Science 1.4-7
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

28 Terms
How do Invasive Species succeed in a new environment
-Nothing controlling it
highly competitive
Unchecked population
Niche fits ecosystem
How do you control an invasive specie
Chemicals (pesticides)
Mechanical (physical borders)
Biological (release insects to prey on them)
Problems caused by invasive species
alters energy flow cycles
Effects beauty of ecosystem
Damaging agriculture
Spreads diseases
Invasive species compared to non native
Invasive species impact the environment negatively
Non native species don’t naturally occur in an environment
Difference between bioaccumulation and biomagnification
bioaccumulation is the build up in a singular organism
Biomagnification is the increase in toxins progressing through the food chain
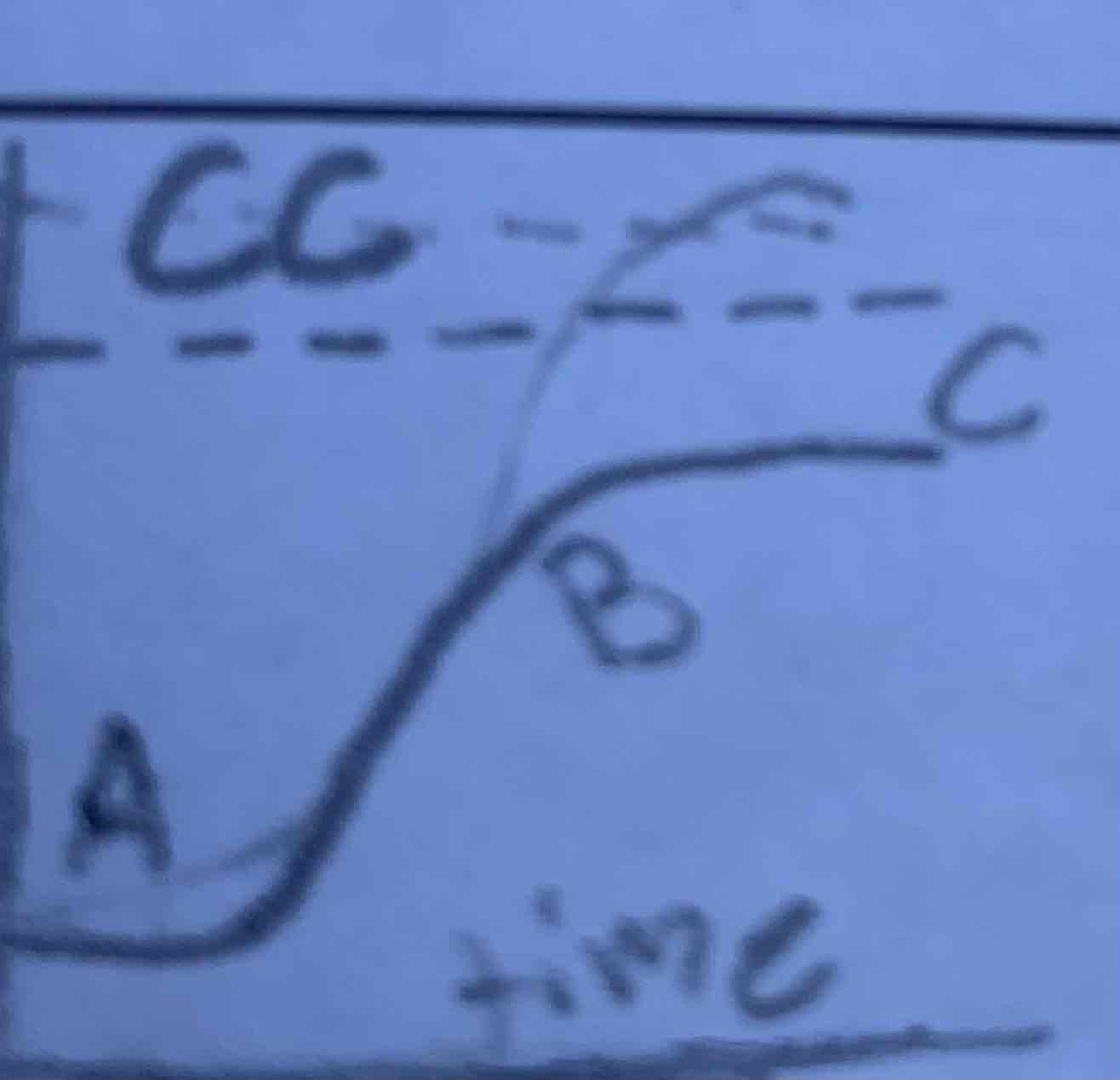
What is A,B, and C
A is the slow population growth
B is the rapid population growth
C is the steady population growth
Is the time the dependant variable or the independent
Time is the independent variable because no matter what happens, time keeps flowing
What is the carrying capacity
