clinical 1/2- hypothalamus + pituitary
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Hypopituitarism
diminished or absent secretion of one or more pituitary hormones
hypopituitarism results from
pituitary, hypothalamic, or parasellar diseases
acquired loss in hypopituitarism follows what pattern
1. GH
2. LH/FSH
3. TSH
4. ACTH
5. PRL
9 I's of hypopituitarism
invasive, infarction, infiltrative, injury, immunologic, iatrogenic, infectious, idiopathic, isolated
invasive causes of hypopituitarism
adenoma
craniopharyngioma
CNS tumors
metastatic lesions
causes of infarction leading to hypopituitarism
Sheehan's syndrome
pituitary apoplexy
Sheehan syndrome
ischemic infarct pituitary follow post partum hemorrhage
Sheehan syndrome presents with
failure to lactate
amenorrhea
cold intolerance
Pituitary apoplexy
sudden hemorrhage of pituitary gland
often in presence of existing pituitary adenoma
s/s of pituitary apoplexy
sudden onset severe headache
visual impairment
features of hypopituitarism
infiltrative causes of hypopituitarism
sarcoidosis
hemochromatosis
langerhan's histiocytosis
immunologic causes of hypopituitarism
lymphocytic hypophysitis
iatrogenic causes of hypopituitarism
surgery and radiation
infectious causes of hypopituitarism
TB
syphilis
mycotic infections
effect of opiates on pituitary function
suppress GnRH
can cause ACTH deficiency
inc prolactin
checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy can lead to
hypophysitis
Empty sella syndrome
subarachnoid space extends into the sella turcica
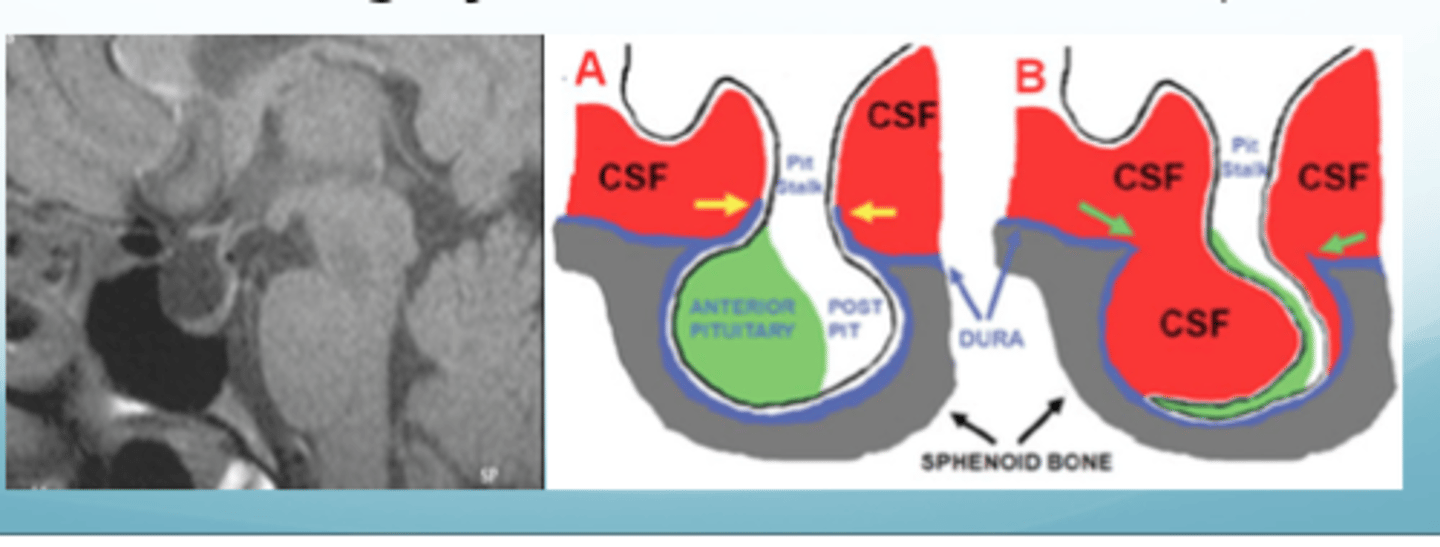
empty sella syndrome is associated with
benign intracranial HTN
what percent of the pituitary tissue has to be compressed/atrophied in empty sella syndrome for pituitary failure
> 90%
pts with sellar mass may also have what s/s
headache
visual loss
diplopia
due to mass effect
Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
low FSH/LH
ovarian hypofunction is dec
estradiol
s/s of ovarian hypo function in premenopausal women
amenorrhea/irregular menses
infertility
vaginal atrophy
hot flashes
late manifestations of ovarian hypofunction
dec breast tissue
dec bone mineral density
s/s of testicular hypofunction
infertility
dec libido
erectile dysfunction
hot flashes
late manifestations of testicular hypofunction
dec muscle mass
dec bone density
prolactin def s/s
failure of postpartum lactation
TSH def s/s
hypothyroidism- cold intolerance, dry skin
ACTH def (secondary adrenal insufficiency) s/s
weakness
N/V
anorexia
fever
weight loss
hypotension
RAAs intact
how is primary adrenal insufficiency different from secondary
salt wasting
volume contraction
hyperkalemia
skin hyperpigmentation (inc ACTH)
dec aldosterone
treatment of hypopituitarism
hormone replacement therapy
medical alert bracelets
causes of sellar masses
pituitary adenomas
pituitary hyperplasia
craniopharyngioma
meningiomas
pituicytomas
malignant tumors
most common cause of sellar masses
pituitary adenoma
vision changes from pituitary tumors
compress optic chiasm --> bitemporal hemianopsia
if the pituitary adenoma extends laterally what CN can be affected
CN III, IV, VI
Microadenoma
< 1cm
Macroadenoma
> 1cm
top 3 MCC of secreting pituitary adenomas
1. prolactinoma
2. GH secreting
3. ACTH secreting
imaging of choice for pituitary
MRI w/ contrast
pituitary incidentaloma
unsuspected pituitary lesion discovered in imaging
when should a pt with a pituitary adenoma be referred for formal visual field testing
if > 1cm
do we expect FSH to be high or low in postmenopausal women
high
physiological factors that cause inc prolactin
pregnancy
nursing
nipple stimulation
pharmacological factors that cause inc prolactin
TRH
estrogen
VIP
