Topic 6 Chemical Signals
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
two organ systems used for regulation
nervous system (NS), endocrine system (ES)
nervous system (NS)
regulates overall activity and function, responds to sudden stimuli
endocrine system (ES)
not as associated with sudden stimuli, typically regulates slower processes, responses are slower
nervous system (features)
working cell: neuron
distance from target cells: very close
type of signal: nerve signal (electrical)
speed of signal: fast
duration of signal: very brief
specificity of signal: very specific
coordinated signals? highly coordinated
endocrine system (features)
working cell: endocrine cell
distance from target cells: very far
type of signal: hormones (chemicals)
speed of signal: slow
duration of signal: prolonged
specificity of signal: nonspecific
coordinated signals? relatively not coordinated
transducers
things that can take one form of energy or information and convert it into another form of energy or information
BOTH NS and ES ARE ACTING AS TRANSDUCERS!
nervous system (process)
receptor for stimulus
electrical signal
gap between control cell and target cell
NS: synaptic cleft
secretion of chemical signal
NS: neurotransmitter
ES: hormone
receptor for chemical signal
signal transduction (may use 2nd messengers)
response by target cell
neurotransmitters
neural signaling
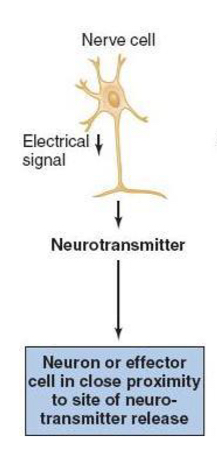
autocrines
autocrine signaling
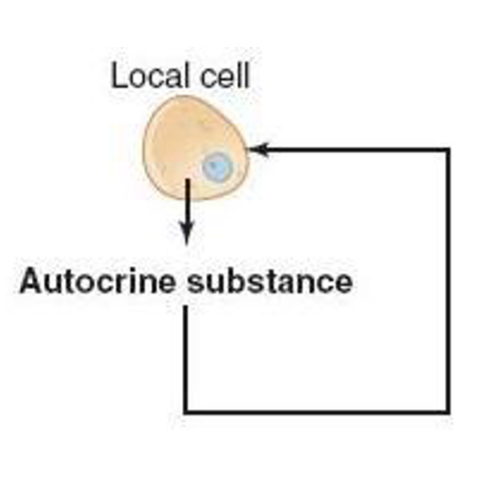
paracrines
paracrine signaling
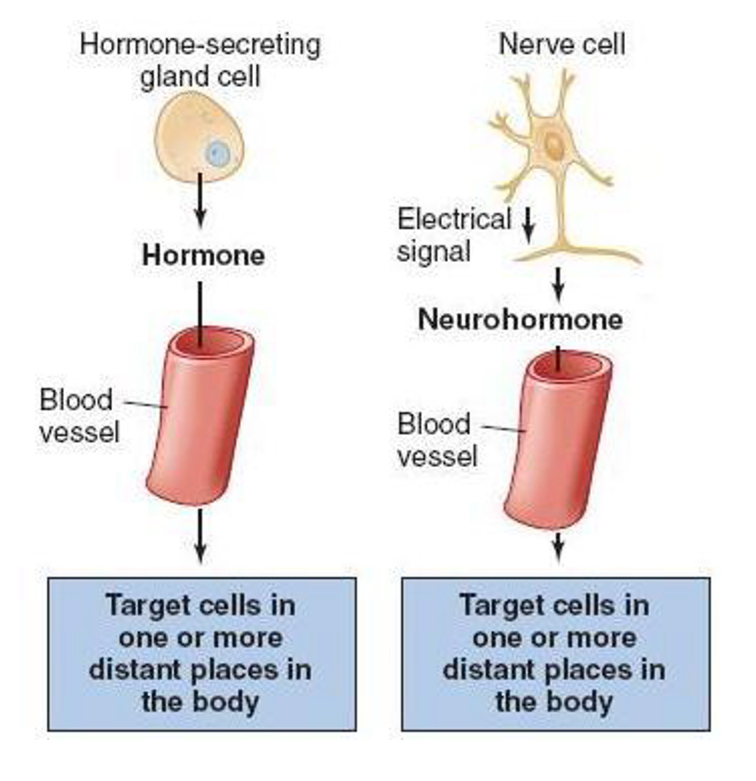
hormones and neurohormones
endocrine signaling
pheromones
pheromonal signaling
first messengers
neurotransmitters, chemical signaling
come out of regulatory cell
second messengers
intracellular
