Muscular System
1/32
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
skeletal
smooth
cardiac
Skeletal and cardiac muscle are both striated, while smooth muscle is not.
Skeletal muscle cells have […] nucleus/nuclei and they are located on the […] of the cell
multiple; periphery
Cardiac muscle cells have […] nucleus/nuclei. Individual cells/fibers are […] such that the heart contracts as one unit.
one to two; electrically connected
Smooth muscle cells have […] nucleus/nuclei. They are not […]
one; striated
All skeletal muscles are wrapped in a sheath of dense, irregular connective tissue called the […]. It allows the whole muscle to contract while maintaining structural integrity. It also separates the muscle from other tissues, allowing it to move independently.
epimysium
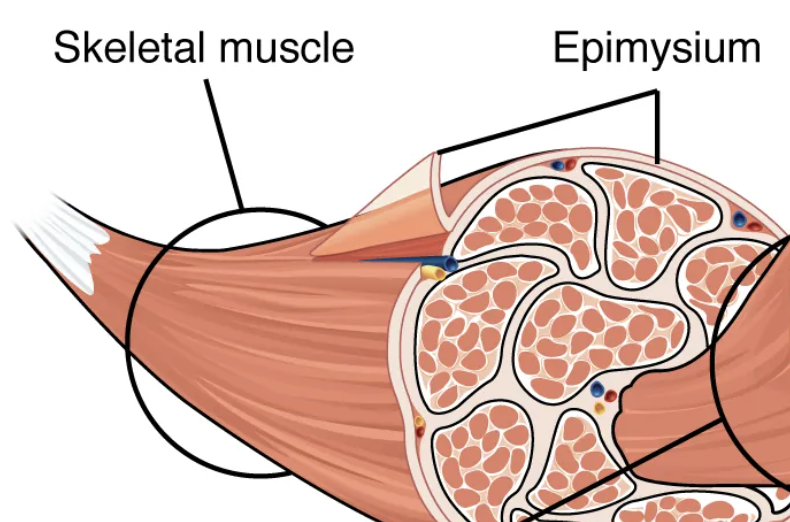
Skeletal muscle fibers are organized into individual bundles, each called a […], by a middle layer of connective tissue called the […]. This organization is common in muscles of the limbs; it allows the nervous system to trigger a specific movement of a muscle by activating a subset of muscle fibers within a bundle.
fascicle; perimysium
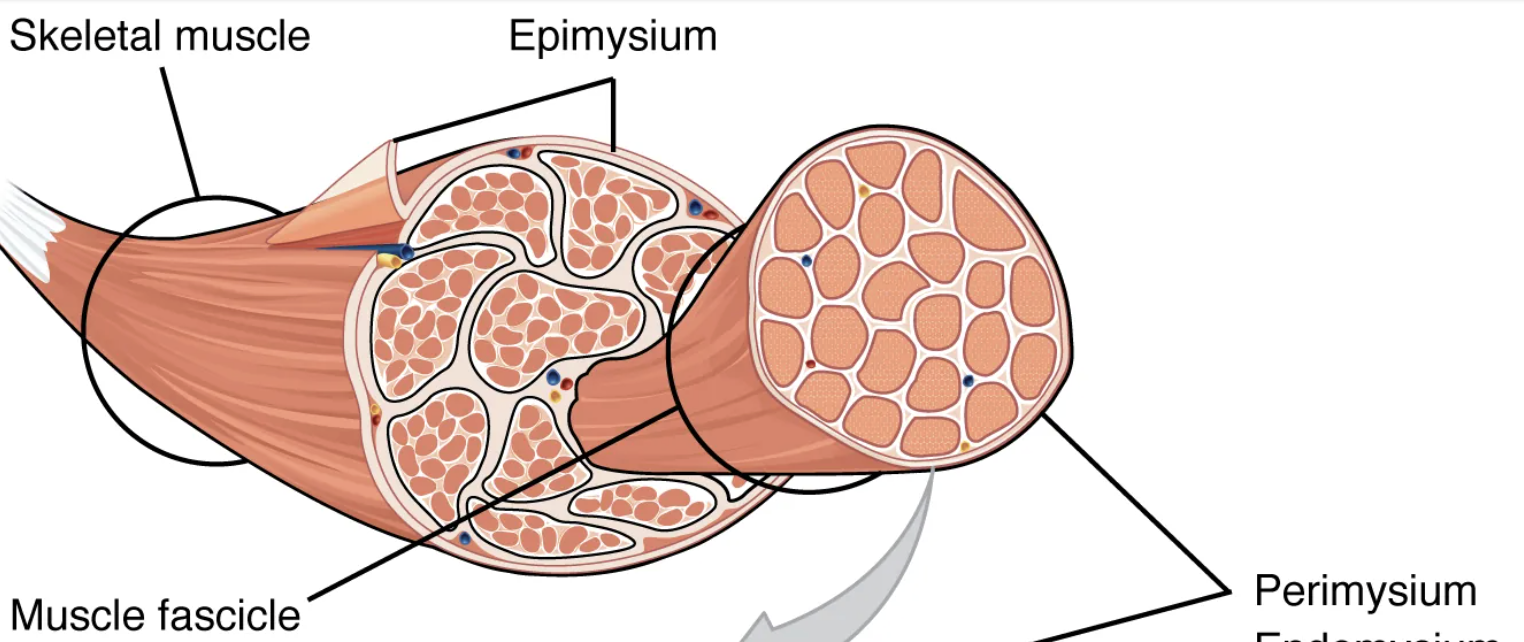
Inside each fascicle, each muscle fiber is encased in a thin connective tissue layer of collagen, and reticular fibers called the […]. It contains the extracellular fluid and nutrients to support the muscle fiber.
endomysium
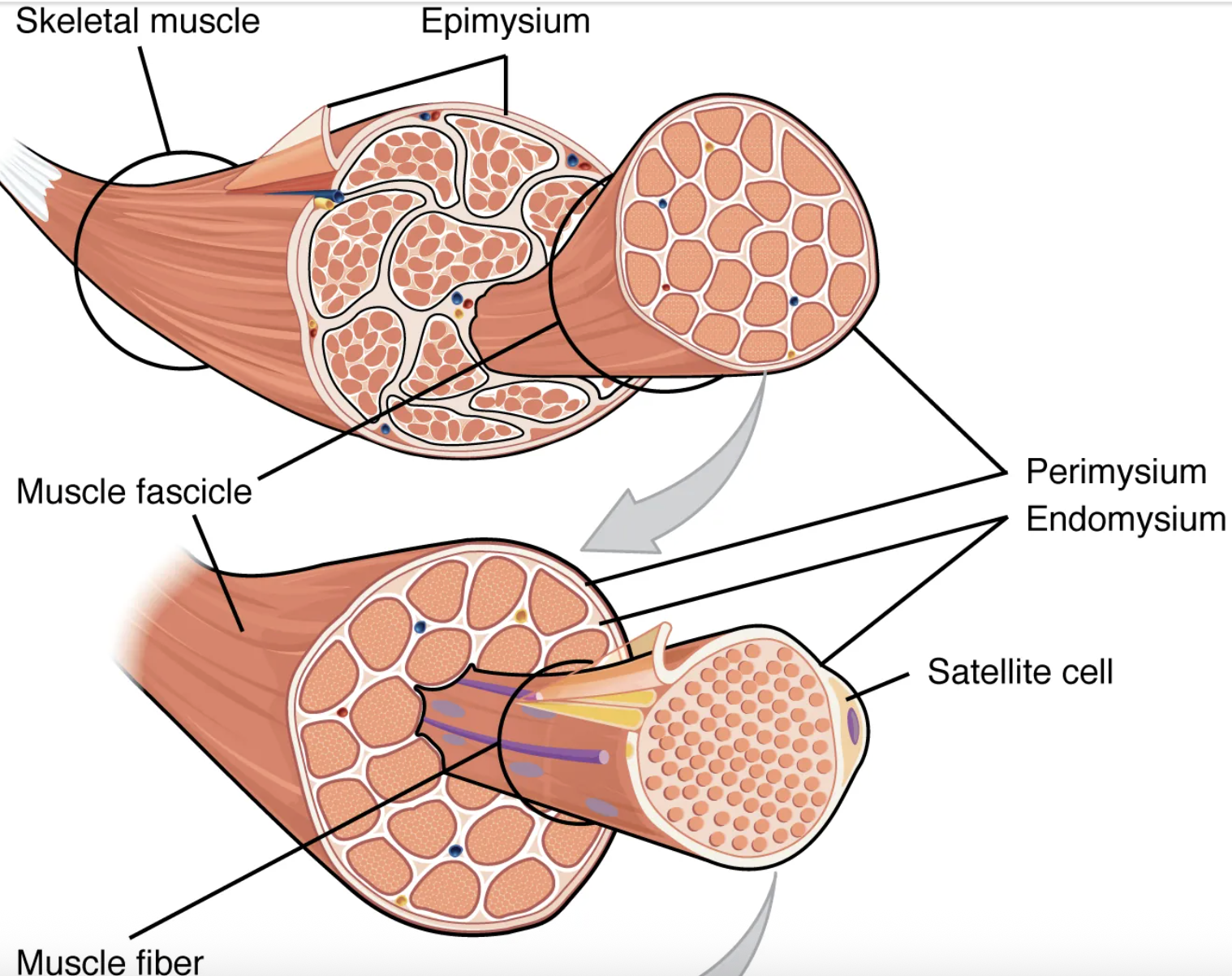
The plasma membrane of muscle fibers is called the […], the cytoplasm is referred to as […].
sarcolemma; sarcoplasm
Sarco- is rooted in Greek and means “flesh.”
