AP BIO Unit 1
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Topics: data collection, functional groups, properties of water, organic chemistry (macro molecules, isomers, etc.).
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
mean vs median
mean is affected by outliers, median is not
mean > median
outliers on the high end of the data
mean < median
outliers on the low end of the data
standard deviation
shows the spread of the data
high standard deviation
high variation in data
low standard deviation
data is consistent
standard error (of means)
compare our data to all possible data
low standard error of means
our data is similar to all the data
high standard error of means
our data is different than all possible data
covalent bonds
sharing of electrons
non-polar covalent bonds
electrons are shared equally
polar covalent bonds
electrons are shared unequally
functional group
group of atoms within a molecule that interacts in predictable ways with other molecules (hydroxyl, amino, carboxyl, carbonyl, methyl, sulfhydryl, phosphate)
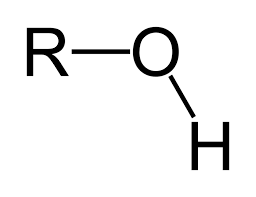
hydroxyl group
OH, consists of a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an oxygen atom, represented as (-OH); polar, weakly acidic (donates proton H+), can form H bonds (water soluble), high BP, ex. ethanol, methanol, etc.
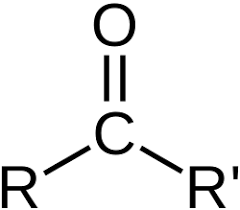
carbonyl group
-CO, consists of a carbon atom double bonded to an oxygen atom (C=O); reactive and versatile, polar, high BP, can form H bonds (water soluble), used to make new bonds with other molecules, ex. aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, amides
aldehyde
an organic molecule with a carbonyl group located at the end of the carbon skeleton
ketone
when the carbonyl group is in the center of the carbon skeleton
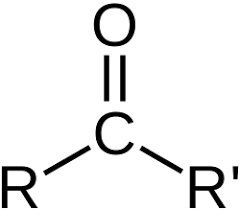
carboxyl group
COOH, functional group consisting of a carbonyl group (C=O) and a hydroxyl group (OH) bonded to the same carbon atom; weak acid (bc of hydroxyl group donating H+), polar, H bonding (donor H in OH and acceptor O in C=O), high MP and BP
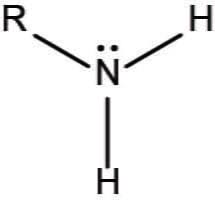
amino group
NH2, functional group that can accept a proton (H+) from a solution, becoming positively charged (NH3+); basic, classified based on R groups, polar, can form H+ bonds, water soluble, high BP and MP
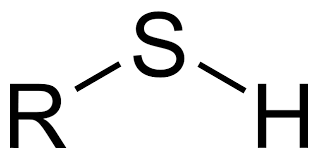
sulfhydryl group
-SH, strong, unpleasant odor, low BP, limited H+ bonds, can form disulfide bridges with other sulfhydryl groups (-S-S-), strong slightly polar covalent bond (S more EN than H), low water solubility, ex. cytesine, glutanthoine, etc.
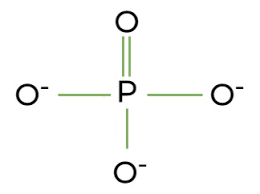
phosphate group
PO4, soluble in water, added and removed from molecules easily, gives molecule a negative charge, polar, low BP
polymer
large compound formed from combinations of many monomers
monomer
a simple compound whose molecules can join together to form polymers
ionic bonds
the transfer of electrons
electronegativity
how strongly an atom pulls electrons towards itself, EN increases diagonally up right, noble gases not included bc they achieve octet rule, F is the most EN
hydrogen bond
a weak attraction between a hydrogen atom and a highly electronegative atom (O, N, F) in another molecule or within the same molecule
water molecule properties
high polarity, can form H bonds, high heat capacity and heat of vaporization, can act as a solvent
cohesion
water molecules sticking to water molecules
adhesion
water molecules sticking to other molecules
surface tension
cohesion causes a film of surface water
c+a capillary action
due to cohesion and adhesion, water climbs narrow tubes
high specific heat (water)
how much energy it takes to raise the temp; stabilizes the temp
high vaporization point (water)
takes effort to move molecules fast
why is water able to stick to itself and other molecules?
bc the H bonds between H and O has a charge to it; it is bc the polar covalent bonds (sharing electrons)
why is ice less dense than water?
bc water is slightly polar (H+) and (-), forming hydrogen bonds; molecules slow down, ice created more space with it’s bonds, they push farther apart
organic chemistry
the study of structure, properties, composition, preparation, and reactions of carbon containing compounds; these elements might include other elements such as CHONPS
properties of carbon
only has 4 VE (needs 8), forms 4 covalent bonds with other atoms, can be single, double or triple bonds
why do bonds matter?
