Biblical Theology of Worship Midterm
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
In the Old Testament, what worship practices were considered to be the most important?
No images were to be worshipped
The temple used in the old testament worship can be best described as
a central place of worship
Franklin Segler mentions about worship practices in the New Testament that are considered "merging" with the traditional Judaic worship. This includes
Temple Worship
What would be considered a distinction of the Early Church worship?
All of these.
A worship example of the new testament christian church included...
All of these.
Clement wrote a letter in 96 A.D which specified certain elements of worship that were important. This includes...
repentance
Who was the author of the first worship order in 140 A.D?
Justin Martyr
From the time of the 3rd and 4th centuries until Martin Luther's reformation, What did not change in worship?
the ritualism
What did the puritans hold with high regard in worship?
the sermon being the climax
the late 19th century church emphasized what type of worship service(s)
intellectualism
Franklin Segler, our author, describes worship as...
devoting our will
Worship, according to Ralph Martin, can best be described as...
our "Worth-ship"
Barry Leisch used which biblical model to describe liturgical services and the structure of these services?
the Isaiah 6 model
In understanding the psychology of worship, there is an effect of learning styles on worship. What preference example does Segler mention?
auditory
Ralph Martin created an agenda for reforming our worship today. The Greek action words he used were...
lateria
The test for finding good vs. bad hymn/choruses should be:
Is it singable?
the fundamental difference between a hymn and a chorus is:
their structure
Barry Liesch, in his book, "The New Worship", described worship songs as "stars", which are best described as:
a song that transcends time
Barry Leisch makes some contemporary comparisons for the Temple furniture and symbols of Hebrew worship. The basin or laver of the temple represents:
our cleansing
the table of shewbread is represented today as...
our salvation
Aaron's "budding rod" can represent to us today as
Christ's resurrection
Franklin Segler in his chapter on the Psychology of Worship states some basic needs that we have as Christians. This can include:
all of these- a sense of mystery, insecurity, finiteness, loneliness
When referring to a musical "firework", Leisch means:
A short lasting song
Looking at computer software and projection equipment, Liesch encourages ministers to choose a projector with appropriate brightness. It is important:
to make sure the lumens are bright enough that the lights do not need to be dimmed.
What can a pastor do to inspire people to participate in musical worship?
All of these- Communicate the purpose of the song, paraphrase the hymns and choruses, insist on variety of music materials, ensure that God is the primary object of worship
John Calvin was bolder than Martin Luther in the changing of the liturgy because:
of it's doctrinal beliefs
Who were the "radical reformers" of the Post-Reformation?
all of these-
what was one of the streams of baptist history in England?
Particular
Worship on the early American frontier can be characterized as:
All of these
Segler states that the Holy Spirit should be more prominent in the sermons and hymns because:
all of these
Hymns are defined as "poetry set to music."
true
The ordinary is the changing aspect of the Mass.
false
Ralph Martin states that the term "worship" comes from the Welsh word "word-ship," which everything should surround the sermon and the Word of God.
false
The Puritans believed that the Eucharist was the climax of the worship service.
false
Spiritual songs stated in Ephesians 5:19-20 and Colossians 3:16 is best compared to our modern choruses because they are intimate.
false
True worship in the church will move toward the goal of Christian unity among the people of God.
true
One of the purposes of worship is the edification of the individual.
false
Free churches sought true worship by insisting on freedom from traditional rites and ceremonies.
true
11 element of Medieval Mass in order
Liturgy of the word
Introit by two choirs as clergy center
Kyries
celebration salutations
collects
Prophecy
antiphonal chant
epistle
gradual
Alleluia
Gospel, with lights, incense, responses
dismissal of those not communicating
he biblical terms used to designate the various aspects of our personality are not to be considered independently of one another. An example of the "mind" is:
nous
The "object" of our worship is
to a person, place or thing...a noun
What is a brace?
A bracket connecting two or more staves
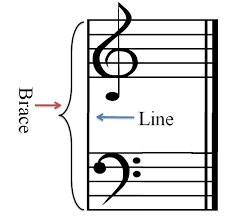
What is a staff?