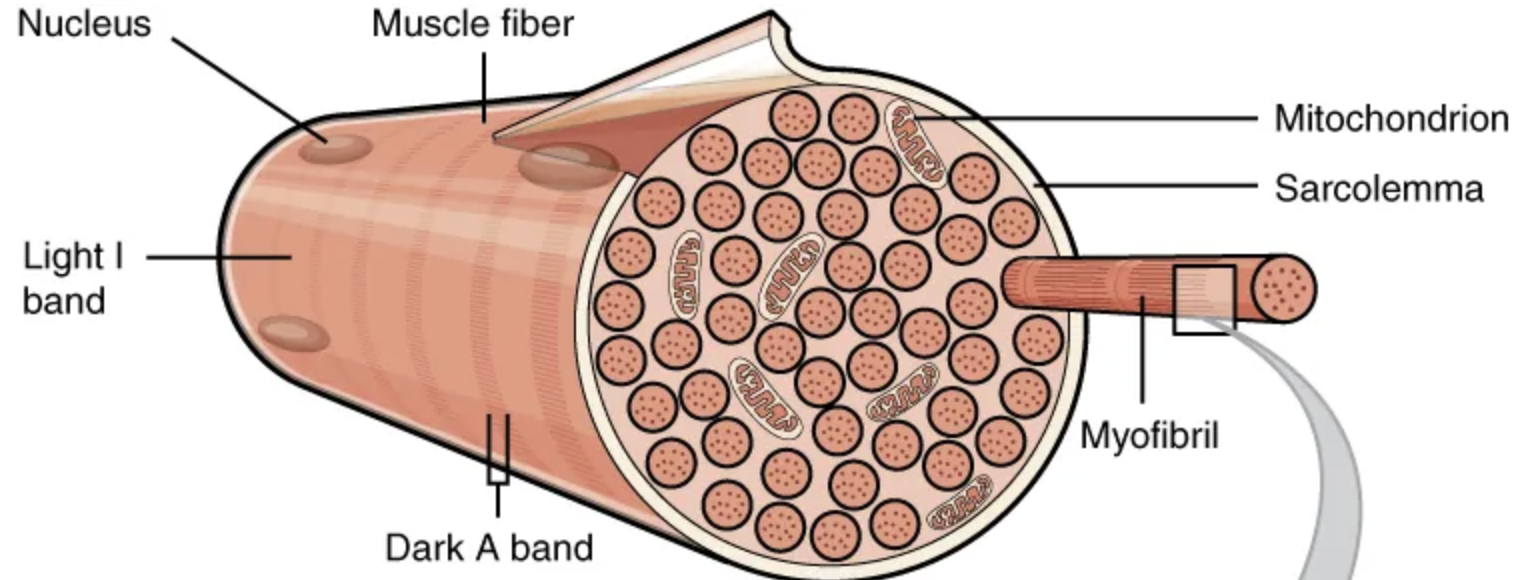
The specialized smooth endoplasmic reticulum of muscle fibers, which stores, releases, and retrieves […] is called the […]
calcium ions (Ca2+); sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
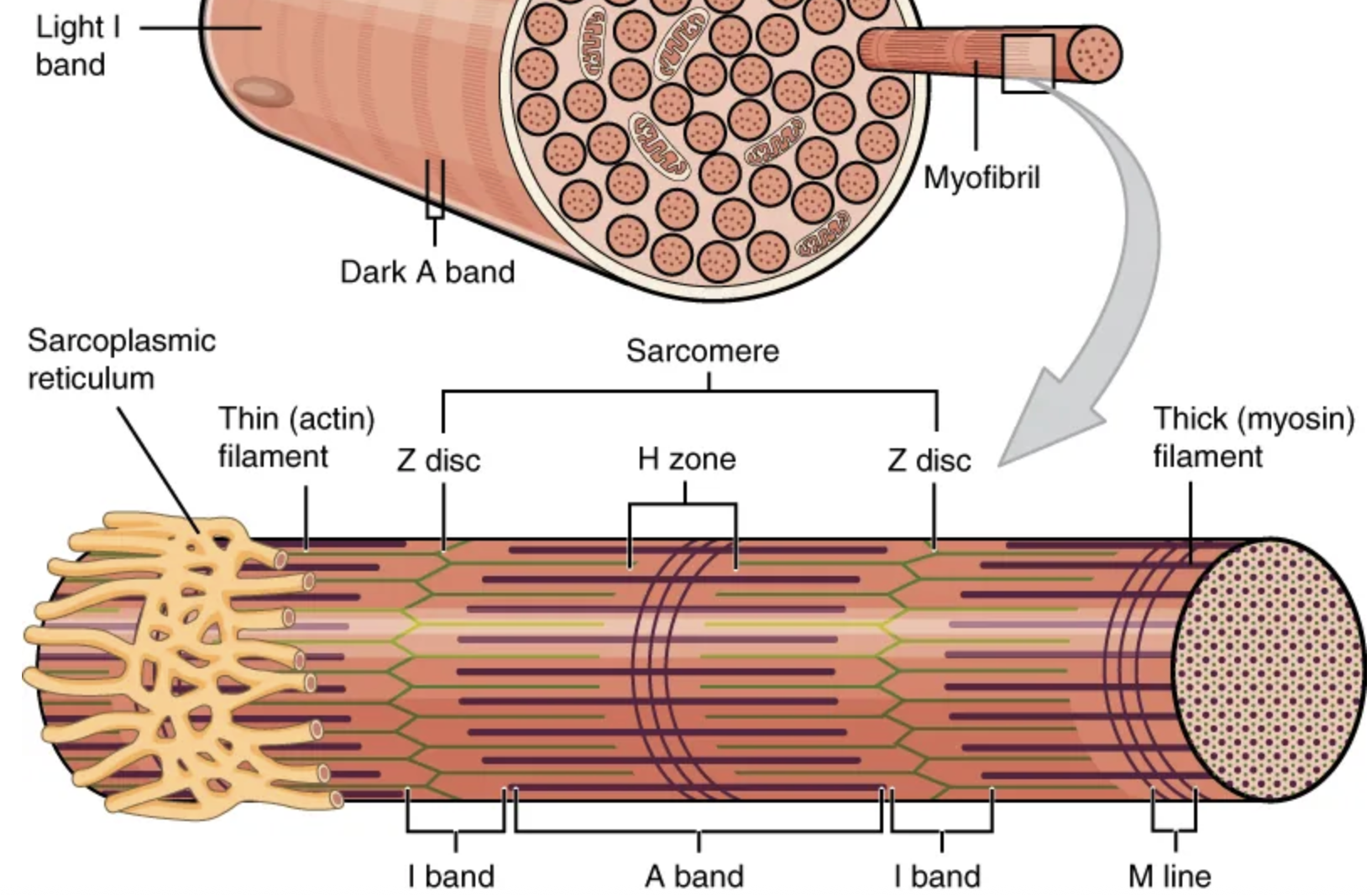
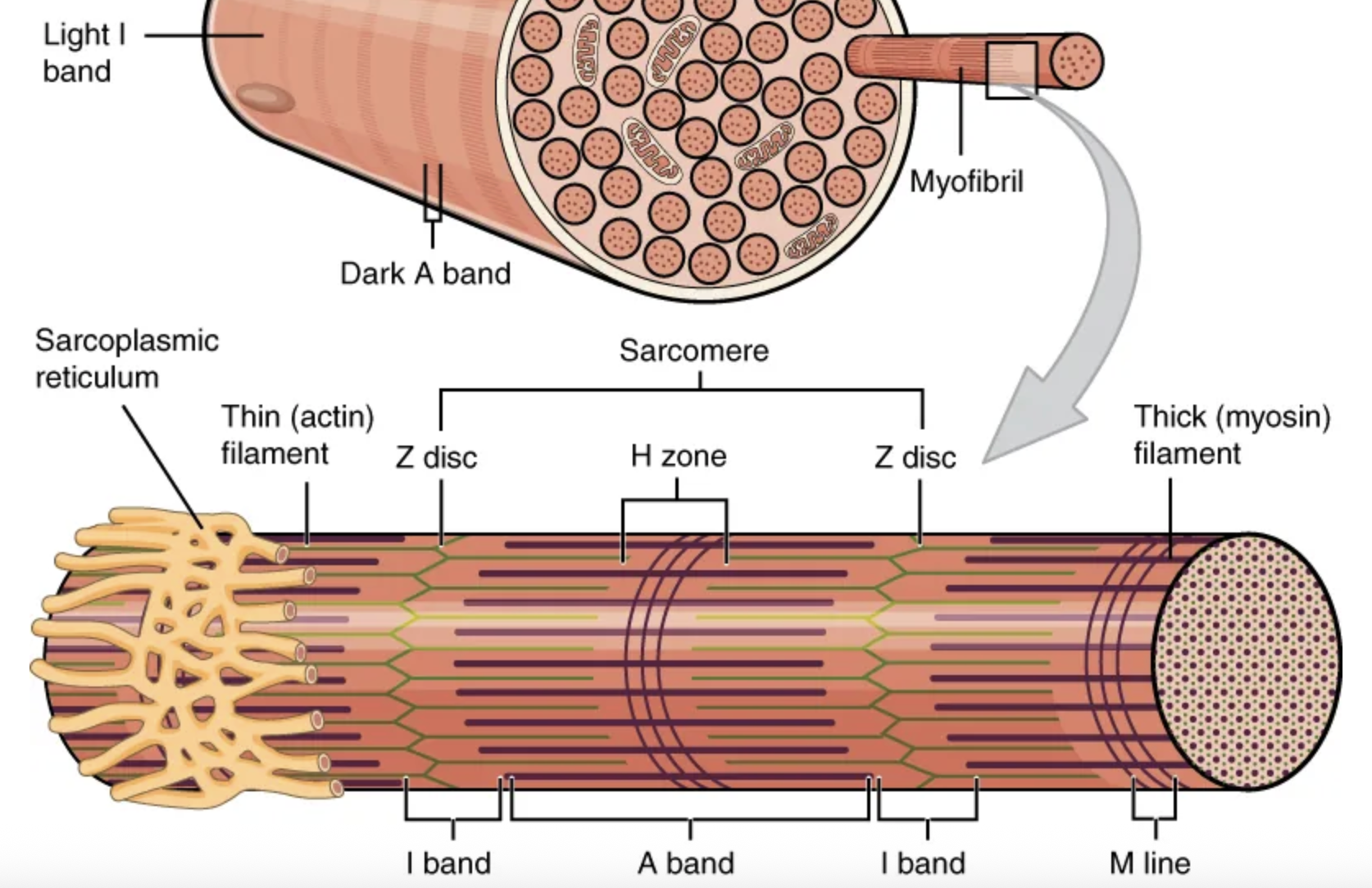
The functional unit of a skeletal muscle fiber is the […], a highly organized arrangement of the contractile myofilaments […] (thin filament) and […] (thick filament), along with other support proteins.