The limit of species in an ecosystem
How do we know we’ve reached the carrying capacity
Over competition
Over crowding
How can you alter the carrying capacity
Adding or removing resources
Adding or removing species
What is the difference between tolerance and optimal
Tolerance is how much a organism can handle
Optimal is the ideal environment to survive
What are some A-biotic factors
light
Water
Nutrients
Weather
Acidity
What are some biotic factors
Biotic interactions (predation, parasitism, competition, and mutualism)
What is a natural ecosystem
not man made
Forests ponds
Sustainable
Requires no maintenance
What is an artificial ecosystme
Man made
Not sustainable
Farms gardens
Requires maintenance and management
What can affect a plants health
Soil quality
Water quality
Access to nitrogen
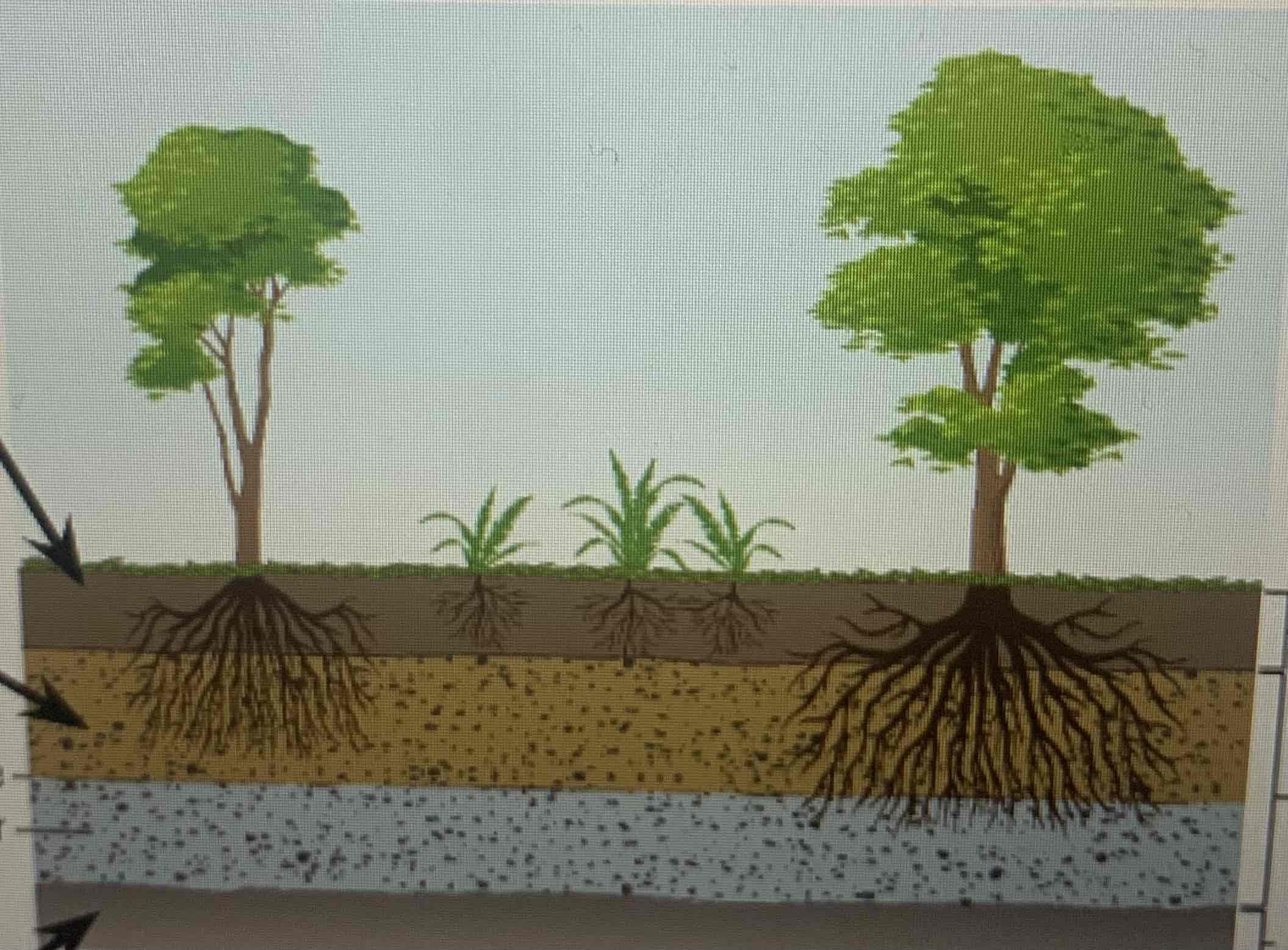
What are the three layers of soil
Top soil (rock particles and organisms
Sub soil (little organism matter)
Bedrock (water can’t pass, sits on top *water table)
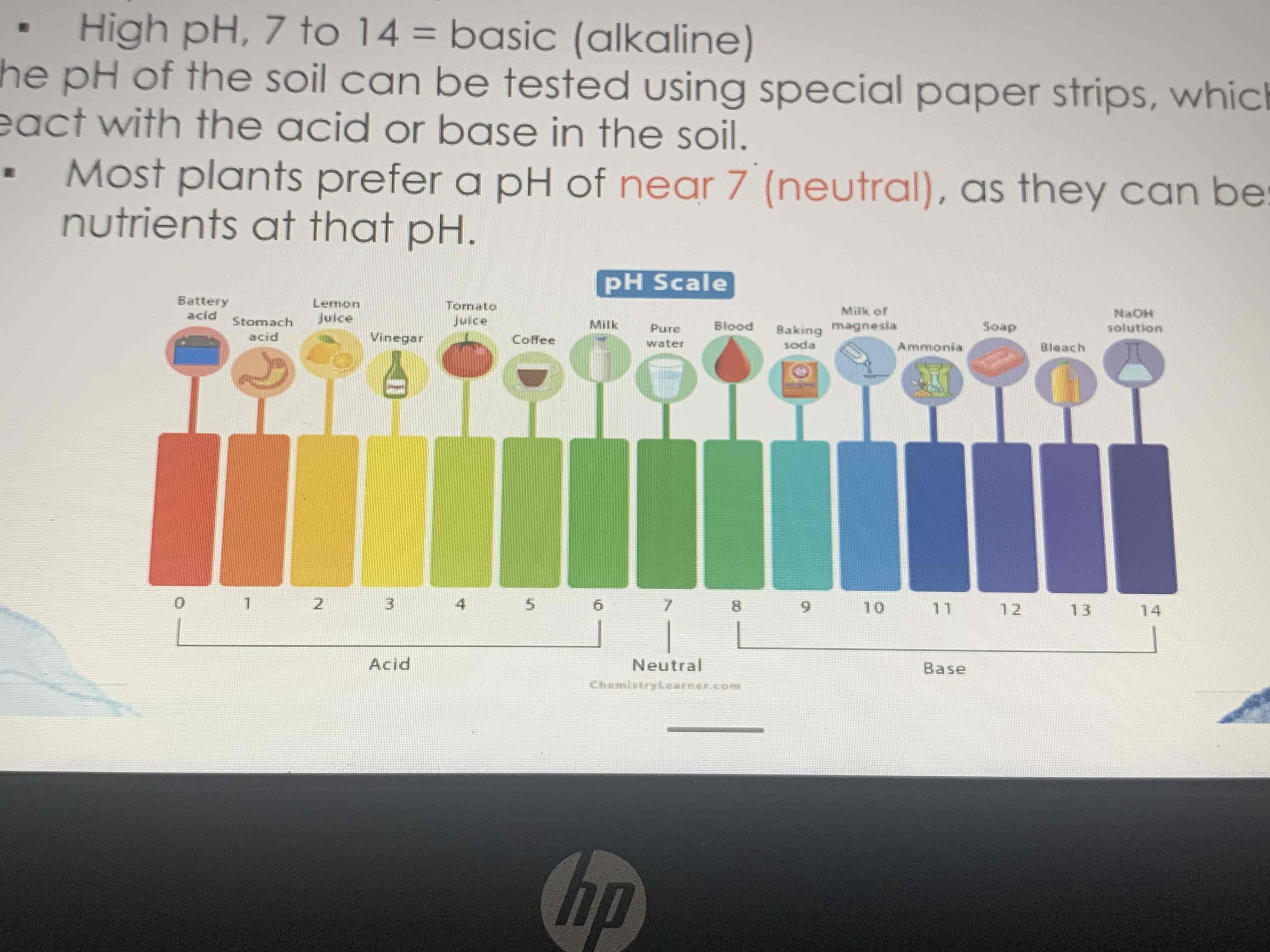
What is the PH Scale
7 is neutral
To the left of 7 is acid
To the right of 7 is base
The further away from 7, the more acidic or bad it is
Battery acid is 0, bleach is 13
What is overexplotiation
Overing using a resource
Ie. overfishing and fresh water
What is crop rotation
Planting certain crops based on the time
What are 3 ways urban forests are sustainable
Removes carbon
Provides shade consuming less energy
Maintains soil quality
What is sustainability
Being able to maintain ecological balance, ensuring enough resources for the future
What would happen if all producers were removed from the food chain
Producers use light energy from the sun to create chemical energy using the process of photosynthesis. Without chemical energy from the producers, primary consumers cannot survive, Without chemical energy from the producers, primary consumers cannot survive.
what is population growth curves
its how population organisms in an ecosystem change over time
meaning of biodiversity
a range of species that remain plentiful
acidity
any substance that is added to the environment that produces a condition that is harmful to organism
point source pollution
pollution that enter water sources at specific places
non-point source pollution
pollution that enters water sources indirectly