The five horizontal lines on which music is written
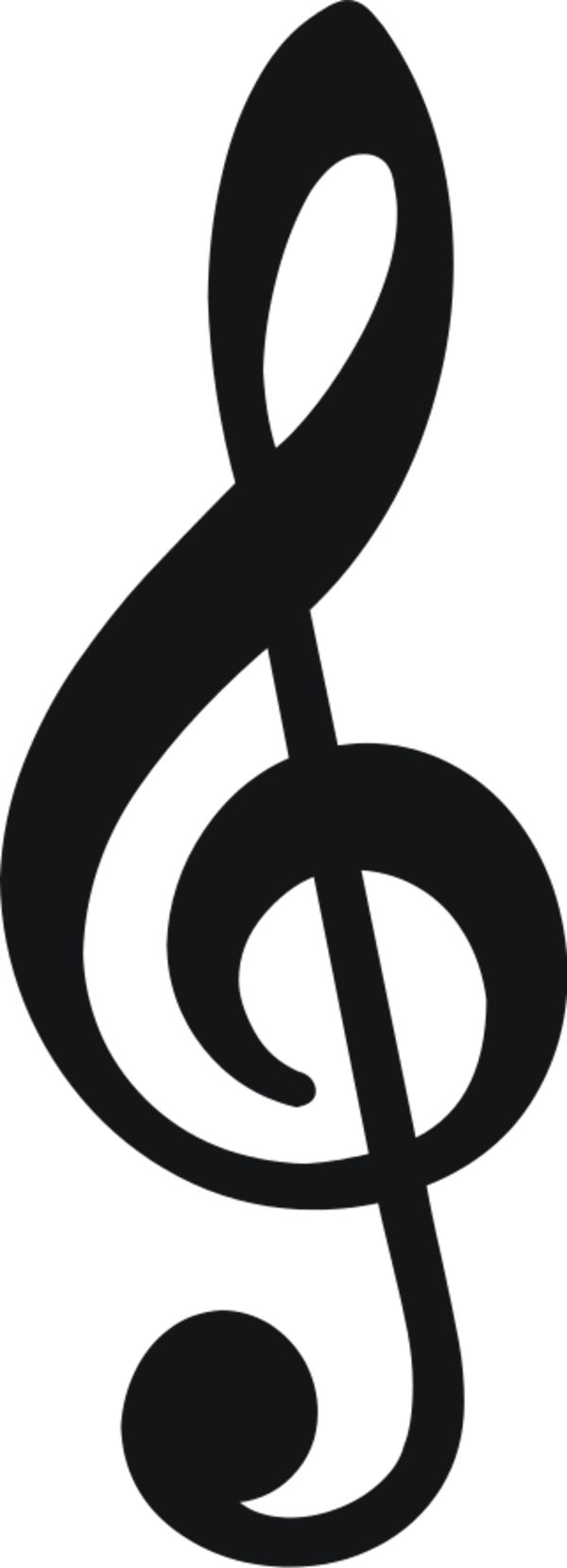


What is a treble clef?
A symbol indicating tones above middle c; in hymnbook the treble clef is usally on the upper staff and indicates notes to be sung by sopranos and altos (women voices)

What is a bass clef?
A symbol that indicates tones below middle c which are to be sung by the bass or tenor. (Men voices)
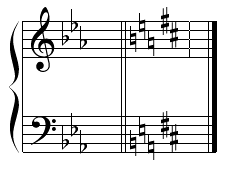
What is a key signature?
The sharps or flats at the beginning of each staff that indicates the key or tonality of a song
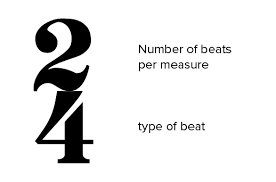
What is a time signature?
The numbers on the staves at the beginning of a song; the top number indicates the number of beats (counts) in a measure and the bottom number indicates the kind of note (note value) that gets one count.
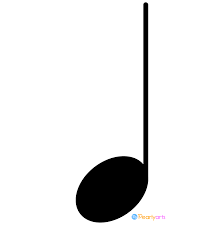
What is a quarter note?
Gets 1 count in 4/4 meter
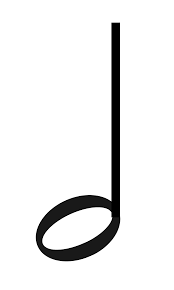
What is a half note?
Gets 1 count in 2/2 meter
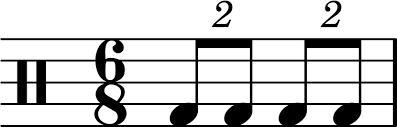
What is an eighth note?
Gets 1 count in 6/8 meter
What is upbeat?
One or several notes that occur before the first complete measure and this before the first metrically accented beat (downbeat) of a song. Sometimes also called the pickup.