sarcomere; actin; myosin
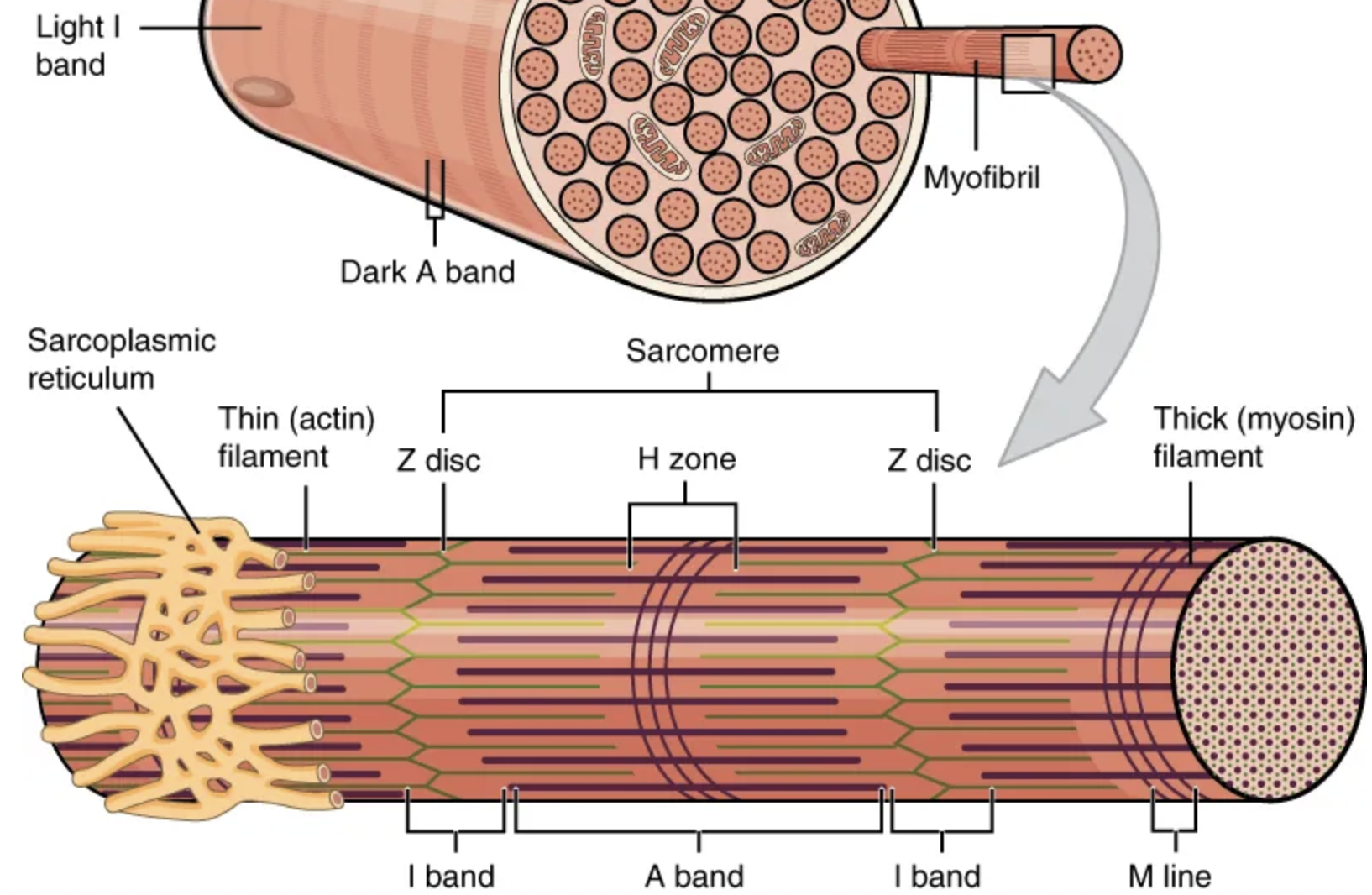
The sarcomere itself is bundled within the […] that runs the entire length of the muscle fiber and attaches to the sarcolemma at its end.
myofibril
As myofibrils contract, the entire muscle contracts.
Hundreds to thousands (each with thousands of sarcomeres) can be found inside one muscle fiber.
The regulatory proteins of a sarcomere are …
troponin and tropomyosin
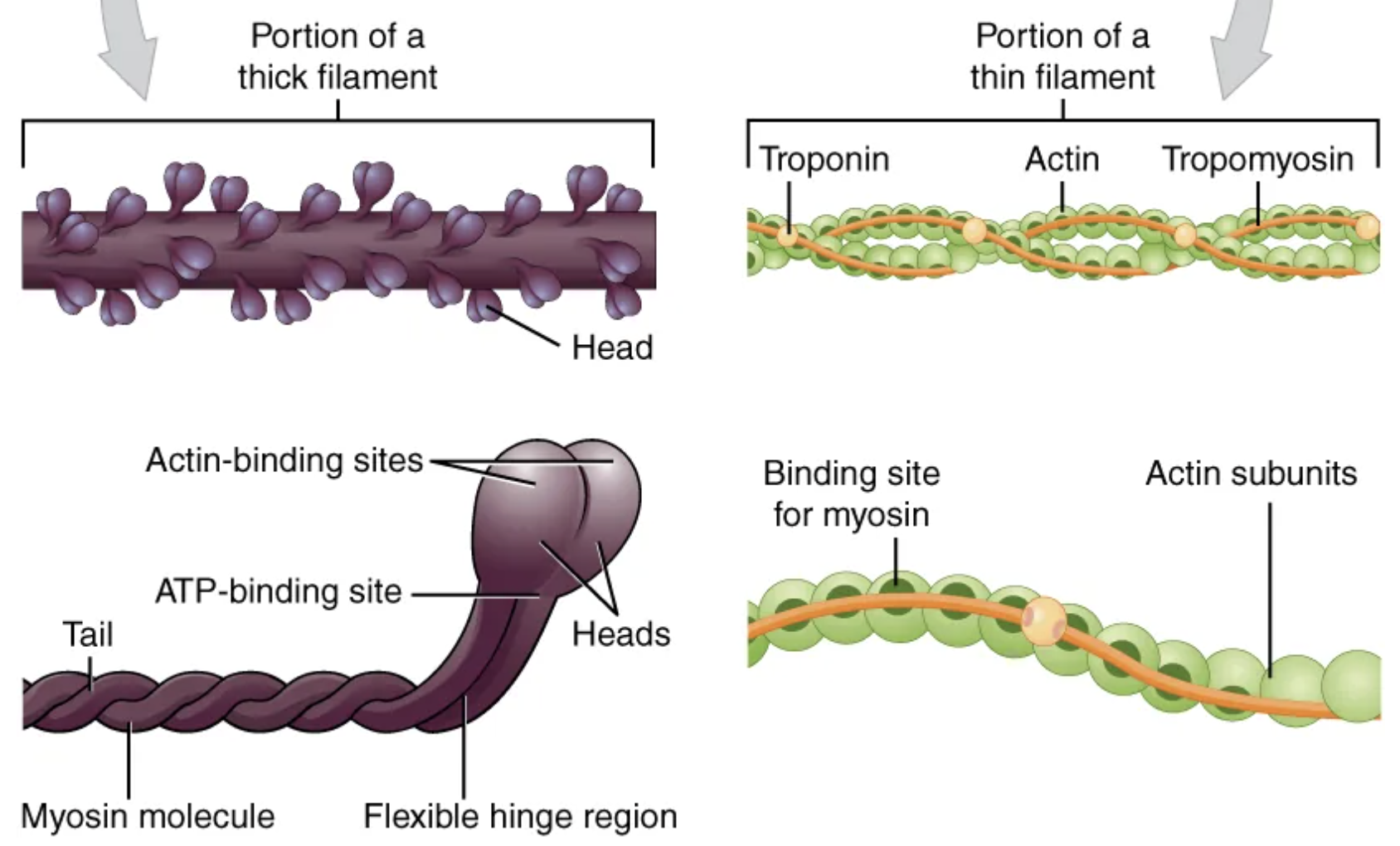
Each sarcomere is approximately 2 μm in length with a three-dimensional cylinder-like arrangement and is bordered by structures called […] (also called […], because pictures are two-dimensional), to which the actin myofilaments are anchored.
