Soil Mechanics Exam 1 Ch 1-3
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What are the five most common elements?
Oxygen (47%), Silicon (28%), Aluminum (8%), Iron (5%), Calcium (4%)
Three rock types?
Igneous (hot to cool), Sedimentary(results of weathering and deposition), and Metamorphic (pressure and heat, denser)
What are the minerals that are apart of the discontinuous series?
OPAB (Olivine, Pyroxene, Amphibole, Biotite Mica)
What Mineral is a part of the continuous series?
Plagioclase Feldspar
What minerals do both series in the Bowen’s Reaction Series lead to?
Potassium Feldspar, Muscovite Mica, Quarts
What are some characteristics of Basic Rocks in BRS?
Form fine-grained soils due to weathering, darker, low silica, as temperature decreases their compositions change significantly, need enough silica and slow cooling temperatures to change to next mineral.
What are some characteristics of Acidic Rocks in BRS?
Form coarse-grained soils due to weathering, lighter, high silica, rich in sodium and potassium, temperature only changes calcium-rich to sodium-rich while still being Plagioclase Feldspar, if high enough silica and slow cooling temp will form quarts and potassium feldspar
Physical Weathering
No change in chemical composition, only reduction in particle size, caused by stress (thermal or mechanical), exposes more surface.
Chemical Weathering
reduction in form, chemically breaks down in parent material, usually reduces unit weight, new form is more stable than old, more important with more surface area
What are some processes for chemical weathering?
Hydration (water into struct.), Hydrolysis (water breaks down chemical bonds), Oxidation (in iron-rich minerals), Carbonization (removal of limestone)
What are two common crystal compounds?
Silicon Tetrahedrons and Aluminum Octahedrons
Kaolinite characteristics
weathering product of feldspars, stable phys. and electrically, not affected by water, 0.72 nm thick (Silicon Tetrahedron/Aluminum Octahedron)
Montmorillonite Characteristics
Not stable physically or electrically, very affected by water, crystal attracts water and cation, 0.96 nm thick (Silicon Tetrahedron/Aluminum Octahedron/Silicon Tetrahedron)
Illite Characteristics
Similar to Montmorillonite but balanced by Potassium ions (K/Silicon Tetrahedron/Aluminum Octahedron/K)
Micelle
a mixture of solid and water that traps soil particles forming the structure of the clay deposit
Diffuse Double Layer
distance from clay particle to the limit of attraction
Why do DDL form?
Clay minerals repel each other since they have negative charges, this attracts cations in the soils moisture, this then attracts the negative charges of the water
What are the two structures of clay deposits?
Dispersed and Flocculated
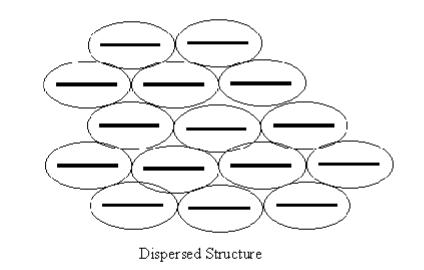
Characteristics of a Dispersed Structure
Non-isotropic, different properties in different directions, higher permeability in horizontal direction, low shear strength in horizontal, low cation concentration (freshwater) , presence of potassium and sodium forming a thick DDL
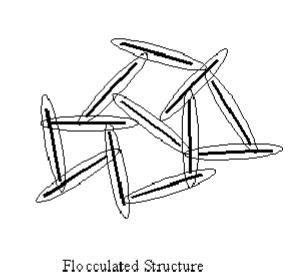
Characteristics of Flocculated Structure
Isotropic, same properties in different directions, lower permeability, occur when cation concentration is high (seawater), presence of calcium and hydrogen that suppresses DDL
What are the different deposition processes of transportation by water?
Rivers and Streams (Fluvial Deposit), Lake Deposits (Lacustrine Deposit), Marine Deposit (Flocculated and Uniform), Glacial Deposit (Glacial Till, Soil very compacted and dense, surface soil much looser)
Characteristics of Transportation by Wind (and fancy name)
Aeolian Deposit, predominantly sand and silt, Loess: Layered Soil Build up, Dunes: Loose blown sand like waves
Characteristics of Transportation by Gravity (and fancy name)
Colluvial Deposit, No sorting of soil, from upper sided slopes above valley, 40x mor sediment from colluvium from strambed
Residual (NOT a transport mechanism)
Weathering of Rock or accumulation of organic material, remains at origin, a wide range of sizes/shapes/compisitions
Fill out table