types of bonds change the shape; shape gets smaller with more bonds (single, double or triple)
properties of an acid
more H+ ions, pH below 7
properties of a base
more OH- ions, pH above 7
CHONPS
key elements found in living things; carbon (is the central element), hydrogen (is often used in energy exchange, used to create energy gradients as an ion, basis of acidity/alkalinity), phosphorus (in phosphate groups such as ATP), nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur
carbon skeleton
forms long chains containing single and/or double bonds; forms ring structures, hydrocarbons
isomers
molecules with the same molecular formula, but different structural formula (which indicates different properties)
dehydration synthesis (condensation rxn)
enzymes pull a hydroxyl group (an -OH) off of one monomer (or a group of already connected monomers); a hydrogen atom is pulled off the other; pulling out water
hydrolysis
enzymes insert a water molecule between the monomers making up the polymer; breaks the polymer apart
structural isomers
have different bonding patterns and organization
stereo isomers
different bond angles
cis-trans isomers
cis (same), trans (opposite); cis bonds are on the same side (I), trans bonds are on opposite sides (diagonal \)
enantiomers
one pair of molecules that are mirror images of each other; inverted, essentially (KL | LK)
what is the relationship between monomers and polymers?
polymers are made up of monomers; dehydration synthesis makes polymers; hydrolysis turns polymers into monomers
monosaccharides
are monomers, carbohydrates
disaccharides
are 2 monomers connected; carbohydrates
polysaccharides
are many monomers connected together; carbohydrates; can be homopolysaccharides or heteropolysaccharides; can be linear or branched
primary function of carbohydrates
production and storage of energy; mechanical support; every sugar ends in “-ose”; molecular recognition
carbohydrate structure
often drawn in linear forms but usually forms a ring structure in aqueous solutions; can be aldose sugars or ketose sugars; have the general formula of 1C: 2H: 1O
carbohydrates
important macromolecule; can be monosaccharides, disaccharides, or polysaccharides (sugars, essentially)
proteins
important macromolecule; made up of amino acids; fully formed and functional polypeptide
protein properties
structural, enzymatic, storage, transport, chemical messengers, receptors, movement, defense
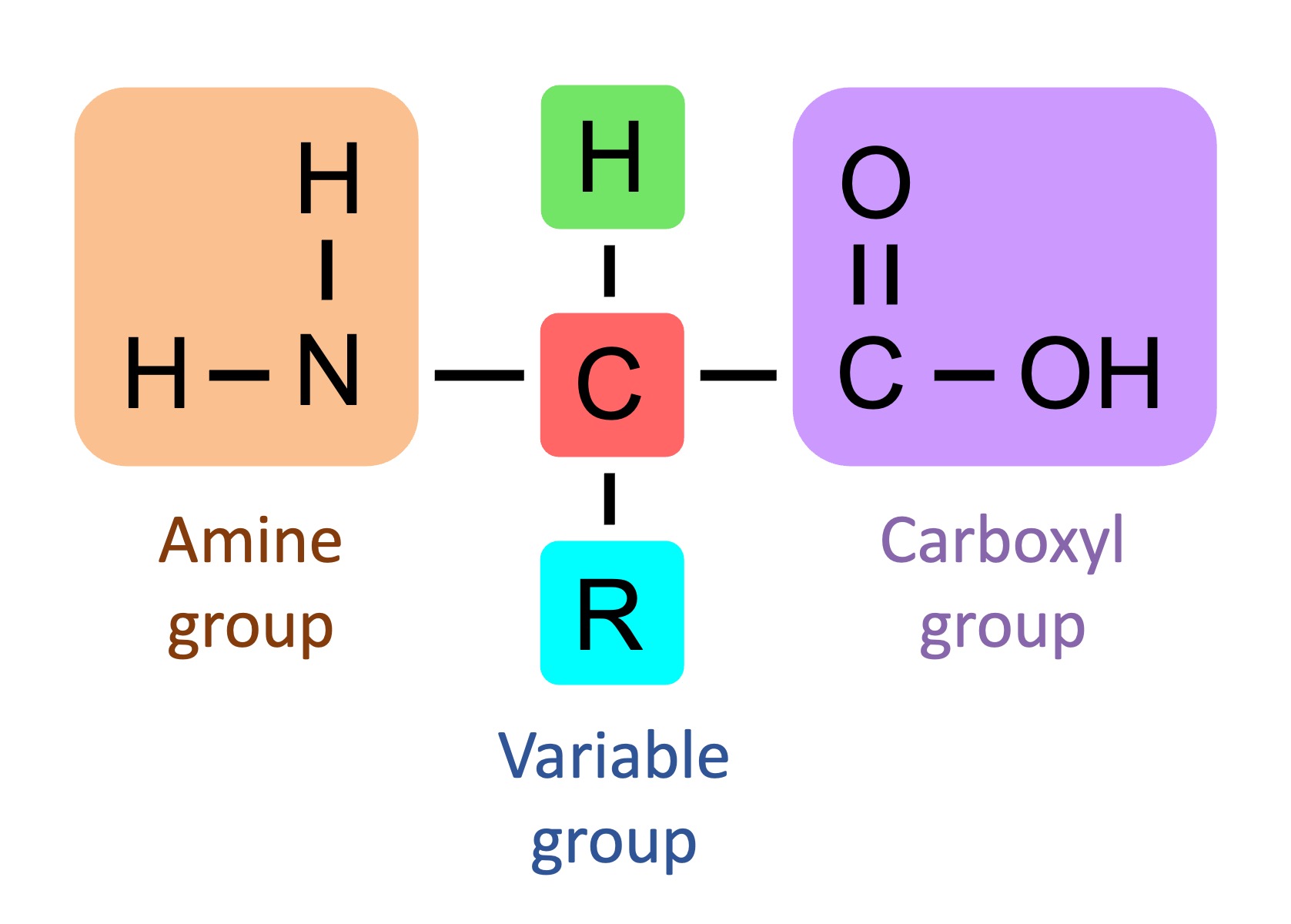
amino acid structure
consists of three parts: amino group, carboxylic acids group, side chain (R group); side chain attaches to the central C atom
non-polar amino acids
have no charge; side chains almost exclusively hydrocarbons; are always hydrophobic
polar amino acids
always hydrophylic, tend to play important roles in active sites of enzymes
electrically charged amino acids
acidic amino acids are negatively charged; basic amino acids are positively charged at body pH; interact with other amino acids bc their charge
peptide bonds
dehydration reaction occurs; carboxylic acid groups of one amino acid connects to amino group of another amino acid
polypeptides
short chains while proteins are long, functional chains of amino acids
4 levels of organization (proteins)
primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
primary structure of protein
sequence of amino acids (lvl 1); the chain has an N-terminus and a C-terminus; covalent bonds (peptide bonds) are formed between the carboxyl group of one AA and the amino group of the next, linking them together