don’t work outside cells
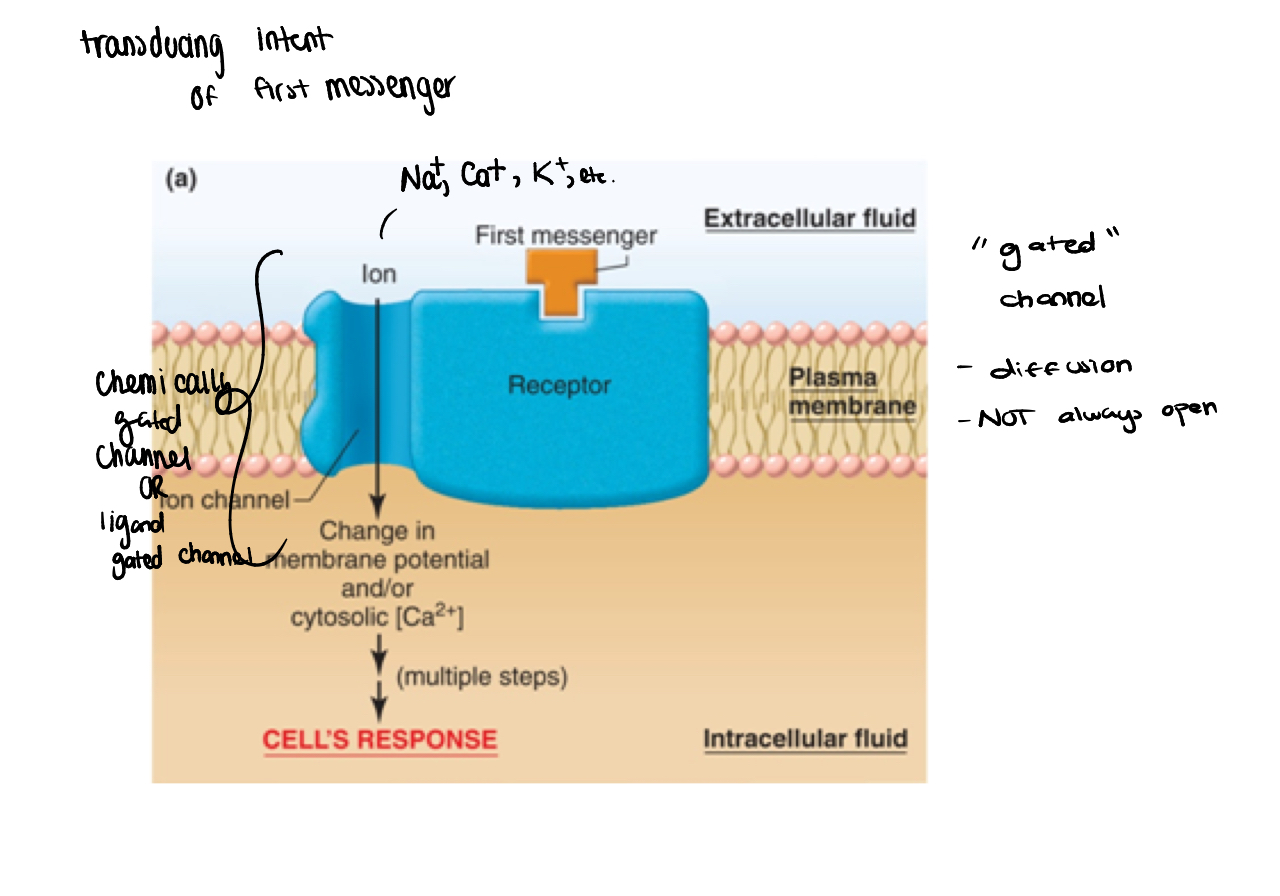
signal transduction using ion channels
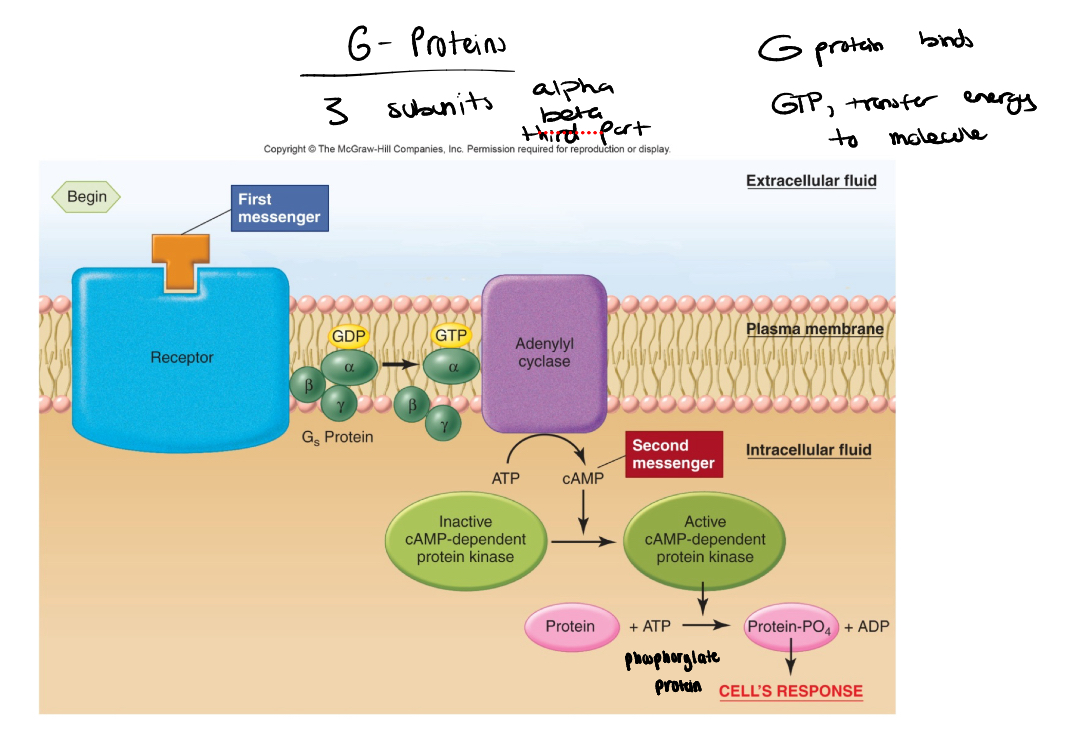
signal transduction using cAMP/PK (diagram)
signal amplification by adenylate cyclase
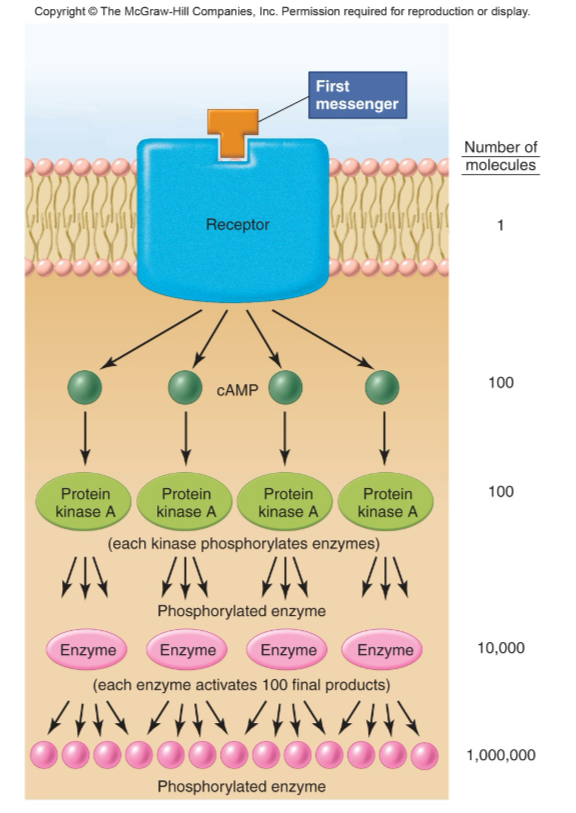
signal transduction using cAMP/PK
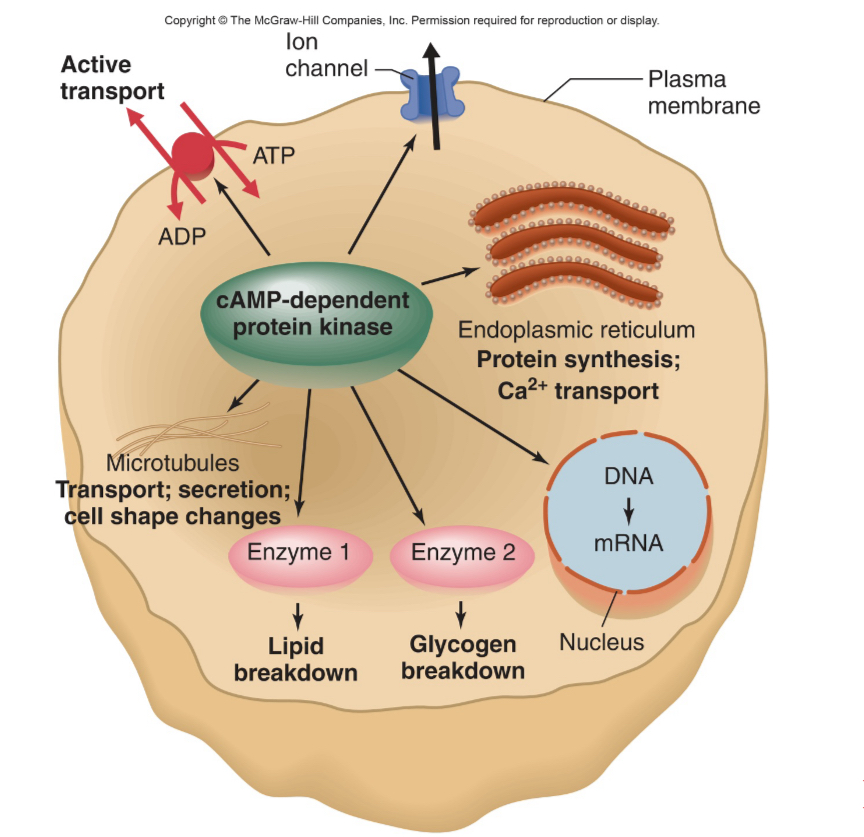
stimulatory G-protein (Gs)
enhances activity
inhibitory G-protein (Gi)
inhibits activity