Z-discs; Z-lines
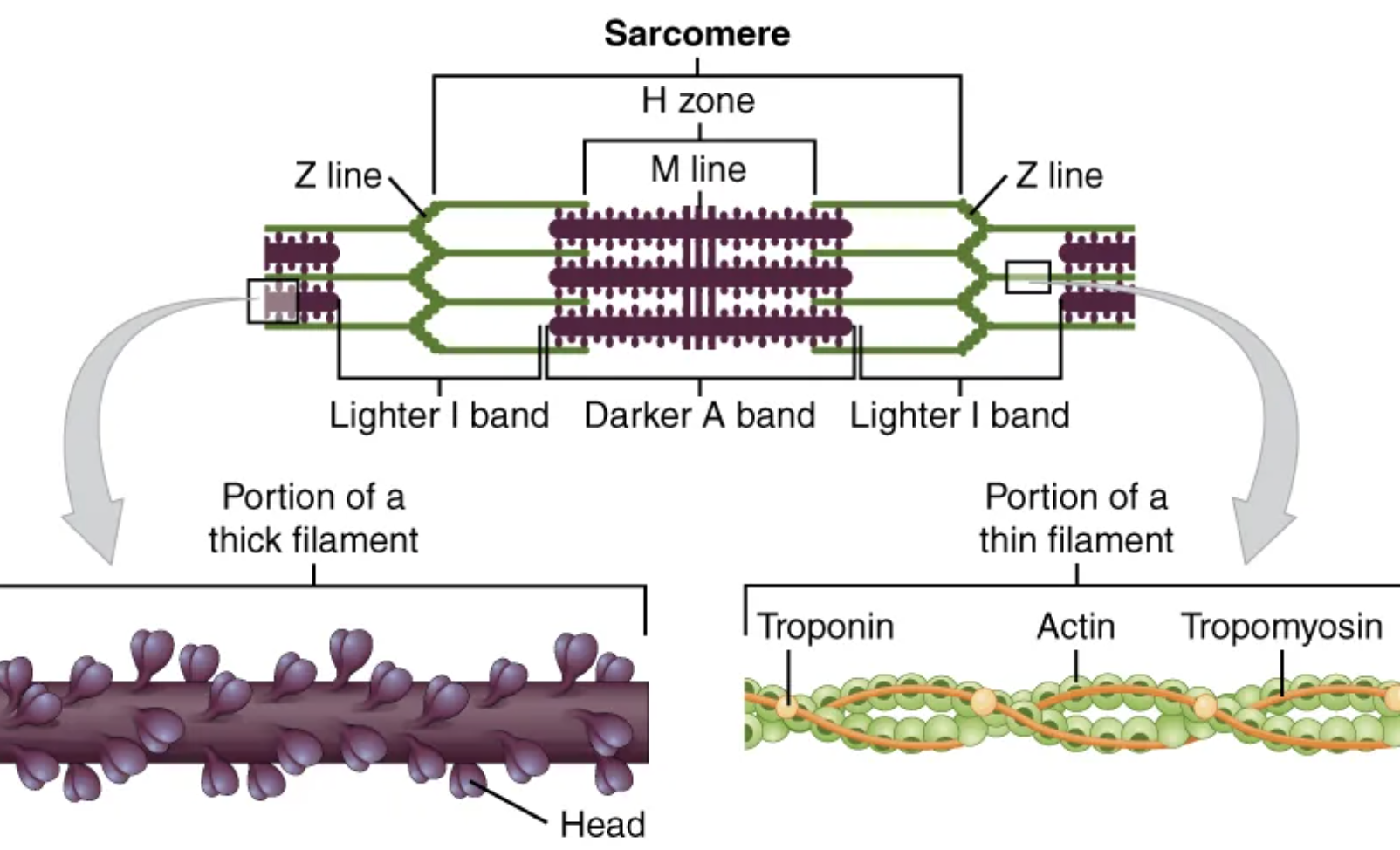
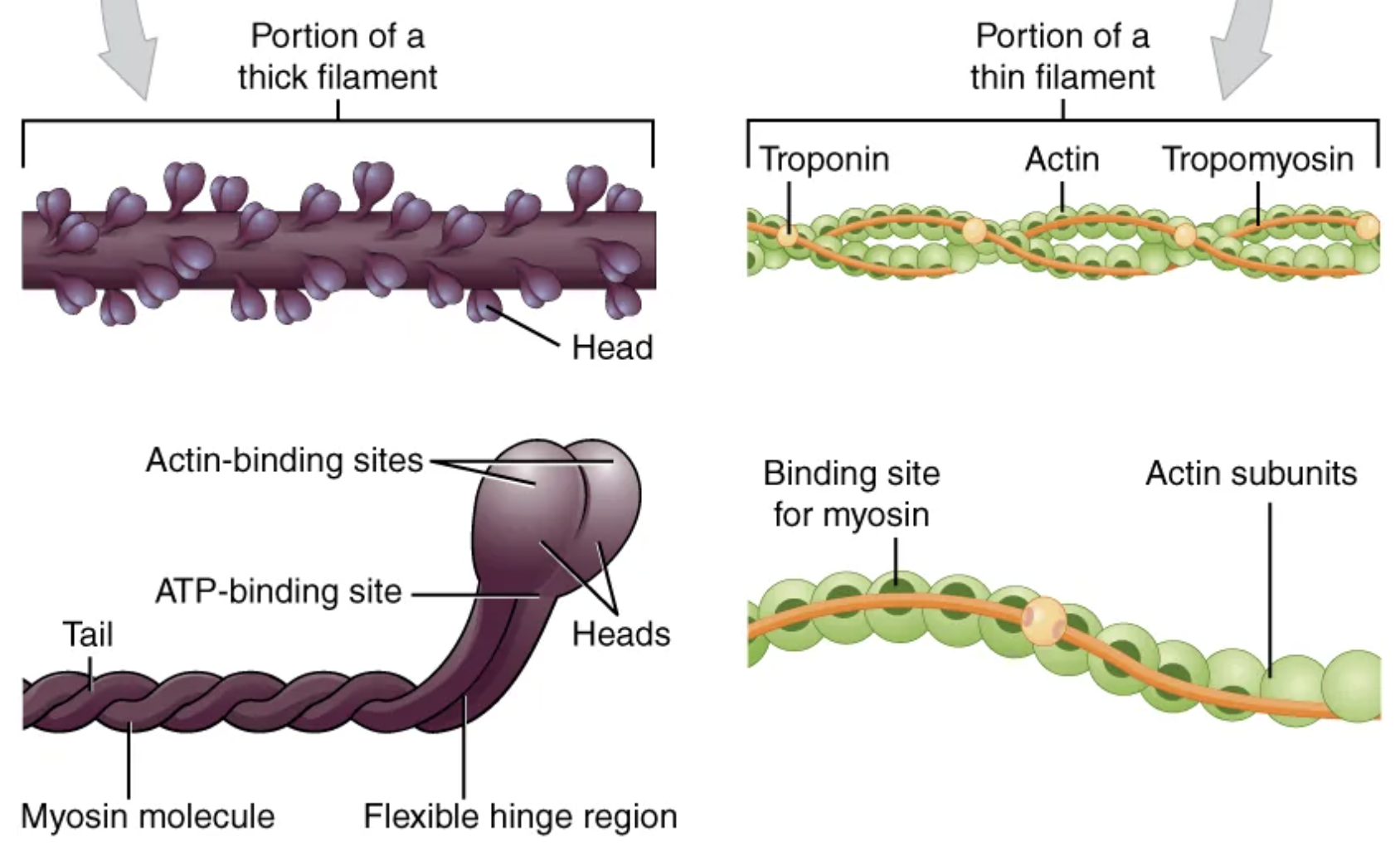
Because the actin and its troponin-tropomyosin complex (projecting from the Z-discs toward the center of the sarcomere) form strands that are thinner than the myosin, it is called the […] of the sarcomere.