secondary structure of protein
forms bc of H bonds between parts of the polypeptide backbone; B sheets form bonds with parallel chains (pleated); A helixes form bonds between every 4th amino acid in a spiral (curly); describes local folded patterns
tertiary structure of protein
3D arrangement of a protein’s polypeptides chain; forms bc of interactions between parts of amino acid side chains
quaternary structure of protein
the organization of multiple polypeptide chains (subunits) into a larger, functional protein complex; interaction between 2 or more seperate proteins to make one complete, functional protein.
what is the name of the monomer and polymer for a protein? what do proteins do for cells?
amino acid; polypeptide - they provide structure, transport, catalysts, etc.
denaturation
the process where a protein or nucleic acid loses its native structure, changing its function; can’t change the primary structure; the shape of the protein is altered
nucleic acids
large biomolecules, essential in all living cells and viruses, that serve as the primary information-carrying molecules
nucleotides
monomer; consists of three things: 5 carbon sugar, nitrogenous base, 1-3 phosphate groups
nitrogenous bases
purines have 2-ring structure; pyrimidines have 1-ring structure; A, T, and U form 2 hydrogen bonds (RNA has U); G, C form 3 hydrogen bonds
pentose sugar
deoxyribose contains one less oxygen than ribose; carbon numbering is extremely important for understanding polymer structure and function
phosphate group (NA)
phosphate groups are unstable, high energy functional groups; addition of groups require energy; removal of groups releases energy
nucleic acid polymers
phosphate group of 1 nucleotide connects to the 31 carbon of the sugar in the previous nucleotide; single stranded NA; in double-stranded DNA, the nitrogenous bases form hydrogen bonds between parallel strands; coils into a double-helix structure
deoxyribo nucleic acid (DNA)
double-stranded; used to store and transmit genetic info
ribo nucleic acid (RNA)
used to carry and translate genetic info; controls gene processes, etc.; uses sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose; uses bases G, C, A, U; single-stranded
adenosine triphosphate
stores and carries energy; acts as a coenzyme; can exist as ATP, ADP, or AMP (M is for mono)
lipids
only macromolecule that's not a polymer; hydrophobic; fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, steroids; long-term energy storage; membrane structure; protection'; chemical messengers; longer energy storage than carbs
triglycerides
composed of glycerol and 3 fatty acids
fatty acids
can be saturated or unsaturated (H vs no H); saturated only have single bonds between carbons; unsaturated have at least 1 double bond between carbons
saturated fatty acid
pack tightly together; form rigid aggregates; solid at room temp
unsaturated fatty acid
packed together loosely depending on # of bonds; greater potential for movement; liquid at room temp; form oils
phospholipids
glycerol with 2 fatty acids and a phosphate group; phosphate group often has other molecules linked to it; has polar head and non-polar tail; used by living things to create membranes; keeps internal and external environment separate bc hydrophobic
steroids
consists of a carbon skeleton of 4 fused rings; have many diverse functions
cholesterol in membranes
embedded within the phospholipid bilayer; makes the membrane more fluid in water
waxes
mixtures of various lipids; play protective structural role; leaf cuticle, cercumen, lanolin, spermaceti