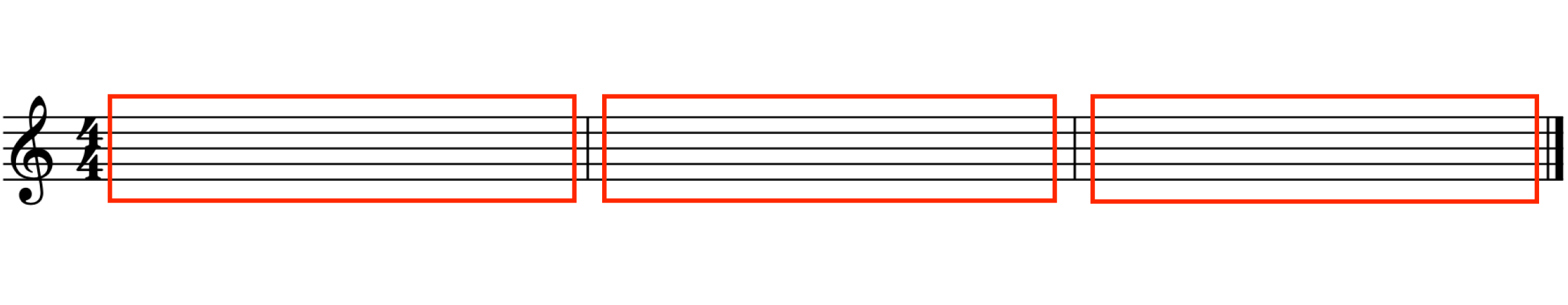

What is a measure?
A group of beats (units of musical time) marked off in musical notations by bar lines. The distance between two bar lines.
What is the bar lines?
A vertical line drawn through the staff to make off measures.
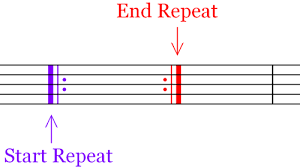
What is a repeat?
Signs marked in the beginning and the at the end of a section, which call for the repetition of that section.
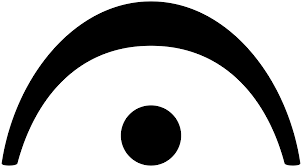
What is a fermata?
Indicates to pause or to hold a note
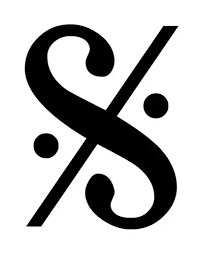
What is a dal segno (D.S.)?
Indication for repetition not from the beginning but from another place (frequently near the beginning) marked by the sign.
What is a da capo (D.A.)?
To beginning of the piece
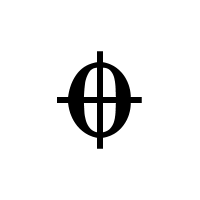
What is a coda?
A concluding section of Music
What is a fine?
The end, finish
What is a alle breve?
A tempo marking (equivalent to the time signature that looks like a cent) indicating quick duple time, i.e. with the half note rather than the quarter note receiving the beat
What is a refrain?
In a song, each repetition of the refrain is of course, set to the same melodic so that the term refers to both textual & musical repetition. The “refrain” is often called “chorus”, while the changing text is referred to as a “verse” or “stanza”.
What is temple worship?
Central place of worship (traditional place of worship) that was built during Solomon's reign as the King of Judah
Christians no longer needed to worship there because Jesus had become their place to worship God
What is synagogue worship?
□ New centers of worship; became well established in third century BC
□ First established for teaching but then used as the place of worship for Jews
§ Less formal
§ Teachers were the central figures
§ Lay participation was more prominent
What is medieval worship?
□ reverted to the priestly system of the Old Testament with certain customs of the mystery and pagan religions added.
§ the practice of worship became too objective, centering in symbols (verbal or otherwise) which became ends in themselves
§ ceased to meet the deep needs of the people, and a restless spirit and a desire for reformation developed within the church.
□ Emphasis placed on building design, mass, and the Lord's supper
What is the reformation?
Preachers of this era: John Hus, Martin Luther, and John Calvin (the Huguenots, the Puritans, and contemporary Christians)
Three main forms of worship
Lutheran and Anglican (most conservative)
Presbyterian or Reformed (most moderate and produced)
Puritan: Anabaptists and Quakers (most radical)
What is purtian worship?
carried individualism and subjectivity to the extreme.
collection of individuals at prayer; the service was more concerned with the individual than the corporate body.
centered on a simple, Bible-focused approach, emphasizing long sermons, the singing of psalms, prayer, and the sacraments of baptism and the Lord's Supper, with a focus on both individual and corporate piety
What is 19th century worship?
the Second Great Awakening emphasized revivalist practices like camp meetings and a focus on personal piety and social reform, while also seeing the rise of new musical styles and hymns
What is tabernacle worship?
a portable sanctuary constructed by Moses, served as a central place of worship for the Israelites during their journey through the wilderness, symbolizing God's presence and guiding their worship practices
What are the three parts of the tabernacle?