thin filament
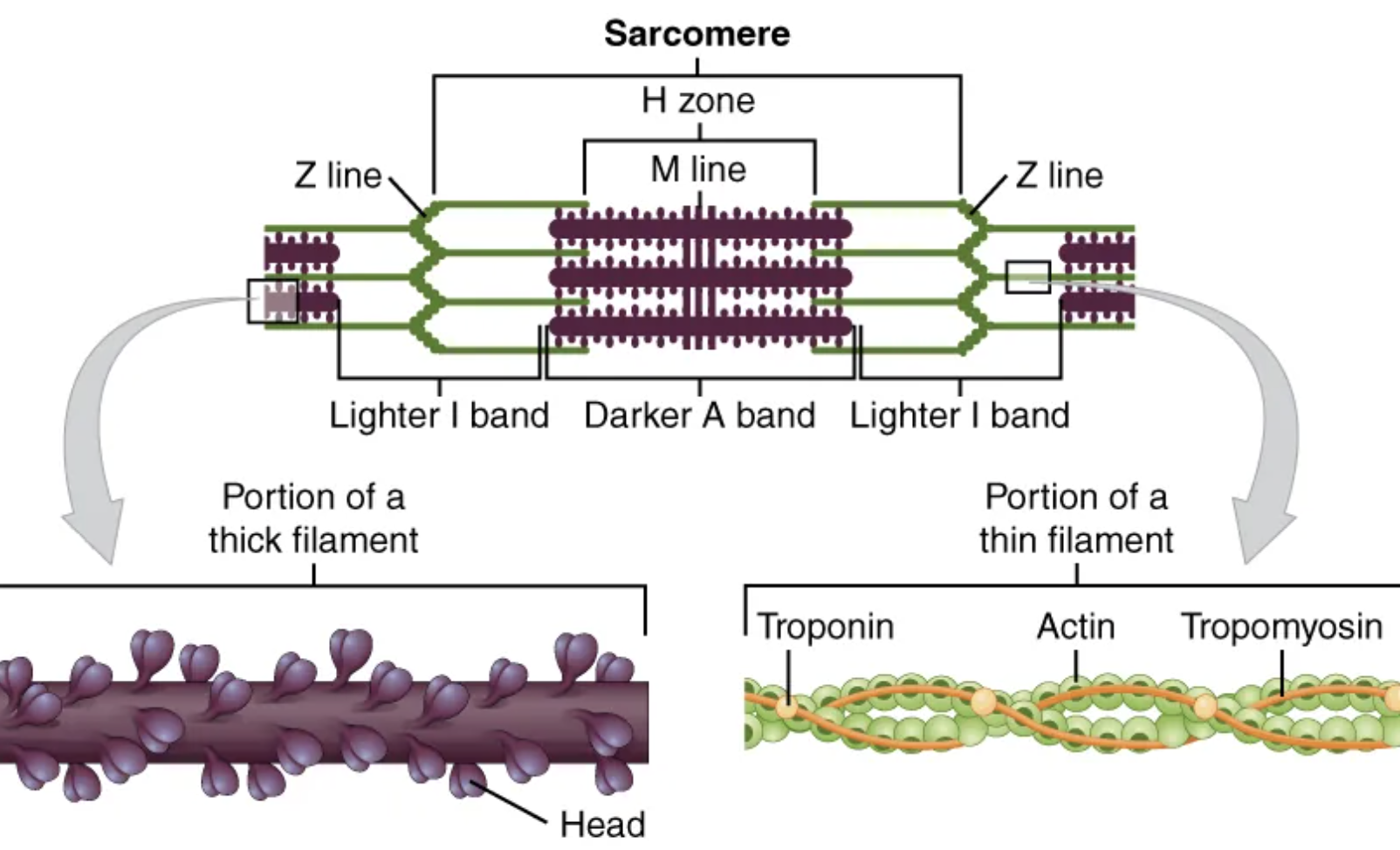
Myosin strands and their multiple heads (projecting from the center of the sarcomere, toward but not all to way to, the Z-discs) have more mass and are […] than the actin and troponin-tropomyosin complex, they are called the […] of the sarcomere.
thicker; thick filament
Another specialization of the skeletal muscle is the site where a motor neuron’s terminal meets the muscle fiber—called the […]. This is where the muscle fiber first responds to signaling by the motor neuron.
neuromuscular junction (NMJ)
Excitation-contraction coupling involves the coupling of an […] with the release of […] from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR).
action potential; Ca2+
When an action potential reaches the neuromuscular junction (NMJ), the axon terminal releases the neurotransmitter […].
acetylcholine (ACh)
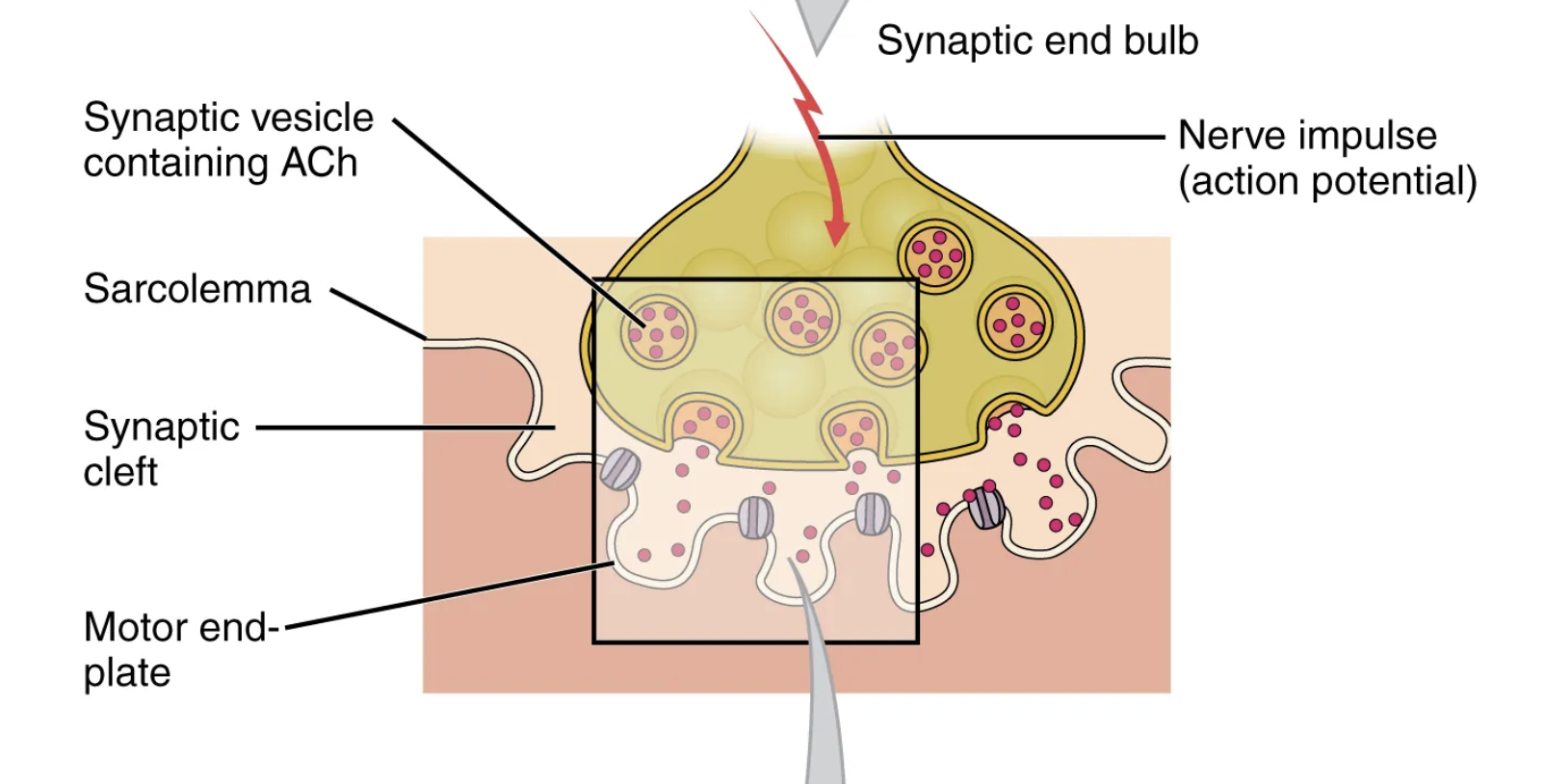
The acetylcholine (ACh) molecules diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to ACh receptors located within the […] of the sarcolemma.
motor-end plate
The postsynaptic portion of the NMJ
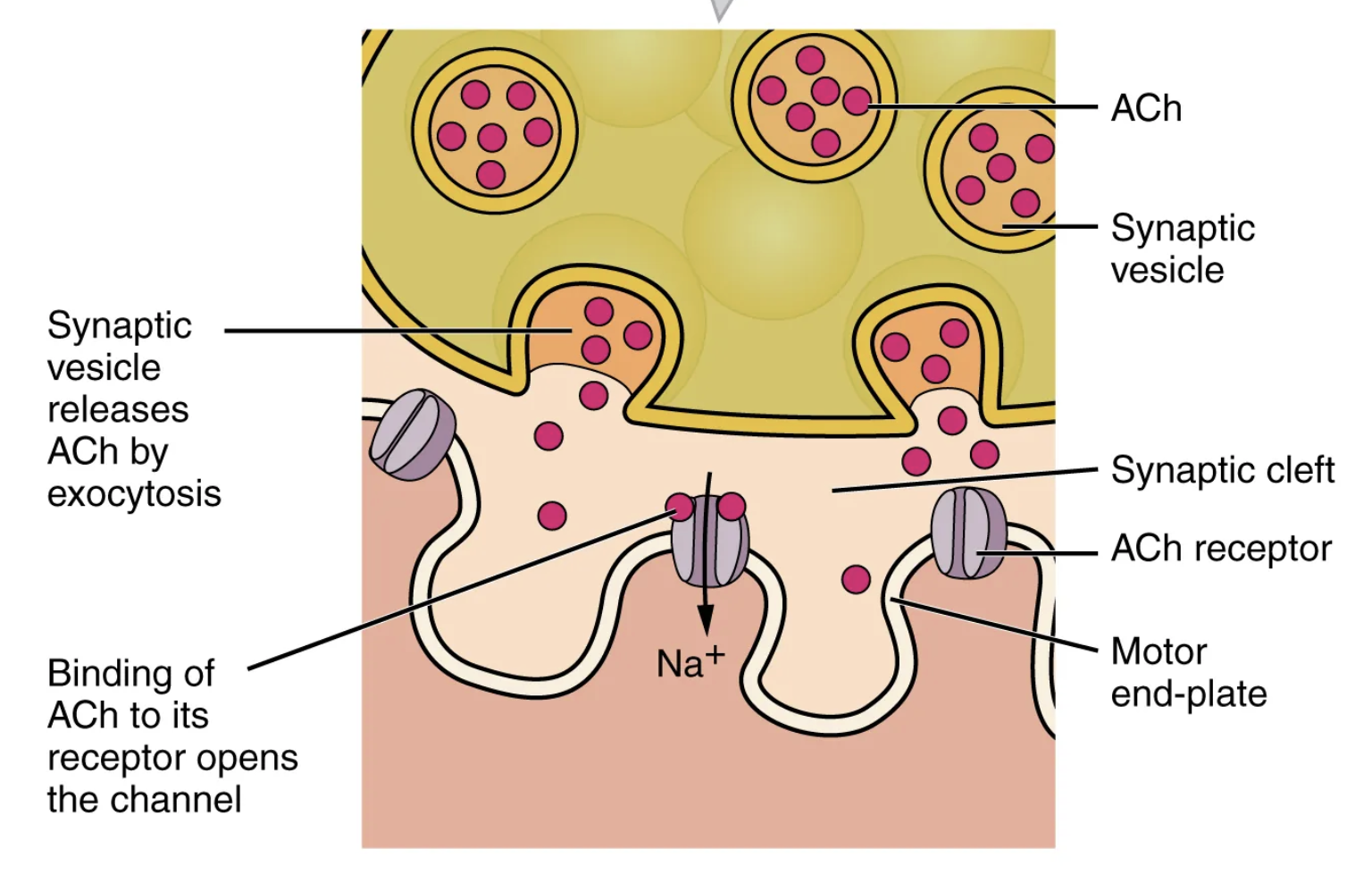
Once ACh binds, a channel in the ACh receptor opens and positively charged ions can pass through into the muscle fiber, causing it to […], meaning that the membrane potential of the muscle fiber becomes […].
depolarize; less negative
As the membrane depolarizes, another set of ion channels called […] are triggered to open.
voltage-gated sodium channels
Sodium ions enter the muscle fiber, and an action potential rapidly spreads (or “fires”) along the entire membrane to initiate the excitation portion of excitation-contraction coupling.