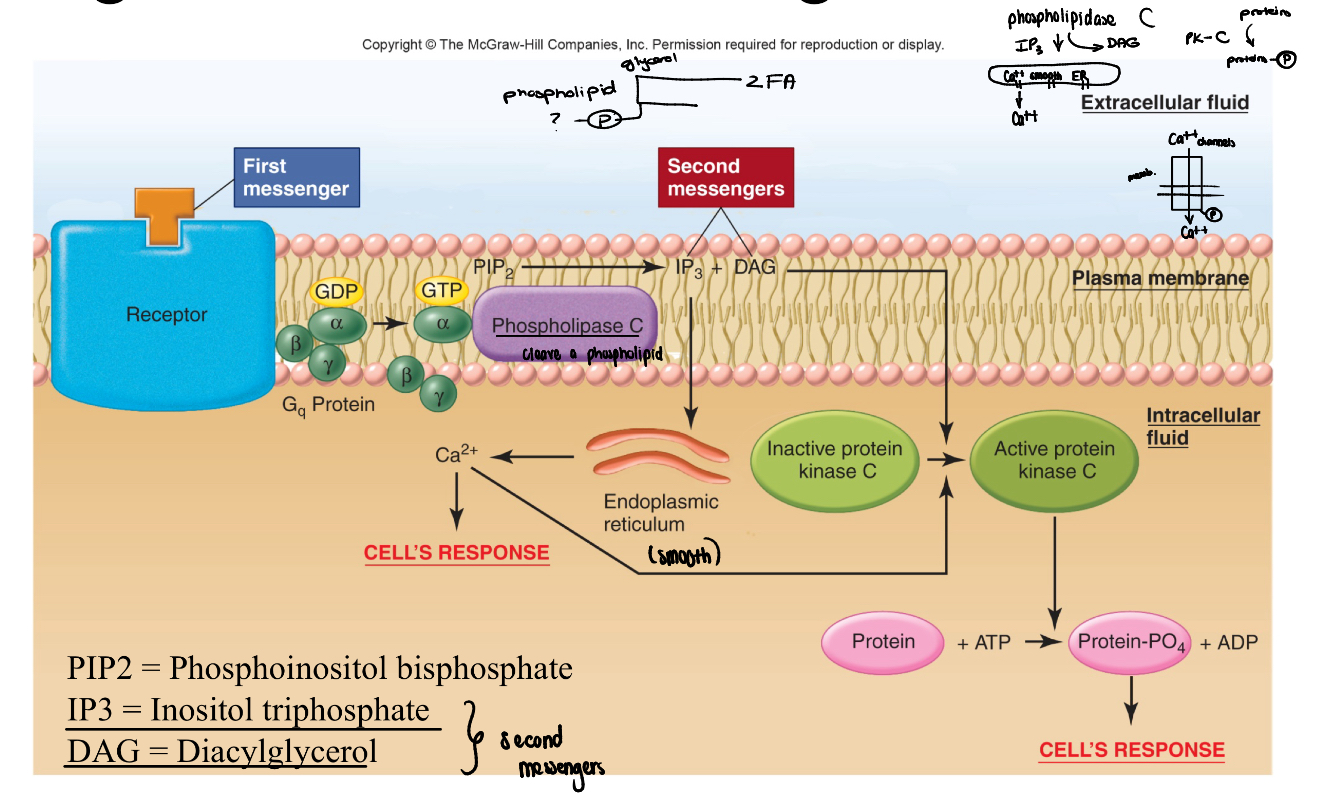
signal transduction using IP3 and DAG
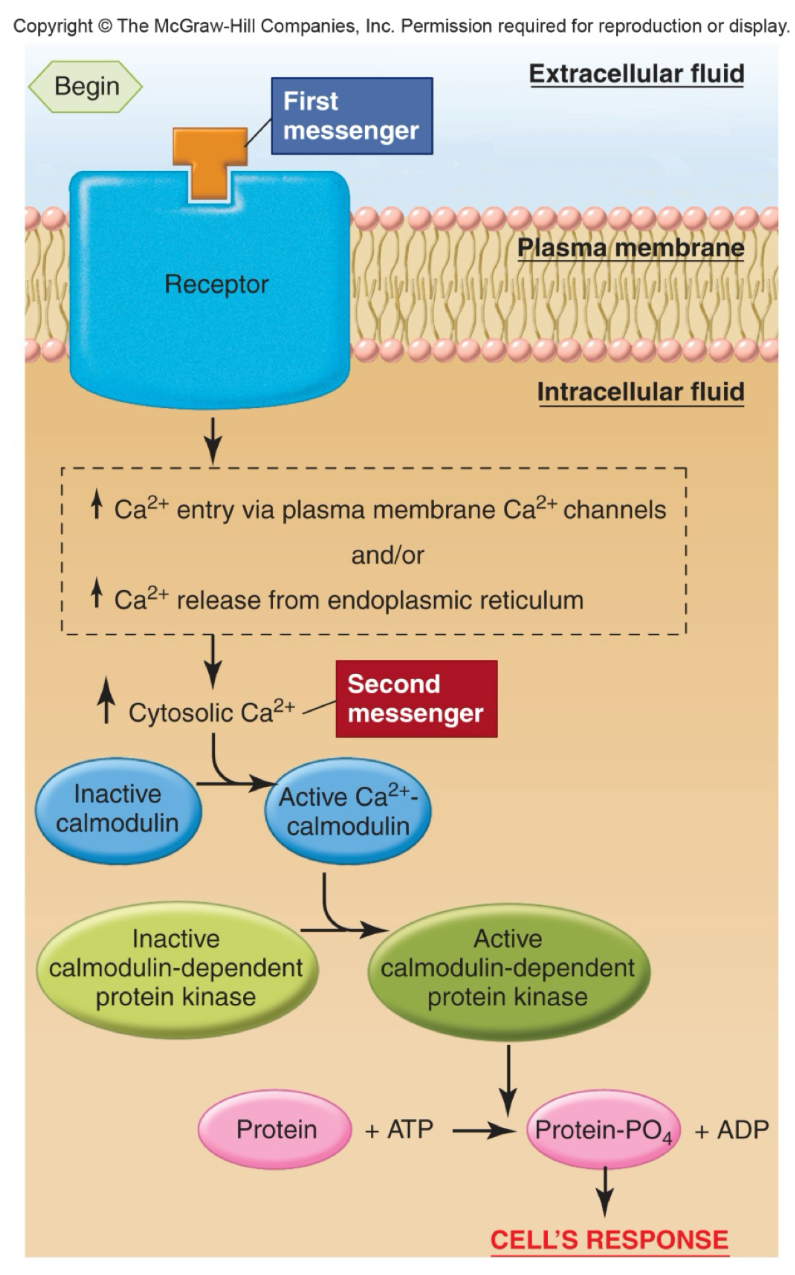
signal transduction: ca++ and calmodulin
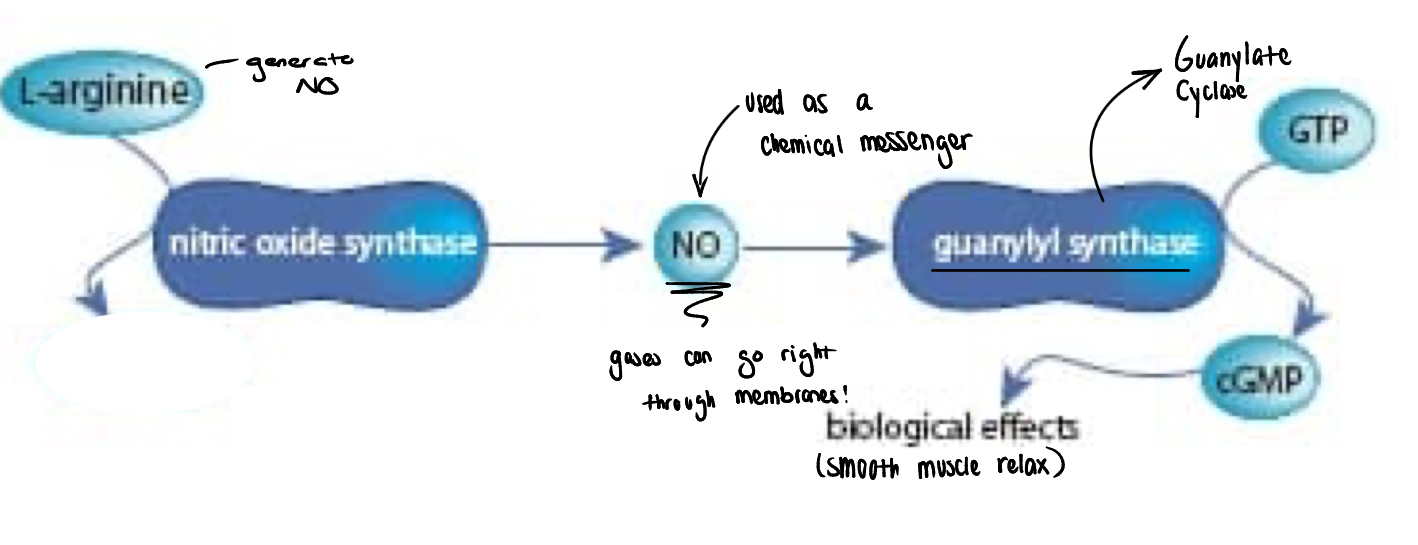
signal transduction: nitric oxide (NO) (w/ or w/o cGMP)
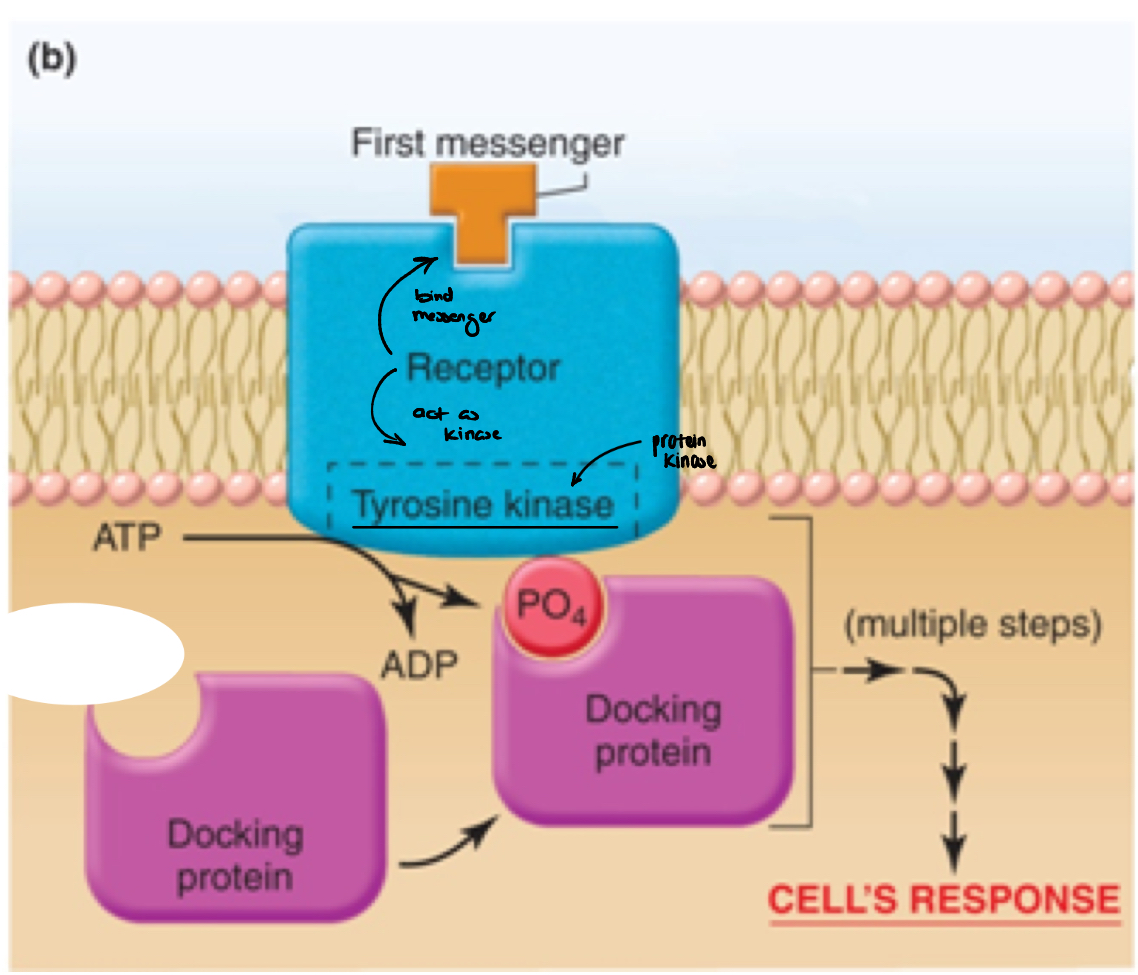
signal transduction using inherent Tyr-K
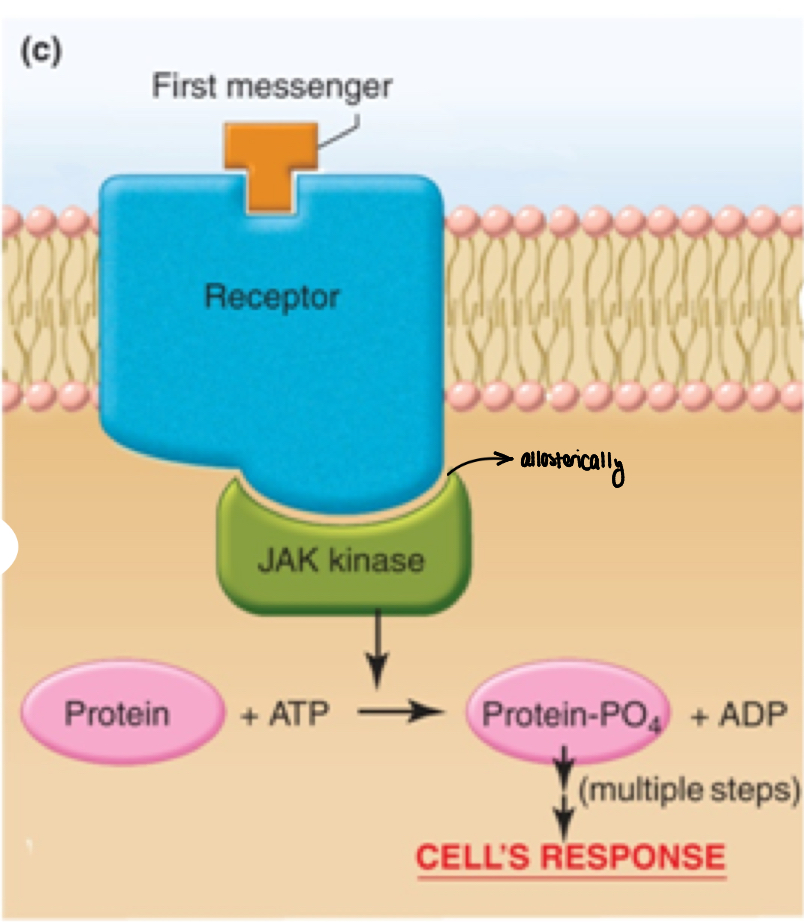
signal transduction using JAK (Janus Kinase)
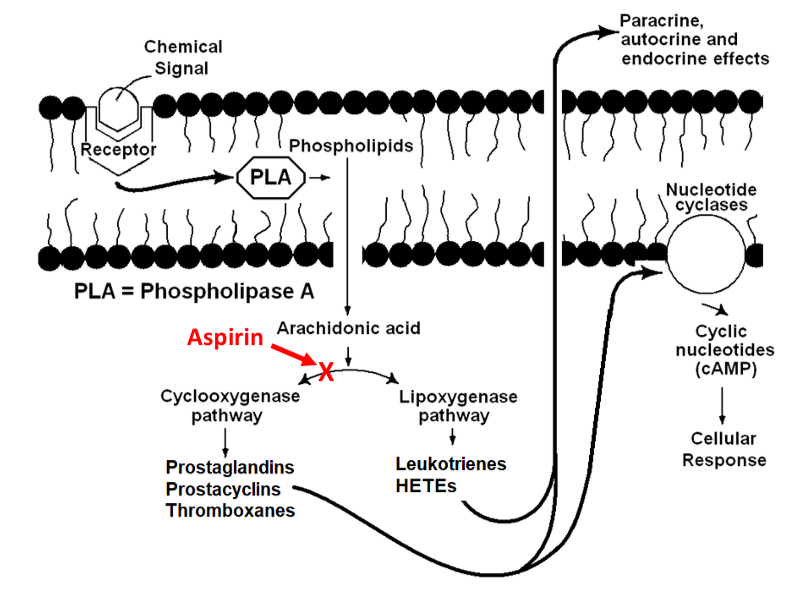