opioids
prolactin levels for prolactinoma
> 200-300
most common pituitary adenoma
Prolactinoma
s/s of prolactinoma in women
amenorrhea
galactorrhea
s/s of prolactinoma in men
dec libido
erectile dysfunction
in what pts should you order a prolactin level
galactorrhea
enlarged tella turcica
hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
treatment for prolactinoma
meds FIRST
surgery 2nd option
radiotherapy 3rd option
meds for prolactinoma
cabergoline (preferred)
bromocriptine
(dopamine agonists)
first thing done if a pt presents with amenorrhea
pregnancy test
second most common pituitary tumor
GH secreting pituitary tumor
GH secreting pituitary tumor causes clinical syndromes of
acromegaly
gigantism
GH secreting pituitary tumor is associated with increased
mortality rate
best test to screen/diagnose acromegaly
IGF-1 level (elevated)
confirmatory testing for acromegaly
oral glucose tolerance test
oral glucose tolerance test for acromegaly
no suppression of GH w/ glucose admin
what is seen in skull radiograph for acromegaly
thickening of calvarium
what is seen in plain hand films for acromegaly
distal phalangeal hypertrophied with spade appearance
what is seen in foot plain films for acromegaly
inc heel pad thickness
treatment for acromegaly
1. transsphenoidal surgical resection (treatment of choice)
2. meds
3. radiation
medical therapy for acromegaly if the pt cant have surgery
octreotide
cabergoline
pegvisomant
what should also be screened for in pts diagnosed with acromegaly
colonoscopy (associated with colon polyps)
causes of Cushing syndrome
glucocorticoid use
ACTH secreting pituitary adenoma (Cushing disease)
MCC of Cushing syndrome
exogenous steroids
Pituitary Cushing's
ACTH secreting pituitary tumor
cushing syndrome
too much glucocorticoids
Cushing disease
ACTH-secreting pituitary adenoma
classification fo Cushing syndrome
ACTH dependent
ACTH independent
causes of ACTH dependent Cushing's syndrome
pituitary adenoma (Cushing disease)
non pituitary neoplasm (ectopic ACTH production)
causes of ACTH independent Cushing's syndrome
iatrogenic (exogenous steroids)
adrenal tumor
nodular adrenal hyperplasia
s/s of cushing syndrome
central obesity w/ thin extremities
buffalo hump, moon facies
purple abdominal striae
3 steps to diagnosing cushing syndrome
first must exclude exogenous glucocorticoids
demonstrate inappropriate cortisol secretion
localize cause
what tests can we use to establish endogenous increased production of cortisol
24 hour free cortisol
1 mg dexamethasone suppression test
midnight salivary cortisol test
most widely used screening test for cushings
24 hour urinary free cortisol
what is diagnostic for cushings from the 24 hour urinary free cortisol
3-4x above upper limit of normal
what physiological test would cause the 24 hour urinary cortisol test to be abnormal
1mg dexamethasone suppression test
1mg dexamethasone by mouth at 11pm
measure cortisol at 8am the following morning
what is normal for the 1mg dexamethasone suppression test
cortisol < 1.8 ug/dL
considerations for late night salivary cortisol
must have normal sleeping pattern
once endogenous hypercortisolism is confirmed, what is done next
measure plasma ACTH determine if ACTH dependent or independent
ACTH suppressed --> ACTH independent
ACTH > 20 --> ACTH dependent
if the pt has a high cortisol and ACTH, how do we differentiate btw pituitary and ectopic causes
high dose dexamethasone suppression
will suppress pituitary cause
will not suppress ectopic causes
treatment for cushing disease
transphenoidal resection of pituitary adenoma
once a biochemical diagnosis of cushing disease is made, what is done next
MRI w/ contrast (attention to pituitary)