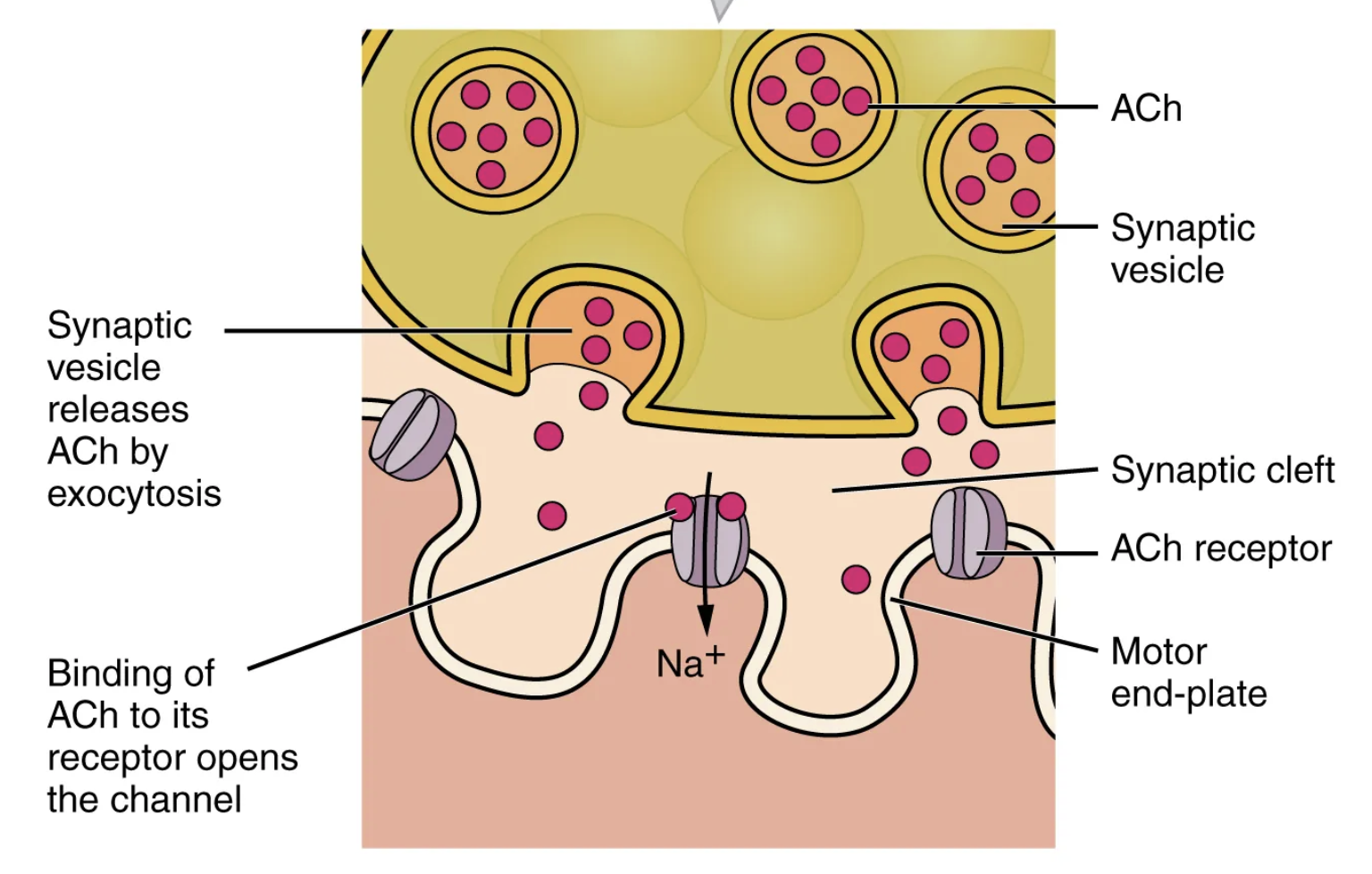
For the action potential to reach the membrane of the SR, there are periodic invaginations in the sarcolemma, called […].
T-tubules
“T” for “transverse”
The diameter of a muscle fiber can be up to 100 μm, so these T-tubules ensure that the membrane can get close to the SR in the sarcoplasm.
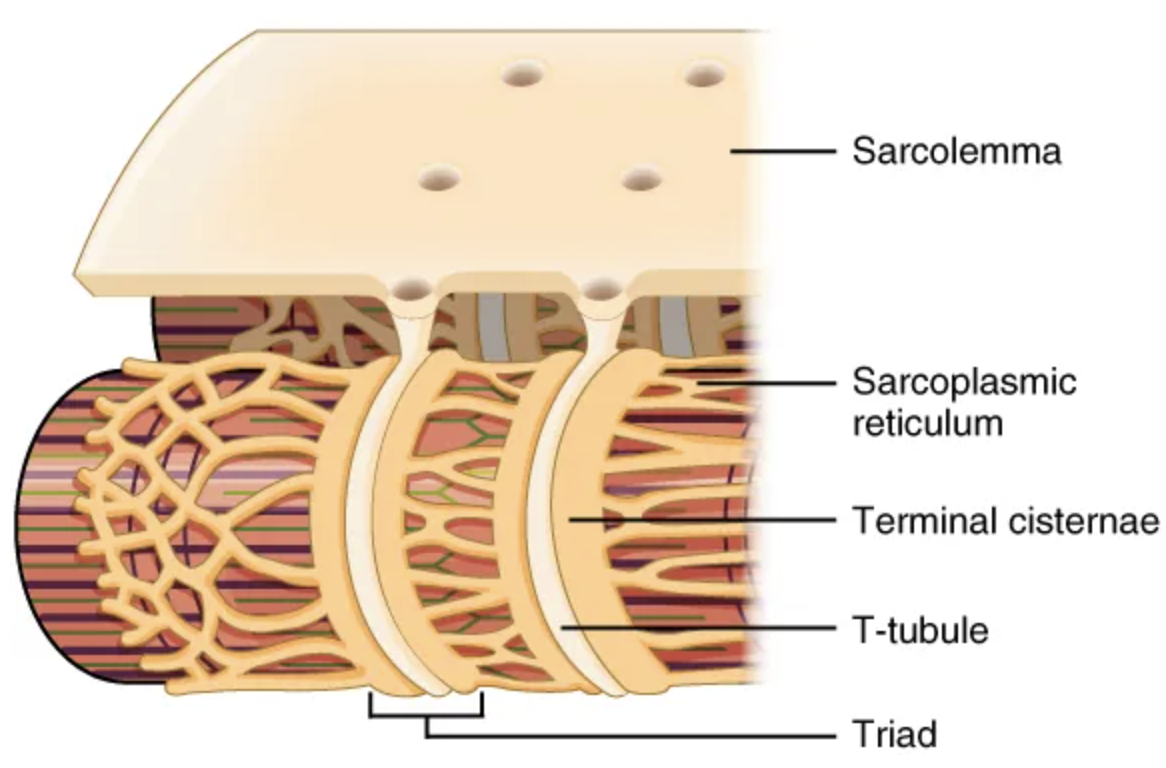
The T-tubules carry the action potential into the interior of the cell, which triggers the opening of […] in the membrane of the adjacent […]
calcium channels; sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
This causes Ca2+ to diffuse out of the SR and into the sarcoplasm.
The arrival of […] in the sarcoplasm initiates the […] of the muscle fiber by its sarcomeres.