signal transduction using eicosanoids
prostaglandins & prostacyclins: vascular actions, (stimulates) inflammation
leukotrienes & HETEs: mediate allergic and inflammatory reactions
thromboxanes: blood clotting, other vascular actions
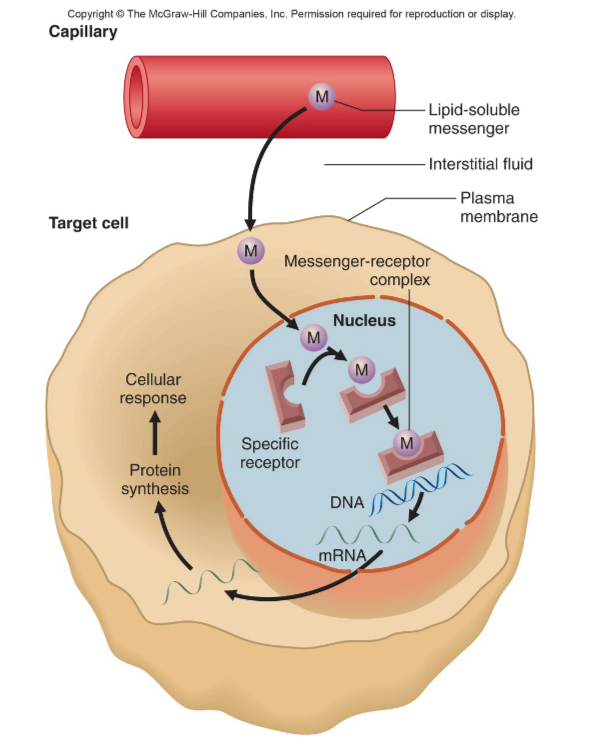
signal transduction by gene expression
a cell's external signal activates intracellular signaling pathways that modify transcription factors, ultimately changing the expression of specific genes to produce a cellular response. This begins with a ligand (signal) binding to a receptor, triggering a intracellular cascade of molecular events, often involving second messengers. This cascade leads to the activation or modification of transcription factors, which then move to the nucleus to initiate or suppress the transcription of specific genes, altering the cell's function or behavior