Outer place, Holy Place, Holy of Holies
Outer place
Symbolism
Represents the physical world and the body, where people first encounter God and His commands
Altar of Burnt Offering
A place for sacrifices and atonement for sins, symbolizing the need for sacrifice and Jesus's atoning death.
Bronze Basin (Laver)
Used for ritual washing, symbolizing cleansing and purification from sin
Holy Place
Symbolism
Represents the soul, where people engage in worship and seek God's guidance.
Table of Showbread
A table with bread perpetually placed on it, symbolizing God's provision and sustenance for His people.
Golden Lampstand (Menorah)
A seven-branched lampstand providing light, symbolizing God as the source of light and truth.
Altar of Incense
A place for burning incense, symbolizing the prayers and pleas of the people ascending to God
Holy of Hokies
Symbolism
Represents the spirit, the innermost place of God's presence and where His glory dwells
Veil
A curtain separating the Holy of Holies from the Holy Place, symbolizing the mystery and inaccessibility of God's presence until Jesus's sacrifice.
Ark of the Covenant
A sacred chest containing the Ten Commandments, symbolizing God's law and covenant with His people.
Mercy Seat
The lid of the Ark, where God's presence was believed to dwell, signifying God's grace and forgiveness.
Cherubim
Angelic figures above the Mercy Seat, symbolizing God's majesty and power.
Who is Justin Martyr?
a prominent early Christian apologist and philosopher who, after studying various pagan philosophies, converted to Christianity and defended the faith through his writings, including the "First Apology" and "Dialogue with Trypho," eventually dying a martyr's death
What is Clement’s letter?
encouraged the Corinthian Christians to remember their high calling in Christ. His exhortation to unity, humility, and forgiveness speak to the church in any place and generation.
Martin Luther and the Reformation
a German monk and professor of theology, sparked the Protestant Reformation in 1517 by challenging the Catholic Church's practices, particularly the sale of indulgences, leading to a division in Western Christianity and the emergence of new Protestant traditions
What is the 95 thesis?
outlining his arguments against the Catholic Church's practice of selling indulgences (pardons for sins).
What are Martin Luther’s key beliefs?
Justification by Faith:
Scripture as the Ultimate Authority
Rejection of Indulgences
What are the 11 musical elements of medieval worship?
Introit (1) - Their call to worship (where we get the word introduction; usually from the book of psalms)
Kyrie (2) - (about the trinity; God)
Gloria (3)
Gradual (4)
Tract/Alleluia (5) - (Singing Alleluia)
Credo (6) - (Declaration of faith)
Offertory (7) - (Offering ourselves to the Lord)
Sanctus (8)
Agnus Dei (9)
Communion (10) - (Everything in mass is leading up to this)
Ite Missa Es/Benedictus (11)
Domino
What is ordinary?
employs texts that remain the same for every mass
What is proper?
the stuff that changes every Sunday; pronunciation and how it's done changes but the order stays the same
Segler’s ideas of “merging” Christian worship and “distinctions” with Jewish worship.
Types of Merging Worship
Temple worship - Traditional
Synagogue - Teaching
Homes - Informal Places of Meeting
Distinctives of N.T. Christian worship
Used the gospels and the writings of Paul
Hymns were added to the Psalm singing
Water Baptism & Communion Celebration
Emphasis of The Holy Spirit
Meeting times different - 1st Day of the Week
Segler’s function of worship.. ie. “Devoting the will”, etc.
Quicken the conscience
Feed the mind
Purge the imagination
Open the heart
Devote the will
What is worship?
Preoccupation with who God I sand his attributes
His personality, his love, etc.
What is praise?
Focused on what great things God has done - thanksgiving
Characterized by celebration and exhilaration
Expressed by singing, shouting, musical instruments, dancing, etc.
What is subjective worship?
about how I feel right now and my struggles but God is still here and worthy of praise
What is objective worship?
all about God, who he is and his characteristics. Great is they faithfulness, Holy Holy Holy, Forever Yahweh
What are stars?
Shine for long periods of time
What are fireworks?
Beautiful but for a short period of time
What is the test for a good hymn/chorus? “Singability”
Puts us in the right frame of mind
Articulates our response to God as a believer