Ca2+; contraction
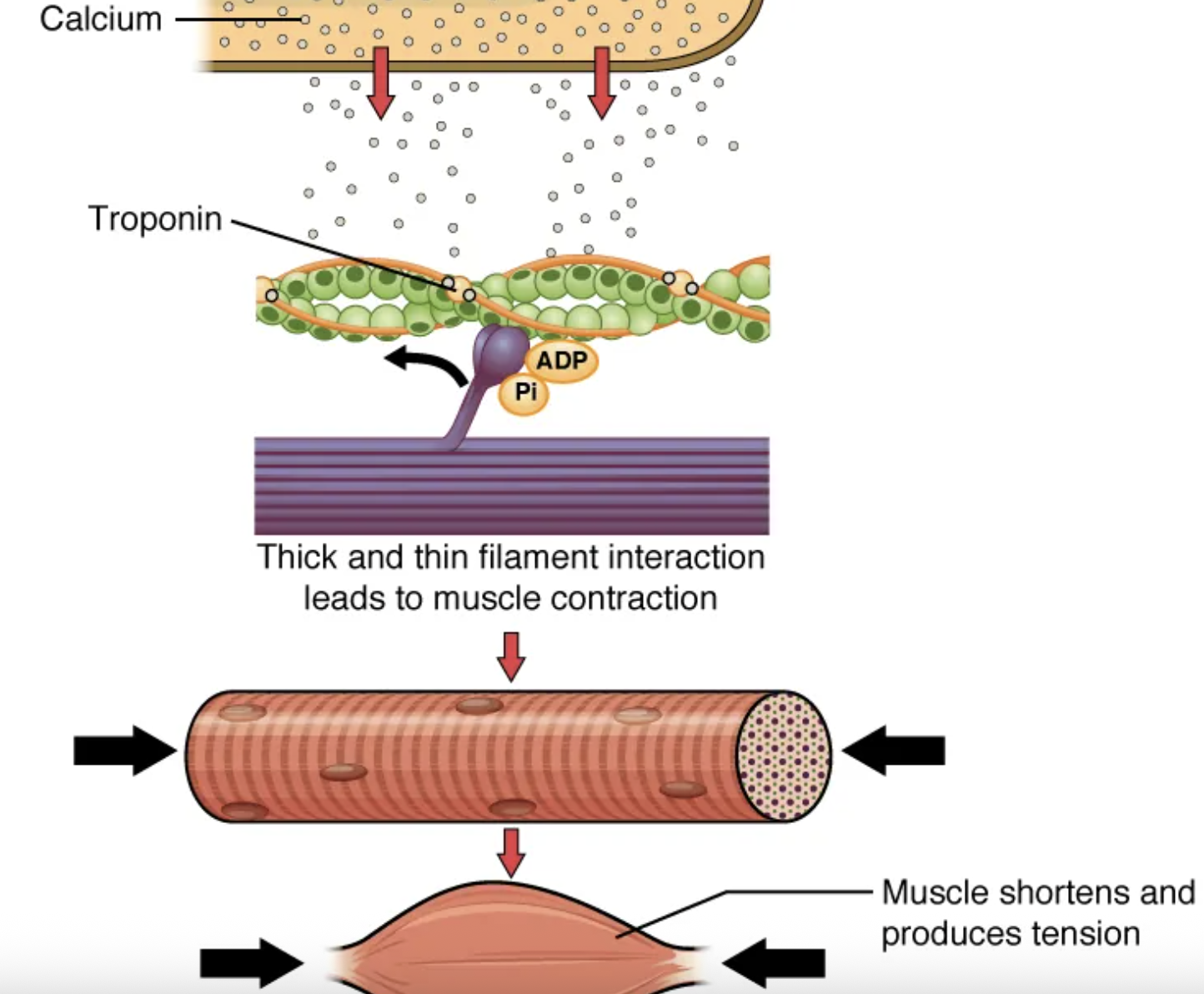
The molecular events of muscle fiber shortening occur within the fiber’s sarcomeres. The contraction of a striated muscle fiber occurs when the […] shorten as […] heads pull on the […] filaments.
sarcomeres; myosin; actin
Thick filaments, located at the central region of the sarcomere, are anchored at their bases at a spot called the […].
M-line
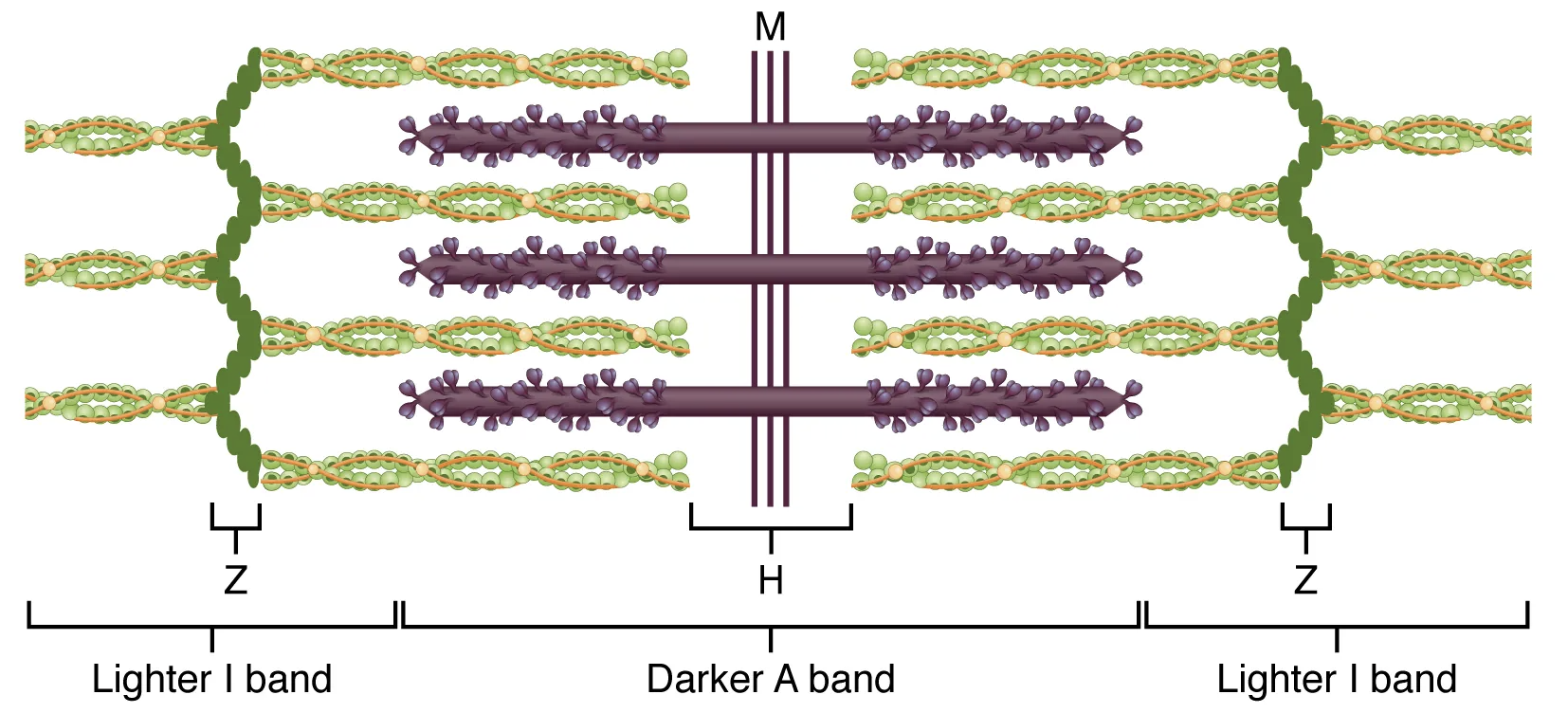
When a sarcomere contracts, the […] move closer together, and the […] becomes smaller. The […] stays the same width.
Z lines; I band; A band
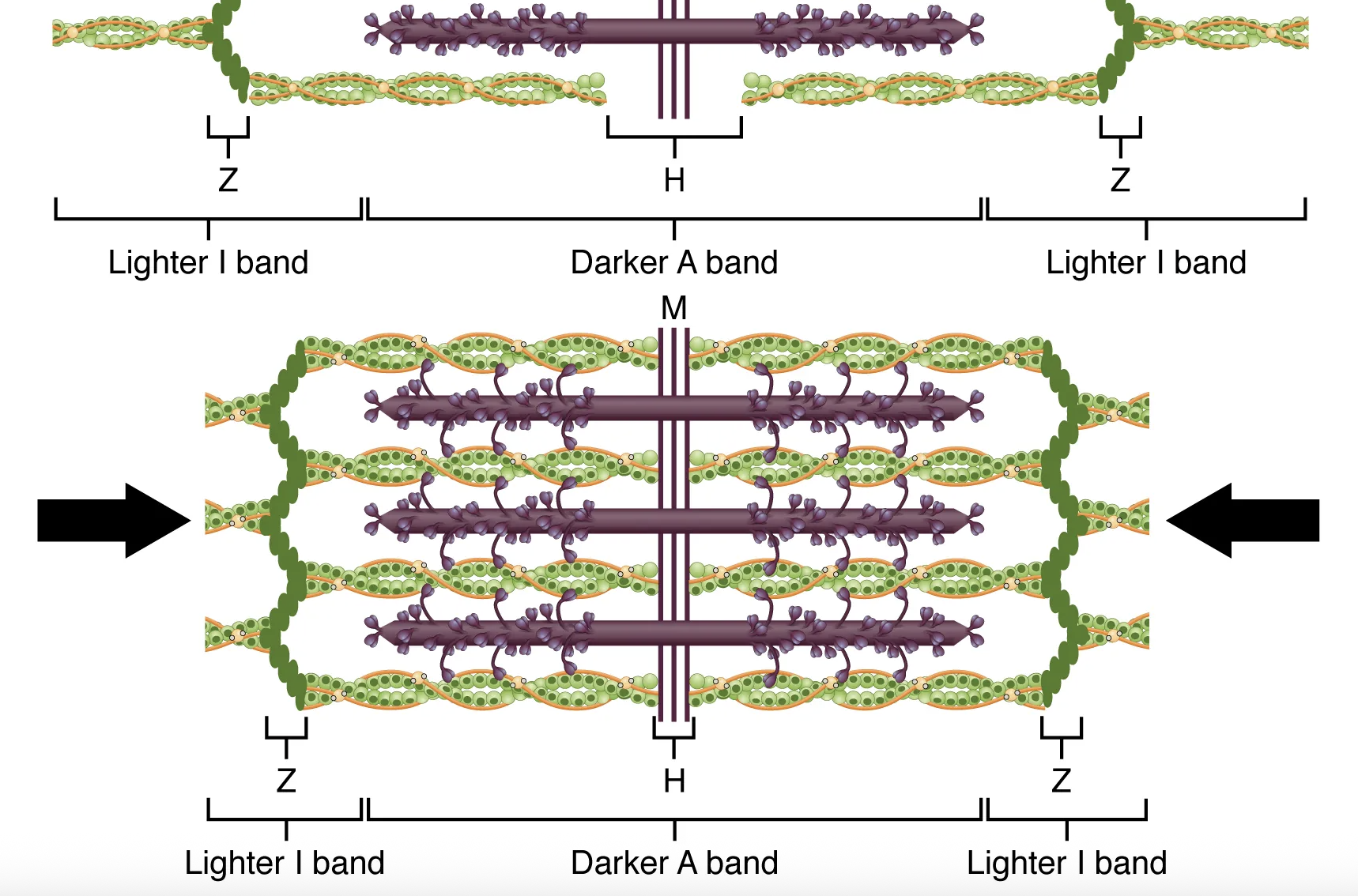
When signaled by a motor neuron, a skeletal muscle fiber contracts as the thin filaments are pulled and then slide past the thick filaments within the fiber’s sarcomeres. This process is known as the […] of muscle contraction.
