the load
What are the installation styles of transformers?
Open type or totally enclosed
Enclosed transformers can be used in outdoor elements if safe
Pictorial: shows actual images of components
Connection (line diagram): shows wire terminals and physical locations best for tracing or locating wires
Ladder: shows logic and symbols, but not physical locations of components
R: power feed to thermostat (usually 24VAC)
W: initiates heating (R to W)
Y: initiates cooling (R to Y)
G: activates blower
(R to G) may also trigger higher blower speed during cooling
Residential units often aren’t and may overheat
Varnish that holds core laminations can fail, leading to short circuits
Always ensure proper airflow around the transformer
Causes excess current draw
May damage primary wires
Eddy current losses result in heat inside the core Single solid cores have higher losses, laminations reduce this If laminations separate, eddy losses increase and heat rises
A = 55°C
B = 80°C
F = 115°C
H = 150°C
Based on a 40°C starting internal temperature