sliding filament model
The sliding can only occur when myosin-binding sites on the actin filaments are exposed by a series of steps that begins with Ca2+ entry into the sarcoplasm.
[…] winds around the chains of the actin filament and covers the myosin-binding sites to prevent actin from binding to myosin. It also has a binding site for Ca2+ ions.
Tropomyosin
The troponin-tropomyosin complex prevents the myosin “heads” from binding to the active sites on the actin microfilaments.
To initiate muscle contraction, tropomyosin has to expose the myosin-binding site on an actin filament to allow […] formation between the actin and myosin microfilaments.
cross-bridge
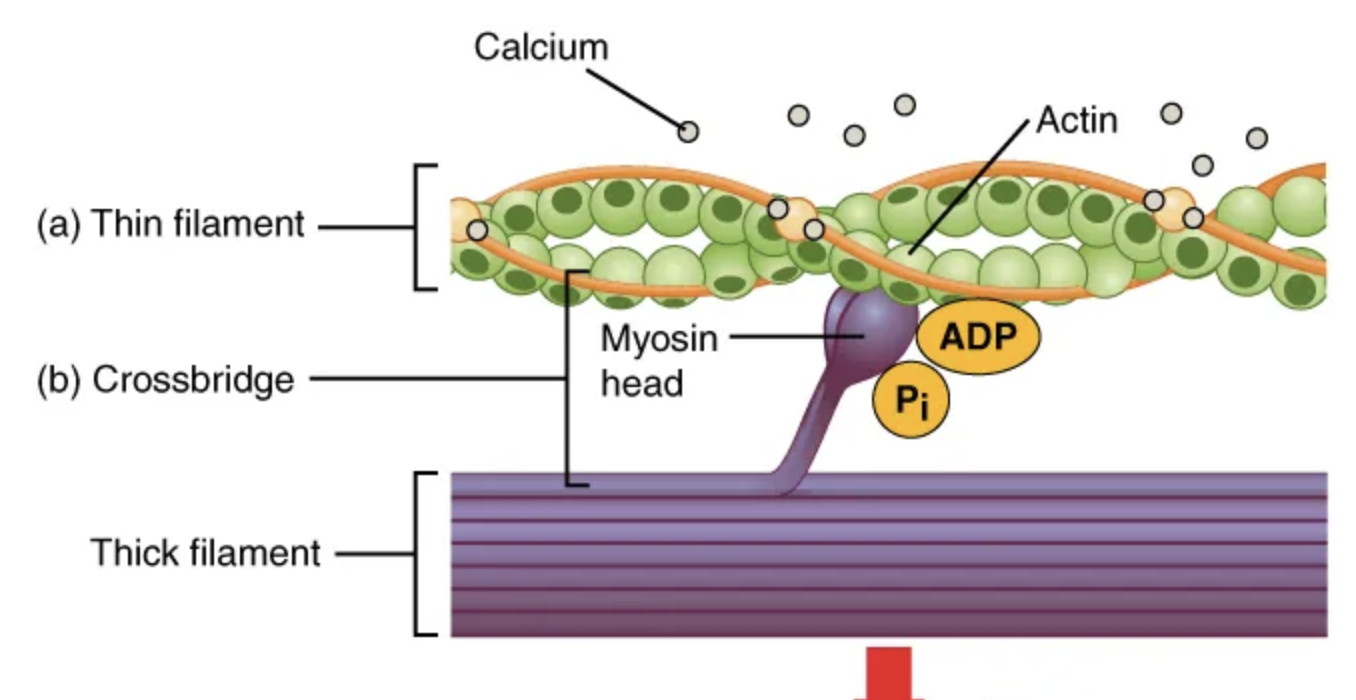
Once myosin binds to the exposed actin, the thin filaments are then […] by the myosin heads to […] past the thick filaments toward the center of the sarcomere.
pulled; slide
![<p><span><span>For thin filaments to continue to slide past thick filaments during muscle contraction, myosin heads must pull the actin at the binding sites, then […] to more binding sites.</span></span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/561bf8b0-44ca-485b-9384-1652e36ebc55.png)
For thin filaments to continue to slide past thick filaments during muscle contraction, myosin heads must pull the actin at the binding sites, then […] to more binding sites.
detach, re-cock, and attach
Repetition of this movement is known as the cross-bridge cycle.
Each cycle requires energy.
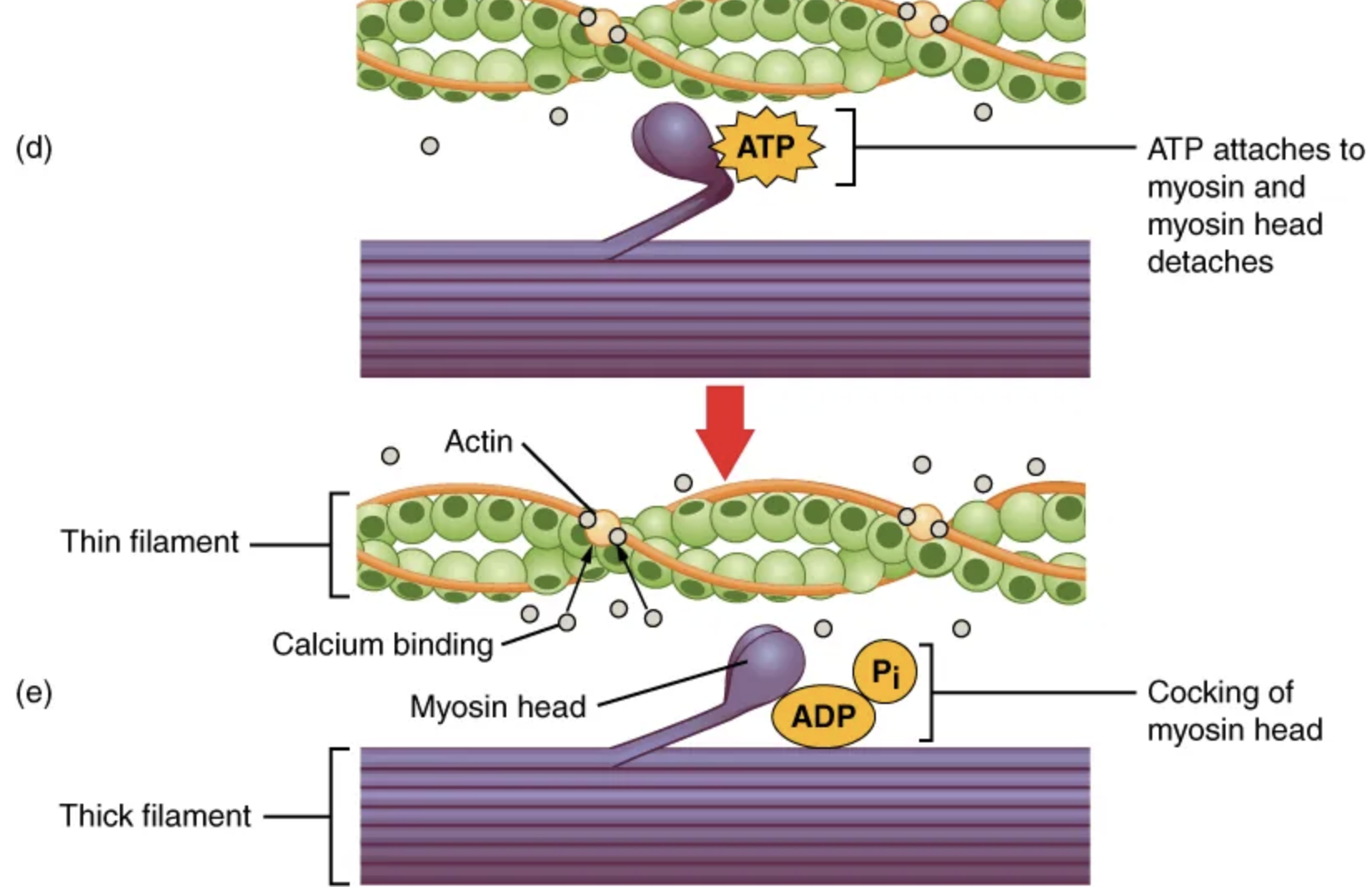
[…] formation occurs when the myosin head attaches to the actin while adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi) are still bound to myosin.
Cross-bridge